Tachycardia
Tachycardia is an increased frequency of heart contractions and beats. It develops when the number of beats exceeds 90 per minute. Tachycardia is a normal physiological phenomenon if it appears after exercise or emotional stress. Pathological tachycardia manifests itself at rest.
Symptoms of tachycardia appear:
- chest pain;
- increased heart rate at rest;
- strong shocks and “failures” in the work of the heart;
- darkening of the eyes, dizziness.
Diagnosis and treatment . Tachycardia is diagnosed by measuring the number of heart contractions, and an ECG allows the diagnosis to be clarified. For treatment, antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed, for example, lidocaine. If the blood pressure is low, norepinephrine is prescribed. At the same time, medications are prescribed that treat the root cause of tachycardia.
Difference in origin
Arrhythmia and tachycardia have a similar origin, so the reasons why they occur are usually the same. Physiological rhythm disturbance occurs in the following cases:
- strong emotional shocks;
- hard physical labor;
- playing sports;
- eating disorders;
- lack of sleep;
- use of caffeinated drinks;
- lack of microelements;
- sudden changes in ambient temperature.
All pathological causes of arrhythmia or increased myocardial contractions can be divided into cardiac and extracardiac. In the first case, the main disease is:
- Inflammatory processes (myocarditis, pericarditis).
- Ischemic disease (angina pectoris).
- The appearance of scars as a result of post-infarction or cardiomyopathic sclerosis.
- Valve defects.
- Chest injuries.
Deviation from normal sinus rhythm can also occur in the case of other diseases or conditions:
- Excessive consumption of cardiac glycosides, diuretics and antiarrhythmic drugs.
- Diseases of the endocrine system with increased production of adrenaline, thyroid and adrenal hormones.
- Poisoning with heavy metals and other toxic substances.
- Severe infections with severe fever and intoxication.
- Excess of harmful substances in the blood due to kidney or liver failure.
- Consumption of drugs, alcohol, smoking.
In some cases, a violation of the rhythm of contractions occurs for an unknown reason, then they are considered idiopathic.
The main difference between arrhythmia is the unevenness of the intervals between contractions of the heart muscle. With tachycardia, the intervals are the same, but their frequency reaches 90 or more beats/min.
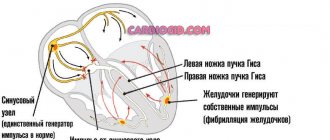
AV block
AV block occurs when the heart partially or completely stops conducting impulses from the atria to the ventricles. Because of this, the heart rate is disrupted, and organs and tissues do not receive enough blood and oxygen.
Symptoms . When the disease develops:
- weakness, shortness of breath;
- angina pectoris – pain in the sternum;
- dizziness, darkening of the eyes;
- bradycardia - a decrease in heart rate to 30-50 beats per minute.
Diagnosis and treatment . AV block is diagnosed by ECG and echocardiography. If the problem appears due to taking certain medications (for example, papaverine or drotaverine), to eliminate it, it is enough to stop taking the medications. If there are concomitant heart diseases, beta-agonists are prescribed; in severe cases, a pacemaker is implanted.
Action tactics: what's the difference
If abnormalities of a physiological nature occur in the functioning of the heart, treatment is usually not required. It is enough to eliminate the cause of their appearance, and everything returns to normal. It’s another matter if the etiological factor is a disease. In this case, it is necessary to carry out full-fledged treatment, the goal of which is to completely eliminate the disease or transfer the pathology to a state of stable remission.
We remove provoking factors
To normalize the rhythm, it is recommended to remove factors that contribute to the appearance of tachycardia or arrhythmia:
- Review your diet. Eat often and in small portions, exclude spicy, salty, and caffeinated drinks from your diet.
- Try to avoid physical and psycho-emotional overload.
- Observe the work and rest schedule.
- Take walks at an average pace and breathe clean air.
- Stop drinking alcohol and quit smoking.
Paroxysmal tachycardia can be stopped by acting on the vagus nerve. For this purpose, pressure on the eyeballs and massage of the sinocarotid zone are used.
You can get more detailed information about what tachycardia is, what its types are, and also find out how to eliminate the pathology here.
We use medications
Medicinal methods include the use of the following medications:
- sedatives (motherwort, Valocordin);
- beta blockers (Atenolol, Bisoprolol);
- calcium antagonists (Amlodipine).
You can add herbal decoctions to general therapy. Chamomile, valerian, and hawthorn are used to improve cardiac activity. But they should not be used as the main means of stopping an attack.
A detailed description of tablets and other medications, as well as the features of their use for tachycardia, can be seen by going here.
Surgical treatment of severe pathology
Severe forms of rhythm and conduction disorders require the use of surgical treatment methods. Depending on the cause, the specialist recommends the following radical methods:
- radiofrequency ablation;
- installation of an artificial pacemaker;
- implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator;
- valve restoration;
- shunting for blood flow problems.
The prognosis for arrhythmia depends on the etiological factor of its occurrence. But in general, compared to tachycardia, it is more severe and more often leads to various complications and even death.
If you want to know everything about tachycardia, we recommend watching the video below at the link. Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and signs that it’s time to see a doctor - talk about all this in 7 minutes. Enjoy watching!
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disorder in which the atria contract faster than the ventricles. Muscle fibers are excited frequently and chaotically, this is called tissue flicker.
With atrial fibrillation, the following symptoms develop:
- heart rate increases;
- tingling, chest pain occurs;
- causeless attacks of fear develop;
- sweating increases;
- the urge to urinate becomes more frequent.
Diagnosis and treatment . Atrial fibrillation is diagnosed during a standard examination, and an ECG is prescribed to confirm the diagnosis. The disease is treated with drugs that reduce the heart rate, normalize heart rhythm, and prevent the formation of blood clots. If drug treatment does not help, the heart cells that provoke the arrhythmia are removed or a pacemaker is installed.
Consequences and complications
In the absence of timely treatment, arrhythmias and heart block provoke attacks of angina, pulmonary edema, and thromboembolism. Acute heart failure and even cardiac arrest are possible. According to statistics, in 10-15% of cases, blockades and other types of arrhythmia lead to death. Pathological tachycardia can provoke myocardial infarction. Complete atrioventricular block or asystole can provoke loss of consciousness, which is associated with a decrease in blood supply to the brain. Every sixth case of thromboembolic complications of atrial fibrillation leads to stroke. For arrhythmias caused by different causes, treatment is selected individually.
Sick sinus syndrome
What is this . Sick sinus syndrome is damage to the sinus node (the part of the heart that conducts impulses). Due to damage, the sinus node no longer controls the heart correctly, and arrhythmia occurs.
Sick sinus syndrome manifests itself:
- dizziness, fainting;
- loss of consciousness with convulsions;
- constant weakness, inability to concentrate;
- a rare pulse, which is replaced by a rapid heartbeat.
Diagnosis and treatment . To diagnose the disease, an examination is carried out, general blood and urine tests, an ECG, and an echocardiogram are prescribed. To eliminate sick sinus syndrome, treat the underlying disease that caused it. If the syndrome is accompanied by constant complaints, a pacemaker is installed, which artificially sets a normal heart rhythm.
Diagnostics
The primary stage of diagnosing arrhythmia and heart block is carried out by a therapist or cardiologist. Based on the patient’s complaints and examination results, the following examinations may be prescribed:
- electrocardiography (including 24-hour Holter monitoring);
- transesophageal/intracardiac electrophysiological study;
- treadmill test (diagnosis of arrhythmias with imitation of conditions causing blockade or other disorders).
If necessary, the doctor prescribes auxiliary diagnostic studies and tests. The accuracy of the results affects the effectiveness of treatment of the blockade or arrhythmia.
Atrial flutter
Atrial flutter is a rapid, uniform rhythm of the atria, which contract at a frequency of up to 200-400 beats per minute. An attack of atrial flutter lasts from 1-2 seconds to several days.
Symptoms . For atrial flutter:
- general weakness develops, endurance decreases;
- discomfort appears in the chest, angina pectoris - pain behind the sternum;
- sudden attacks of rapid heartbeat develop;
- shortness of breath increases.
Diagnosis and treatment . The problem is diagnosed by ECG and ultrasound of the heart. Drug treatment is aimed at normalizing atrial contractions, preventing attacks and reducing the risk of blood clots. Beta blockers, potassium supplements, and anticoagulants are prescribed.
The Medicenter clinic diagnoses and prescribes effective treatment for all types of arrhythmia. Drug therapy is used and surgery is prescribed.
Treatment methods
They depend on the type of arrhythmia and the reasons that caused its development:
- For tachycardia, rest, avoidance of alcoholic and caffeine-containing drinks, smoking, and chocolate are indicated. The same rules should be followed for other heart diseases. It is possible to prescribe medication in particularly severe cases.
- Mild bradycardia does not require treatment. For more serious forms, drug therapy is used. In severe cases, implantation of a pacemaker is indicated.
- Treatment of extrasystole consists of combating the diseases that contributed to its development.
- Atrial fibrillation is treated with antiarrhythmic drugs. It is possible to use electrical cardioversion (delivery of electrical discharges to the heart). The procedure is performed under anesthesia and is highly effective.
Selecting the most effective treatment regimen in each specific case requires time and constant monitoring of the patient’s health condition. Self-medication of arrhythmia is strictly prohibited.
Read also
Hypotension
What is hypotension Hypotension, or low blood pressure, is most often not considered a serious disease because in many people it is asymptomatic.
However, some... Read more
The problem of myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction remains a very significant social problem. This condition leaves quite serious consequences, which in almost all cases lead to disability. In other cases…
More details
Heart rhythm disturbances
What Are Heart Rhythm Abnormalities? Heart rhythm problems occur when the impulses that coordinate the heartbeat travel in the wrong direction, with more...
More details
Dyspnea
What is shortness of breath? Few sensations are as frightening as not being able to take a breath. Shortness of breath, or dyspnea, is often described as intense chest tightness, air hunger, or a feeling...
More details
Palpitations
Palpitations are sensations of a rapidly beating, fluttering, or vibrating heart. What causes palpitations? They can be caused by stressful situations, physical activity,…
More details
Our specialists
Shcherbakova Lyudmila Aleksandrovna
The doctor is a cardiologist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.
Gabrielyan Julietta Grigorievna
The doctor is a cardiologist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences. Experience: 25 years
Logacheva Olga Alexandrovna
The doctor is a cardiologist of the first category. Functional diagnostics doctor. Experience: 17 years.
Roshchina Ekaterina Anatolevna
Functional diagnostics doctor of the second category. Ultrasound diagnostics doctor. Cardiologist. Experience: 15 years.
Heart rhythm disturbances - we answer your questions
Heart rhythm disturbances – we answer your questions.
What does arrhythmia, heart rhythm disturbances mean?
Heart rhythm disturbances, arrhythmia, is a disturbance in the frequency, rhythm and sequence of contractions of the heart muscle.
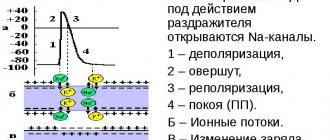
The human heart works throughout life. It contracts and relaxes 50 to 150 times per minute. During the systole phase, the heart contracts, ensuring blood flow and delivery of oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. During the diastole phase it rests. Therefore, it is very important that the heart contracts at regular intervals. If the systole period is shortened, the heart does not have time to fully provide the body with blood movement and oxygen. If the diastole period is shortened, the heart does not have time to rest.
What causes arrhythmia and what types of it occur?
The causes of heart rhythm disturbances are not fully understood. It is believed that the main two reasons are changes in nervous and endocrine regulation or functional disorders, and abnormalities in the development of the heart and its anatomical structure - organic disorders. Often there are combinations of these underlying causes.
The reasons may be:
inflammation and dystrophy of the heart muscle, hypertension, coronary disease, heart defects, etc.;
diseases of the endocrine system, most often the thyroid gland;
neuroses, emotional experiences, stress;
unhealthy lifestyle: unbalanced diet, absence or systematic violation of the daily routine, lack of physical activity, smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, etc.
Risk factors for developing cardiac arrhythmias include:
Age. With age, the heart muscle becomes depleted, weakens and loses some of its nutrition. This can affect the formation and conduction of electrical impulses.
Genetics. In people with congenital abnormalities of the heart, arrhythmias occur more often. Moreover, a number of arrhythmias (eg, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, some supraventricular tachycardias, some forms of long QT syndrome) are congenital.
Coronary heart disease, other heart diseases, open heart surgery. Narrowing and occlusion (complete closure) of the lumen of the coronary arteries (arteries that supply the heart muscle), pathology of the heart valves, previous open-heart surgery, cardiomyopathies and other factors damaging the heart are a serious risk factor for the development of almost all types of arrhythmias.
Thyroid diseases. With increased thyroid function, increased production of hormones occurs, overall metabolism increases, and heart contractions become more frequent and irregular. Atrial fibrillation most often develops. With insufficient thyroid function, metabolism decreases, which causes bradycardia, and in some cases, extrasystole.
Medications. Most often, arrhythmia is caused by uncontrolled and excessive use of cold medications containing ephedrine and pseudoepinephrine, as well as a number of other drugs, for example, diuretics, laxatives or anti-asthmatics.
High blood pressure. This increases the risk of developing coronary heart disease. High blood pressure also causes the wall of the left ventricle to thicken, which can change the way impulses are conducted through it.
Obesity. Being a risk factor for the development of coronary heart disease, obesity also increases the risk of developing arrhythmias.
Diabetes. Diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation (uncontrolled blood sugar levels) greatly increases the risk of developing coronary heart disease and arterial hypertension. In addition, episodes of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) can be a trigger for the development of cardiac arrhythmias.
Pathological sleep apnea syndrome. This pathology may be accompanied by bradycardia and atrial fibrillation.
Electrolyte disturbances. Electrolytes such as potassium, magnesium, sodium and calcium form the basis for the formation, maintenance and conduction of electrical impulses in the heart. Too high or too low concentrations of electrolytes in the blood and in heart cells affect the electrical activity of the heart and can cause the development of arrhythmias.
Alcohol consumption. Drinking large doses of alcohol increases the risk of developing atrial fibrillation. Sometimes, the development of atrial fibrillation after excessive alcohol consumption is called “holiday heart syndrome”. Chronic alcohol abuse has a detrimental effect on heart cells and can lead to cardiomyopathy, which is also the basis for the development of cardiac arrhythmias.
Use of stimulants. Psychostimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, etc. cause the development of extrasystole and can also lead to the development of more severe heart rhythm disturbances over time. The use of amphetamines and cocaine can damage the heart muscle with the development of any of the existing arrhythmias and even lead to sudden cardiac death due to the development of ventricular fibrillation.
The most common heart rhythm disturbances are:
•extrasystole (extraordinary contraction),
•atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation),
•paroxysmal tachycardia (sharp increase in heart rate from 150 to 200 beats per minute).
An increase in heart rate of more than 100 per minute is called sinus tachycardia. In this case, the full contractions of the heart muscle and the cardiac complexes on the electrocardiogram do not change, an increased rhythm is simply recorded. This can be a healthy person’s reaction to stress or physical activity, but it can also be a symptom of heart failure, various poisonings, and thyroid diseases.
A decrease in heart rate below 60 beats per minute is called sinus bradycardia. Cardiac complexes on the ECG also do not change. This condition can occur in well-trained physically people (athletes). Bradycardia is also accompanied by diseases of the thyroid gland, brain tumors, mushroom poisoning, hypothermia, etc.
Disturbances in cardiac conduction and rhythm are very common complications of cardiovascular diseases.
What symptoms can be used to identify rhythm disturbances?
The classification of rhythm disturbances is very complex. Arrhythmias and blockades can occur anywhere in the conduction system of the heart. Their type depends on the place of occurrence of arrhythmias or blockades.
Extrasystoles or atrial fibrillation are felt by the patient as palpitations, the heart beats faster than usual or there are interruptions in the heart.
If the patient feels fading, cardiac arrest, and at the same time he experiences dizziness and loss of consciousness, most likely the patient has a heart rhythm block or bradycardia (decreased heart rate).
If any heart rhythm disturbance is detected in a patient, it is necessary to conduct a full examination to determine the cause of the arrhythmia.
The main method for diagnosing heart rhythm disorders is an electrocardiogram. An ECG helps determine the type of arrhythmia.
But some arrhythmias occur sporadically. Therefore, Holter monitoring is used to diagnose them. This study provides an electrocardiogram recording over several hours or days. At the same time, the patient leads a normal lifestyle and keeps a diary, where he notes the actions he performs hourly (sleep, rest, physical activity). When interpreting the ECG, the electrocardiogram data is compared with the diary data. The frequency, duration, time of occurrence of arrhythmias and their connection with physical activity are determined, while signs of insufficiency of the blood supply to the heart are analyzed.
Echocardiography allows you to identify diseases that contribute to the development of arrhythmias - valve prolapse, congenital and acquired heart defects, cardiomyopathies, etc.
More modern research methods are also used:
•endocardial (from the internal cavity of the heart),
•transesophageal electrophysiological research methods.
Transesophageal ECG is a study that allows you to cause a patient’s heart rhythm disturbance. It is carried out using a thin electrode, which is inserted through the esophagus to the level of the patient’s right atrium and is activated to provoke an arrhythmic attack. At this time, the doctor takes data on the patient’s heart using standard sensors attached to the patient’s arms, legs and chest. A transesophageal ECG allows you to obtain more accurate data about the disease that caused rhythm disturbances and build a competent treatment plan for it;
ultrasound examination (echocardiography). Allows you to obtain and analyze an image of the heart, which in turn helps to identify the cause of problems in the functioning of the heart;
Endocardial catheterization - the procedure involves inserting a thin radiopaque tube - a catheter - into the heart through large blood vessels. This method allows you to measure pressure in different parts of the heart muscle, as well as obtain samples of heart tissue for analysis, etc. Catheterization is used to confirm and clarify the diagnosis of a systemic disease that has caused a disturbance in the rhythm of contractions of the heart muscle: ischemic heart disease, pulmonary hypertension, etc.
In order to identify the reasons that caused the patient’s arrhythmia, the doctor may prescribe additional laboratory tests of blood, urine and other examination methods.
How should arrhythmia be treated?
When the first signs of cardiac dysfunction appear, you should consult a doctor to make a diagnosis and receive recommendations for treatment.
Treatment of patients with obvious heart rhythm disturbances directly depends on the type of arrhythmia, as well as its degree. As a rule, doctors begin by treating the underlying disease that caused the development of this disease. Most types of heart rhythm disturbances do not require drug treatment and can be eliminated by simple changes in a person’s lifestyle: giving up caffeine in all its forms, quitting smoking, judicious consumption of alcoholic beverages, avoiding stressful situations.
For some heart rhythm disorders, the only treatment method is surgery. This type of treatment is used for arrhythmias such as severe bradycardia, severe AV block, sick sinus syndrome. People suffering from ventricular tachycardia or episodes of ventricular fibrillation are implanted with a defibrillator, which only begins to function when there is an abnormal heart rhythm. When, as a result of research, a pathological focus with increased activity is revealed, which is the source of heart rhythm disturbances, it is destroyed surgically through cardiac catheterization.
What is the prevention of heart rhythm disturbances?
To reduce the risk of arrhythmic disorders it is necessary:
•avoid stress, physical and emotional overload;
•build a daily routine and stick to it: sleep at least 8 hours a day, regularly take walks in the fresh air, conduct moderate physical activity;
•normalize nutrition: eliminate undereating and overeating, give up foods that are too fatty, high in calories and contain a large amount of artificial additives. Patients with heart rhythm disturbances should include in their diet fruits and vegetables containing vitamins C, group B, biotin, carnitine, calcium and magnesium. Their use helps improve the conductivity of cardiac impulses and muscle nutrition; regularly (at least once a year) undergo a full medical examination by qualified specialists;
• give up “bad habits” (smoking, alcohol).
Heart rhythm disturbances are a common manifestation of many diseases of the cardiovascular, endocrine and nervous systems. Therefore, you should remember about prevention and, if necessary, treatment of underlying diseases that lead to rhythm disturbances.
Prevention, timely diagnosis and treatment help prevent the occurrence of pathological consequences dangerous to human health and life.
When the first signs of heart rhythm disturbances appear, you should consult a doctor for a diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Clinical manifestations of irregular heartbeat can be very varied. At the same time, the patient himself is most often not able to determine what may threaten him with certain interruptions in the work of the heart. For example, such a harmless rhythm disturbance as a single extrasystole (premature contraction of the heart) is quite difficult for many to tolerate and forces them to immediately consult a cardiologist. At the same time, a more serious disorder - a series of extrasystoles - can be perceived as palpitations or “fluttering” in the chest or neck, which the patient gradually ceases to notice.
In the case when the arrhythmia occurs with periodic attacks, the patient feels periods of acceleration of the heart rate or, conversely, a slowdown. If the arrhythmia is permanent, the patient may eventually get used to it and will not seek help from a doctor. This is quite dangerous, because if the arrhythmia becomes protracted, its effect on the functioning of the heart becomes quite significant and the consequences can be serious.
More serious systemic symptoms occur when an arrhythmia causes the heart to stop pumping enough blood. If the arrhythmia is based on weakness of the heart muscle or atherosclerosis (deposition of fats, cholesterol and other substances) in the coronary arteries, then the pumping function of the heart may decrease even more. The patient begins to feel tired, dizzy, and short of breath. Some people begin to experience fainting. In patients with coronary heart disease, angina begins to progress. With chronic heart failure, swelling in the legs increases, heaviness appears in the right hypochondrium and attacks of cardiac asthma occur. If you are concerned about any interruptions in the functioning of your heart, it is better to consult a doctor in a timely manner, who will be able to determine their cause and, if necessary, give valuable recommendations, prescribe treatment, and begin to monitor the condition of your heart.
Prevention measures are best focused on the following:
1.Control cholesterol and blood pressure.
2.Diet low in fat and salt. Regular exercise. Your doctor can tell you what level of activity is appropriate and safe for you.
3. Quit smoking.
4.Limit your alcohol consumption.
5.Take your medications as prescribed.
6. Visit your doctor regularly for periodic examinations, examinations and ongoing monitoring.
Print Email
- Back
- Forward
Causes
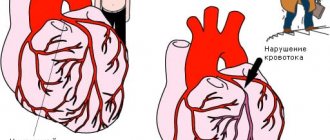
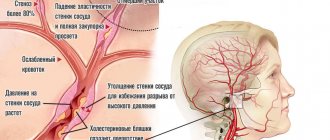
Coronary arteries can narrow for several reasons, but the main one is, of course, atherosclerosis.
Due to improper nutrition, fatty plaques and blood clots form on the inner walls of blood vessels. In places where they are deposited, the lumen noticeably decreases. If a blood clot breaks away from its place, it can travel with the blood flow into any thin artery, including the coronary artery, and block it. But usually this happens in places where the vessels are already narrowed. As a result, blood flow is noticeably reduced, and oxygen starvation occurs in the tissues of the heart. The cause of angina, as mentioned above, can also be vasospasm (this is how nicotine acts on them, for example). Almost all of the above does not appear by itself. In 90% of cases, the causes of angina are poor diet, smoking, alcoholism and a sedentary lifestyle. However, regardless of this, signs of angina pectoris are most likely to appear in people whose relatives died from coronary heart disease or suffered from angina pectoris.
Etiology of arrhythmia
of diseases can become fertile ground for the onset of arrhythmia.
, both
cardiovascular
and other body systems.
These are hypertension, coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction, heart failure, inflammatory, dystrophic diseases of the myocardium, valve defects (congenital and acquired), anomalies of heart development. Often the cause of rhythm disturbances is the dysfunction of the endocrine
system (hypo- and hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, Conn's syndrome, pheochromocytoma, menopause),
nervous, bronchopulmonary, and digestive systems
. Diseases affecting the entire body (anemia, infectious diseases and poisoning) can provoke arrhythmia.
Significant risk factors: abuse of alcohol, strong tea or coffee, any form of smoking, taking certain medications.
In addition, fasting, an unbalanced diet, food depletion of vitamins and microelements, dehydration, that is, any circumstances of disruption of water-electrolyte metabolism or acid-base status can lead to a failure of the normal electrical activity of the heart. Hereditary predisposition also matters.
However, in approximately 1/10 patients, even with high-quality examination, the cause of the arrhythmia cannot be determined (idiopathic arrhythmia).