Causes of cardiosclerosis
1. Functional disorders:
- Damage to the heart muscle as a result of inflammatory diseases.
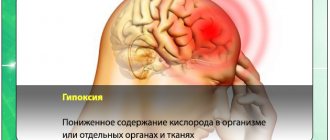
- Hypoxia due to insufficient blood supply to the heart muscles due to narrowing of large cardiac vessels.
- Stretching of the walls of the heart, which leads to an increase in its volume.
2. Lifestyle and bad habits of the patient:
- Alcohol abuse and smoking.
- No, minimal or excessive physical activity.
- Repetitive stress.
- The habit of overeating and, accordingly, excess body weight.
Hereditary factors play an important role in the occurrence of the disease.
Development mechanism
Atherosclerosis develops as a result of disruption of two mechanisms that ensure the functionality of tissue blood supply.
1st mechanism
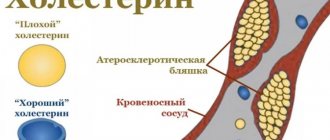
The first mechanism is a metabolic disorder that directly affects lipid (fat) metabolism. This leads to an increase in the concentration of cholesterol, non-esterified (free) fatty acids and triglycerides. At the same time, the content of phospholipids in the blood decreases, and cholesterol is converted into a finely dispersed state:
- alpha lipoproteins - strong compounds with proteins and triglycerides;
- beta lipoproteins are fragile molecules – prebeta lipoproteins.
Once in the walls of blood vessels, lipoproteins quickly break down, releasing triglycerides and cholesterol, and have an atherogenic effect on the arteries, that is, they damage them. In atherosclerosis, due to a decrease in the level of alpha proteins, the concentration of fragile lipoproteins increases. Depending on the nature and characteristics of lipid metabolism, the predominance of certain groups of lipoproteins, there are 5 types of hyperlipidemia (increased fat content in the blood).
The most pronounced pathogenic effect is observed when hyperlipidemia of types 2 and 3 occurs, which develop due to the predominance of beta and prebeta lipoproteins, respectively. In addition, an important factor is the increase in free fatty acids necessary for the production of triglycerides and cholesterol.
Their effect also helps to reduce the sensitivity of body cells to insulin, which reduces the speed and quality of transformation of glucose into glycogen, leading to hyperglycemia (increased blood sugar) and other local disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. In parallel, pathologies of protein metabolism are also observed, which is due to the direct interaction of proteins and lipids.
Cholesterol plaque in the lumen of the artery
2nd mechanism
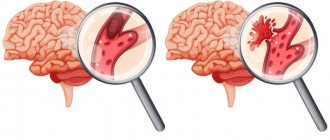
The second mechanism, interruptions in which occur during atherosclerosis, is a morphological change in the vascular walls, that is, a violation of their permeability. As a rule, the ability to pass certain substances through the walls of blood vessels increases, which is caused by a decrease in the quality of microcirculation and an increase in the level of acidic mucopolysaccharides.
At the same time, the number of pores increases, resulting in increased permeability of the vascular walls. Often the cause of such disorders is a high level of concentration of local hormones, for example, bradykinin, which, in turn, causes an increased formation of catecholamines.
In the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, a significant role belongs to the growth of enzyme activity directly in the vascular wall itself, and specifically elastase, which causes changes in the vascular framework. An additional aspect of the development of this pathology can also be an increase in blood pressure (blood pressure), which is a mechanical factor in the appearance of damage.
Classification of cardiosclerosis
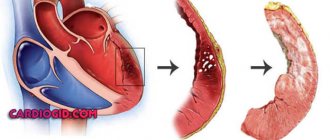
According to the morphological principle, focal (most often occurs as a complication after myocardial infarction and myocarditis) and diffuse cardiosclerosis, in which the connective tissue spreads to the entire myocardium, are distinguished.
For etiological reasons, the following types are distinguished:
- Post-infarction. As a result of myocardial infarction, scars form at the site of necrotic damage, which reduces the contractility of the heart muscle. The more cases of myocardial infarction a patient has suffered, the more scar tissue is formed. The threat of chronic aneurysm increases due to protrusion of the walls of the heart muscle, which is stretched and weakened by connective tissue. Aneurysm rupture is associated with high mortality.
- Myocardial. Myocardial inflammation develops mainly in young patients with chronic allergic and infectious diseases. With this form, the right ventricle of the heart increases in volume and is insufficiently supplied with blood.
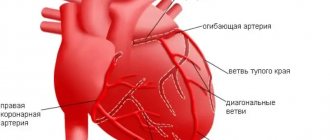
- Atherosclerotic. As a rule, it is the result of atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels and coronary heart disease. This form of the disease develops over a long period of time, because due to damage to blood vessels, heart cells do not receive enough oxygen, hypoxia develops, the course of coronary heart disease is complicated, and cholesterol levels increase. This leads to diffuse cardiosclerosis, which is accompanied by arrhythmia.
Alternative medicine
Non-traditional methods of treatment for this pathology can only be auxiliary. Doctors include home recipes in a set of measures aimed at maintaining myocardial function. Any adjustments in treatment should be discussed with your doctor. It is unacceptable to self-prescribe a course of therapy. In myocardial cardiosclerosis, the course of the disease is improved:
- ginger - used as an additive to tea or as a tincture to prevent the formation of blood clots and eliminate atherosclerotic plaques;
- garlic - helps reduce cholesterol concentrations, normalize blood pressure, and is a powerful tool for strengthening vascular walls;
- hawthorn - has a positive effect on blood flow, normalizes cholesterol and blood pressure, restores heart rhythm (tea or alcohol tincture);
- parsley - strengthens the heart muscle, the walls of blood vessels (all components of the plant are used);
- artichoke - consumed in tinctures or in tablet form to strengthen blood vessels and reduce bad cholesterol;
The approach to eliminating the problem and alleviating symptoms should be comprehensive. A competent specialist combines conservative therapy with unconventional methods, recommends the patient to walk more, swim, and dance. It is important to correctly assess your capabilities and not overwork.
Symptoms of cardiosclerosis
Very often the initial stages of the disease are asymptomatic. In the clinic of the onset of sclerosis, the first symptom may be arrhythmia. Typical manifestations of the diffuse form should be considered heart failure and disturbances in the rhythm of the heartbeat.
Symptoms regardless of the form (post-infarction or atherosclerotic):
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- dyspnea;
- the appearance of fluid in the abdominal and pleural cavities;
- pain in the heart area;
- increased heart rate;
- pulmonary edema;
- increase in liver size.
As the area of affected heart tissue increases, the severity of symptoms increases.
Very often the course of cardiosclerosis is accompanied by arterial hypertension. In this case, high blood pressure alternates with long periods of normal blood pressure.
Power Requirements
If you are diagnosed with myocardial cardiosclerosis, you should reconsider your gastronomic habits. The following are completely excluded from the food basket:
- coffee, caffeinated drinks;
- alcohol containing drinks;
- fast food, street food;
- scrambled eggs;
- rich meat broths;
- sauces, butter.
The diet should mainly consist of vegetables, herbs, fermented milk products, and sea fish. You will have to give up bad habits.
At-risk groups
The risk of cardiosclerosis is highest in patients with pathologies in the development of the heart and cardiovascular diseases, as well as in people with various types of allergies.
Pregnant women can be identified as a separate group. Pregnancy causes hormonal, autonomic, metabolic and hemodynamic changes in the body of women and can act as a proarrhythmogenic factor. Complex heart rhythm disturbances are diagnosed both in pregnant women with cardiovascular pathology and in patients without changes in metabolism and the condition of internal organs.
Cardiosclerosis in children is possible against the background of myocardial pathologies, for example, inflammatory and dystrophic processes, in particular diseases of the heart muscle caused by metabolic disorders in heart cells. These biochemical disorders significantly weaken the contractile, conductive, excitatory and automatic functions of the myocardium.
Diagnosis of the disease
The doctor can make a diagnosis of atherosclerosis of the aorta and its branches by carefully studying the patient’s medical history and prescribing a full examination. At the initial appointment, the specialist collects anamnestic data, detailing each of the complaints. Next, the patient is sent to undergo laboratory tests, the main one of which is a lipid profile . This study fully characterizes the state of lipid metabolism, recording the slightest deviations.
The next stage is instrumental methods for diagnosing pathology. ultrasound method is the gold standard for detecting atherosclerosis, including the walls of the aorta. What it is? Using a special device that emits ultrasonic waves, a sonologist examines the area of the main artery and its branches. He records all echo signs indicating this disease.
- Atherosclerosis of the aorta of the heart: causes, symptoms, treatment with folk remedies and medications
To assess the degree of blood flow disturbance, Doppler ultrasound . To assess the extent of the pathological process, doctors sometimes prescribe magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
Sometimes atherosclerosis of the aortic arch is detected completely by accident, during an annual fluorogram. Often, an x-ray image quite clearly visualizes the pathological changes that have affected this section of the aorta.
Cardiosclerosis medications
The European Society of Cardiology recommends the following medications for the treatment of cardiosclerosis, eliminating the symptoms of the disease, as well as its root cause:
- Antihypertensive drugs. To maintain vascular tone and normalize blood pressure, ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Enalapril, Ramipril) are prescribed; calcium antagonists (Amlodipine, Semlopin, Phenigidine), beta blockers (Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Metoprolol), antiplatelet drugs (Aspirin), lipid-lowering drugs (Simvastatin, Atorvastatin, Allesta).
- Cardioprotectors (antianginal agents). Their task is to maintain the functional activity of the heart and counteract the influence of negative exo- and endogenous factors on it. These include organic nitrates (Nitroglycerin, Isosorbide Mono- and Dinitrate); sydnonimines (Mosikor, Sidocard); metabolic agents (Trimetazidine).
- To normalize heart rate and conduction: amiodarone (Amiodarone), dronedarone (Multak).
- To normalize metabolic processes - potassium and magnesium preparations: Panangin, Asparkam, Magnerot.
- Antibiotics and corticosteroids: for myocarditis and other inflammatory processes.
List of used literature
- Stryuk R.I., Shoikiemova D.U., Borisov I.V.; State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after. A.I. Evdokimov" Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russia / Pregnancy as a risk factor for heart rhythm disturbances
- POKROVSKAYA E.M., 2, Ph.D., N.A. VOLOV 2, Ph.D., I.S. VASILYEVA 2, GORDEEV I.G. 1, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, PAVLIKOVA E.P., 2, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor 1 State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education “Russian National Research Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogov" of the Ministry of Health of Russia, Department of Hospital Therapy No. 1, Faculty of Medicine 2, State Budgetary Institution "City Clinical Hospital No. 15 named after. O.M. Filatova "DZ Moscow / NEW OPPORTUNITIES FOR TREATING PATIENTS WITH HEART FAILURE DUE TO POST-INFARCTION CARDIOSCLEROSIS
- Berezin A. E., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Internal Medicine No. 2 of the 1st Medical Faculty of Zaporozhye State Medical University / Combined potassium and magnesium preparations in the treatment of patients with high cardiovascular risk.
Frequently asked questions about cardiosclerosis
Which doctor treats cardiosclerosis?
If you suspect cardiosclerosis, you should contact a cardiologist.
What signs should you see a doctor for?
High blood pressure; arrhythmia; increased fatigue and swelling of the limbs.
Can cardiosclerosis develop in children?
Cardiosclerosis in children can develop against the background of inflammatory and dystrophic processes in the myocardium - in particular, diseases of the heart muscle caused by metabolic disorders in heart cells.