What is angina and why does it occur?
To help a patient with an attack of angina, you should know what this condition is and what are the reasons for its development. Angina pectoris is a clinical syndrome accompanied by sudden and acute pain in the sternum due to impaired blood circulation in the coronary artery. Previously, this symptom was called “angina pectoris,” but now this concept is outdated.
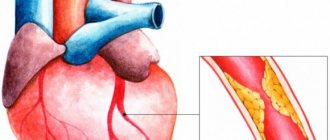
The main cause of the pathology is a disruption of blood flow through the vessels due to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on their walls. The following provoking factors lead to this:
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drugs);
- hypertonic disease;
- increased blood cholesterol levels;
- poor nutrition;
- sedentary work, lack of physical activity;
- excess body weight;
- diabetes;
- anatomical aging of the body;
- frequent stress;
- metabolic disorder.
Together with hormonal disorders, changes in blood composition and many other reasons, these factors provoke the development of diseases of the heart and blood vessels, the symptom of which is angina pectoris.
How to recognize an attack
First aid for angina pectoris should be provided in a timely manner. To do this, it is important to know how an attack manifests itself. In this condition, the patient experiences symptoms such as burning, sharp pain in the sternum. Sometimes it spreads to the area of the collarbone, shoulder blade, and neck.
Chest pain and shortness of breath often indicate an attack of angina.
You can suspect angina in a person if you have the following symptoms:
- pale facial skin;
- jump in blood pressure;
- abnormal heart rate;
- dyspnea;
- cold sweat;
- nausea, less often vomiting;
- headache.
The duration of this condition usually lasts a few minutes, but sometimes the pain lasts longer. In some patients, the attack goes away on its own, but despite this, these symptoms cannot be ignored. Often, prolonged angina leads to the development of myocardial infarction. If an attack is detected, the patient should be provided with emergency assistance.
In what cases is Nitroglycerin contraindicated during an attack of angina?
The patient or his relatives should be aware that if signs of low blood pressure are detected (with collaptoid angina), taking drugs from the group of organic nitrates (Nitroglycerin, Isoket, etc.) is contraindicated. The following signs may indicate hypotension:
- the patient experiences severe weakness;
- dizziness;
- pallor;
- cold sweat.
In such cases, the sequence of actions should be as follows:
- Lay the patient down.
- Call an ambulance.
- Give him a crushed Aspirin tablet.
- To reduce pain, you can use tablet analgesics (Baralgin, Sedalgin, etc.).
First aid to a patient
First aid for angina pectoris should be provided at home before doctors arrive. In this case, the algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Provide the person with complete physical and emotional peace. This will help relieve excess stress from the myocardium.
- The patient should take a horizontal position with his head elevated. You need to let fresh air into the room. Clothes should not restrict the victim; to do this, unfasten the belt and collar. It is important to avoid crowds if the attack occurs on the street.
- If the state of rest does not bring relief, you need to give the patient a Nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue. Usually one or two tablets help achieve the desired effect, but in particularly severe cases, 4-5 tablets may be needed.
- It is recommended to reduce blood pressure using antihypertensive drugs. The victim should be asked if he is taking any medications to lower blood pressure.
- Often during an attack, the patient is worried about fear for his life, so it is allowed to give him any sedatives (tincture of motherwort, valerian and others).
First aid must be correct and timely
Important! If the pain does not go away within 10–15 minutes after re-taking Nitroglycerin, you should call an ambulance.
“Online registration for vaccination against Covid-19 infection”
Angina pectoris is a serious disease that should not be ignored. Properly provided emergency care for angina pectoris will help prevent the development of a heart attack.
Angina pectoris is a consequence of coronary heart disease. The reason for its development is coronary insufficiency, which occurs due to narrowing of the arterial lumen.
What are the causes of an angina attack?
To help the victim, you need to know how an angina attack manifests itself, as well as the reasons for its development. It usually develops during physical activity. Often the trigger is stressful situations. In this case, they talk about exertional angina.
There is another variant of an angina attack; it can occur even at rest. This usually happens during sleep or in the morning. This type of disease is called resting angina. The unpredictable development of an attack is the most dangerous.
The following factors can also provoke angina:
- increased blood pressure;
- consumption of energy drinks and alcohol;
- smoking;
- listening to loud music.
The frequency of attacks is influenced by the degree of reduction in the lumen of the coronary artery. With pronounced pathology, pain appears up to several times a day. With age, the number of ailments increases. If angina is diagnosed, emergency care is necessary.
Angina attacks can occur at different intervals. The most severe of them lead to necrosis in the heart muscle, namely myocardial infarction. Subsequently, a scar will remain in this place.
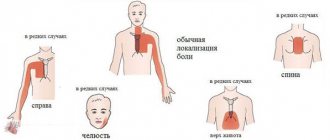
The disease is accompanied by pressing pain accompanied by burning sensations. The pain syndrome is localized in the sternum area. The pain is reflected in the neck, in the arm, and even moves to the jaw.
The attack is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pale skin;
- increased blood pressure;
- heart rhythm failure;
- dyspnea;
- nausea;
- perspiration;
- headache.
The duration of the illness on average is no more than five minutes, but there are longer options when the illness causes concern for more than 10 minutes. The attack may be short-lived and go away on its own.
Prolonged attacks of angina are the most dangerous; they are the cause of the development of cardiac complications, such as, for example, myocardial infarction. In order to avoid complications, it is important to provide the victim with adequate emergency care.
Emergency care for angina pectoris
Angina attacks require emergency care. The algorithm of actions for eliminating the symptoms of the disease includes the following procedures.
If the illness was provoked by physical activity, the patient must immediately stop moving, take a comfortable position, any exertion is prohibited, and he must not get up or walk. It is important to monitor your breathing; it should be even and deep.
In addition, the patient needs fresh air. You need to remove tight clothes from him and create a suitable temperature regime. First aid for angina pectoris includes taking medications, which should always be on hand for people suffering from heart disease.
To relieve an attack, the patient is given the following medications:
- Lay the sick person down with his head raised.
- Unfasten the belt, collar, loosen the tie, which will help relieve suffocation.
- Provide air access to the room.
- Chew an aspirin tablet 250-300 mg, take a nitroglycerin tablet 0.5 mg or as a spray under the tongue (if there is no effect, repeat twice after 5-7 minutes, under control of blood pressure and heart rate).
- If severe weakness appears, raise your legs to a level above your head, give them water to drink and no longer give nitroglycerin.
- Do not leave the patient until the doctor arrives.
- The doctor must show all medications taken.
- Call “103” immediately if the attack is not stopped.
An attack of angina can cause panic and anxiety. Close people urgently need to reassure the patient. You may need to take a sedative. These actions will help eliminate the ailment. After the attack has stopped, the patient should remain in bed. To prevent relapses, it is important to dose physical activity and avoid psycho-emotional stress.
Features of taking Nitroglycerin during an attack of angina
Nitroglycerin is the most effective remedy for relieving an attack of angina. But it should be taken with caution.
The action of Nitroglycerin should begin within a couple of minutes; if this does not happen, the dose can be repeated. But you should know that you should not take more than three tablets at a time.
Nitroglycerin is not always indicated for use. In some cases you cannot drink it. Contraindication is low blood pressure - hypotension.
Hypotension is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- general weakness;
- dizziness;
- paleness of the skin;
- cold sweat appears.
Taking Nitroglycerin for hypotension will worsen the patient's condition and reduce blood supply to the myocardium. It is advisable to measure your blood pressure before taking the medicine, if possible. In addition, this drug causes severe headaches. To relieve these effects, you will need to take painkillers.
Not every angina attack requires calling an ambulance. You will need to call a doctor in cases where:
- an attack of angina occurred for the first time;
- the discomfort did not go away after five to ten minutes;
- if the illness has become severe, symptoms appear that were not there before;
- it was not possible to eliminate the symptoms of the disease in the usual way;
- An unbearable growing pain appeared in my heart.
For angina pectoris, first aid plays a very important role.
Prevention
An active lifestyle is the main recipe for preventing all diseases. In addition to exercise, proper nutrition (more raw fruits and vegetables, low salt and carbohydrate intake), and quitting smoking and alcoholic beverages are necessary. After 40 years, regular monitoring of blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol levels is required. It is important to be in a positive mood in life and avoid stressful situations.
A primary attack of angina is an alarming sign that can signal possible heart disease. The patient needs to consult a cardiologist.
Cardiologist Sushko O.F.
Recommendations for the use of Nitroglycerin
Nitroglycerin is the medication most often used during emergency treatment for angina. The drug reduces the myocardium's need for oxygen, restores its transportation to all parts of the heart, eliminates coronary artery spasm, and has an analgesic effect. The peculiarity of the medicine is that after 45 minutes it is completely eliminated from the body.
To provide first aid to a patient during an attack, medication in the form of tablets, drops or capsules is usually used. Depending on the form of the medicine, you need to take it as follows:
- The tablet or capsule is placed under the tongue. It needs to be absorbed until completely dissolved;
- Drops drop onto a piece of sugar or bread (2-3 drops) and place under the tongue. If you don’t have sugar on hand, you can simply drip the medication under your tongue.
Some patients do not tolerate Nitroglycerin well. For them, it is recommended to take drops containing this component, as well as tincture of belladonna, lily of the valley or menthol. This helps reduce discomfort in the form of headaches after taking Nitroglycerin. One dose – up to 15 drops of the product.
People who are prone to a sharp decrease in blood pressure should take this drug with caution. The product may cause severe headache, weakness, and nausea. Patients suffering from glaucoma or who have suffered an acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain area should take Nitroglycerin only as prescribed by a doctor in a limited dosage.
Nitroglycerin should be in every first aid kit
If the medicine described is not in your medicine cabinet, you can take Phenigidine, Captopres or any other antihypertensive medicine. Immediately after the pain has subsided, you should not get out of bed; it is recommended to lie down for another 15–20 minutes until you feel completely restored.
Symptoms of angina
Unpleasant sensations in the chest are often described as a feeling of pressure, compression, heaviness, tightness, suffocation, burning, that is, angina is not always perceived as pain.
Discomfort and pain are usually localized behind the sternum. The pain can radiate (spread) to the left arm, under the left shoulder blade, and to the neck. Such irradiation is observed quite often. Sometimes the pain “radiates” to the right half of the chest, right arm, or to the lower jaw, or to the upper abdomen.
In some cases, pain or discomfort is not observed specifically behind the sternum, but only radiating pain. It is also possible that there is no pain at all, but so-called angina equivalents
: shortness of breath, sweating, severe fatigue, dizziness, etc.
A sign of angina pectoris is the paroxysmal nature of the pain. As a rule, pain occurs under conditions of increased heart activity (during physical activity or emotional stress). This type of disease is called angina pectoris.
. The attack lasts from one to 15 minutes. After which the patient experiences weakness (feels “broken”). A nitroglycerin tablet placed under the tongue helps (if nitroglycerin does not help, then the chest pain is probably caused by another disease other than angina). As a rule, with the onset of an attack, the patient stops the physical activity that caused it, and this is a condition for the cessation of pain. However, in some cases, the pain disappears even under conditions of continued stress (the so-called “passing through the pain”). And sometimes there is a “warming up” effect: at first the load causes pain, but after some time repeating the same load does not cause pain.
There is also angina at rest
. With this type of disease, pain may appear at night, and the patient wakes up from an attack of pain. Angina at rest is less common than angina at exertion, and is a more dangerous type of disease.
There are also stable
and
unstable angina
. In stable angina, a certain amount of exertion, when repeated, leads to a recurrence of the attack (an attack occurs at a certain level of exertion). Unstable angina is diagnosed as the disease progresses (the attack is caused by less and less load). This is a more dangerous condition. Unstable angina also includes spontaneous angina (attacks in this case are not caused by physical activity) and new-onset angina (attacks observed within a period of less than a month). New angina may regress (the attacks will stop), become stable or progressive.
Angina and other types of chest pain
Not all chest pain is angina. Pain can be caused by various reasons (in some cases, several at once), these can be:
- other heart diseases (such as heart disease, aortitis, etc.);
- osteochondrosis of the cervical or thoracic spine;
- shingles;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (peptic ulcer, diseases of the esophagus);
- lung diseases (pleurisy, pneumonia).
Pain caused not by ischemic heart disease, but by other reasons, is called cardialgia
. Cardialgia usually differs from angina in the nature of pain. In the case of cardialgia, the pain can be lightning fast, tingling, or vice versa - last for several hours or days. However, you should not try to diagnose yourself: pain in the heart area is serious. If such pain occurs, you should consult a doctor.
Angina and myocardial infarction
An attack of angina is not a heart attack. Pain during angina pectoris only indicates that the heart muscle is experiencing a temporary lack of nutrition. Once the situation returns to normal, nutrition will be restored.
However, it should be remembered that angina and heart attack are stages of the same process. If atherosclerosis progresses, angina will also progress, and this process may end with a heart attack. Therefore, angina (even stable) should not be treated as a necessary evil. Angina pectoris requires treatment, and above all, diagnosis of the condition of the blood vessels.
If an angina attack occurs for the first time, or the pain does not go away within 5 minutes after taking a nitroglycerin tablet (sublingually), you should call an ambulance.
Algorithm of actions for a prolonged attack
Emergency care for an angina attack that cannot be relieved with Nitroglycerin is provided in a hospital setting. In this case, the scheme has the following character:
- Nitroglycerin under the tongue with simultaneous intravenous administration of glucose solution and non-narcotic painkillers;
- administration of antihistamines (Diphenhydramine) and tranquilizers (Seduxen);
- taking Aspirin in effervescent form.
If there is no effect, narcotic analgesic drugs (morphine hydrochloride, Promedol) are administered within 10 minutes, which are combined with a neuroleptic and a tranquilizer.
After normalization of the patient's condition, echocardiography is mandatory. This is necessary to diagnose a possible myocardial infarction.
Help with myocardial infarction
Competent first aid for the development of myocardial infarction is the key to its successful treatment and prevention of many dangerous consequences. A heart attack is a severe condition accompanied by necrosis of individual areas of the myocardium. Emergency diagnosis of such a condition in a patient includes an assessment of his well-being and the presence of certain symptoms. Laboratory blood testing is valuable, which allows us to identify the presence of markers formed in the blood during the development of a heart attack. Among the clinical manifestations, the following signs indicate a heart attack:
- pain syndrome localized behind the sternum, spreading to the area of the arm, shoulder blade, neck and jaw;
- the duration of the attack is more than 2 hours, which makes it possible to differentiate this condition from angina pectoris;
- the appearance of nausea, vomiting, fainting;
- lack of effect after repeated administration of Nitroglycerin;
- development of cardiogenic shock, coma.
An ECG helps confirm or refute a heart attack. Necrosis is characterized by such changes on the electrocardiogram as displacement of the ST segment (it exceeds the isoline), as well as deformation of the Q wave.
Each of the subsequent actions during treatment is carried out in the absence of a therapeutic effect from the previous one. The algorithm for providing assistance in case of a heart attack is as follows:
- solution of Omnopon, Droperidol or Diphenhydramine through a dropper for 5 minutes in combination with saline solution. In parallel, acetylsalicylic acid orally;
- Fentanyl is used to lower blood pressure. The dosage is selected individually, depending on blood pressure;
- therapy aimed at dissolving blood clots and preventing their formation using beta-blockers;
- Nitroglycerin solution (1 ml per 100 ml of physiological solution). The medicine is administered with constant monitoring of blood pressure at a rate of 25 mcg/min. If the dose is well tolerated, the doctor increases the drip rate by 10 mcg every minute.
Treatment of myocardial infarction is carried out in an inpatient setting
When respiratory function is depressed, oxygen therapy is used. Inhalation using nitrous oxide and pure oxygen. Throughout the entire period, respiration, blood pressure, pulse and other vital signs are monitored. If necessary, analgesic drugs are reintroduced.
Important! The most favorable prognosis for the patient is possible if medical care was provided within the first 72 hours after the development of myocardial infarction.
Treatment methods for angina pectoris
The course of treatment for angina pectoris is prescribed individually, depending on the general condition of the patient and the form of the disease. A cardiologist treats angina pectoris. Treatment of angina pectoris is aimed at reducing the risk of myocardial infarction, reducing the frequency of attacks and normalizing quality of life. First of all, factors contributing to the development of atherosclerosis must be eliminated. Treatment of angina includes:
Lifestyle change
Treatment of angina will be more successful if the patient changes his lifestyle. You should stop smoking and provide the necessary physical activity. and follow an appropriate diet.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy for angina includes:
- nitrates. These drugs dilate blood vessels and thus reduce the load on the heart. This group of drugs includes nitroglycerin;
- antiplatelet drugs that prevent the formation of blood clots (acetylsalicylic acid has a similar effect);
- beta blockers, which reduce heart rate. As a result, the myocardial oxygen demand decreases;
- statins, which lower cholesterol levels and slow down the development of atherosclerosis;
- other drugs.
Revascularization
If the risk of myocardial infarction is high, revascularization is performed - surgical treatment aimed at restoring coronary blood flow. For revascularization, balloon angioplasty and coronary artery bypass grafting are used.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.