The term “Coronary heart disease” includes a group of diseases:
- myocardial infarction
- atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis
- angina pectoris.
Angina pectoris (synonymous with angina pectoris) is characterized by attacks of sharp chest pain and discomfort in the chest due to lack of blood supply to a certain area of the heart. The severity of the attacks varies, and in rare cases it ends in death. The main cause of the disease is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries of the heart.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a number of other diseases that may manifest as pain in the heart area should be excluded: spinal osteochondrosis, herpes zoster, diseases of the esophagus and stomach, lung diseases, cardioneurosis, pericarditis.
Types of angina
There are the following types of disease, which depend on the clinical picture:
Angina pectoris
One of the main manifestations of IHD. As a result of a discrepancy between the myocardial need for oxygen and its delivery through arteries narrowed due to atherosclerosis, myocardial ischemia occurs, which is manifested by chest pain or shortness of breath and severe fatigue during exercise.
Stable exertional angina is divided into four functional classes. Functional classes of angina are designed for accurate diagnosis and include a wide variety of clinical information (eg, easy walking on level ground and brisk climbing of stairs).
Variant (spontaneous) angina
Characterized by unpredictable appearance, i.e. pain may also occur at rest. It does not occur as a response of the heart to emotional and physical stress and differs from angina pectoris in that it is usually based on spasm of the coronary arteries of the heart, and not just atherosclerotic damage.
Unstable angina
Requires immediate hospitalization, there is a high probability of developing myocardial infarction.
Load tests
Electrocardiography with physical activity (Stress ECG, Veloergometry) is a very useful method that helps diagnose angina pectoris. Also, do not forget about stress echocardiography, which allows you to clarify the diagnosis. Since angina pectoris manifests itself during physical activity, the method allows you to accurately determine the load threshold, the recovery period, and study the work of the heart after pain relief. Such diagnostics are carried out on a special bicycle ergometer and treadmill (treadmill). However, it is not suitable for everyone: stress tests are contraindicated in patients with acute angina.
Symptoms
Main symptoms include:
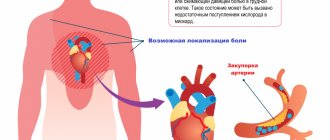
- acute chest pain radiating from the left (or right) side to the lower jaw, arm, shoulder blade
- shortness of breath
- feeling of suffocation and lack of air
- feeling of fear, anxiety
- increased pain in the left chest area when trying to take a deep breath
- increased sweating
- tachycardia
- deviation of blood pressure from normal (low or high).
The main factors in the development of the disease that cause symptoms of angina pectoris include
- age (usually after 40 years)
- gender (men develop CHD on average 10 years earlier than women)
- hereditary factor.
An important role in the formation of the disease is played by excess body weight, a history of diseases such as diabetes, arterial hypertension, increased blood clotting, metabolic syndrome, emotional lability, lack of physical activity, smoking and alcoholism.
Reasons for the development of pathology
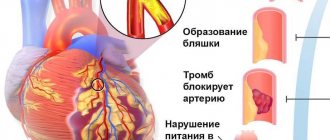
Often the symptoms of angina pectoris develop against the background of atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. The lumen of the blood vessels narrows by 50-70%, which leads to the delivery of less oxygen to the heart muscle with constant consumption. Common causes of angina remain arterial hypertension, coronary spasm, aortic stenosis, and congenital anomalies of the coronary arteries. Pathology can become a complication in acute coronary thrombosis.
Risk factors include:
- systematic smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- age over 55 years;
- obesity 3-4 degrees;
- early menopause;
- diabetes.
The risk group includes patients with pathologies of the cardiovascular system in a family history. Severe forms of anemia and hypoxia can complicate the course of the disease.
Diagnostics
In diagnosing angina, a balanced and competent approach is necessary, because with unstable angina, the patient's condition may worsen until the development of myocardial infarction. Each study must be substantiated.
- ECG
- 24-hour ECG monitoring
- bicycle ergometry or treadmill (stress test with simultaneous ECG recording)
- EchoCG
- stress echocardiography
- coronary angiography
- myocardial scintigraphy
At the EXPERT Clinic, cardiologists are also functional diagnostics doctors. They will weigh all the risks before conducting the examination.
Holter monitoring
Daily, or Holter, monitoring is a continuous process of monitoring the patient’s heart throughout the day using a special recorder, the data from which is sent to the stationary equipment of the attending physician. This type of ECG allows you to diagnose unstable angina and angina in the absence of symptoms, helps evaluate previously prescribed treatment, records changes in the cardiogram during exercise, stress, sleep, etc. It can be either outpatient or inpatient, it depends on the purpose of the study and the patient’s well-being.
Treatment
The goals of treatment are to improve the prognosis (prevent heart attack) and eliminate symptoms of the disease. Non-medicinal (sports, diet), medicinal (tablets and drip infusions) and surgical treatment methods are used.
At the EXPERT Clinic, patients have the opportunity to receive a full consultation with a cardiologist on lifestyle changes and modification of risk factors. If necessary, treatment in a day hospital under the supervision of experienced medical personnel is possible.
Recommendations
To prevent angina attacks you must:
- quit smoking
- control cholesterol levels, if necessary, eat a low-fat diet
- perform a dosed and doctor-selected set of physical exercises
- avoid stress
- lead a healthy lifestyle
A balanced diet, dosed physical activity and regular monitoring by a qualified doctor can save a patient with angina pectoris from heart surgery.
FAQ
How to avoid angina pectoris?
To avoid angina pectoris, it is necessary to prevent the development of atherosclerosis if possible, because in the vast majority of cases it is the cause of angina. As is known, many factors directly influence the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. Gender, age, heredity are predisposing factors that cannot be changed, but other factors can be controlled and even prevented:
- high blood pressure
- smoking
- high cholesterol
- overweight
- diabetes
- low physical activity
- stress
Changing these factors is in your hands!
Is it possible to completely recover from angina?
Angina pectoris, as a rule, occurs as a result of damage to the coronary arteries supplying blood to the myocardium by atherosclerosis, and this is a chronic incurable process. However, with a properly selected treatment regimen, it is possible to ensure that long-term remission occurs and angina attacks will not bother you. Also, at present, if necessary, it is possible to install a stent into the narrowed lumen of the vessel to restore blood circulation, or MCS/CABG surgery is a surgical intervention that restores the blood flow of the heart below the site of the narrowing of the vessel. In this surgical procedure, another path for blood flow is created around the narrowing site to the part of the heart that is not supplied with blood.
Where does it hurt during an angina attack?
Characteristic of angina is paroxysmal pain behind the sternum, in the center of the chest. The pain is of a compressive, pressing nature, more often associated with physical or psycho-emotional stress and goes away when it stops. The pain may radiate to the left arm, shoulder blade, lower jaw and collarbone. If nitrates are used, the effect on angina is not delayed, it develops immediately, within 1-2 minutes.
Are there ways to cope with an angina attack without medications?
Since many people experience angina attacks during physical activity, sometimes simply stopping the activity (walking, etc.) and resting can lead to the cessation of pain. However, people suffering from angina pectoris should always have nitroglycerin or nitrospray with them in order to relieve an attack of pain within one to two minutes. You should not delay the time before taking nitroglycerin, since pain is a manifestation of myocardial ischemia (insufficient blood supply), and if it persists, then foci of necrosis may occur in the myocardium (myocardial cells may die). If angina attacks become more frequent, you should urgently consult a cardiologist.
What medications will help with an attack of angina?
An attack of angina must be stopped as soon as possible from the moment of its occurrence, because prolonged ischemia will lead to the development of necrosis, i.e. myocardial infarction. If an attack occurs for the first time in your life, call an ambulance. You can take a nitroglycerin tablet on your own or use a nitro spray under the tongue. The effect will occur within 1-2 minutes and does not last long, 10-15 minutes. It is better to take the drug while sitting or lying down, as a short-term decrease in blood pressure, dizziness, headache, tinnitus may occur - these symptoms are safe and are a consequence of the action of nitroglycerin. If pain returns, you can take nitroglycerin again, because it does not accumulate in the body; multiple doses of the drug are possible during the day (up to 6 tablets per day). If your blood pressure is high, you need to lower it to normal levels.
All patients who have suffered an attack of angina pectoris need to have an ECG performed and a decision by a cardiologist on hospitalization.
Why is it necessary to quit smoking? How does smoking worsen angina?
If you smoke and have angina, the best thing you can do to help your heart is to quit smoking!
Studies have shown that the mortality rate in those patients with angina who quit smoking decreased by 2 times compared to those who continued to smoke. Why? Angina is based on a lack of oxygen in the heart muscle, and smoking increases the level of carbon dioxide in the blood, and it displaces oxygen in the blood. This leads to oxygen starvation of the heart muscle. Smoking also increases blood viscosity. Smoking increases the frequency and aggravation of angina attacks and greatly increases the risk of myocardial infarction. Quitting smoking eliminates the adverse effects of nicotine on the coronary arteries, and angina attacks disappear or become less frequent.
Important: replacing cigarettes with cigars and pipe tobacco, switching to cigarettes with less tar and nicotine do not reduce cardiovascular risk!
Contrary to popular belief, abruptly quitting smoking is not harmful; overcoming this bad habit has an undeniable positive effect, regardless of smoking experience.
You need to be prepared for the fact that sometimes depression and irritability occur when quitting smoking, in which case you can seek help from a psychotherapist.
I suffer from angina pectoris, but I dream of losing excess weight. What physical activities are acceptable for people with such problems?
For people suffering from angina, 30–45 minutes of physical activity per day is recommended. The best choice is walking (preferably at a brisk pace) or Nordic walking with ski poles, cycling, swimming. It is important that the exercises do not cause pain, palpitations, or shortness of breath. When practicing swimming or water aerobics, you should remember that cold water can provoke angina attacks, so the water temperature in the pool should be comfortable for you. It is better to do water aerobics under the supervision of a trainer and according to a program specially adapted for people with cardiac problems. In this case, the loads should increase very gradually. However, to lose weight, you need not only physical activity, but also proper nutrition; a nutritionist will help you choose the right menu during your consultation.
Can you have angina if there is no pain?
Unfortunately yes. For example, with diabetes mellitus, diabetic polyneuropathy develops, and the patient may not feel pain, this is the so-called silent ischemia. This condition is dangerous because the patient does not take action in time, and myocardial infarction will develop. In some cases, shortness of breath during exercise can be considered equivalent to pain, so you can suspect the presence of angina pectoris and come for examination to a cardiologist.
Treatment history
Case No. 1
Kirill, 57 years old. Experienced smoker, hypertensive (“working” pressure 150/95 mmHg). Five years ago, according to the patient, he had problems with his heart and blood pressure, was examined, took prescribed medications for six months, then stopped taking them on his own. During the visit to the clinic, attacks of chest pain appeared during physical activity, which went away when the exercise stopped. At the doctor’s appointment, blood pressure is 170/100 mmHg, rapid pulse is 90 beats per minute. The patient was examined - an increase in the level of “bad” cholesterol was detected, ECG and ultrasound of the heart without signs of ischemia, and ischemia was recorded on the 24-hour ECG monitor at the time of significant physical activity, i.e. there is angina pectoris. The patient was given a treatment regimen for angina pectoris, which resulted in normalization of blood pressure and cholesterol levels within 3 months, and a significant increase in exercise tolerance. With the help of a psychotherapist, the patient decided to quit smoking and took up Nordic walking with a gradual increase in loads under the supervision of a cardiologist. Over the past year, angina attacks have not bothered me. It is recommended to continue taking medications and undergo regular preventive examinations.
Thanks to cooperation with doctors and the desire to feel better, the patient was able to change his lifestyle, prevent complications of the disease and prolong his life for many years.
Questions and answers
Is there a set of preventive measures to prevent the development of angina pectoris?
Recommendations from cardiologists are addressed to people with a family history of coronary heart disease. Doctors insist that patients stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Fatty foods should be excluded from the diet. The dosage of medications prescribed for pathologies of the cardiovascular system should be observed.
Is surgery necessary for exertional angina?
The need for surgical intervention is determined by the clinical picture of the disease. For mild cases, patients are prescribed medication. The risk of complications or a severe form of pathology can become a decisive factor when a doctor makes a decision on surgical treatment.