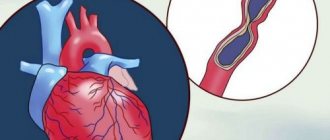
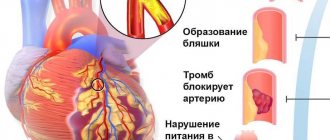
Each muscle of the human body is equipped with arteries that supply it with all the necessary substances and oxygen. Their origin comes from the main vessel - the aorta. If a healthy person increases the load on his body, then the heart’s need for oxygen increases, and, consequently, the volume of blood flow through the vessels also increases. If cholesterol deposits have formed on the coronary arteries, then atherosclerotic plaques appear on their walls, reducing vascular patency. Thus, the free access of oxygenated blood to certain areas of the heart muscle is limited. This condition is defined as oxygen starvation. 30 minutes are enough, during which oxygen does not enter the heart, for the death of myocardial cells to occur. Pain during oxygen deprivation that occurs in the heart is called angina. If it appears during physical activity, it is considered angina pectoris.
Definition
Functional classes of angina pectoris are the division of the disease depending on the patient’s tolerance to physical activity.
Functional classes (FC) of angina are distinguished according to the classification proposed by the Canadian Heart Association. Angina pectoris occurs as a result of insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle during work. When performing physical exercises, stress and anxiety, the heart's need for oxygen increases, which is why attacks with angina pectoris are associated with any kind of stress. There are four functional classes of angina: I-III refer to stable angina, IV - to unstable form. The higher the class, the less the patient is able to freely perform physical activity.
Symptoms
Regardless of the class of angina pectoris, it has common symptoms that range from slight discomfort in the chest to intense pain in the heart, which increases over time. A classic attack of angina has a clear beginning and end. It can stop if you complete physical activity and take an ester of glycerin and nitric acid (nitroglycerin). Pain can be localized in different places:
- behind the sternum;
- on the left side of the chest;
- give to the left arm, shoulder blade, jaw or neck.
The nature of the sensations can also be:
- pressing;
- contracting.
And by intensity: high and moderate. Accompanying factors of angina pectoris are a feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath, interruptions in heart rate, cold sweat and fear of death. Important! Interesting fact: angina pectoris does not always manifest itself as pain; sometimes it can be a cough, sudden unexplained weakness, or shortness of breath.
In cases where the pain is wave-like, too intense, and cannot be controlled by taking appropriate medications, you must call an ambulance. These symptoms may indicate the development of myocardial infarction.
Angina pectoris 1 FC
With 1 FC of exertional angina, the patient copes well with normal daily activity. Activities such as vigorous walking and climbing stairs do not cause an angina attack in the patient. It is quite rare for people with this functional class to go to the hospital, since the person may not even know about the presence of the disease. As a rule, symptoms of angina pectoris appear when performing fairly intense exercises, very fast and long runs, and loads that are unusual for an ordinary person. To diagnose angina pectoris FC1, it is necessary to use the bicycle ergometer test method.
Diagnosis and treatment
The medical definition of the disease is carried out by a cardiologist on the basis of complaints, clinical and laboratory, and instrumental examinations. These include:
- an electrocardiogram performed during an attack of angina (possible use of provoking methods of influence);
- echocardiography to assess myocardial contractility;
- a biochemical blood test will indicate the presence of atherosclerotic vascular lesions;
- Coronagraphy determines the location and degree of narrowing of the cardiac arteries.
Only a qualified doctor can distinguish angina pectoris from many other heart diseases.
In treatment, the main thing is to eliminate all provoking factors. Nitroglycerin is most effective for pain relief. If nitrate intolerance is present, then medications based on nitric oxide donors (molsidomine) are prescribed. It makes sense to take a preventative dose of nitrates if physical or emotional stress is coming. An important role in all this is played by the treatment of arterial hypertension, which is concomitant, as well as the control of risk factors (smoking, obesity, diabetes, cholesterol, sedentary lifestyle).
Important! It is necessary for the doctor to monitor the patient’s condition, because if drug therapy is ineffective, endovascular or surgical treatment should be performed.
Angina pectoris 2 FC
Angina pectoris FC 2 suggests minor restrictions on physical activity. An attack may occur when:
- walking more than 200 m;
- quickly climbing stairs;
- strong emotional overexcitation;
- walking against the wind;
- smoking;
- overeating.
If the patient avoids these factors, angina may not manifest itself for quite a long time. The pain usually stops soon after taking nitroglycerin or at rest. However, over time, symptoms may begin to appear with less significant stress. In this case, angina is often a symptom of coronary heart disease.
Stable angina pectoris FC 2 requires some restrictions in the patient’s physical activity, as well as drug treatment. Usually the patient is prescribed drugs that stop the attack, normalize blood pressure and improve blood quality. Prevention is no less important, in particular, quitting smoking, healthy eating, and physical activity within the limits allowed by the doctor.
First aid for a seizure
Angina pectoris is a chronic disease. Therefore, a complete cure is not always possible and only through surgical intervention.
But first of all, the patient and his immediate environment need to learn how to provide first aid during attacks.
Nitroglycerin and drugs based on it are the main means for stopping a crisis. At the first symptoms, the patient needs to put one tablet under the tongue and dissolve it. If the attack is severe, you can give it twice. It is better if the oral cavity is sufficiently moist. The maximum dose, 5 tablets, is taken in extremely severe cases when medical help is not expected.
You can also use a spray instead of tablets. The results of the action of nitroglycerin can be seen within a couple of minutes.
- Progressive angina: classification, symptoms and treatment
Sometimes they try to stop the attack with validol. This is a grave mistake, since this medicine not only does not help, but can cause serious harm to health.
But those around you can use simple ways to ease the crisis. To do this, it is necessary to stabilize the patient’s condition as much as possible, both physically and morally:
- the person must be allowed to stand for a while and catch his breath if the attack was provoked by intense physical activity;
- if the cause is stress, the patient needs to be reassured;
- it is important to provide the person with a sitting or semi-sitting position, as well as an influx of fresh oxygen;
- the body should be freed from any oppressive objects, including belts, collars, and excess outerwear;
- You can place heating pads with warm water on your feet.
Angina pectoris 3 FC
Angina pectoris FC 3, in contrast to functional classes 1 and 2, involves significant restrictions on physical activity, since at this stage an attack can occur when moving at a normal pace or when climbing stairs just one flight. Sometimes an attack can be triggered by hypothermia or excessive eating or smoking. Very rarely in this functional class is angina at rest, which occurs during a supine position or severe anxiety.
In this case, treatment of angina pectoris is carried out as part of the treatment of coronary artery disease. It includes taking medications that lower cholesterol and thin the blood. In addition, the patient is prescribed medications that relieve pain and normalize blood pressure. However, if angina pectoris type 3 becomes unstable, pain syndromes become more frequent and last longer, then a decision is made about surgical intervention.
How it manifests itself
Stable angina pectoris is divided into classes depending on the factors that provoke the appearance of pain. The mildest degree (FC 1) corresponds to the occurrence of an anginal attack when performing extremely strong work.
A pathology with a slight limitation of normal physical activity is placed one step higher, when the patient finds it difficult to walk more than two blocks or climb to the second floor.
Angina pectoris, in which an attack develops when climbing one flight of stairs or walking at a normal pace of 100-200 m, corresponds to FC 3.
Functional class 4 is considered the most severe, with the development of the syndrome at rest up to difficulty in self-care.
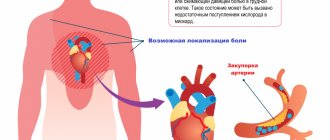
The nature of pain in ischemic heart disease:
- Localized behind the sternum;
- They have a pressing, squeezing character. Some patients describe burning pain.
- They radiate to the shoulder blade, left shoulder girdle, arm, lower jaw.
The clinical picture is complemented by increased heart rate, pallor, the appearance of sweat on the forehead, and other subjectively unpleasant sensations.
Among the common features inherent in cardiac ischemia, some individual differences can be identified for each form of coronary artery disease.
- Emergency care for angina pectoris: algorithm of actions during an attack
Pain syndrome with stable angina is characterized by attacks lasting up to 3–5 minutes, which subside on their own or after taking nitrates.
The equivalent of pain can be shortness of breath, which impedes activity and replaces cardiology.
Angina pectoris 4 FC
4 FC of angina is the most difficult, because a painful attack in this case often occurs without obvious reasons (angina at rest). Any minor load can provoke an attack. In this functional class, the patient’s medical history may already include myocardial infarction or cardiovascular failure. Against the background of a recent heart attack, attacks are especially dangerous - with early post-infarction angina, they occur spontaneously and can lead to a second heart attack.
If a person has difficulty walking, shortness of breath, or pain in the sternum that does not go away within 15 minutes, it is necessary to urgently call the Ambulance Service, because in this case we may be talking about acute coronary syndrome and the patient requires treatment and observation in a hospital.
Distinctive features of angina pectoris FC 3
The most common form of cardiac angina is FC 3, it develops in acute ischemic disease and has several features:
- The attacks are spontaneous and not necessarily caused by physical exertion;
- The patient's mobility is limited, he tries to rest more;
- Pain occurs when climbing one flight of stairs or walking 100-500 meters;
- Patients can control their condition and feel well the approach of attacks.
The main distinguishing feature is that you can always determine the beginning and end of an attack.
Some doctors regard FC 3 as a disability, and in combination with other diseases, for example, tachycardia, the clinical picture worsens. The disease is accompanied not only by pain, but also by associated pathologies.
When should you see a doctor?
The severity, duration and form of angina may vary. It is important to determine whether your chest pain is changing or developing new sensations. A signal of a more dangerous form of unstable angina or a heart attack (myocardial infarction) may be the appearance of new symptoms or a change in existing ones.
If you notice that angina attacks have begun to recur more often, their nature and intensity have changed - this is a reason to think about a cardiac examination as soon as possible. You can make an appointment with a specialist at our clinic or get answers to your questions using a service such as online consultation with a cardiologist - it is available on our website at any time.
How to live with a diagnosis of angina pectoris?
When diagnostics have shown that a person has progressive angina of functional class 3, they will have to significantly change their lifestyle. This is necessary in order to reduce the number of attacks and avoid other pathologies, such as heart attack, post-infarction cardiosclerosis, leading to the death of coronary cells.
Several precautions need to be taken:
- Make sure you always have Nitroglycerin with you - at home, at work, in your pocket or purse;
- If you feel an attack approaching or expect that you will have to endure stress, place the tablet under your tongue in advance;
- Change your diet - you don't need to stick to strict diets, but you will have to reduce your intake of foods with high cholesterol levels. Eat small portions, controlling your sensations;
- Move as much as possible - you cannot completely give up exercise, take at least daily short walks.
When you have found out how angina pectoris type 3 manifests itself, what it is, what therapeutic and preventive measures can be taken, the main thing is to remember that it is prohibited to take medications without the help and prescriptions of a cardiologist. To protect yourself from exacerbations and attacks, carefully monitor your daily routine, do not forget to take the necessary medications and regularly visit a specialist for diagnostics.