Early ventricular repolarization syndrome does not belong to any arrhythmias according to the clinical and functional classification of cardiologists. The electrocardiographic phenomenon has a typical picture, recorded graphically, but is not considered a disease. Sometimes changes are not considered a pathology at all. They are characteristic of healthy people and do not require treatment.
The danger lies in the unpredictability of further physiological abnormalities in the heart muscle, as well as in the combination of early ventricular repolarization syndrome with serious heart pathology. Therefore, its detection on an ECG requires careful examination by a cardiologist and observation.
What changes in the heart cause the syndrome?
Normal repolarization is caused by the process of the predominant exit of potassium from the cell over the entry of sodium ions into the cell. Due to this, a positive charge appears on the outside and a negative charge on the inside. This mechanism for stopping the excitation of one fiber spreads in the form of an impulse to neighboring areas like a chain reaction; it corresponds to the diastole phase.
Repolarization prepares the myocardium for the next systole and ensures the excitability of muscle fibers. The contraction (depolarization) phase of the heart depends on its quality and duration. These electrical changes have their own direction. They begin in the septum between the ventricles, then spread to the myocardium, first of the left, then of the right ventricle.
Premature repolarization disrupts the balance of electrolyte metabolism and changes the conduction of impulses along conductive pathways
Existing hypotheses explain early repolarization by the presence of three types of cells with different electrophysiological potentials. They are named by their location in the layers of the heart wall:
- epicardial,
- endocardial,
- M cells.
Experimental data have been obtained on the creation of prerequisites for re-excitation in these structures. The role of the endings of the autonomic nervous system in early repolarization (sympathetic and vagus nerve fibers) cannot be ruled out. The activating effect of the sympathetic nerve on the repolarization of the anterior wall and apex zone is shown.
Pathogenesis
Contraction of the chambers of the heart occurs as a result of changes in the electrical charge in myocardial cells - cardiomyocytes . As a result, sodium, calcium and potassium ions move into the intercellular space and back. The process is carried out in alternating main phases:
- depolarization – contraction;
- repolarization is relaxation before a new contraction.
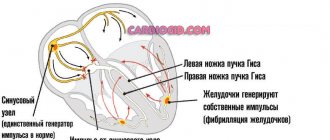
Early repolarization of the ventricles is formed as a result of improper conduction of the impulse through the conduction system of the heart from the atria to the ventricles. To transmit the electrical impulse, abnormal conduction pathways . The development of the phenomenon is due to an imbalance between repolarization and depolarization in the basal regions and apex of the heart. Characterized by a significant reduction in the period of myocardial relaxation. On the ECG, along with the SRRS, a disturbance of repolarization processes in the myocardium is often recorded, in particular, a violation of the repolarization of the lower wall of the left ventricle.
What meaning do clinicians attach to the syndrome?
No typical symptoms and complaints of patients with the syndrome have been identified. However, the signs identified on the ECG cannot be safely attributed to the manifestations of the norm. The syndrome of early ventricular repolarization is known for “simulating” the picture of myocardial infarction, making it difficult to diagnose hypertrophy and dystrophic changes.
In patients, it can be detected simultaneously with rhythm disturbances such as:
- paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia,
- attacks of atrial fibrillation,
- extrasystoles.
The danger lies in the transition of an attack of fibrillation into ventricular fibrillation with a fatal outcome.
This causes special attention in clinical monitoring of patients with ECG changes such as early repolarization syndrome.
Classification
In children and adults, early ventricular repolarization syndrome can have 2 development options:
- without damage to the cardiovascular system;
- with defeat.
According to the nature of the flow, they are distinguished:
- transitory form;
- permanent form.
Depending on the location of the ECG signs of SRGC, they are divided into 3 types.
- I characteristic signs are observed in a healthy person. ECG signs are recorded only in chest leads V1, V2. The likelihood of complications developing is extremely low.
- II ECG signs are recorded in the inferolateral and lower sections, leads V4-V6. The risk of complications is increased.
- III ECG changes are recorded in all leads. The risk of complications is the highest.
Risk factors and causes
The reasons for extraordinary repolarization, in addition to additional bypass paths of the impulse, are considered:
- neuroendocrine diseases (most common in childhood);
- increased manifestations during sleep and when the influence of the vagus nerve predominates, indicates the importance of the autonomic nervous system;
- excessive physical activity;
- hypercholesterolemia in the blood;
- the use of drugs from the group of α2-adrenergic agonists in the treatment of patients (Gemiton, Clonidine, Catapresan, Clonidine);
- hypertrophic type cardiomyopathy;
- congenital or acquired heart defects (including impaired structure of the conduction system);
- changes in the structure of connective tissue in systemic diseases.
Tracking phase changes on an ECG
Diffuse changes in the repolarization process cause changes in the T wave. But it will be too early to talk about an exact diagnosis, since this is typical for any metabolic disorders, and not just in the heart muscle. If deviations of not only the T wave, but also the ST segment are observed, then there is a diffuse imbalance of cell electrolytes.
When deciphering the ECG results, the duration of the intervals between its components is measured
Prescribing treatment and making a diagnosis based on ECG results is difficult. It is necessary to collect a complete clinical picture and conduct additional studies. It is impossible to interpret the results of the electrocardiogram curve unambiguously, since the nature of the bioelectric processes is heterogeneous.
The repolarization process can be disrupted by a very serious pathology - hypersympathicotonia. This disease begins in childhood and is accompanied by increased levels of adrenaline in the blood.
Also, the reasons for deviations in the repolarization phases on the ECG curve may be due to heavy physical labor or constant stressful situations. Women during pregnancy or menopause are susceptible to the disease. A huge number of people have changes in the lower wall of the heart muscle, but are not aware of it.
Types and criteria of premature ventricular repolarization
The main criteria for the ECG picture in diagnosing the syndrome are:
- Shift upward of the ST interval. Usually it does not have a strictly horizontal direction and smoothly passes into the ascending knee of the T wave. A sharp rise indicates the process of necrosis during a heart attack, severe dystrophy, digitalis intoxication, and pericarditis. Accelerated repolarization gives an increase in the interval by no more than 3 mm.
- Tall T wave with a wide base (to be distinguished from hyperkalemia, ischemia).
- “Notch” on the descending section of R.
ECG signs do not always include all elements of the syndrome
In functional diagnostics, it is customary to distinguish two variants of the syndrome:
- with the participation of other manifestations of heart pathology;
- without cardiac signs of damage.
According to the duration of manifestations, the syndrome can be:
- transient,
- permanent.
A. Skorobogaty’s classification provides for the connection of types of premature repolarization with chest leads on the ECG:
- pronounced signs in V1-V2;
- changes predominate in V4-V6;
- without any patterns in the leads.
Tests and diagnostics
The main changes are recorded precisely on the electrocardiogram. Some patients simultaneously experience clinical symptoms of cardiovascular diseases, but most often patients feel absolutely healthy and do not notice any changes.
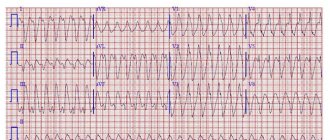
Early ventricular reoplarization syndrome on ECG:
- elevation of the ST segment above the isoline;
- the convexity when raising the ST segment is directed downwards;
- an increase in the R wave with a parallel decrease in the S wave or its complete disappearance;
- point J is located above the isoline, at the level of the descending knee of the R wave;
- expansion of the QRS complex on the ECG;
- a “notch” is recorded on the descending limb of the R wave.
Who has similar disorders?
Premature repolarization is characterized by manifestation against the background of:
- overload of the left ventricle during hypertensive crisis, acute circulatory failure;
- ventricular extrasystole;
- supraventricular tachyarrhythmia;
- ventricular fibrillation;
- in adolescence with active puberty of the child;
- in children with problems of placental circulation during pregnancy, congenital malformations;
- in people involved in sports for a long time.
The absence of any influence of the syndrome of premature repolarization of a pregnant mother on the development of the fetus and the gestation process has been proven, unless other serious arrhythmias occur.
Symptoms
Clinical symptoms are observed only in the form of the disease that is accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system:
- loss of consciousness, fainting ;
- rhythm disturbances ( tachyarrhythmia , extrasystole , ventricular fibrillation );
- vagotonic, hyperamphotonic, tachycardial, dystrophic are formed under the influence of humoral factors on the hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- systolic and diastolic dysfunction of the heart caused by its hemodynamic disorders ( pulmonary edema , hypertensive crisis , shortness of breath , cardiogenic shock ).
Features of the syndrome in an athlete
Observations of athletes who train four hours a week or more showed the development of adaptive thickening of the wall of the left ventricle and the predominance of vagal influence. These changes are considered normal in sports medicine and do not require treatment.
80% of trained people have a heart rate of up to 60 per minute (bradycardia).
Early repolarization syndrome is determined, according to various sources, in 35–90% of athletes
How to identify the syndrome?
Diagnosis is based on an ECG examination. For unstable symptoms, Holter monitoring is recommended throughout the day.
Drug tests can provoke or eliminate typical ECG changes. They are carried out only in a hospital under the supervision of the attending physician.
The most acceptable test for a clinic setting is physical activity. It is prescribed to identify hidden pathology and the degree of adaptability of the heart. Squats, treadmills, and walking on stairs are used.
Such a test is considered mandatory when deciding on military service, joining the police, special forces, or when applying for a medical certificate for military educational institutions.
Isolated premature repolarization is not considered a contraindication in these cases. But the accompanying changes may be regarded by the military medical commission as an inability to work in a difficult sector or serve in special forces.
A complete examination is necessary to exclude cardiac pathology. Appointed:
- biochemical tests (lipoproteins, total cholesterol, creatine phosphokinase, lactate dehydrogenase);
- Ultrasound of the heart or Doppler sonography.
Differential diagnosis necessarily requires the exclusion of signs of hyperkalemia, pericarditis, dysplasia in the right ventricle, and ischemia. In rare cases, coronary angiography is necessary for clarification.
Does the syndrome need to be treated?
Uncomplicated early repolarization syndrome requires the following:
- refusal of increased physical activity;
- changing the diet to reduce the proportion of animal fats and increase fresh vegetables and fruits rich in potassium, magnesium, and vitamins;
- It is necessary to maintain a healthy routine, get enough sleep and avoid stress.
It is not recommended to burden your child with additional activities
Drug therapy includes, if necessary:
- in the presence of cardiac pathology, specific drugs (coronary lytics, antihypertensive drugs, β-blockers);
- antiarrhythmic drugs that slow down repolarization if accompanied by rhythm disturbances;
- some doctors prescribe drugs that increase the energy content in heart cells (Carnitine, Kudesan, Neurovitan), you should pay attention to the fact that these drugs do not have a clear evidence base confirming their effectiveness;
- B vitamins are recommended as coenzymes in the processes of restoring the balance of electrical activity and impulse transmission.
Surgery is used only for severe cases of arrhythmias contributing to heart failure.
By inserting a catheter into the right atrium, additional pathways of impulse propagation are “cut” by radiofrequency ablation.
If there are frequent attacks of fibrillation, the patient may be offered a defibrillator-cardioverter to eliminate life-threatening attacks.
Data correction
If a comprehensive examination is carried out and an accurate diagnosis is established, the specialist will prescribe treatment aimed at eliminating the causes that caused the disruption of the repolarization phases. In cases where the disease is life-threatening, surgery is prescribed - cardiac ablation.
A person who has been found to have abnormalities in the repolarization process must:
- discuss the possibility of physical activity with your doctor;
- register with a dispensary;
- do ECG regularly;
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle;
- Take medications/vitamins prescribed by your doctor.
Control the functioning of your heart by keeping it healthy!
What does the forecast say?
Modern cardiology is aimed at preventing all pathologies that affect fatal complications (sudden cardiac arrest, fibrillation). Therefore, it is recommended to observe patients with impaired repolarization, compare ECG dynamics, and look for hidden signs of other diseases.
Athletes must be examined at physical education clinics. Check before and after intense training and competitions.
There are no clear indications of the transition of the syndrome to a typical pathology. The risk of death is much greater with alcoholism, smoking, and overeating fatty foods. However, if a doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination, it should be completed to exclude possible hidden abnormalities. This will help avoid problems in the future.
Possible manifestations and consequences for the body
As a rule, if repolarization is disrupted, nothing bothers a person. Therefore, in almost everyone, this syndrome is detected either during a preventive medical examination or during examination for another disease.
If symptoms appear, then only if a repolarization disorder occurs against the background of some kind of cardiac pathology. Then the patient may complain of heart pain, dizziness, rapid pulse, etc.
I am often asked whether impaired myocardial repolarization is dangerous, especially during pregnancy. No, but it may indicate the presence of cardiac disease.
As for SRRH, for a long time it was considered absolutely harmless, it was taken for an “accidental find”. However, many years of clinical studies have cast doubt on this.
It turned out that those people who had signs of SRR on the ECG have a very high risk of developing paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in the future (in a few years).