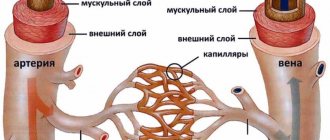
Retinal angiopathy develops against the background of organic and functional disorders of the fundus vessels. They lead to circulatory failure and subsequent degeneration of retinal tissue. Most often, angiopathy is a secondary pathology that develops against the background of other ophthalmological or general systemic diseases.
Causes of angiopathy
The following diseases can lead to disruption of the vascular system of the eye:
- hypertension or hypotension;
- atherosclerosis;
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrine disorders;
- eye injuries;
- autoimmune diseases;
- genetic predisposition.
In most cases, disorders of the vascular system affect the entire body, and angiopathy is combined with other diseases. Only angiopathy of traumatic origin can be local in nature.
The developing pathology causes serious functional and trophic disorders of the tissues and structures of the eye:
- dystonia of the vascular wall;
- vascular spasms;
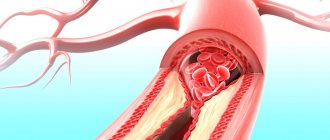
- formation of atherosclerotic plaques;
- thrombosis of veins and capillaries.
Angiopathy always carries the risk of ischemic changes in the retina. Dysfunction of the circulatory system leads to slow metabolism, accumulation of metabolic products in tissues and hypoxia. Over time, this causes degeneration and functional failure of the light-sensitive cells of the eye and, as a consequence, loss of visual acuity.
Classification
In addition to unilateral and bilateral pathology, there are three types of angiopathy, which differ in the mechanism of development, age and physical condition of the patient:
- Retinal angiopathy of prematurity is a rare and at the same time the safest type of pathology. It is diagnosed in children who have suffered birth injuries or gone through protracted labor in the first weeks of life. The essence of the changes is the narrowing of the capillaries in the fundus. Over time, microcirculation is restored.
- Angiopathy in pregnant women is a condition caused by changes in hormonal levels and an increase in the total volume of circulating blood. It is diagnosed in the second half of gestation and is expressed by weakening of the vascular walls. During childbirth, retinal detachment or rupture may occur.
- Juvenile angiopathy is a pathology that is diagnosed in patients at a young age. The essence of the changes is inflammation of the capillaries and their destruction. This form of the disease most often ends with profuse hemorrhage under the retina or into the vitreous body. In severe cases, it can lead to instant loss of vision and cataracts.
- Diabetic angiopathy is a pathology accompanying advanced diabetes, which is expressed by a weakening of blood flow in the capillaries, the development of retinal ischemia and its gradual degeneration.
- Hypertensive angiopathy is a condition in which excessive dilatation of the vessels of the fundus occurs, which causes pinpoint hemorrhages, and then clouding of the vitreous body.
- The traumatic form of the pathology is diagnosed in patients with osteochondrosis of the cervical back. Accompanied by weakening of microcirculation and thrombosis of the ocular vessels.
For each form of pathology, specific treatment is used, so during the diagnostic process it is important for the doctor to establish the type of disease.
Types of retinal angiopathy
The classification of angiopathy is based on etiology. There are 5 types of angiopathy:
Hypertensive. General vascular disorders in hypertension affect the functioning of the veins and capillaries of the fundus. The retina that feeds from them does not receive the necessary substances in full and accumulates metabolic products. This causes tissue degeneration, functional failure of light-sensitive cells, and then irreversible organic changes. Angiopathy caused by vascular hypertonicity is further complicated by atherosclerotic changes in the lumen of blood vessels.
Hypotonic. Constantly low pressure in the vascular system is also not beneficial, since low tone causes slower blood flow. The consequence of this is sluggish metabolism, nutritional deficiency and general functional weakness of both the eye muscles and light-sensitive elements.
Diabetic. Elevated blood glucose levels have a toxic effect on the walls of blood vessels. Their elasticity and permeability are impaired. Diabetes is often accompanied by atherosclerosis, which causes the formation of plaques that narrow the lumen of blood vessels, which also impairs trophism.
Traumatic. Impaired blood supply to the fundus can be caused by mechanical damage. Especially often, angiopathy develops after traumatic brain injury and as a result of a violation of the integrity of the upper parts of the spine.
Youthful. Angiopathy that occurs before the age of 30 is considered “youthful.” The reasons for such early development of pathology, as a rule, are chronic, sluggish infections (toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis and others). Over time, the disease leads to vasculitis - inflammatory changes in the vascular system. The consequence of this is insufficient blood supply and retinal dystrophy.
Our advantages
"Moscow Eye Clinic" offers comprehensive diagnostics and effective treatment of eye diseases. The use of modern equipment and the experience of specialists working in the clinic eliminate diagnostic errors.
Based on the results of the examination, each visitor will be given recommendations on choosing the most effective methods of treating the eye pathologies identified in them.
The high level of theoretical training and practical experience of our doctors guarantees the achievement of good treatment.
Author:
Mironova Irina Sergeevna 5/5 (1 rating)
Honey. portal:
Symptoms of angiopathy
Developing angiopathy may not manifest itself for a long time. This complicates diagnosis in the early stages. Most often, the disease is detected by complications that have already arisen, which give clear symptoms. Only with further research does it become clear that the disorders are secondary, and the underlying cause was the existing angiopathy.
Characteristic symptoms in the presence of angiopathy may be:
- episodic blurring of the visual field;
- headache;
- unpleasant and painful sensations in the eye area;
- loss of visual acuity;
- narrowing of the field of view, loss of peripheral vision areas.
These symptoms in any combination are a serious reason for immediately contacting an ophthalmologist. Even if the cause is not angiopathy, such disorders indicate existing organic disorders or developing pathological processes.
Manifestations of the disease depending on the stage
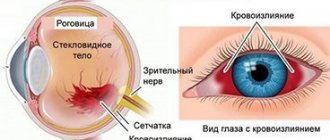
As a rule, the initial stage of the disease does not cause discomfort in patients. Complaints appear at a later stage, when the patient experiences a decrease in visual acuity and blurred vision. Upon examination, the ophthalmologist reveals a narrowing of the lumen of the retinal arterioles, their excessive tortuosity, and corkscrew-shaped tortuosity of the venules. In severe cases, vascular obstruction, the formation of hemorrhages, and the appearance of extravasation from blood clots are recorded.
Corkscrew tortuosity of venules near the macula
Characteristic signs of the disease:
- Decreased visual acuity (appearance of “cloudiness” before the eyes).
- Addition of myopia (inability to focus vision on distant objects).
- The appearance of bright flashes, “lightning” before the eyes (disorder of the blood supply to light receptors).
- Narrowing of visual fields (decreased peripheral vision).
- Headache (provoked by hypoxia).
- A feeling of pulsation occurs in the eyeballs (increased blood circulation through the narrowed arterial lumen).
- Visual dysfunction (as the disease progresses, blindness is possible).
- Bleeding from the nose (the area located on the surface of the mucous membrane of the nose and eye may bleed).
Minor hemorrhage in the eyeball
Since hypertension affects the vascular system throughout the body, hypertensive angiopathy of both eyes is observed. In medical documentation, this condition is recorded as a lesion of the retina OU, that is, of both eyes. The disease is aggravated by obstruction of the central retinal artery, the lumen of which is subsequently blocked. Malnutrition of the optic nerve leads to its atrophy.
No ads 3
Diagnostics
Even completely healthy people are recommended to have an annual preventative visit to an ophthalmologist. If you have risk factors, you should visit your doctor twice a year. This is especially important for identifying angiopathy and other eye diseases that do not have obvious symptoms in the early stages. Many of them have a favorable prognosis only with timely treatment.
The basis for diagnosing angiopathy is examination of the fundus. At the same time, even minor disorders are quickly and painlessly identified, threatening serious complications in case of untimely treatment.
Our ophthalmological center carries out a full range of diagnostic measures aimed at early diagnosis of angiopathy. After examining the fundus, experienced doctors, if necessary, conduct a more thorough examination using modern equipment. To clarify the diagnosis, the following may be prescribed:
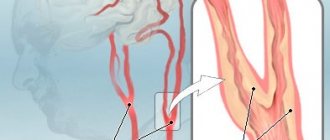
- duplex study of brachiocephalic vessels;
- Ultrasound of the eyeballs;
- other hardware and instrumental methods for studying the vascular system of the eye.
Prevention
To prevent retinal angiopathy of both eyes from leading to dire consequences, it is important to follow measures to prevent its occurrence. The first rule for preventing any ophthalmological disorders is regular visits to the doctor. For those diagnosed with diabetes, hypertension, endocrine and cardiovascular diseases, it is worth examining at least once a year.
Important! An annual examination will help to identify hidden disorders in time, begin treatment and significantly improve the prognosis.
Simple measures will help reduce the risk of problems with the vessels that supply the retina:
- maintaining visual hygiene - the load on the eyes should be dosed and interrupted for a 10-15 minute rest every hour;
- maintaining eye hygiene - when in dusty, gas-filled rooms, as well as in places where there is a risk of foreign objects getting into the eyes, you should protect them with goggles or a mask;
- treatment of any diseases under the supervision of a physician, prevention of the development of chronic pathologies, regular medical examinations and medical examinations for the early detection of systemic diseases;
- moderate physical activity - walking, cycling, swimming, running in the morning will help maintain tone, strengthen blood vessels and heart, and increase immunity.
An important point in the prevention of all types and forms of angiopathy is the abandonment of bad habits. Long-term intoxication of the body with nicotine, ethanol and its metabolites destroys small blood vessels and leads to many chronic diseases.
Treatment of angiopathy
The first task in the treatment of angiopathy is to identify and eliminate the negative factors that served as the background for the development of the disease. As a rule, these are chronic diseases. It is necessary to monitor blood pressure and prevent hypertensive crises. Diabetics must maintain optimal blood sugar levels. These measures are ensured by appropriate treatment regimens prescribed by specialized specialists. The ophthalmologist monitors how the treatment affects the blood vessels of the eyes, and also prescribes treatment aimed at eliminating hypoxia, normalizing the blood supply to the optic nerve head, and strengthening the walls of the blood vessels of the eye. Vitamins, antioxidants, neuroprotectors and mineral complexes can also provide good support to tissues experiencing dystrophy.
Specialists of the Moscow Ophthalmological Center will offer an individual treatment regimen, which may include drugs in the form of:
- tablets;
- injections;
- parabalbar injections into the eye area;
- intravenous drips.
Additionally, hardware treatment programs, physiotherapeutic procedures and massage are prescribed.
Surgical care can be aimed mainly at eliminating complications that have already developed. Most often, laser surgery is used to treat and prevent retinal detachment caused by angiopathy.
conclusions
A change in the nervous regulation of retinal vessels, leading to their weakness (relaxation) or spasm. Blood supply processes are disrupted, as a result of which vision suffers. The causes are usually other diseases: diabetes mellitus, the development of hypertension (essential hypertension). As well as spinal and brain injuries. If angiopathy is detected at the initial stage, its further development can be prevented. Lack of timely treatment is fraught with the development of dangerous complications, for example, retinoschisis. The main methods of treating retinal angiopathy are medications and surgery. It is necessary to periodically visit an ophthalmologist for a preventive examination, since the pathology usually does not manifest itself in the initial stages.
Treatment depends on the type of disease. It should be timely and aimed at getting rid of the root cause - the underlying disease (diabetes, hypertension, etc.).
Medicines
If the problem of treating the underlying disease is solved, drugs such as pentoxifylline (Pentyline), Trental, Vazonit (help to improve blood flow) are used in treatment.
Xanthinol nicotinate and ginkgo biloba preparations (Bilobat, Tanakan) improve the condition of the vascular wall. To normalize microcirculation, take vitamins C, A, E, B.
ATP-long, actovegin, cocarboxylase drugs have a metabolic effect: they activate blood circulation and improve metabolism.
Soft antiplatelet agents: Magnicor, dipiradamole prevent the formation of blood clots.
Since all such pathologies seriously affect the quality of life, and in some cases are threatening, drug therapy should be agreed with the attending physician.
List of used literature
- Babaeva A.R., Tarasov A.A., Davydov S.I., Emelyanova A.L. // Bulletin of VolSMU. - 2006. - T. 19, No. 3. - P. 18-23.
- Voskanyants A. N., Nagornev V. A. // Cytokines and inflammation. - 2004. - T. 3, No. 4. - P. 10-13.
- Gurevich V.S. // Diseases of the heart and blood vessels. - 2006. - No. 4. - P. 4-8.
- Demyanov A.V., Kotov A.Yu., Simbirtsev A.S. // Cytokines and inflammation. - 2003. - T. 2, No. 3. - P. 20-35.
- Dedov I.I., Aleksandrov A.A. // Consilium med. — 2004. —T. 6, No. 9. - P. 620-624.
- Dedov I. I., Antsiferov M. B., Galstyan G. R., Tokmakova A. Yu. Diabetic foot syndrome. — M.: Federal Diabetology Center of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 1998
Therapy
Diabetic angiopathy
The leading role is played by therapy of the underlying disease. It is necessary to follow a strict diet, quit smoking and alcohol, and control body weight.
Since most diabetic angiopathy is associated with damage to the vessels of the lower extremities, special attention should be paid to the condition of the legs (feet). If the doctor suspects a patient has a “diabetic foot” (deformation, infection of soft tissues, the appearance of trophic ulcers), hospitalization and inpatient treatment in the clinic are carried out. Physiotherapy is used during the rehabilitation period. In case of severe pathologies, surgical intervention is indicated.
Retinal angiopathy
This type of angiopathy responds better to conservative treatment than others (taking into account the underlying disease). The use of medications, laser therapy, physiotherapy, and massage of the collar area can be effective. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is necessary.
Hypertonic, striatal and CAA
Hypertensive angiopathy is treated by stabilizing blood pressure and normalizing blood circulation.
For striatal angiopathy, drugs to improve cerebral metabolism and hemodynamics are prescribed. If there is no effect, minimal surgical intervention is required.
For cerebral amyloid angiopathy, symptomatic treatment is indicated; it is not possible to achieve positive dynamics in the treatment of the underlying disease.