Familiarize yourself with other diseases starting with “C”: Sacroiliitis, Salmonellosis, Salpingitis, Salpingoophoritis, Glanders, Beck's Sarcoid, Sarcoidosis, Kaposi's Sarcoma, Ewing's Sarcoma, Diabetes mellitus, Diabetes mellitus type 1, Diabetes mellitus type 2, Mumps, Porcine influenza, rectal fistula, Seborrhea, Sepsis, Cardiac asthma, Heart failure, Sertoli
Cardiac asthma: can it be prevented?
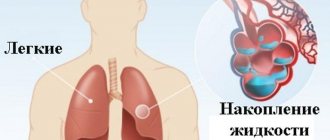
Cardiac asthma manifests itself in the form of attacks of suffocation and shortness of breath caused by left ventricular failure. This leads to stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation. Blood plasma penetrates the bronchi and lung tissue, causing pulmonary edema and causing suffocation and difficulty breathing. This pathology requires emergency medical care; if the attack is not stopped quickly, it can be fatal.
Reason
Cardiac asthma is a combination of other important cardiovascular diseases. All stinks are mainly associated with the increasing deficiency of the left sac. Most often, SA develops at the stage of decompensation of the following illnesses:
- Myocardial infarction.
- Mitral valve stenosis.
- Chronic cardiac aneurysm.
- Aortic defect.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Cardiosclerosis.
Such illnesses as acute nephritis and diffuse glomerulonephritis can also lead to cardiac asthma, and then to swelling of the lungs.
Causes of the disease
Factors provoking pathology are:
- Cardiac ischemia;
- Mitral stenosis;
- Cardiac aneurysm;
- Acute myocardial infarction;
- Exacerbation of chronic glomerulonephritis;
- Post-infarction conditions;
- Paroxysm of atrial fibrillation;
- Cardiosclerosis;
- Defect or deficiency of the heart valves;
- Atrial flutter;
- Heart failure provoked by increased physical activity, horizontal body position or intravenous administration of a large volume of fluid;
- An increase in the blood mass filling the vessels.
What is heart failure?
Our heart is like a pump that pumps blood and supplies oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body. Impaired ability of the heart to pump blood leads to stagnation and leads to the development of heart failure .
Poor blood supply puts other organs and tissues at risk. In terms of prevalence, heart failure rivals the most well-known infectious diseases.
According to statistics, around 28 million people suffer from heart failure throughout Europe. In our country, the number of patients with this disease exceeds 9 million (more than 25% of them are under 60 years of age)! At the same time, Russians die from it 10 times more often than from myocardial infarction.
1 Tests for heart failure
2 Tests for heart failure
3 Tests for heart failure
Characteristic symptoms
Cardiac asthma attacks most often occur at night. They are accompanied by:
- Dry cough;
- By suffocation;
- Cyanosis, that is, blue discoloration of the fingertips, face and nasolabial triangle;
- Pale skin;
- Hard breathing caused by swelling in the lungs;
- Moist rales in the lower parts of the lungs;
- Reflex bronchospasms.
Diagnosis is complicated by the fact that similar symptoms also occur with bronchial asthma. If an attack occurs, you must immediately call a doctor.
Diagnostics
Cardiac asthma in its clinical progression may be similar to low-grade asthma. For example, lack of breath and other signs of shortness of breath are also characteristic of bronchial asthma. Violent breathing and panic attacks often intensify during a hysterical attack. Other similar signs may be mistaken for SA for laryngeal stenosis or mediasthenic syndrome.
In making a correct diagnosis, we are first aided by the patient's history of illness. It is known that the patient had early history of hypertension or heart failure, so the development of cardiac asthma is highly likely. When the SA attacks, it is difficult to carry out diagnostics, the fragments in the first blood are to blame for the attack on the buttocks. However, doctors conduct a thorough objective examination of the pulse, evaluate the mucous membrane and skin, listen to the breath and heart tones.
An important diagnostic criterion that indicates the presence of cardiac asthma is the appearance of the first attacks in adulthood. Also, such patients almost always have another cardiac pathology.
With AS, the following changes may occur:
- The pulse is thread-like or weakly palpable.
- Tony's heart is muffled, you can hear the rhythm of a gallop.
- Arterial pressure on the kidney is indicated as movement, and then decreases.
- In the lungs, you may hear either wheezing or dry irritation.
To clarify the diagnosis, instrumental methods of investigation must be carried out. Firstly, electrocardiography, which shows characteristic signs of left ventricular insufficiency, arrhythmia or myocardial ischemia.
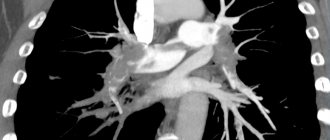
If possible, take a chest x-ray. The image will show signs of blood stagnation in a small amount of blood circulation: enlargement of the root of the legs, thickening of the leg muscles, and the contours of the heart may change.
Treatment
Therapy for cardiac asthma includes:
- Immediate medical assistance to stop the attack;
- Taking medications that relieve an acute condition: nitroglycerin, nifedipine;
- Subcutaneous or intravenous administration of furosemide;
- Oxygen inhalations;
- Administration of cardiac glycosides;
- If heart rhythms are abnormal, defibrillation is indicated.
When an attack first occurs, hospitalization is required. For the treatment of cardiac asthma, it is necessary to correctly identify the disease that provokes this condition and its treatment. Unfortunately, in many cases the outcome is unfavorable, but with complex therapy and lifestyle correction, repeated attacks can be avoided, work capacity can be maintained, and well-being can be maintained for several years.
The danger of cardiac asthma
This pathology has a high risk of death, which can only be avoided with timely medical care.
Diagnosis of heart failure
When diagnosing a disease, it is extremely important to identify the true cause of its development - only then can treatment be as successful as possible.
After collecting an anamnesis and physical examination, a cardiologist may prescribe:
- general clinical, biochemical blood and urine tests;
- electrocardiography (at rest);
- Ultrasound of the heart (Echocardiography);
- chest x-ray;
- coronary angiography;
- Holter ECG monitoring and other studies.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a pulmonologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Professor consultation | 4500 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Study of external respiratory function (RPF) with drug tests | 1800 rub. |
| X-ray of the chest organs (survey) | 1900 rub. |
| X-ray of the chest organs in 2 projections | 2900 rub. |
What does an asthma attack look like in children?
An attack can develop in different ways, but usually has a fairly typical clinical picture. It begins with a cough, which may be accompanied by a skin rash and rhinitis. The baby's breathing becomes uneven, there are short inhalations, and exhalations are clearly difficult. Breathing is accompanied by wheezing; from the outside, the attack looks as if the child is gasping for air. This may cause pale skin and blue lips. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6591438/ Shyamali C. Dharmage, Jennifer L. Perret and Adnan Custovic Epidemiology of Asthma in Children and Adults // Front Pediatr. 2019; 7:246
How to treat bronchial asthma in children?
To stop attacks, reduce their frequency, and improve general condition, a set of measures can be taken:
- the use of inhalers to relieve attacks;
- immunotherapy during remission;
- eliminating allergens that cause attacks; Source: O.V. Zaitseva, O.A. Murtazaeva Bronchial asthma in children: modern aspects of therapy // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2011, v. 10, no. 6, pp. 148-156
- and other techniques that are selected individually for each patient.
To improve the child’s condition, parents need to:
- use humidifiers and air purifiers;
- carry out wet cleaning very often;
- remove carpets;
- do not purchase down or feather bedding; the filling must be synthetic;
- promptly eliminate mold and carry out thorough prevention of its occurrence;
- Do not buy soft toys for your baby.
Why should you choose SM-Clinic?
Our medical center has some of the best pulmonologists and other pediatric doctors in the city, advanced diagnostic equipment and attentive attention to every little patient.
Come to us if you notice the first signs of bronchial asthma in your child. We will diagnose the disease as soon as possible and select effective therapy.
Sources:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6591438/ Shyamali C. Dharmage, Jennifer L. Perret and Adnan Custovic. Epidemiology of Asthma in Children and Adults // Front Pediatr. 2019; 7:246.
- O.V. Lavrova, Yu.R. Dymarskaya. Bronchial asthma in children: predisposition factors // Practical Pulmonology, 2015, No. 2, pp. 2-9.
- O.V. Zaitseva, O.A. Murtazaeva. Bronchial asthma in children: modern aspects of therapy // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2011, v. 10, no. 6, pp. 148-156
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Causes of bronchial asthma in children
- Heredity. A child whose both parents are sick has more than 6.5 times the risk of asthma. If only one parent is sick, the risk increases by about 2.5 times.
- Mother's smoking. If a mother smoked during pregnancy, her child's risk of asthma is a quarter higher than that of others.
- Passive smoking. The likelihood and severity of the disease directly depend on how much adults smoke around the child.
- Untreated atopic dermatitis at an early age.
- Bad ecology.
- Frequent colds with complications in the bronchi. Source: O.V. Lavrova, Yu.R. Dymarskaya Bronchial asthma in children: predisposition factors // Practical Pulmonology, 2015, No. 2, pp. 2-9
Also, bronchial asthma often develops in children for psychosomatic reasons. There is a theory that this disease develops against the background of strong dependence on the mother and is an expression of lack of attention. The attack becomes like a crying baby calling for its mother.
What to do during an attack?
When children develop bronchial asthma, parents experience fear and often panic, but they need to calm down and take measures such as:
- place the child on something solid;
- tilt your torso forward, ask to rest your elbows on your knees;
- open the window, but without overcooling the room;
- Give your child an inhaler prescribed by your doctor;
- Until the unpleasant symptoms go away, calm the child down, distract him by talking or reading aloud.
Even if you are worried and worried, do not show it, do not provoke fear in the child - this will significantly aggravate his condition.
If the child’s condition does not change while taking the drug and the measures taken, it is necessary to call an ambulance.