Since the last quarter of the twentieth century, cardiovascular diseases have steadily occupied a leading position among the most common diseases of mankind. They overtook all possible infectious diseases and even cancer. Cardiovascular diseases are such a widespread phenomenon that scientists, when talking about them, often use the term epidemic, emphasizing their prevalence.
But about a century ago, at the beginning of the twentieth century, they were extremely rare. But by the 50s of the last century, heart disease was already in 10th place in overall statistics. Today, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), they are in sad first place.
Angina: main causes
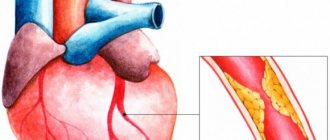
The key reasons for the development of an angina attack are vascular spasm, narrowing of the lumen due to atherosclerotic damage to the wall or temporary thrombosis, embolism (blockage with a blood clot or plaque fragments) of a vessel.
Much less frequently, angina pectoris is caused by congenital anomalies of the heart vessels, Marfan syndrome, bacterial endocarditis, Kawasaki disease, coronary artery vasculitis, side effects, and drug overdose. Seizures are more likely to develop in people who have one or more risk factors. This:
- overweight or obesity;
- bad habits (smoking, excessive alcohol intake);
- physical inactivity, sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work;
- hypertension or symptomatic hypertension;
- diabetes;
- imbalance of blood plasma lipids.
More often, problems occur in men, people over 50 years of age and patients whose relatives have problems with the heart and blood vessels.
How does the pulse behave in such patients and what can be done about it?
Not only pressure, but also pulse is important during angina.
An increase in heart rate (HR) above 70 beats per minute indicates that the heart is working hard. This means that the muscle's need for oxygen increases. In addition, since the coronary arteries receive blood during relaxation (diastole), when the heart rate increases, the duration of their filling is reduced. Under such conditions, chronic ischemia occurs, which leads to degeneration of the muscle fibers of the heart. If the heartbeat increases sharply during physical and emotional stress, for example, when you are simply catching up with a minibus, the need for oxygen rapidly increases. If against this background an attack of angina occurs with spasm of the coronary vessels, ischemia can have serious consequences.
Beta blockers are the drugs of choice in patients with high heart rates. They are included in treatment regimens for arterial hypertension.
Signs and symptoms
The most typical manifestation of angina is pain and burning in the heart area. Many patients describe it as a feeling of heaviness or severe discomfort, squeezing, bursting, pressing or burning sensations, which are often accompanied by a lack of air. The localization of pain is behind the sternum, on the left side of the chest, often radiating to the jaw and neck, collarbone, between the shoulder blades, elbow or hand. The attack lasts up to 15 minutes, is provoked by physical exertion or emotional stress, when pressure is increased, heart rate is increased, and the myocardium is working under load. The attack goes away when taking nitro drugs, stopping exercise, resting in a sitting or standing position. Without treatment, attacks begin to occur more frequently, including at rest.
Serious question: what happens to the heart during an angina attack?
Have you heard of such a diagnosis as “angina pectoris”? Such an unusual term actually existed before. So what was it that “compressed the chest” of a person?
With questions about a common disease of modern civilization - angina pectoris, we visited our regular consultant, general practitioner, cardiologist at the Expert Voronezh Clinic, Angelina Anatolyevna Kalinina.
— Angelina Anatolyevna, what is angina pectoris and what is the danger of this disease?
Angina is a syndrome that is manifested by a feeling of discomfort or pain in the chest, often of a squeezing, burning or pressing nature. In most cases, they are localized behind the sternum and can “give” to the left arm, neck, lower jaw, under the scapula, and to the epigastric region. Usually the pain stops with rest after 3-5 minutes or a few seconds or minutes after taking nitroglycerin under the tongue in the form of tablets or spray.
How to distinguish between heart pain and pain due to intercostal neuralgia? The story is told by neurologist, leading specialist of the neurology department of the Expert Kursk Clinic Natalya Vladimirovna Umerenkova
Angina pectoris is one of the types of coronary heart disease (CHD). It is dangerous because there is a risk of myocardial infarction.
Read material on the topic: Coronary heart disease: diagnosis and treatment
- What are the causes of angina?
The cause of classic angina pectoris in more than 90% of cases is atherosclerosis of the heart arteries. Sometimes angina is caused by vasospasm (vasospasm) or functional disorders at the microcirculation level. Often there is a combination of the above reasons.
Risk factors for the occurrence of angina pectoris are divided into so-called modifiable (i.e., those that a person can influence) and non-modifiable (those that cannot be changed).
Modifiable factors include dyslipidemia, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol-containing beverages, physical inactivity, obesity, dietary patterns, etc.
Non-modifiable are male gender, age, hereditary predisposition.
What can cause chest pain? These are cases when a person subjected himself to physical activity, walked quickly, climbed a mountain or stairs, or carried heavy loads. Pain can also appear with increased blood pressure, exposure to low temperatures, overeating, and stress.
Read the material on the topic: It's off scale! Looking for reasons for high blood pressure
— By what signs can angina be recognized?
A detailed interview with the patient is very important. There are typical, probable (or atypical) angina, as well as cardialgia (in which the pain is not associated with a deterioration in the blood supply to the myocardium).
Symptoms of typical angina include chest pain or specific discomfort. Caused by physical activity or psycho-emotional stress. They go away with rest or after using nitroglycerin. With this type of angina, all three manifestations must be present.
In atypical angina, only two of the three are present.
With cardialgia, one or none of the above symptoms are noted.
Taking this into account, either a cardiologist or another specialist works with the patient and further searches for the causes of pain in the heart area.
- What is angina pectoris?
The following types are distinguished: stable, unstable and spontaneous.
Separately, there is the so-called cardiac X-syndrome (X-syndrome, otherwise known as microvascular angina). With it, there is a combination of classic signs of angina pectoris with unchanged heart arteries. This species has not yet been fully studied.
— What happens to the heart during an angina attack?
The process develops as follows. Initially, the blood supply to the myocardium is disrupted, later metabolic and electrophysiological “shifts” are noted in it. Then the heart’s ability to relax is impaired, and then to contract. And only then does pain appear and corresponding changes on the electrocardiogram.
Read the material on the topic: Why is ultrasound of the heart prescribed?
— How to provide emergency assistance during an angina attack?
The drugs taken are short-acting nitrates (tablets or spray), under the tongue. It is better to take them in a sitting or lying position (to prevent low blood pressure, dizziness and possible falls associated with this). Tablet dosage: 0.5 mg. In total, up to 3 tablets are taken - 1 tablet every 5-7 minutes. You need to focus on the disappearance of pain.
Nitroglycerin should not be used if the “upper” (systolic) blood pressure is less than 90 mmHg. rt. Art.
This blood pressure should also be monitored while taking nitroglycerin, even if it was initially above 90-100 mm. rt. Art.
If the pain does not subside within 15-20 minutes while taking nitroglycerin, you must call an ambulance to rule out myocardial infarction.
— Are angina pectoris and coronary heart disease the same thing or is there a difference between them?
Angina pectoris is one of the types of coronary heart disease.
— Who has angina pectoris more often: men or women?
In general, its frequency increases with age in both sexes.
In middle age, it is angina pectoris (and not ischemic heart disease in general) that occurs more often in women, probably due to the higher prevalence of vasospasm and cardiac syndrome X. For older age groups, the situation is the opposite, i.e. both ischemic heart disease in principle and angina pectoris as a special case are more often observed in men.
- Who is predisposed to developing angina? What risk factors provoke the development of angina?
These are the modifiable or non-modifiable factors that we talked about earlier.
— Angelina Anatolyevna, how is angina diagnosed?
Firstly, a thorough collection of complaints and anamnesis (with clarification of the nature of the pain, its location, duration, conditions of occurrence, the effect of taking various medications - in particular nitroglycerin, if taken).
Upon examination, signs of atherosclerosis, heart failure, high blood pressure, and obesity may be detected as additional risk factors.
A general blood and urine test, lipidogram (total cholesterol and its fractions, triglycerides), glucose, creatinine clearance are performed. In unstable and acute conditions, markers of myocardial destruction (troponins T and I, creatine phosphokinase (CF fraction).
Instrumental diagnostics. Invasive and non-invasive methods are used here.
The first one is an ECG. How is angina visible on it? These are specific ST segment changes.
Echocardiography and ultrasound duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries are mandatory.
Load tests - bicycle ergometry and treadmill test.
Holter monitoring. It is performed when stress tests are contraindicated, if it is impossible to record an ECG at the time of pain, etc.
Read the material on the topic: Holter (24-hour) ECG monitoring - complete instructions for the patient
Stress echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart under stress).
Perfusion scintigraphy with exercise.
Invasive methods. The “gold standard” for imaging diagnosis of atherosclerosis of the heart arteries is coronary angiography (especially in those at high risk of cardiovascular complications and death), as well as multislice computed tomography with assessment of coronary calcium, or calcium scoring.
— What is the purpose of treatment for angina pectoris? Is this diagnosis an indication for surgery?
The main goals are to eliminate manifestations and improve the prognosis.
If symptoms cannot be eliminated with drug therapy, it is recommended to refer the patient for a consultation with a cardiovascular surgeon to determine the possibility of surgical treatment of angina.
— Is angina responding well to treatment? Is it possible to cure it completely?
Treatment of angina pectoris at the present stage of medical development is effective. You can either significantly reduce its manifestations or eliminate them completely. At the same time, even after surgical treatment with complete restoration of adequate blood supply to the myocardium, drug therapy continues indefinitely, because the risk of cardiovascular complications remains very high.
— Can angina be resisted? How to properly prevent this disease and at what age should it start?
The main measures are aimed at preventing the occurrence and progression of atherosclerosis and, accordingly, damage to the arteries of the heart. Those. it is the effect on modifiable risk factors. It is necessary to stop smoking, control weight, and eat rationally. If you have diabetes, you need to achieve your blood glucose targets. Provide rational, regular physical activity. Monitor blood pressure. Regularly take medications prescribed by a cardiologist or cardiac surgeon and be observed by these specialists.
You may also be interested in:
Heart, why don't you want peace? What causes tachycardia?
How to keep your heart healthy?
What do you need to know about health before buying a gym membership?
For reference:
Kalinina Angelina Anatolevna
In 2007 she graduated from the Voronezh State Medical Academy named after. Burdenko.
From 2007 to 2008 she completed an internship in therapy, in 2010 she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “General Medical Practice (Family Medicine)”, and in 2017 – in the specialty “Cardiology”.
Since 2015, he has held the position of general practitioner at Clinic Expert Voronezh. Reception is conducted at the address: st. Pushkinskaya, 11.
Classification
WHO experts have proposed dividing angina into several options.
Angina pectoris (or its second name is stable) has 4 functional classes:
- I – in general, the patient tolerates habitual physical activity well, painful attacks are provoked by heavy loads or psycho-emotional stress;
- II – the patient has limited usual physical activity, but these restrictions are not very significant. Ischemic attacks are provoked by walking about 500 m or climbing above the second floor;
- III – the patient’s physical activity limitation is already pronounced, attacks are provoked when climbing one floor, normal, leisurely walking up to 150 m;
- IV – an attack of angina occurs even with little physical activity, walking less than 100m.
Unstable angina is divided into types. This:
- appeared for the first time less than a month ago;
- progressive (attacks increase in frequency and duration, pain becomes more intense);
- early post-infarction (occurs within two weeks after a heart attack or surgery).
Spontaneous or vasospastic angina (Prinzmetal) is also distinguished.
Why is angina pectoris dangerous? Transition to myocardial infarction.
An angina attack usually goes away within 2 to 10 minutes.
after the first dose of a nitrate drug.
If an attack lasts more than 20–30 minutes
, it runs the risk of developing into
a myocardial infarction .
necrosis (death) of cells in one or more areas of the heart muscle occurs
Why does necrosis occur in the heart muscle?
Myocardial infarction is the result of severe oxygen starvation of the heart, when blood flow to the heart is reduced to a very low, dangerous level.
In such cases, the body uses compensatory mechanisms: additional small arteries send blood to the heart. But compensatory mechanisms cannot always cope with their task. For example, during a prolonged attack of angina.
In such a situation, first irreversible damage occurs, and then the death of those areas of the heart muscle that do not receive sufficient oxygen.
Diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, anamnesis data are required (medical history, indication of unfavorable heredity, the presence of bad habits, excess weight), typical manifestations and data from laboratory and instrumental examinations indicating problems with the heart, blood vessels and lipid metabolism Source: Stable angina: principles of diagnosis and treatment. Frolova E.V. Russian family doctor, 2008. pp. 4-29.
A cardiologist performs an examination, measures blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate, assesses body composition, abdominal volume, and calculates BMI. Appointed:
- general blood and urine tests;
- biochemical tests (lipid profile, protein profile, plasma glucose level and other indicators);
- coagulogram.
Instrumental tests include ECG and Holter monitoring, stress tests (treadmill test, bicycle ergometry), ECHO-CG (ultrasound of the heart), including stress tests. Pharmacological tests, transesophageal pacing, chest radiography, multislice tomography, myocardial perfusion scintigraphy can be used. To identify narrowing of the coronary vessels, coronary angiography is indicated, a radiographic method using contrast agents.
How to treat angina pectoris at home?
ETHNOSCIENCE
To treat angina pectoris at home, mainly decoctions and mixtures are used. They should include agents with an anticoagulant effect, that is, preventing rapid blood clotting,
as well as cardiotonic drugs - they improve blood circulation.
The list of such drugs includes: hawthorn, rose hips, motherwort, fruits and herbs of dill, roots and herbs of chicory, rhizomes and shoots of asparagus.
Recipes
- Take seven tablespoons of a mixture of hawthorn berries and rose hips, pour two liters of boiling water, wrap in a warm cloth and leave for a day. Strain, squeeze out the swollen berries and put the infusion in the refrigerator. Drink a glass a day with meals for 2-3 weeks.
- Place seven tablespoons of hawthorn berries (whole or chopped) and seven glasses of boiling water in a jar. Then close the jar and wrap it, put it in a warm place for a day. After infusion, strain the medicine, place it in the refrigerator and take three glasses a day with meals. You can add 1-2 tablespoons of rose hips to the preparation for sweetness and increasing the vitamin C content. At the beginning of treatment, you can mix hawthorn berries with motherwort herb in equal proportions, and then you can use only hawthorn berries.
- Hawthorn fruits, sweet clover herb, wild strawberry - two parts each, calendula flowers, meadowsweet herb, lemon balm herb, rue herb, yarrow herb, dill fruits, immortelle flowers - one part at a time (8 g of collection) pour 300 ml of boiling water, heat over water bath without boiling for 15 minutes, leave in a warm place for two hours, strain. Take everything 4-5 times warm an hour before meals and the last time an hour before bedtime. For night attacks, take half a glass hot.
- Take two parts of caraway fruits, periwinkle leaves, three parts of rhizomes with valerian roots, lemon balm leaves, four parts of hawthorn flowers, six parts of mistletoe leaves. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave for two hours and strain. Take two glasses a day for angina pectoris.
- Mix two parts of wild strawberries and one part each of lingonberry leaf, yarrow herb and dog violet herb. Pour a tablespoon of this mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave for an hour and strain. Drink half a glass three times a day.
- Take two parts of canine violet herb and one part of the rhizome with valerian roots. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave for an hour, strain. Take half a glass of the folk remedy three times a day.
TREATMENT OF ANGINA WITH GARLIC
Like hawthorn, garlic occupies a special place in the treatment of angina. It is ineffective in combating angina pectoris, but it seriously helps prevent coronary heart disease, as it fights atherosclerosis and cholesterol plaques.
Recipes
- Grind 200-300 grams of peeled garlic cloves into a paste and mix with the same amount of honey. The mixture is sealed in a jar and infused for at least a week. Take a tablespoon three times daily before meals (30-40 minutes). The course can last up to 3 months.
- For angina pectoris, ascorbic acid is indispensable. You can add freshly squeezed lemon juice to the honey-garlic mixture, and this will only increase its medicinal qualities. You will need 10 lemons, a kilogram of honey and 10 large heads of garlic. This mixture is infused for the same amount of time, a week, and taken 3-4 teaspoons once daily. It is important to take your time and take at least a minute break after each spoon.
- You can boil thick chicken broth and pour two glasses of it into a dozen large cloves of garlic. Then the broth is boiled for 15 minutes, and about 50 g of parsley is added three minutes before removing from the heat. Boiled garlic and parsley are ground through a fine sieve and mixed again with the broth. This is a ready-to-use product that is useful to drink 75 ml half an hour before meals.
Treatment for angina: lifestyle, medications
All principles of treatment of any form of angina are reflected in clinical guidelines, which are regularly reviewed and serve as instructions for doctors. Therapy consists of non-drug and medicinal interventions, and sometimes cardiac surgery. Source: Stable angina: choice of treatment tactics. Kirichenko A.A. Clinical medicine, 2021. p. 78-83.
First of all, it is necessary to reconsider your lifestyle, nutrition, give up bad habits, lose weight, and move more. It is important to gradually train the body so that it adapts to physical activity and does not cause attacks of pain.
The doctor will supplement these measures by prescribing medications that should be taken for angina. Source: Problems of drug therapy for stable angina. Samoilenko V.V. Clinician No. 3, 2006. p. 32-39. This is usually a combination of statins, which lower bad cholesterol, as well as beta blockers, sartans and ACE inhibitors (especially in hypertensive patients). Nitrates provide emergency assistance for angina pectoris - they dilate blood vessels and relieve spasms. Additionally, it is recommended to take cardio-aspirin, a blood thinner.
For emergency treatment of intractable attacks and the threat of a heart attack, surgical interventions are used. Stenting, balloon dilatation of the affected arteries, or coronary artery bypass surgery are performed. Source: Effective methods for treating angina pectoris. Arzikulov A.Sh., Abdurakhimov A.Kh., Nugmanov O.Zh. Re-health journal, 2021.
Medicines with proven effectiveness in treatment
| Acetylsalicylic acid | This is regular aspirin in a dosage of 75-100 mg. The trade name often includes the prefix "cardio". Resists thrombosis. |
| Beta blocker | Blocks the effect of adrenaline on receptors. Reduces the heart's need for oxygen during exercise, which has a positive effect in the treatment of angina pectoris. Lowers systolic and diastolic blood pressure. |
| ACE inhibitors | Suitable for those who have diabetes, preventing the development of nephropathy. Reduce left ventricular hypertrophy. |
| Nitroglycerine | Nitric oxide, which is released from the drug in the vascular wall, dilates the coronary arteries during myocardial ischemia, thereby restoring blood circulation in the muscle area. |
| Calcium antagonists | Prescribed when beta blockers are contraindicated (heart failure, blockade of the conduction system, bronchial asthma) |
| Lipid-lowering therapy | Statins, fibrates and bile acid sequestrants - drugs that normalize cholesterol and lipoprotein levels |
You should not completely rely on medications, because without changing your lifestyle, they partially lose their effectiveness.
Hypotension with angina pectoris
Until recently, it was believed that low blood pressure was better than high blood pressure. However, the statistical analysis suggests that systolic blood pressure 110 and below, and diastolic blood pressure 60 and below are no less a risk factor for the development of myocardial infarction than hypertension.
Hypotension is characteristic of women of reproductive age, as well as patients with severe atherosclerosis. Low blood pressure occurs in patients who mistakenly take high doses of antihypertensive drugs.
As a rule, a person feels that the pressure is low - dizziness, staggering, and fatigue appear. Yes, at the moment the optimal method for correcting this condition is normal physical activity, consuming caffeine-containing products in moderation and wearing compression stockings.
Treatment of angina attacks with hypotension appears to be a difficult task, since most drugs prescribed for this disease exhibit a blood pressure-lowering effect.
Prevention
The basis of prevention for angina pectoris is maintaining a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits and controlling weight and plasma cholesterol levels. With high levels of “bad” cholesterol, it is necessary to take medications that reduce it, adjust the diet, and expand the range of physical activity Source: Secondary prevention for stable angina. Kirichenko A.A. Consilium Medicum, 2021. p. 27-33.
Sources:
- Ischemic heart disease and angina pectoris. Skvortsov V.V., Tumarenko A.V., Skvortsova E.M., Neklyudova D.A., Kalinichenko E.I. Nurse No. 7, 2015. pp. 3-9
- Effective methods of treating angina pectoris. Arzikulov A.Sh., Abdurakhimov A.Kh., Nugmanov O.Zh. Re-health journal, 2020
- Stable angina: principles of diagnosis and treatment. Frolova E.V. Russian family doctor, 2008. p.4-29
- Problems of drug therapy for stable angina. Samoilenko V.V. Clinician No. 3, 2006. p. 32-39
- Stable angina: choice of treatment tactics. Kirichenko A.A. Clinical medicine, 2021. p. 78-83
- Secondary prevention for stable angina. Kirichenko A.A. Consilium Medicum, 2021. p. 27-33
Blood pressure correction
Hypertension with angina pectoris
The main goal of treating angina with high blood pressure is to reduce the risk of death from myocardial infarction, stroke and kidney failure.
Medicines for angina are also used for hypertension. The drugs cannot completely cure coronary heart disease, but they can reduce the frequency of attacks and their intensity to a minimum. Also, when taken correctly (long-term and regularly), they reduce blood pressure to a safe level. This significantly improves the quality and life expectancy, performance and general psychophysical state and emotional background. The person feels less sick.