- What does upper and lower pressure show?
- What can lead to a decrease in lower pressure?
- Types of arterial hypotension
- Causes of low lower pressure
- Mechanisms of reduction in systolic and diastolic pressure
- Symptoms
- Diagnostic procedures
- Treatment methods
The state of low blood pressure is called arterial hypotension. It occurs if the readings fall below 100/60 mmHg. In some patients, upper and lower pressure (systolic and diastolic) decreases. Sometimes a situation arises when the upper indicator is normal, and the lower indicator falls below normal. This is regarded as isolated arterial hypotension and requires the attention of specialists.
What does upper and lower pressure show?
The upper pressure is called systolic. It refers to the force with which blood is pushed out of the heart and moves through the vessels, saturating organs and tissues with oxygen. Diastolic - lower pressure, indicates the pressure of blood on the walls of blood vessels at the moment between heartbeats.
As a rule, as people age, they experience an increase in upper blood pressure. Elevated lower levels are more common in patients under 50 years of age and then begin to decline. Problems with diastolic pressure begin due to deterioration in the elasticity of blood vessels. The capillaries narrow, become stiffer, and this leads to excess blood pressure on their walls. This phenomenon is observed even at rest.
Diagnostics
Since there are no drugs that can increase diastolic pressure without increasing systolic pressure, when developing a therapeutic regimen you need to know exactly what the cause of the deterioration is. To do this, examinations are prescribed in the following areas:
- brain - to identify a neurogenic factor in time;
- endocrine system - with adrenal dysfunction, the synthesis of hypertensive hormones decreases;
- liver - the organ responsible for metabolic processes.
The patient is recommended to do a biochemical analysis, donate blood for thyroid hormones, and may have to undergo diagnostic procedures - MRI, CT, angiography, encephalography, ultrasound, x-ray. It is necessary to completely exclude (or confirm) the presence of neoplasms.
What can lead to a decrease in lower pressure?
Arterial hypotension can act as an independent disease (primary form) or one of many symptoms (secondary form). According to statistics, low upper and/or lower blood pressure is more common in women than in men. This phenomenon can also occur in adolescents.
In older people, lower blood pressure decreases due to decreased vascular tone. The main culprit of the problem is atherosclerosis. Secondary hypotension can occur against the background of neurological and cardiac diseases, and hormonal disorders.
Increase in DBP
It is quite difficult to raise the lower pressure without raising the upper one. Pharmacological drugs and folk remedies do not act selectively and can increase both indicators at the same time. With a small rupture, such an action will only worsen the condition. Therefore, when taking medications prescribed by a doctor, you should analyze the effects. You can only find out what is suitable through experimentation. Folk remedies are milder, but they also affect both indicators.
Attention! Decoctions or infusions of medicinal herbs have a cumulative effect. The maximum duration of treatment with one drug is 2 months. In the future, the recipe should be changed.
Medicines alone are not enough. To raise heart pressure at home, it is necessary to change your diet, and, often, adjust your lifestyle, change your perception of the influence of negative external factors.
Types of arterial hypotension
There are three types of arterial hypotension:
- physiological;
- pathological;
- symptomatic.
Low blood pressure as a physiological norm may be a congenital feature characteristic of a particular person due to his constitutional type. A similar situation is observed among professional athletes, residents of high mountain areas and tropical latitudes. Thanks to the decrease in pressure, the body adapts to physical activity and climate conditions. In this case we are talking about a compensatory function.
The pathological form of the disease is of two types: orthostatic and neurocirculatory. Orthostatic hypotension occurs when there is a change in body position when a person gets up after resting or sleeping. The neurocirculatory form is associated with disruption of the autonomic nervous system. The patient may periodically experience low blood pressure or have hypotension, in which diastolic pressure is chronically low.
Symptomatic hypotension is secondary. Its causes are disruption of the functioning of various organs and systems, intoxication.
What foods can help with low blood pressure, and which ones should not be consumed?
– For low blood pressure, as I said earlier, it is recommended to consume large amounts of table salt (up to 10 g/day) and liquids (up to 3 l/day), and caffeine-containing drinks.
With postprandial hypotension, you need to adhere to a certain type of diet: eat often, in small portions, more proteins and fats, avoid carbohydrates (especially refined ones), eat warm or cold (not hot) foods. And you should give up alcohol.
In what situations should you definitely consult a doctor – and which one? – Patients with fainting, especially those that occur for the first time, need to consult a cardiologist, and, if necessary, a neurologist.
If blood pressure was previously normal or elevated, and then became chronically low, you should also contact a cardiologist to find out the cause. How to monitor your blood pressure and control its reduction?
– In order to prevent another decrease in blood pressure, it is necessary, firstly, to determine the cause (hypothyroidism, anemia, adrenal insufficiency, taking high doses of antihypertensive drugs, etc.) and, if possible, eliminate it.
Secondly, try to avoid provoking situations and factors, observe safety conditions during verticalization, and lifestyle recommendations.
And in situations where a person anticipates developing hypotension or fainting (increased sweating, nausea), you can help yourself by using the physical counterpressure maneuvers that I described earlier.
Causes of low lower pressure
According to statistics, the main cause of primary hypotension is neurocirculatory dystonia (NCD). It is otherwise called heart neurosis. With neurocirculatory dystonia, various disorders of autonomic regulation are observed, and this condition is not associated with damage to the endocrine or nervous systems.
NCD and the resulting decrease in diastolic pressure are most often observed in women during puberty and at the onset of menopause, with impaired ovarian function. In young people and middle-aged patients, hypotension occurs against the background of chronic fatigue, stress, psycho-emotional and physical overload. The high-risk group includes people with alcohol and tobacco addiction, patients who have recently experienced psychological trauma, and who are depressed.
Secondary arterial hypotension can be acute or chronic. Low diastolic pressure is encountered by patients with stomach ulcers, diabetes, low thyroid function, osteochondrosis, arrhythmia, heart failure, and chronic infectious processes. In people with such diseases, blood pressure may be constantly low, but due to the body's ability to adapt, the disease does not manifest itself with pronounced symptoms.
A sharp drop in upper and lower blood pressure occurs with significant blood loss, dehydration, anaphylactic shock, or poisoning. These conditions are extremely dangerous for health and life, as they lead to serious circulatory disorders.
One of the possible reasons for a decrease in diastolic blood pressure is a lack of vitamins B, C and E in the diet. The body can also respond to a strict diet or an overdose of drugs (adrenergic blockers, anti-hypertension drugs) with arterial hypotension.
Recommendations of Dr. Shishonin
Alexander Yuryevich recommends that every home always have ammonia on hand. After all, this substance reflexively improves blood circulation in the nasal cavity. Ammonia is a fairly strong toxic substance. As a result of its use, a hypertensive reflex appears, that is, the pressure rises so that the kidneys can remove this substance from the body.
In cases where the pressure drops significantly, for example 80/40 mm. rt. Art., A.Yu. Shishonin recommends using Cardiamine. This medicine is good for lowering blood pressure. People of normal build should take no more than 30 drops of this drug. For obese patients, the dose can be increased to 40 drops.
If Cardiamine is used according to the instructions, it will never provoke the development of a hypertensive crisis, that is, it is not a dangerous drug. Doctors often prescribe it to normalize blood pressure.
Note.
Only an experienced specialist can answer why the blood pressure of a hypertensive patient has dropped; his competence includes prescribing treatment.
If you have neither Cardiamine nor ammonia at hand, then you can use the knowledge of Eastern healers to increase blood pressure. Thanks to the effect on reflex points, blood pressure is normalized. To carry out this procedure you will not need any medications.
FIRST POINT
It is located on the little finger immediately behind the periungual fold at the root of the nail on the side of the ring finger. With strong compression of the little finger, cardiac activity is activated, which leads to normalization of blood pressure.
SECOND POINT
This is the point of general stimulation. In Eastern medicine it is also called the He-Gu point. It is located in the center of the triangle, which is placed between the thumb and forefinger. This point needs to be stimulated on both sides using your fingers.
THIRD POINT
It is located between the upper lip and nose. You need to stimulate the indicated point for 10 to 15 seconds. With a slight decrease in pressure, 5 seconds is enough.
All of the above methods provide 100% therapeutic results. It should also be noted that there are never any failures when working on these points.
Mechanisms of reduction in systolic and diastolic pressure
A decrease in blood pressure is caused by one of four possible reasons:
- the stroke and cardiac output decreases;
- the flow of blood to the heart through the veins decreases;
- vascular resistance decreases;
- the volume of circulating blood decreases.
A decrease in cardiac output and stroke is observed in cases of disturbances in myocardial function caused by infarction or myocarditis. The same situation occurs with an overdose of adrenergic blockers.
Vascular tone can decrease with infectious diseases, intoxication, and anaphylactic shock.
A decrease in the volume of circulating blood occurs against the background of bleeding due to trauma to tissues and blood vessels, rupture of the spleen, and ulcerative lesions of the stomach.
A decrease in venous return of blood to the heart occurs with massive ascites or pleurisy due to blood retention in the smallest vessels.
Medicinal correction at home
An isolated decrease in diastolic reading occurs in a maximum of 10% of cases. In the remaining 90%, this is a combined change in the upper and lower levels, therefore, when prescribing drugs that promote the growth of DBP, one cannot ignore the level of systolic pressure.
For example, caffeine-containing drugs (Citramon, Pentalgin-N, Caffeine, Farmadol) will easily raise the diastolic reading, but if diastolic hypotension is combined with systolic hypertension, a crisis may occur, since caffeine will raise the already high systolic pressure.
Therefore, doctors prefer to prescribe beta blockers to increase low lower pressure: Coronal, Concor, Micardis, Telmisartan, Losartan or calcium antagonists: Isoptin, Verapamil, Finoptin, Diacordin. They additionally exhibit antiarrhythmic properties, so their self-prescription is unacceptable. A complete clinical and laboratory examination is required.
The drugs are prescribed in individual dosages depending on the general condition of the patient and his age
This is especially important for the elderly or those people who suffer from diseases of the vegetative-vascular system, heart, kidneys
In emergency cases, when there is a critical decrease in blood pressure, the following is administered: Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Cordiamin, Dopamine, Mezaton.
Adaptogens
Low blood pressure can be raised using a large group of herbal or synthetic medicines that stimulate the human immune system and increase its ability to withstand negative influences. These include:
- ginseng – prevents stroke, improves immunity;
- basil is an excellent antioxidant, removes free radicals, toxins, rejuvenates the body, is used in Ayurscience, increases vascular tone, improves concentration, memory, and improves mood;
- ashwagandha (Chinese ginseng) – relieves anxiety by correcting cortisol in the bloodstream, exhibits antioxidant properties, rejuvenates cells, improves memory, prevents Alzheimer’s disease, alleviates menopausal symptoms;
- Eleutherococcus – stimulates the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, reduces sugar and cholesterol in the vascular bed;
- Schisandra is considered an excellent detoxifier and antioxidant;
- Rhodiola rosea – provides protection against stress, relieves fatigue;
- Astragalus is a legume, detoxifier, antioxidant, supervises the endocrine glands;
- licorice root – soothes, stimulates endurance, improves immunity;
- Schisandra (Chinese lemongrass) increases the resistance of internal organs to negative influences;
- reishi – the mushroom stimulates the immune system, prevents cardiovascular pathology;
- Peruvian maca – balances hormonal levels;
- rosemary relieves stress, improves the functioning of the cardiovascular and digestive systems.
Adaptogens play a significant role in raising lower low blood pressure, but are prescribed only on the recommendation of a doctor, since they do not have an isolated effect on DBP. Among synthetics we can note Pantocrin, Tonginal. These drugs are taken for no more than two weeks, since an overdose may lead to an increase in SBP with a hypertensive crisis.
Vitamin and mineral complexes
A deficiency of minerals and vitamins can provoke a decrease in diastolic blood pressure. They are an alternative to a balanced diet. Use:
- Pikovit:
- Doppelhertz OMEGA 3;
- Complivit,
- Supradin;
- Vitrum;
- Centrum;
- Alphabet.
Symptoms
With a physiological decrease in lower pressure, patients do not experience a deterioration in their well-being. If the problem is caused by pathology, then oxygen starvation gradually develops. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- weakness and dizziness;
- colored spots before the eyes;
- pallor;
- fainting state.
Patients with chronic arterial hypotension constantly feel fatigue, drowsiness, and a desire to rest. A person with low blood pressure experiences increased sweating and may experience headaches. Low blood pressure makes it difficult to concentrate on work or study and makes a person emotionally unstable. Women with chronic hypotension may experience menstrual irregularities, and men have reduced potency.
In severe forms of arterial hypotension, patients experience vegetative crises. They are accompanied by a decrease in temperature, sweating, difficulty breathing, chest pain, nausea and vomiting, slow pulse, and loss of consciousness.
First aid
Sometimes a decrease in diastolic pressure can take a person by surprise not only at home, but also at work or in transport. This often happens in hypotensive people in the summer, during the heat. Therefore, you should know what to do in this case:
- Lie in a horizontal position. There is no need to put a pillow under your head, you need to put it under your feet - they should be slightly above the level of your heart. This will provide additional blood flow to the brain and supply it with oxygen.
- If it is not possible to lie down, for example, a sharp decrease in pressure caught you in transport, you need to sit down and bend over, lowering your head below your knees.
- Open a window or vent to let in fresh air.
- Remove tight clothing or at least unbutton it.
- Drink a cup of strong sweet tea, to which you can add something tonic (tincture of ginseng, eleutherococcus). Remember that coffee and caffeinated drinks increase tachycardia, which can adversely affect your well-being in this case.
- Measure your blood pressure every fifteen minutes. If it remains low for half an hour, despite all the measures taken, you should call an ambulance. In addition, you should immediately seek medical help in cases where the acute occurrence of hypotension is accompanied by the appearance of other serious symptoms: for example, pain in the heart, impaired consciousness, weakness in half the body.
Diagnostic procedures
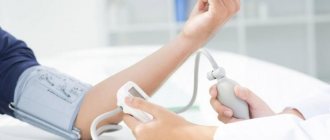
To normalize blood pressure, it is important to identify the reasons for its decrease. The approach to diagnosing arterial hypotension is complex. First of all, the doctor needs to assess the blood pressure level. Daily monitoring is best suited for these purposes. The procedure helps to identify how pressure readings change during the day. A technique for measuring blood pressure three times with an interval of 3-5 minutes is also used.
To choose treatment, you need to determine whether a decrease in lower pressure is an independent disease or a symptom of another disease. The patient is prescribed laboratory tests for hormones, electrolytes, glucose and other indicators. Among the hardware methods for diagnosis, electroencephalography, ECG, and orthostatic test are used.
A person with chronic arterial hypotension needs to consult a neurologist, cardiologist, or endocrinologist.
Piracetam
- Helps improve brain activity;
- Increases concentration and improves cognitive functions;
- Promotes recovery after various cerebral injuries due to hypoxia, intoxication or electroconvulsive therapy.
More details
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS. BEFORE USE, READ THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY OR CONSULT A DOCTOR
Prevention
If you have a tendency to lower blood pressure, you need to be careful about your own health. Get enough sleep, spend enough time in the fresh air, normalize your work and rest schedule, master self-massage techniques, and adhere to a rational diet. It is necessary to control blood pressure and monitor it throughout the day. People who have not experienced hypotension also need to think about their health. They should also adhere to a healthy lifestyle, especially after 40 years of age. At this time, indicators may change.
Hypotension with a decrease in DBP is asymptomatic for a long time, and when it is diagnosed, normalizing the condition will be problematic. As already mentioned, drugs that affect one of the indicators have not yet been developed. It is better to prevent this disease at the very beginning, so that later you do not have to select pharmacological agents and recipes from the arsenal of traditional medicine in order to increase heart pressure.
Basic principles of nutrition
To maintain good health, hypertensive patients should pay special attention to their diet. Remember, the patient’s health depends 80% on compliance with the doctor’s instructions and diet therapy.
Nutrition rules for hypertension:
- Limit your daily salt intake. Considering that NaCl increases fluid retention in the body, consumption of large doses of salt is fraught with swelling of the tissues surrounding the capillaries. At the same time, due to increased pressure on the arteries, blood release from the heart cavities increases (the beginning of the development of hypertension). However, the product cannot be completely excluded from the daily menu of hypertensive patients (due to the possible accumulation of nitrogenous compounds in the blood plasma). The optimal portion of salt is 4–5 grams per day. To improve the taste of food, you can use spices (basil, dill, garlic, parsley, onion), cranberry and lemon juice.
- Sharply limit animal fats (saturated) in the menu. The most common cause of high blood pressure is blockage of blood vessels with “bad” cholesterol. To improve capillary permeability, it is extremely important to avoid foods that worsen lipid metabolism. Namely: offal, sausages, fried or smoked lard, processed cheese, fatty meats.
- Enrich your diet with foods containing potassium and magnesium. Arterial hypertension, in 70% of cases, is accompanied by massive edema, circulatory failure, and cholesterol metabolism disorders. To minimize these problems, potassium and magnesium are included in the patient’s daily diet. These microelements improve myocardial function (including increasing its endurance), accelerate the removal of excess fluid from tissues, have a relaxing effect on the arteries, reducing spasm of smooth muscles, and prevent the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of capillaries.
Natural sources of potassium are dried apricots, bananas, prunes, potatoes (baked), melon, watermelon, raisins, pumpkin, rose hips (fruits), avocado.
Magnesium is present in large quantities in bran, cereals (oatmeal, barley, buckwheat, wheat), leafy greens (parsley, lettuce), vegetables (carrots, beets), nuts (almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts).
- Eliminate alcohol, nicotine, and caffeine-containing drinks from your diet. When taking stimulants, most hypertensive patients experience increased heart rate and some parts of the brain are overexcited. Due to the increased load on the cardiovascular system, blood pressure readings “grow” upward.
- Replace simple carbohydrates with complex ones. Saccharides are the main suppliers of energy to the human body. When consuming simple carbohydrates (sugar, confectionery, jam), a sharp increase in blood glucose levels occurs, which leads to the release of large doses of insulin. As a result, its excess is transformed into adipose tissue (since the monosaccharides in the modern human diet are 4 times higher than normal). In addition, excessive intake of monostructures is fraught with the development of metabolic syndrome, which, in 90% of cases, is accompanied by arterial hypertension.
Complex saccharides (as opposed to simple ones) are absorbed more slowly, without causing metabolic disorders and sudden increases in blood glucose. The best sources of high molecular weight carbohydrates are whole grain bread, cereals, berries, herbs, vegetables, and fruits.
- Use gentle cooking methods. The best options for heat treatment of food are baking, stewing, steaming, and boiling. Avoid frying food, as heating fat releases large amounts of carcinogens and “bad” fats.
- Follow a fractional diet. The optimal frequency of meals is 5 – 6 times a day.
- Maintain the ratio of the main components of food. The daily diet of a hypertensive patient should include: 15% proteins (90–100 grams), 30% fats (80–85 grams), 55–60% complex carbohydrates (350–400 grams).
- Maintain drinking regime. Among hypertensive people, there is an opinion that you need to consume less water, since it increases blood pressure. This is a dangerous misconception. In fact, with a lack of fluid in the body, blood viscosity increases, vascular turgor decreases, and the concentration of low-density lipoproteins increases.
The daily portion of water (in addition to drinks) is calculated based on the ratio of 35 - 50 milliliters per kilogram of body weight.
Interestingly, each cup of coffee drunk (volume 150 milliliters) removes 4 equal portions of liquid (600 milliliters) from the body. The body, trying to retain such a valuable resource, creates edema, as a result of which blood pressure rises.
In case of hypertension accompanied by obesity, the energy value of the daily menu is reduced to 1000–1500 kilocalories (by reducing the daily dose of carbohydrates and increasing the daily portion of proteins and healthy fats).
Strict low-calorie diets and fasting with high blood pressure are contraindicated. Overweight hypertensive patients are allowed to have vegetarian fasting days 2 times a week.
Treatment
First of all, the underlying disease is treated. If you have, for example, hypothyroidism, you will be prescribed medications to normalize the functioning of the thyroid gland. And drugs to increase diastolic pressure are used as an addition to the main treatment.
Medicines
To increase lower pressure, tonics and vascular strengthening drugs are used.
In case of low lower pressure, the cause of which has not been identified, as well as vegetative-vascular dystonia and astheno-neurotic syndrome, treatment is carried out using tonic drugs. They increase diastolic pressure, eliminate lethargy, weakness, drowsiness, and apathy.
Tonics include:
- ginseng;
- lemongrass
Medicines that strengthen blood vessels will help prevent further problems with blood pressure and prevent bleeding:
- ascorutin;
- quercetin.
For astheno-neurotic syndrome, nootropics can be prescribed. They will improve your psycho-emotional state. They will eliminate lethargy, increase performance, and improve blood circulation in the vessels of the brain. This:
- phenibut;
- pantogam.
Contraindications and side effects of medications
Herbal tonic preparations:
| Name | Contraindications | Side effects |
| Ginseng | Increased systolic pressure, chronic insomnia, bleeding tendency, epilepsy, acute infectious diseases, chronic liver diseases | Sometimes: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. Very rare, usually in case of overdose: insomnia, anxiety, rapid heartbeat, headache |
| Schisandra | Insomnia, cardiac disorders (eg, arrhythmias) | Insomnia, emotional agitation |
Drugs that strengthen blood vessels:
| Name | Contraindications | Side effects |
| Ascorutin (vitamin P with vitamin C) | Increased blood clotting, tendency to thrombosis, history of thrombophlebitis, diabetes mellitus, gout, urate stones in the kidneys or bladder, oxalates in the urine, renal failure, potassium deficiency, excess calcium. | They usually occur with prolonged use. These are headache, nausea, heartburn, feeling hot. With long-term use in large doses, it is possible to increase blood sugar levels and disrupt heart function. |
| Quercetin | Individual intolerance. | Nausea, tingling in fingertips, headache. |
Nootropics:
| Name | Contraindications | Side effects |
| Phenibut | Pregnancy, breastfeeding, renal failure, liver failure. | Nausea, headache, sleep disturbances, diarrhea, abdominal pain. Long-term use has a negative effect on the liver. |
| Pantogam | Kidney failure. | Sleep disturbances, tinnitus. |
In addition to these side effects, any medications can cause allergies. It manifests itself as a skin rash, runny nose, red eyes, and digestive disorders.
If any side effects occur, consult your doctor.
Folk remedies and lifestyle
Increasing diastolic pressure using folk remedies:
| Tea with currant leaves | Take 1 teaspoon of black tea and 1 teaspoon of crushed black currant leaves. Pour a glass of boiling water. Leave for 15 minutes. Drink a glass a day after meals. |
| Chicory root | Take 2 tablespoons of crushed roots, pour in 0.5 liters of warm water, and simmer over low heat for 30 minutes. Strain. Drink 1/3 glass 3 times a day. |
The course of treatment should last no more than 3–4 weeks.
Before using folk remedies, consult your doctor.
What to do with your lifestyle? Observe the following rules:
- Get rid of all bad habits.
- Sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Observe the work and rest schedule (there should be no less than 1 day off per week, work no more than 8 hours a day, an hour lunch break should be every working day, a 15-minute rest - at least once every 3 hours).
- Take a contrast shower. This will help strengthen and tone blood vessels. However, such water procedures are contraindicated in acute and chronic inflammatory diseases (acute respiratory infections, bronchitis, tonsillitis, cystitis, etc.).
- Do physical exercise (swimming, running, cycling).
- Spend at least 2 hours a day outdoors.
What to take
If the doctor has determined for sure that a person has hypotension, then he prescribes a number of medications. The treatment complex includes the following means:
- When a patient with hypotension experiences fainting, frequent dizziness, and vision deterioration, the doctor prescribes Fludrocortisone. The medicine relieves symptoms well and improves general condition.
- For severe deviations in vascular tone, the drug Deoxycorticosterone helps.
- Epinephrine tablets quickly increase the diastolic reading due to active vasoconstriction.
- Heptamil tablets effectively combat arterial hypotension. This drug is harmless; it has a positive effect on the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
- The drug Dopamine (drops, intravenous injections) tones blood vessels located on the periphery.
How to normalize blood pressure?
To normalize arterial diastolic pressure, it is first necessary to accurately determine what the systolic indicator is. If the lower blood pressure is low and the upper blood pressure is high, you cannot do without the help of a doctor. After all, by raising the lower indicator, you can excessively increase the upper one.
Drug therapy
Drugs to increase lower blood pressure should only be used after consultation with a doctor. If both indicators are reduced, then you can take the Citramon or Farmadol tablet. These medications contain caffeine and help increase vascular tone, so the patient’s condition quickly normalizes.
Citramon is an affordable tablet and is found in almost every first aid kit.
If the lower pressure is reduced, and the upper pressure, on the contrary, is increased, then the above medications should not be taken under any circumstances. The doctor will prescribe several medications, one of which will increase the lower reading, and the other will stabilize the upper blood pressure. For such cases, beta blockers and calcium channel blockers are prescribed.
Folk remedies
A good way to increase lower blood pressure is to use unconventional methods of therapy. It is strictly forbidden to use them without first consulting a doctor.
Doctors may recommend home remedies such as:
- 20 drops of ginseng tincture.
- 20 drops of rose radiola tincture.
- A medicinal decoction prepared from a tablespoon of herbal mixture of immortelle and tansy, poured with a glass of boiling water.
You should not increase the prescribed dosage, because ginseng can be poisonous to the body
After taking any of these folk remedies, it is recommended to lie down and try to fall asleep or lie down for 30 minutes so that the body is in a calm state.
Nutrition
An important component of normalizing blood pressure, both lower and upper, is adjusting nutrition. Many foods can adversely affect blood pressure
The patient must avoid such unhealthy foods as:
- Fat meat.
- High fat dairy products.
- Smoked meats.
- Sausages.
- Sweets.
- Fast food.
The menu needs to include more vegetables, fruits, herbs, and cereals. Meat and fish should be chosen so that they contain a minimum amount of fat.
A balanced diet is the key to good health