It will hurt and stop - that’s what we usually think when we feel an unpleasant tingling of the heart. Until the age of 30, such signals are completely ignored; after 40, heart pills always appear in our medicine cabinet, and only after 50 do we understand that it’s time to pay attention to our health.
But by ignoring the symptoms in the early stages, we deliberately worsen our condition and turn a blind eye to a possible illness. Thus, by not paying attention to the preconditions for angina, we increase the risk of coronary heart disease.
We have already talked about the latter in our blog. Therefore, today we will talk about angina: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention of coronary heart disease.
Angina pectoris, or angina pectoris, is an early manifestation of coronary heart disease. It occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the heart caused by cholesterol deposits on the walls of the arteries (atherosclerotic plaques).
Due to atherosclerosis, the lumen of blood vessels narrows and the heart does not receive enough blood, and therefore oxygen. Oxygen starvation occurs, which provokes chest pain.
There are several forms of angina:
- stable;
- unstable;
- angina at rest;
- angina pectoris;
- variant - the rarest type.
Forms of angina are classified differently. Some experts classify stable and unstable forms as exertional angina, that is, in both cases, attacks occur during physical exertion. In a stable form, they proceed the same way from time to time, but in an unstable form, the pain can increase.
Angina at rest refers to the late stages of angina, when attacks occur without physical activity. Variant angina is the rarest type, which occurs not due to atherosclerotic plaques, but due to spasm of the arteries of the heart. This type of angina occurs in young people.
Separately, new-onset angina is distinguished. The first attack almost always requires hospitalization, since the patient does not yet understand what to do in this case and what medications to take. Therefore, it is important to clearly know the symptoms of angina pectoris and recommendations for stopping the attack.
Symptoms of an angina attack:
- feeling of pressure and burning pain in the chest;
- increased sweating;
- nausea or vomiting.
The pain can spread from the chest to the lower jaw, radiate to the abdomen, left arm and left shoulder. There may be a feeling of tightness in the chest. Breathing becomes rare, at intervals of more than two seconds.
When an attack occurs, you should take an antianginal medication (usually nitroglycerin) under your tongue and follow your doctor's instructions. In addition to this it is worth:
- stop physical activity;
- take a half-sitting position (if there is no severe weakness and sweating), that is, sit on a bed or sofa, lean on the back and stretch your legs;
- open the windows if the attack happened indoors.
If the attack happened for the first time, then eyewitnesses who happened to be near you need to call an ambulance.
This rule also applies to cases where the pain does not go away for more than 5-7 minutes. If an attack lasts more than 20 minutes, it can lead to myocardial infarction.
What to do if you don’t have any medicines at hand?
If you are having an attack and there is no nitroglycerin or other medicine prescribed by your doctor nearby, you can eat a clove of garlic. This folk method will slightly stop the attack and ease the pain. In case of exacerbation, it is also recommended to rub fir oil in the chest area on the side of the heart, 5-6 drops.
Other folk remedies are mainly aimed at preventing attacks rather than relieving them.
Pathogenesis
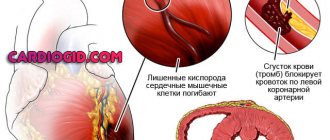
A loss of blood supply to the heart muscles, called ischemia, often occurs due to damage to the coronary arteries leading from the heart. They reduce their permeability, leading to a decrease in the volume of incoming blood.
Angina usually occurs after the arteries are 75% blocked. This can be triggered by a variety of factors, including physical activity and stress.
Also, for the normal functioning of the heart, a constant flow of blood is necessary to the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the myocardium. Diseases of the esophagus, some parts of the spine, and the gallbladder can worsen the patient’s condition, as they provoke reflex impulses and arrhythmia.
Symptoms and varieties
A clear signal of a symptom of angina pectoris is the occurrence of acute pain in the heart area. In many cases, this disease occurs due to chronic stress and tension. The latter can occur when climbing stairs or walking with weights.
angina symptoms
This disease is divided into several types, depending on the causes of its occurrence. If the pain goes away immediately after stopping the exercise, then these are signs of angina pectoris .
Angina at rest, unrelated to physical activity, is also distinguished. In this case, attacks usually occur at night, while the patient is asleep. They are characterized by suffocation and respiratory failure.
Angina pectoris. When “angina pectoris” suffocates
Angina pectoris
is a type of coronary heart disease that clinically manifests itself when there is insufficient oxygen delivery to the heart muscle through the coronary vessels that does not meet the needs. The heart requires a certain amount of oxygen to perform its functions, and as a result of its deficiency, a dysfunction of the myocardium occurs, which in the patient is manifested by chest pain - this is angina pectoris. The main cause of angina is narrowing of blood vessels, most often due to atherosclerotic lesions. Interesting fact: Angina pectoris has been known to mankind for a long time; it was first described by the English doctor William Heberden. In 1772, Heberden first used the term “angina pectoris” and described the classic attack of angina.
Risk factors leading to vascular damage can be divided into 2 groups:
- non-modifiable
, they cannot be influenced: heredity, gender - men suffer more often, age - manifests itself more often after 55 years. - Motivable
– lifestyle factors that can be influenced: smoking, alcohol, stress, excess weight, increased blood cholesterol, increased blood clots.
The combination of several factors increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis and, as a consequence, angina. The main symptom of this disease is pain, which has characteristic signs. The pain is paroxysmal, pressing, burning in nature, localized behind the sternum (most common), can radiate to the left arm, lasts no more than 20 minutes and quickly disappears while taking nitroglycerin. The patient feels a lack of air, fear of death, and possible development of arrhythmia. Pain is provoked by lifting weights, fast walking, cold, large meals, increased blood pressure, and emotional stress. If pain occurs while walking or performing physical activity, the patient stops and freezes.
There is vasospastic angina (Prinzmetal's angina), which occurs as a result of spasm of the coronary arteries. Most often, with this type of angina, attacks occur in the morning. There is also stable angina, according to the patient’s degree of tolerance to physical activity, it is divided into 4 classes; in class 4, attacks of pain occur with minimal physical activity, occur at rest, during sleep, walking becomes impossible, and the patient’s quality of life is significantly reduced. In some patients, myocardial ischemia occurs in a painless form.
If an attack of angina occurs, you need to take a supine or semi-supine position, if possible, and take nitroglycerin - 1 tablet under the tongue. The pain should go away within 5 minutes. If the pain and shortness of breath do not go away, taking nitroglycerin can be repeated, but no more than three times. If an attack of angina does not go away within 15-20 minutes, or the pain intensifies, you should immediately call an ambulance team. Diagnosis of stable angina is usually not difficult, as it has characteristic symptoms. To confirm the diagnosis and to carry out a differential diagnosis with other diseases, the following are carried out:
Laboratory research methods
- complete blood count (possible leukocytosis; decreased hemoglobin due to non-coronary causes of symptoms).
- biochemical blood test (increased cholesterol and LDL, decreased HDL levels, increased glucose levels),
- markers of myocardial damage (troponins) with an altered nature of attacks (suspicion of a heart attack),
- analysis for thyroid hormones.
Instrumental research methods
- ECG (ischemic changes);
- 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring;
- ECG with physical activity (bicycle ergometry or treadmill test on a treadmill);
- ECHO-CG (echocardiography) at rest
- ECHO-CG with pharmacological or physical stress
- radionuclide methods (the substance is distributed into the myocardial tissue and clearly visualizes areas with insufficient blood supply)
- MRI of the heart (if there are problems with visualization using ECHO-CG)
- coronary angiography (x-ray examination of blood vessels using a contrast agent, often combined with the surgical treatment of coronary artery disease - stenting)
- intravascular ultrasound (visualization of atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary vessels, used extremely rarely due to the low availability of technology),
- transesophageal electrical stimulation (for diagnosing hidden coronary insufficiency when it is impossible to use non-invasive examination methods).
The last 3 methods are used only in stationary conditions. In most cases, an ECG with and without stress, 24-hour ECG monitoring and ECHO-CG are sufficient to make a diagnosis.
Treatment of angina
involves the correction of modifiable risk factors for the development of angina, conservative tactics - taking medications (statins that reduce cholesterol levels, drugs that prevent thrombosis, antihypertensive drugs, including ACE inhibitors and beta blockers), and surgical treatment if indicated.
If you suspect that you have angina, you should immediately consult a cardiologist, otherwise serious complications of angina such as heart attack and heart failure may occur. The FAMILY CLINIC employs cardiologists with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating complicated and uncomplicated angina. With us you can undergo all the necessary laboratory and instrumental tests, and the therapy chosen for you can significantly improve the prognosis of the disease.
Diagnostics
During the consultation, the specialist must clarify the following details with the patient:
- Localization of pain. Unpleasant sensations can occur not only in the chest area, but also in the shoulder blades and neck.
- Nature of pain. Mostly it is of the pressing type, but there are also cases of burning.
- There is a sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
Other symptoms. For example, pale skin, hypertension, that is, increased blood pressure, tychycardia and tachyarrhythmia are pathologies that cause an increase in heart rate.
Then, for ischemic heart disease, additional studies are carried out:
- ECG.
- Echo-KG.
- Pressure measurement.
- Pulse control.
- Pulse oximetry.
- Pressure measurement.
- Pulse control.
- LF;
Additional checks can help prevent the onset of life-threatening conditions such as myocardial infarction and hypertensive crisis.
diagnosis of angina pectoris
Mechanisms for reducing an attack of angina, symptoms, first signs :
- Sublingual use of an antianginal agent, nitroglycerin, will help alleviate the condition. Improvement occurs within 5-10 minutes after taking the drug.
- Stopping physical activity will relax the heart muscle.
- To remove the root cause of the disease - to establish blood supply to the heart arteries.
- Treatment of chronic pathologies.
ethnoscience
To treat angina pectoris at home, mainly decoctions and mixtures are used. They should include agents with an anticoagulant effect, that is, those that prevent rapid blood clotting, as well as cardiotonic agents, which improve blood circulation.
The list of such drugs includes: hawthorn, rose hips, motherwort, fruits and herbs of dill, roots and herbs of chicory, rhizomes and shoots of asparagus.
Recipes
- Take seven tablespoons of a mixture of hawthorn berries and rose hips, pour two liters of boiling water, wrap in a warm cloth and leave for a day. Strain, squeeze out the swollen berries and put the infusion in the refrigerator. Drink a glass a day with meals for 2-3 weeks.
- Place seven tablespoons of hawthorn berries (whole or chopped) and seven glasses of boiling water in a jar. Then close the jar and wrap it, put it in a warm place for a day. After infusion, strain the medicine, place it in the refrigerator and take three glasses a day with meals. You can add 1-2 tablespoons of rose hips to the preparation for sweetness and increasing the vitamin C content. At the beginning of treatment, you can mix hawthorn berries with motherwort herb in equal proportions, and then you can use only hawthorn berries.
- Hawthorn fruits, sweet clover herb, wild strawberry - two parts each, calendula flowers, meadowsweet herb, lemon balm herb, rue herb, yarrow herb, dill fruits, immortelle flowers - one part at a time (8 g of collection) pour 300 ml of boiling water, heat over water bath without boiling for 15 minutes, leave in a warm place for two hours, strain. Take everything 4-5 times warm an hour before meals and the last time an hour before bedtime. For night attacks, take half a glass hot.
- Take two parts of caraway fruits, periwinkle leaves, three parts of rhizomes with valerian roots, lemon balm leaves, four parts of hawthorn flowers, six parts of mistletoe leaves. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave for two hours and strain. Take two glasses a day for angina pectoris.
- Mix two parts of wild strawberries and one part each of lingonberry leaf, yarrow herb and dog violet herb. Pour a tablespoon of this mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave for an hour and strain. Drink half a glass three times a day.
- Take two parts of canine violet herb and one part of the rhizome with valerian roots. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave for an hour, strain. Take half a glass of the folk remedy three times a day.