Blood pressure indicators are becoming an important marker in determining a person’s well-being. Moreover, doctors equally monitor both the increase and decrease in readings on the tonometer. At the same time, people often have questions. For example, since there are two indicators - upper and lower pressure - which one is more important?
Associate Professor of the Department of Hospital Therapy named after A.N. Academician P. E. Lukomsky Faculty of Medicine, Russian National Research Medical University named after. N. I. Pirogova, Ph.D., cardiologist, therapist, functional diagnostics doctor Maria Benevskaya .
Set priorities
“The first thing I would like to talk about when answering the question about which indicator is more important is what blood pressure actually is and what the measured parameters indicate. Blood pressure (also called blood pressure) is the pressure that blood exerts on the walls of blood vessels. This parameter is one of the indicators of the vital functions of the body,” notes Maria Benevskaya.
When measuring blood pressure, as the cardiologist says, two types are determined: with each heartbeat, the blood pressure fluctuates between the highest, systolic (from the ancient Greek “compression”), and the lowest, diastolic (from the ancient Greek “rarefaction”) "), which are colloquially called upper and lower. Thus, the magnitude of the force acting on the vessels is determined by two parameters: upper (systolic) and lower (diastolic) pressure. Therefore, we cannot say that any of these parameters is more important. They both have their meaning.
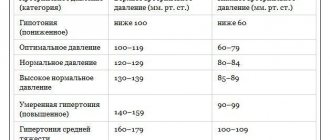
“Everyone knows that the normal blood pressure of a healthy person (systolic/diastolic) is 120 and 80 mmHg. Art., but we must also remember that normal boundaries change depending on age and existing diseases. The difference between systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure is called pulse pressure and is normally 30-50 mmHg. Art.,” the specialist emphasizes.
We fight the pressure. 8 drinks for hypertensive patients Read more
Clinical manifestations
With a pathology of pulse difference, which is provoked by somatics, the patient complains of:
- fatigue;
- mood instability;
- forgetfulness, lack of concentration;
- constant pre-fainting state;
- bluishness of the skin.
In case of cardioshock, the symptoms are different:
- pale dermis, mucous membranes;
- profuse sweat;
- fainting;
- dyspnea.
Isolated systolic hypertension is sluggish, almost asymptomatic, but is characterized by:
- ringing in the ears;
- fainting;
- incoordination;
- emotional lability;
- arrhythmia.
The mild course of the disease spontaneously gives way to a crisis when physical inactivity, diabetes, myocardial dystrophy, kidney pathology, AMI, and a history of stroke predominate.
Renal or cardiac?
There is an opinion that the upper pressure indicator is cardiac, and the lower one is renal. “The top number is systolic blood pressure, it shows the pressure in the arteries at the moment when the heart contracts and pushes blood into the arteries, it depends on the force of the heart contraction, the resistance that the walls of the blood vessels exert, and the number of heartbeats per unit time. Therefore, in general, we can say that this indicator reflects the work of the heart, although, of course, other factors also take part in this process,” says Maria Benevskaya.
It is also not worth ruling out that the lower indicator reflects kidney function. “The bottom number is diastolic blood pressure, which shows the pressure in the arteries when the heart muscle relaxes. This is the minimum pressure in the arteries and reflects the resistance of peripheral vessels. Since vascular tone is regulated by chemicals and the autonomic nervous system, lower blood pressure indicates the extent to which neurohumoral regulation is carried out correctly. In turn, neurohumoral reactions occur mainly in the kidneys, which is why there is an opinion that the “lower” pressure is renal. But it would be more correct to note that lower pressure reflects the work of blood vessels and kidneys,” says the cardiologist.
Lack of oxygen, loss of strength. How pressure surges affect the brain Read more
Diagnostics
After a conversation with the patient, the doctor prescribes a full clinical and laboratory examination, taking into account the direction in which the tonometer deviation occurred. Mandatory for everyone - an ECG, as well as an EchoCG, assessing the electrical activity of the myocardium, the condition of the heart chambers, and the large arteries adjacent to them. Additionally prescribed:
- UAC, OAM;
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound of the urinary system;
- MRI of the aorta;
- angiography of the renal arteries.
The ISH study algorithm is simple: 24-hour monitoring of blood pressure over time. In addition, they prescribe: blood sugar tests, lipid and coagulograms, ultrasound of cerebral vessels. If necessary, the patient is consulted with an angiosurgeon, neurologist, diabetologist, nutritionist, and psychotherapist.
Importance of indicators
So is it possible to conclude which of these indicators is more important? “As we have already figured out, each of these parameters has its own meaning, so they are both important. Currently, it is also customary to distinguish between isolated systolic hypertension, when only the upper pressure is increased, and isolated diastolic hypertension when only the lower pressure is increased. Each of these forms has its own prognostic significance and some features in treatment, so it is necessary to approach the identification and correction of these types of hypertension with equal attention,” notes Maria Benevskaya.
A big difference
A value of more than 50 is considered a high difference.
It correlates with the upper limit, the diastolic remains unchanged. This condition is called isolated systolic hypertension. It is precisely this that is stopped by practicing cardiologists and therapists. ISH cannot be treated radically, but requires constant monitoring of blood pressure and stopping fluctuations. It raises concerns because it warns of the risk of stroke, AMI with a practically asymptomatic course.
A difference of 60, 70, 80 units a priori suggests medical assistance. This indicates a significant overstrain of the myocardium and blood vessels, and the risk of spontaneous failures.
Attention to the gap
Of course, as experts note, it is also necessary to look at the gap between these parameters. “I repeat that the normal difference between upper and lower pressure is from 30 to 50 mm Hg. Art. All values that do not fit within these limits may indicate the presence of pathology, and this is already a reason to undergo additional examination. Although at the same time this may be due to the individual characteristics of the body and physiological conditions. But in any case, it’s better to see a doctor so as not to miss the disease,” notes Maria Benevskaya.
So, for example, the specialist emphasizes, a small difference may indicate:
- the presence of atherosclerosis of the aorta (deposition of cholesterol in the largest vessel);
- damage to the kidney vessels;
- aortic aneurysm (pathological expansion of a separate section of the aorta with the possibility of rupture or dissection of the walls due to excessive load);
- anemia (decreased hemoglobin levels in the blood) and many other conditions.
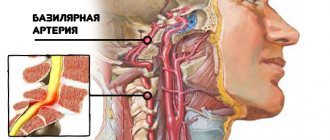
“An increase in the difference may be a consequence of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, aggravated by a malnutrition of the brain (most often vertebrobasilar insufficiency). Diseases of the musculoskeletal system lead to weakening of cerebral blood flow. Hence the problems with upper and lower pressure in general,” notes the cardiologist.
Also, as Maria Benevskaya says, various endocrine diseases can lead to changes in pulse pressure. And this is not the entire range of pathologies that affect this parameter. A change in this indicator can be a “bell” to pay attention to your health.
Hot towel and vinegar. What folk remedies quickly reduce blood pressure? More details
What causes the pathological condition?
A decrease in the pulse difference is accompanied by an increase in the diastolic value or a decrease in the systolic value. Sometimes this occurs simultaneously. The triggers for this difference are the following somatic diseases:
- lipid metabolism disorders, pancreatic dysfunction;
- hypertension of any degree;
- cholesterolemia leading to vascular stenosis;
- imbalance of cerebral blood flow;
- kidney pathology;
- arrhythmias of various origins;
- aortic stenosis;
- myo-, pericarditis, myocardiopathy;
- left ventricular failure;
- tumors of the urinary system;
- neoplasms in the adrenal glands;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- aortic aneurysm;
- cardiogenic shock;
- hypocaloric diets, dehydration, hypothermia.
Age is a cause of isolated systolic hypertension or IHS.
Over time, the layer of muscles in the vessels, which is responsible for their elasticity and lumen, becomes thinner. Against this background, plaques of calcium, blood clots, and cholesterol form. Arteries demonstrate fragility and respond inadequately to fluctuations in biomarkers. As kidney nephrons age, they lose their main function and stop regulating blood pressure.
The myocardial receptors that correct the response of the arteries to the systolic ejection of blood are subject to destruction. At the same time, the oxygen supply to the centers responsible for vascular tone deteriorates; they lose the ability to balance it. All this distinguishes patients over 60 suffering from age-related hypertension.
Adjust individually
The question of whether it is possible to adjust indicators separately is also of concern to many. “Basically, all the drugs that we use to correct high blood pressure act on both upper and lower pressure. However, among the classes of antihypertensive drugs, we have the opportunity to select drugs with a predominant effect on systolic or diastolic pressure. Therefore, it is possible to implement a personalized approach to the patient based on his needs,” notes Maria Benevskaya.
For example, she says, medications that have a vasodilating effect will be more likely to cause a decrease in diastolic (lower) blood pressure. And drugs that reduce the force of heart contractions will reduce systolic (upper) blood pressure to a greater extent.
How to quickly normalize blood pressure
A gap in the pulse difference of 50 units in the upward direction requires contacting specialists.
But the first steps to normalize blood pressure are usually taken independently. Recommend:
- take a horizontal position;
- restore breathing;
- open the window for oxygen access;
- if blood pressure is high, raise your head; if blood pressure is low, raise your legs;
- provide freedom to the neck;
- high blood pressure involves hot foot baths to improve blood flow from the brain;
- acupressure and breathing exercises are acceptable: hypotension requires rubbing the earlobes, hypertension requires circular movements from the ears to the back of the head.
Causes of pathology
Secondary form of ISAH
Secondary ISAH is a complication of a number of pathologies:
| Group of diseases | Specific diseases |
| Hereditary and congenital disorders | Coarctation (narrowing) of the aorta Patent ductus arteriosus Polycythemia (increased red blood cell count) |
| Cardiac and vascular disorders | Complete atrioventricular block (impaired heart contraction) Aortic valve insufficiency Atherosclerosis of the renal arteries Aortoarteritis (inflammation of the vascular lining) |
| Other violations | Anemia Fever Thyrotoxicosis (high level of thyroid activity) |
Primary form of ISAH
Primary, or essential, ISAH develops through the interaction of two or more risk factors (these risk factors are the same for any form of arterial hypertension):
- genetic defect;
- age-related changes in the vascular wall (decreased elasticity) and metabolic disorders (increased activity of pressure-stimulating hormones);
- atherosclerosis;
- smoking;
- excess weight with impaired fat metabolism;
- diabetes;
- female gender (incidence is twice as high).
Prevention
{banner_banstat9}
The patient’s lifestyle is important: giving up bad habits, diet, dosed exercise, walking, proper rest. It is necessary to calculate the daily drinking ration together with your doctor, at least 2 liters of clean water daily. Instead of saunas and hot baths, take a contrast shower. The diet should consist of vegetables, fruits, and foods containing iron: liver, tomatoes, fish, apples. A healthy lifestyle is especially relevant for those who have crossed the forty-year mark.
Features of treatment
A set of measures to relieve a pathological condition is aimed at eliminating the cause.
- Atherosclerosis requires drug therapy or surgery. Among the medications used are: statins and fibrates, which reduce the concentration of blood cholesterol (Rosuvastatin, Fenofibrate); unsaturated fatty acids that stimulate the removal of toxic fats from the body (Linetol); vitamins that nourish the endothelium and block the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. Among the surgical methods that deserve attention are laser angioplasty, vascular stenting, bypass surgery - creating a bypass blood flow, endarterectomy - excision of part of the inner layer of an artery with an atherosclerotic plaque.
- Aneurysms are treated only with surgery.
- Pericarditis involves pericardiectomy of the affected area with recovery in 60% of cases.
- Aortic stenosis requires replacement of the valve with an artificial one, which lasts from 8 to 25 years, taking into account the properties of the selected material.
- Heart rhythm disturbances are treated with antiarrhythmic drugs, sometimes with the help of a defibrillator or the installation of a pacemaker.
- Chronic kidney pathology is treated with anti-inflammatory therapy, antibiotics, anticoagulants, and physiotherapy.
- Tumors are corrected with cytostatics and other antitumor drugs. Failure requires a decision on the operation.
- Left ventricular failure requires either surgery or a combination of medications:
- ACE inhibitors – reduce diastolic pressure;
- cardiac glycosides improve myocardial contractility;
- nitrates to improve oxygen supply to the heart;
- diuretics to relieve swelling.
Acute left ventricular failure requires emergency hospitalization in a specialized hospital.
ISH therapy is prescribed by a cardiologist or therapist after a full clinical and laboratory examination and requires compliance with several rules: the force of the blood hitting the vascular wall is gradually reduced so that adaptation to new conditions occurs and ischemia does not develop; medications are required to affect only the upper blood pressure reading; There should be no negative impact on the kidneys or brain. For this purpose the following are appointed:
- antihypertensive drugs: calcium antagonists, beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin blockers;
- diuretics: a small blood volume reduces the upper limit, cardiac output;
- drugs that stimulate blood flow in the kidneys, brain, heart;
- neuro-, cerebroprotectors – improve the nutrition of nerve cells, prevent stroke.
To increase efficiency, various combinations of drugs are used under medical supervision.