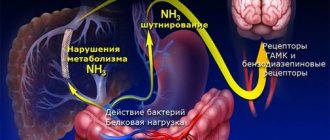
Development and risk groups
The development of a stroke is caused by a sharp increase in blood pressure, physical activity, and emotional stress. In such situations, a vessel ruptures followed by hemorrhage or spasm with ischemia. Predisposing factors are diabetes mellitus, high cholesterol, heart, vascular and blood diseases, and excess weight. In these diseases, blood vessels lose their elasticity and their walls stretch. People who or their close relatives have had a stroke or heart attack should be especially careful.
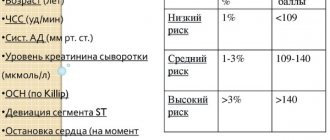
There are scales that determine the degree of risk of developing a stroke: the Framingham scale for assessing individual risk of developing stroke, the London School of Hygiene questionnaire on cardiovascular diseases by J. Rose.
By undergoing such testing, you can identify the degree of risk, undergo an examination and undergo a course of treatment in a timely manner before your health is affected.
Risk groups are identified:
- by age and gender - the likelihood of a stroke increases after 30 years. Ischemic stroke occurs more often in men aged 50-69 years. The incidence of hemorrhagic stroke up to 60 years of age is the same in men and women, then higher in women;
Diagnostic methods
It is important to quickly distinguish a stroke from other diseases that can lead to the development of similar symptoms. It is almost impossible to do this on your own, as well as to determine the type of vascular accident.
The main difference between an ischemic stroke is a gradual increase in symptoms that do not lead to loss of consciousness. With hemorrhagic hemorrhage, the patient passes out quickly. However, stroke does not always have a classic course. The disease may begin and progress atypically.
Diagnosis begins with examination of the patient. The doctor collects anamnesis and determines the presence of chronic diseases. Most often, you can get information not from the victim himself, but from his relatives. The doctor performs an ECG, determines the heart rate, takes a blood test, and measures blood pressure.
It is possible to make the correct diagnosis and obtain maximum information about the patient’s condition thanks to instrumental diagnostic methods. The best option is a CT scan of the brain. Performing an MRI is difficult because the procedure takes a long time. It takes about an hour. It is impossible to spend this amount of time diagnosing an acute stroke.
Symptoms
The first thing patients notice with low blood pressure and high pulse is a distinct sensation of all the contractions of the heart sac, which can be easily counted independently. Patients experience a burning sensation and pain in the chest and stomach. Because of this, a person begins to eat less, and a sharp decrease in body weight is observed.
The person also experiences severe headaches, which are often accompanied by dizziness and a feeling of nausea. In particularly advanced cases, patients complain of a feeling of fear that arises deep in the chest, and constant drowsiness and general weakness of the body. You can also recognize low blood pressure and high pulse by the following symptoms:
- The emergence of a feeling of anxiety and fear that comes from the depths of the chest;
- Full sensation of every heartbeat;
- Pain in the heart, chest and stomach;
- Frequent and causeless occurrence of headaches, which are accompanied by dizziness;
- A feeling of difficulty in the airways that cannot be relieved.
Tachycardia is an acute disorder of the body, characterized by an acceleration of the heart rate. A number of physiological factors, such as emotional stress or intense physical activity, can cause such changes. In such cases, low blood pressure and high pulse gradually return to normal without any therapy.
If such manifestations torment a person on an ongoing basis, then it will be impossible to cope with the problem on your own without the participation of a doctor. If you ignore any manifestations of this disease, sooner or later serious disorders will occur in the body, which will lead to constant fainting and vomiting.
If you do not know what to do in such cases, consult your doctor for advice.
What blood pressure can trigger the development of a stroke?
At what blood pressure level can a stroke occur and can the condition develop at normal blood pressure? It is worth noting that most often a stroke occurs in hypertensive patients. The reasons are:
- Stably high blood pressure, which does not decrease even while taking medications;
- sharp jumps in indicators caused by a stressful situation or significant physical activity;
- refusal of treatment for hypertension and heart disease.
Doctors call the physiological level of blood pressure, at which all body systems operate in a natural mode, a level of 120/80 mm. rt. Art. When it increases to 180/120, we can talk about the development of a hypertensive crisis, which can quite easily turn into an apoplexy (stroke).
The danger in terms of the development of pathology is represented by too small a difference between the upper and lower blood pressure readings. If it is less than 40 units, then the likelihood of blockage of the vascular lumen increases significantly. Therefore, a blood pressure of 130/110 is more likely to trigger the development of a stroke than a blood pressure of 160/90.
What to do if you have low blood pressure?
Physiological hypotension does not require special measures if it does not cause complaints in a healthy person. With a decrease in physical activity, low blood pressure returns to normal values.
If the hypotension is chronic primary, then it is necessary to eliminate mental or physical overload. Massages, swimming, walks in the fresh air and everything that allows a person to forget about pressing problems and relax help with this. At home, it is recommended to add seasonings and spices (cloves, cinnamon) and caffeine-containing drinks to your food. If ineffective, you need to consult a doctor and, possibly, take medications.
If hypotension is chronic secondary, then treatment of the disease that caused it is necessary.
To monitor the state of the cardiovascular system, it is recommended to use Microlife blood pressure monitors, equipped with modern technologies and additional functions. Early detection of hypotension allows you to take measures to increase blood pressure and save lives.
Prevention
- Primary prevention consists of proper nutrition, exercise, giving up bad habits and stress, adequate sleep and rest, and regular medical examinations.
- Secondary prevention of stroke includes the elimination of risk factors - treatment of concomitant pathologies, regular monitoring by the attending physician, elimination of risk factors. This approach will help not only prevent stroke, but also improve overall health. According to WHO estimates, the creation of an adequate system of care for patients with stroke will make it possible in the coming years to reduce mortality during the 1st month of the disease by 20% and ensure independence in everyday life 3 months after its onset in at least 70% of patients.
Treatment
The basis of therapy for high pulse and low blood pressure is a change in the patient’s lifestyle - the patient must become committed to proper nutrition and a good daily routine. It is very important to eradicate all bad habits such as smoking or drinking large amounts of alcoholic beverages or coffee.
You also need to completely avoid all products that contain caffeine - Coca-Cola, chocolate and much more. Try to minimize any impact of stress on the body, and also control mental work. Do not forget about the need for physical exercise, but it should be in moderation.
It will be possible to determine drug therapy only based on the results of detailed diagnostics. Only with it will it be possible to fully understand the state of the body and identify any disturbances in its functioning.
You should not independently determine the scheme of influence, since with the wrong approach you can simply harm your body. If you have a sudden attack and feel acute discomfort in the heart area, call an ambulance immediately. In most cases, high heart rate and low blood pressure are treated as follows:
- Dehydration can be treated by drinking plenty of fluids.
- The impact of internal blood loss can only be minimized through transfusion.
- Avoidance of certain medications that have a negative effect on the body.
In most cases, home therapy is sufficient; in rare cases, outpatient methods are used to get rid of the problem. If a person is in critical condition, then he will definitely be sent to the hospital.
Under no circumstances should you self-prescribe medications. Only a specialist will be able to accurately determine which substances will have a positive effect on the body’s condition and which will cause harm. The occurrence of low blood pressure and high pulse can be caused by different etymologies, so treatment is selected individually in each specific case.
There is no need to deal with the problem on your own, much less practice traditional medicine. Only a doctor can accurately answer the question of what to do with low blood pressure and high pulse.
Low and high blood pressure
During the first 24 hours after the impact, maintaining high blood pressure is an acceptable norm. The danger is high blood pressure that persists for a week after a stroke. The symptom indicates incorrect treatment. In this case, the patient becomes incapacitated and develops neurological disorders.
Such negative consequences for the patient’s health are due to the continuing increase in cerebral edema, which results in wedging of the brain stem into the occipital part. It is possible that breathing processes may be disrupted until a critical condition develops, as well as heart failure and cardiac arrest.
If the pressure, despite the therapy, still jumps, then the consequences may be as follows:
- re-strike;
- expansion of the ischemic focus;
- development of encephalopathy;
- hemorrhage in the skull.
Why does a patient have low blood pressure after a stroke and why is this condition considered negative by doctors? A rapid decrease in blood pressure occurs against the background of the following pathological conditions:
- development of a major stroke;
- brain stem damage;
- the formation of cardiogenic shock against the background of a heart attack;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- dehydration;
- blockage of the pulmonary arteries;
- blood poisoning;
- aneurysm.
Low blood pressure values during the rehabilitation period indicate progression of the pathology. The prognosis in this case is extremely unfavorable, this applies to both recovery and human life. A decrease in blood pressure can occur against the background of regular use of hypertensive drugs that were prescribed to the patient even before the stroke developed.
But if the reason for this is not drug treatment, then this is a signal that the body is unable to independently regulate blood pressure as a result of impaired cerebral blood circulation. Medical statistics show that severe hypotension during the first few days after a stroke causes the death of the patient.
Pressure indicators for apoplexy
It is no big secret that long-term progressive hypertension can provoke certain forms of stroke. But not many people know that with long-term low blood pressure, sudden heavy load or emotional stress, a stroke can also develop.
Rescue of a victim after apoplexy
In turn, the stroke itself can deservedly be considered a rather serious, often life-threatening condition for the patient. Naturally, all medical actions during the acute period of the disease are usually aimed at saving the victim after a stroke and minimizing the negative consequences that stroke pathology causes.
We have already written more than once that the complications/consequences that arise after a stroke can be very different; often, a stroke leads the victim to complete loss of speech, vision, memory, to paralysis or paresis, to the most dangerous relapses, which, in turn, are directly related with whether the patient’s blood pressure is normalized after the primary pathology or not.
Let us recall that increased and not timely corrected blood pressure after primary cerebral pathology quite often leads to the development of a recurrent stroke in its more complex form.
Moreover, in almost eighty-five percent of cases, uncontrolled pressure after primary pathology can be the cause of a secondary hemorrhagic form of stroke.
Why can high blood pressure lead to a brain stroke?
Among medical professionals, hypertension in all its manifestations is usually called the “silent killer.” In fact, this name perfectly reflects the essence of this disease. After all, high blood pressure is often not noticed by the patient, the problem arises completely unnoticed, and the first symptoms are often mistaken for ordinary fatigue.
Sometimes it happens that the patient initially learns about the diagnosis of hypertension from the emergency team doctor, who was called for a completely different reason. From the above, only one thing follows - you should not behave frivolously and neglect regular (often seemingly useless) measurement of indicators indicating your working blood pressure.
Signs of hypertension
Because after usually low blood pressure rises to elevated numbers (about 140/90 or even higher), irreversible processes in the vascular bed can begin in the body, which can subsequently lead to stroke pathology. Many people who consider themselves healthy often wonder: what to do after discovering that you have elevated blood pressure, maybe take some pill and everything will go away?
The answer to this question is quite simple and logical - even if the pill that your neighbor or friend recommends to you turns out to be harmless and effective, consulting a doctor regarding this issue will not be superfluous. It is an experienced doctor who will be able to analyze all your complaints, prescribe the necessary examinations and, ultimately, prescribe truly necessary and important medications that correct blood pressure.
It is important to remember that the most dangerous manifestations of primary arterial hypertension can be considered periodic sharp jumps in blood pressure, which are called a hypertensive crisis. During a hypertensive crisis, the numbers on the mercury column can reach the highest and even critical numbers. Hypertensive crisis is often accompanied by:
- A feeling of fear.
- Severe headaches.
- Significant pain in the cardiac region.
- Sometimes some retardation.
- The most severe crises can be accompanied by a temporary loss of consciousness and develop into transient ischemic attacks, followed by a stroke.
Cerebral aneurysm
In addition, as a result of long-term hypertension, such patients may well develop pathological changes in blood vessels - so-called aneurysms of cerebral vessels, which, if ruptured, can provoke the development of hemorrhagic stroke.
So, the fact that the danger of high blood pressure for healthy people is high, primarily due to the possible development of a stroke, is quite clear, just as it is clear what to do with such jumps in the mercury column - consult a doctor and, possibly, treat hypertension.
But what should those people do for whom hypertension has already provoked a stroke or for those in whom these indicators began to increase after a stroke? We will examine this issue further in our article.
Stroke with hypertension, hypotension and normal pressure
Most often, strokes occur in patients with high blood pressure, but can occur in patients with normal or even low blood pressure. In case of hypertension In hypertensive patients, cerebrovascular accident develops according to the following schemes: The patient has been diagnosed with hypertension, and he is taking medications to stabilize blood pressure. When the patient’s health improves, he stops following the doctor’s recommendations. The pills continue to work for some time, but then the effect wears off, the blood pressure rises sharply and a stroke occurs. A person has constantly high blood pressure, but there is no treatment for it. In some cases, the levels reach 200 mm Hg, but the state of health remains normal, as the body adapts to this condition. A stroke can occur not after a surge, but at any time due to constantly elevated levels. A person is constantly overworked physically and emotionally, and gets tired. Against this background, the pressure in the arteries increases, and the integrity of the vessels at a certain point is compromised. This is how hemorrhagic stroke develops, which is typical for young and middle-aged men. With hypotension and normal blood pressure When a stroke occurs with normal or low blood pressure, this leads to more severe consequences for the body. the affected areas of the brain are surrounded by penumbra - an area of partially damaged, non-functioning, but viable cells. If the patient receives timely assistance, the functioning of these cells can be restored.
Causes
If a person’s blood pressure drops sharply, but their heart rate increases, this is a good reason to sound the alarm. In a healthy, normally functioning body, such changes cannot appear overnight. These phenomena may be indicated by internal bleeding, acute disruption of the endocrine glands, and much more.
It is the violations that can cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure and increased heart rate. Such phenomena can be caused by the release of a large amount of progesterone into the blood, which provokes vascular stretching. In most cases, low blood pressure and high pulse are caused by:
- Large blood loss, severe allergic reaction, traumatic shocks, toxic poisoning, infectious and inflammatory processes.
- Dehydration is a phenomenon in which the body does not have enough fluid to function normally. In such cases, low blood pressure and high pulse are accompanied by nausea and vomiting, and diarrhea for a long period of time.
- Vitamin deficiency or a sharp decrease in body temperature.
- Atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus, in which the specific gravity of the blood changes.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia, which can be recognized by sudden attacks of weakness and dizziness. Pallor of the mucous membrane can also be recognized.
- Pregnancy - during this period of a woman’s life, her blood vessels lose tone due to the production of large amounts of progesterone. The volume of circulating blood also increases, causing the heart to contract much more often.
- Heart problems - if a person has problems with contractile function, then his blood pressure drops and his pulse increases significantly.
- Taking certain medications.
A number of other factors can also affect the occurrence of low blood pressure and high pulse. To get rid of this problem, you will have to find out exactly the reasons for their occurrence.
You should not prescribe treatment for yourself - only a doctor, based on the results of a detailed diagnosis, will be able to determine what suits your body and what will cause it even more harm. If such manifestations occur for the first time, try taking a walk in the fresh air or just sleeping.
Prevention of hypertension after stroke
To prevent a second stroke, after the first stroke, patients are advised to lower their blood pressure and maintain it at a certain level. At the same time, some researchers are of the opinion that it is not worthwhile to normalize blood pressure too persistently and bring it to 120/80. For example, the University of Georgia conducted a study and established optimal blood pressure levels after a stroke. Scientists followed the dynamics of recovery of 4,000 patients and came to the conclusion that the least number of negative health consequences were in patients with blood pressure of about 140/90 mm Hg. Patients after a stroke are recommended to take the following groups of drugs: antihypertensives - reduce blood pressure, maintain it at the same level, help prevent sudden changes; antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants for blood thinning, indicated for patients after ischemic stroke; lipid-lowering drugs to normalize blood cholesterol levels; antidiabetic drugs that are needed by patients with diabetes.
How to help a person with hypotension due to diabetes, anaphylaxis and bleeding?
First aid for hypotension depends on the cause of the drop in blood pressure. If this is due to severe bleeding or anaphylactic shock, the patient needs urgent medical attention. In the first case, doctors take measures to stop the bleeding and replace blood loss.
If a patient develops anaphylactic shock due to an allergic reaction to an injection or an insect bite, there is a sharp drop in blood pressure, heart rhythm is disturbed, swelling of the larynx occurs, which leads to breathing problems.
If you suspect anaphylactic shock, you should urgently call an ambulance. At home, it is necessary to limit the spread of the allergen. To do this, remove the insect sting or apply a tourniquet above the injection site. The victim must be laid on a horizontal surface with his legs raised. If a person is vomiting, the head must be turned to the side. The room should be well ventilated. If the victim loses his pulse, an indirect cardiac massage is performed with a frequency of 60-100 compressions before the ambulance arrives.
To relieve anaphylactic shock, doctors administer adrenaline and glucocorticosteroids and use antihistamine treatment.
Emergency measures are also required in situations in which patients with diabetes may find themselves. If the blood glucose level falls below 3.3 mmol/l, a state of hypoglycemia occurs, which is characterized by weakness, a drop in blood pressure, shallow breathing, a weak pulse, and in some cases, an increased heart rate, and sweating.
To increase blood pressure in diabetes, you must first normalize the level of glucose in the blood. If a person is conscious, he needs to eat or drink a drink with fast carbohydrates. Sugar or honey, glucose-based gel, and a sweet drink are suitable for these purposes.
It is not advisable to use chocolate, cookies or other confectionery products that contain carbohydrates and fat, as it slows down the absorption of glucose.
If a diabetic is unconscious, one should not try to pour a sweet drink or sugar through the mouth, as the person will not be able to swallow. Food can get stuck in the throat and cause asphyxia.
If a person is unconscious, it is permissible to rub honey or sugar syrup into the gums. To treat severe hypoglycemia, health care providers use intravenous glucose injections or the drug glucagon, which releases stored glucose from the liver.
Once a diabetic's blood sugar level is normalized, blood pressure and pulse return to normal.