Most passengers experience tinnitus when boarding an airplane. At what pressure value does the same sensation occur under normal conditions and why? A visit to an ENT specialist will help determine the exact cause of the discomfort. Ringing in the ears is a common symptom of inflammation. It is observed with otitis, eustachimitis, sinusitis, sinusitis or maxillary sinus, in some cases it is a symptom of vascular, cardiac pathology.
The effect of human blood pressure on the ears
High or low blood pressure can cause dizziness, noise, and tightness in the ears. The problem with arterial hypertension does not appear overnight; vascular tone worsens gradually.
Hypotonics - in people with low blood pressure, vascular tone decreases every year. The walls of the capillaries become thinner and become permeable. The mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and the cavity of the Eustachian tube swells, which leads to negative pressure in the middle ear and an unpleasant feeling of shortness of breath.
A sharp change in blood pressure (increase, decrease by 10 points or more) leads to impaired cerebral circulation and vasospasm. Hearing is impaired due to differences in pressure between the outer and middle ear. They are separated by the eardrum, which always shifts towards lower pressure, which leads to shortness of breath in the ears:
- as pressure increases, it bulges towards the outer ear;
- and when it descends, it goes to the middle ear.
People with hypertension and hypotension are more likely to experience ear congestion during a sudden change in weather, accompanied by an increase (fall) in atmospheric pressure. Hypotonic people feel weak, drowsy, during cyclones their ears become clogged in such weather, hypertensive people feel bad with similar symptoms during anticyclones.
Ear congestion due to high blood pressure
Blood vessel spasms, which cause high blood pressure, occur for a variety of reasons. Arterial hypertension or another disease accompanied by symptomatic hypertension cannot be excluded. During an embolism caused by high blood pressure, a person experiences throbbing pain in the back of the head and nausea.
Due to increased intracranial pressure, the head begins to spin, the face turns red, tachycardia appears, and the ears become clogged. After blood pressure normalizes, the symptoms disappear, hearing and well-being return. Nasal congestion occurs when upper blood pressure is ≥ 150.
When to see a doctor
If you couldn't prevent ear congestion and pain, don't worry. Although the pain can be very intense, it usually goes away quickly. Use painkillers such as paracetamol, ibuprofen. If you had a cold before your flight, your Eustachian tube may remain blocked for a long time after landing. If the pain continues to bother you or hearing loss persists, consult a doctor. And if you notice the appearance of blood from the ear canal (a sign of a ruptured eardrum), then this is an indication for an urgent medical examination.
It's easy to be healthy with GMS Clinic!
Source: mommys.ru
Clogged ears due to low pressure
If blood pressure is low, organs have poor blood supply and lack of oxygen. At the same time, the outflow of carbon dioxide is obstructed. Due to an imbalance in the acid-base balance, metabolic products accumulate in the body and stagnation occurs.
Weak vascular tone disrupts venous outflow, so hypotension is often accompanied by ear congestion. Associated symptoms:
- Eyelashes;
- mild nausea;
- increased drowsiness;
- frequent fainting;
- systematic dizziness.
A person with hypotension gets significantly worse when their blood pressure drops below 60.
Clogged ears: a sign of illness or congestion
Often, hearing impairment or loss can be due to a cold with complications in the form of the development of inflammatory processes. Clogged ears are a symptom, not a disease, but in any case it is recommended to get examined.
A visit to the doctor is necessary if:
- the cold has passed, but the symptom of congestion remains;
- hearing impairment persists for several days and pain develops;
- discharge appears from the auricle, often purulent;
- dizziness appears.
General weakness, decreased tone, and increased temperature during inflammatory processes may develop.
The presence of these signs poses a certain health risk, so you should visit a doctor and undergo examinations.
Independent treatment measures are contraindicated, because may cause serious complications. Especially in the case of uncontrolled use of medications.
Diagnostics
The party begins with an examination and interrogation of the patient. The doctor is interested in the history of the development of the disease, this helps to establish an accurate diagnosis. The specialist is interested in:
- symptoms accompanying shortness of breath;
- duration of discomfort;
- their frequency;
- when the first signs of discomfort appear;
- whether one or both ears are swollen.
If the problem is associated with otitis media, the patient experiences high fever, severe pain and intoxication. An ENT examines the ear septum and may refer you for an x-ray of the nasal sinuses. Purulent inflammation is especially dangerous, as it can provoke sepsis.
The combination of dizziness, ear congestion, drop (increase) in blood pressure and headache requires a cardiac examination. X-ray of the spine (cervix) is indicated when the patient experiences an embolism due to changes in atmospheric pressure.
Recognizing spinal pathology and eliminating nerve damage restores normal hearing and alleviates unpleasant symptoms. A feeling of tightness in the ears indicates a migraine or malignant processes in the brain or in the middle ear.
Whistling in the ears in neurological diseases
Neurological pathologies cause tinnitus along with ENT diseases. Let's consider the most common causes of tinnitus, which fall under the competence of neurologists.
Ringing in the ears due to arterial hypertension and hypertensive crisis
With a significant increase in blood pressure (more than 140/90 mm Hg), blood flow to the inner ear becomes uneven. As a result, the nerve endings inside it are excited, and tinnitus occurs. With arterial hypertension, this most often occurs during a hypertensive crisis - an attack of a sharp increase in pressure.
Other manifestations of hypertensive crisis:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the heart area;
- nausea and vomiting;
- convulsions;
- disturbance of consciousness.
During a hypertensive crisis, the patient requires emergency assistance. It is necessary to reduce blood pressure as quickly as possible, otherwise its jump can lead to myocardial infarction, stroke and other serious complications.
If arterial hypertension is accompanied by a chronic disorder of cerebral circulation, then the patient is almost constantly bothered by tinnitus.
Ringing in the ears due to cerebrovascular accident
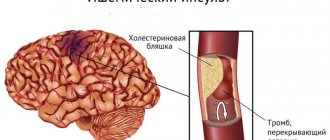
The most common cause of impaired blood flow in the vessels of the brain is atherosclerosis. This is a disease in which cholesterol plaques form on the walls of the arteries, partially or completely blocking their lumen.
Other causes of cerebrovascular accident:
- arterial hypertension (the main cause of which is also often atherosclerosis);
- increased blood viscosity and blood clot formation;
- diabetes mellitus (with this disease, the vessels of the brain, eyes, and kidneys are primarily affected);
- consequences of traumatic brain injury;
- intracranial tumors, hemorrhages.
The main symptoms of chronic cerebrovascular accident: headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, flashing “spots” before the eyes, increased fatigue, drowsiness, impaired memory and attention. Constant oxygen starvation does not leave its mark on the brain. Nerve cells gradually die, which over time can lead to the development of dementia.
The effect of increased intracranial pressure on tinnitus
Tinnitus as a result of increased intracranial pressure occurs with hydrocephalus, intracranial tumors and hemorrhages, after traumatic brain injuries and infections (meningitis, meningoencephalitis).
Headache and tinnitus - characteristic manifestations of increased intracranial pressure - usually occur in the morning, after a person has been in a horizontal position for a long time. During the day the symptoms disappear. The vertical position of the body helps the excess amount of intracranial fluid flow away and its pressure decreases.
Diseases of the cervical spine
The vertebral arteries, vessels that play an important role in the blood supply to the brain, run along the cervical spine on the right and left. They are not just located on the sides of the spine, but pass through holes in the lateral processes of the cervical vertebrae.
Often, pathological changes in the spine - inflammation, displacement of the intervertebral disc, bone growths that form on the vertebrae - lead to impaired blood flow in the vertebral arteries and neck pain. Blood flow to the head decreases. The brain and other organs experience oxygen starvation.
This condition is called vertebral artery syndrome. Its main manifestations:
- constant burning pain in the back of the head, temples, which intensifies after sleeping in an uncomfortable position, traveling by transport;
- hearing loss and tinnitus;
- blurred vision, “fog before the eyes”;
- dizziness, loss of balance when turning the head suddenly;
- loss of consciousness;
- sleep disturbances, the patient does not feel sleepy and rested, in the afternoon there is severe fatigue and drowsiness.
Noise in the ears is a signal of a tumor
Acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor that leads to tinnitus and other symptoms: decreased hearing on one side, pain and impaired movements of the facial muscles of half the face, and speech impairment. For acoustic neuroma, the doctor prescribes surgical treatment or radiation therapy.
Many intracranial tumors lead to impaired cerebral circulation and increased intracranial pressure. Therefore, tinnitus can also be one of the symptoms of such pathologies.
Multiple sclerosis
This is a chronic disease that most often occurs between the ages of 15 and 40 years. All nerve fibers in the human body are covered with a special myelin sheath. It is necessary for the normal transmission of nerve impulses. In multiple sclerosis, the myelin sheath is destroyed, resulting in slower neuromuscular transmission.
The symptoms of multiple sclerosis are varied. In some people, the disease manifests itself in the form of numbness in a certain part of the body, for example, a limb, while in others severe paralysis develops, including breathing problems.
One possible symptom of multiple sclerosis is tinnitus.
Depression and neuroses
Under certain conditions of the nervous system, the hearing organ becomes hypersensitive to sounds and becomes irritated. This is often caused by depression, neuroses (neurasthenia, hysterical neurosis), and nervous breakdowns. The patient comes to see a doctor and complains of constant tinnitus, but during examination and examination no objective abnormalities are revealed.
For psychogenic tinnitus, psychotherapy and appropriate medications are prescribed.
Taking medications for tinnitus
Some medications are ototoxic—they can harm the nerve endings in the inner ear and cause tinnitus. This side effect is most pronounced with the following drugs:
- antimalarials (quinine) and some antibiotics (for example, streptomycin);
- anti-inflammatory drugs (including aspirin);
- antipsychotics (haloperidol);
- antidepressants;
- digitalis preparations;
- furosemide
If you begin to experience tinnitus while taking one of these medications, you should stop taking it and consult a doctor immediately.
Only a doctor, based on the results of the examination and examinations, will determine what disease led to the occurrence of tinnitus. It is necessary to begin proper treatment of this symptom for any pathology as early as possible - this will help eliminate its root cause and prevent serious complications.
The Yusupov Hospital employs experienced neurologists, therapists, cardiologists, and has all the necessary equipment. This allows us to provide patients with modern, high-quality medical care.
Methods for relieving congestion
If the cause of tinnitus is high blood pressure, antihypertensive therapy is recommended, which consists of taking diuretics in combination with ACE inhibitors. A person who experiences discomfort due to a sharp increase in blood pressure will need:
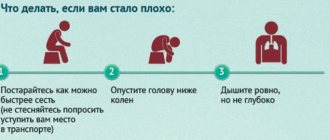
- lie down;
- restore breathing;
- take blood pressure medications or any sedatives;
- in case of critical blood pressure values, seek help.
Hypotonic with low blood pressure, noise and congestion in the ears, he definitely needs to lie down, drink a cup of coffee, black tea with sugar. It won't hurt to eat 1-2 slices of dark chocolate. Hypotonic patients are recommended to take hypertensive drugs: Mezaton, Cordiamin. As blood pressure recovers, hearing also normalizes.
Surgical treatment requires frequent surges in blood pressure caused by serious heart pathology, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and nephroprotective drugs - hypertension caused by kidney pathology.
Ear congestion
Fungus
Allergy
27262 04 February
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Ear congestion: causes, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Congestion in the ear or ears occurs as a result of a violation of sound perception and is characterized by various sensations, which may include deafness, a feeling of squeezing and heaviness, and the sound of one’s own voice being too strong. Ear congestion, regardless of the causes of its occurrence, is difficult for the patient to tolerate and, as a rule, requires the help of a specialist.
Types of ear congestion
Blockage in one or both ears may be accompanied by pain, tingling, noise or ringing in the ears, and dizziness. In some cases, congestion disappears after swallowing.
A dangerous symptom is ear congestion accompanied by fever, headache, discharge from the ear (purulent or bloody), and foreign body sensation.
Ear congestion does not always indicate a pathological process.
This condition can be caused by water getting into the ear, pressure changes
during air travel or diving to depth.
Sometimes too strong and incorrect blowing of the
nose from two nasal passages at the same time leads to a blocked ear (ears), which is associated with an increase in pressure in the middle chamber of the ear due to a sharp intake of air from the Eustachian tube.
Taking certain medications
(antibiotics, psychotropic substances) has a toxic effect on the ear, causing the development of congestion and hearing loss.
Diseases that can cause ear congestion.
Earwax
blocking the ear canal. Attempting to remove earwax yourself using improvised objects significantly increases the likelihood of pushing the plug deeper into the ear and sticking to the eardrum (this increases the risk of injury to the eardrum, which leads to complete or partial hearing loss). In these cases, the condition of congestion in the ears is accompanied by excruciating pain, noise, dizziness and nausea.
Mycotic, or fungal, infection of the external auditory canal
. Infection with fungi can be complicated by narrowing or blockage of the ear canal with a feeling of fullness in the ears. The spread of fungi in the ear is aggravated by hearing aids, in-ear headphones, and inflammatory diseases of the ear. The main signs of the disease are itching, ear congestion and resulting hearing loss, and increased sound of one’s own voice in the affected ear.
Damage to the external auditory canal and middle ear structures
may be accompanied by hearing loss and congestion. Bleeding and the formation of a blood clot that blocks the ear canal lead to deterioration in sound transmission. In addition, injury to the eardrum is possible during cleaning of the ear canal, a sudden change in pressure, or a strong blow to the outer ear. In this case, sharp pain occurs, which is replaced by congestion, ringing, noise and hearing loss.
Acute inflammatory diseases
accompanied by swelling and sometimes the formation of purulent contents.
They can lead to ear congestion and hearing loss. In particular, with otitis media of the middle ear (tympanitis),
the tympanic cavity and auditory tube are involved in the inflammatory process. Swelling, which narrows the lumen of the auditory tube, and suppuration of the soft tissues cause ear congestion and hearing impairment. As a rule, the infection enters this sterile cavity from the Eustachian tube, which is directly connected to the nasopharynx.
In children of the first and second year of life, acute otitis may occur when breast milk or formula enters the nasopharynx during regurgitation.
In older children, otitis media and congestion can be caused by
inflammation of the adenoids
, the lymphoid tissue responsible for the local immunity of the nasopharynx and closing the openings of the auditory tubes in the nasopharynx. The anatomical proximity of the adenoids and the auditory tube ensures the rapid transition of infection from the nasopharynx to the ears. In addition, enlarged adenoids can block the openings of the auditory tube, which causes a feeling of stuffiness.
Allergic reactions
can also lead to acute inflammation and swelling of the middle ear.
Otitis externa
characterized by inflammation of the external auditory canal. Congestion in the ear in this case occurs due to swelling of the tissues of the ear canal.
If the disease is caused by a foreign body entering the ear canal
, then swelling and congestion are complemented by a picture of severe irritation. The patient complains of severe itching, pain, a feeling of fullness, and heat in the ear area. The pain intensifies with chewing movements.
For furunculosis
In the external auditory canal, the picture of the disease is aggravated by a closed space where the inflammatory process develops. Increasing pain in the ear is complemented by its irradiation to the corresponding half of the head. The patient cannot lie on the painful side. Due to severe swelling of the tissues of the external auditory canal, sound transmission into the affected ear is disrupted, and a feeling of stuffiness occurs.
Among the anatomical and postoperative defects
that cause ear congestion include deviated nasal septum, narrowing of the nasal passage due to hypoplasia of the nasal wings, and stenosis of the external nasal valve.
Impaired nasal breathing leads to frequent runny nose, infection of the nasal sinuses and, as a consequence, to the transition of the inflammatory process to the auditory tube.
Ear congestion in these cases appears on the side of the narrow nasal passage. The same consequences occur after operations in the nose area.
Sensorineural hearing loss
occurs due to damage to any part of the auditory nerve. Most often, this is an irreversible phenomenon, the symptoms of which include imbalance, dizziness, nausea, fullness and noise in the ear, and poor perception of low sounds. The causes of sensorineural hearing loss can be previous infectious and vascular diseases, tumor processes, injuries, and toxic effects of various substances.
Meniere's disease
is a non-purulent disease of the inner ear, which is accompanied by congestion. An increase in the volume of lymph in the labyrinth of the ear leads to increased pressure and attacks of progressive deafness, tinnitus, and sudden dizziness. In most cases, one ear is affected first. The disease begins either with attacks of dizziness or with deterioration of hearing, which is completely restored between attacks. However, after a few years, hearing loss becomes irreversible.
Myofascial pain syndrome, temporomandibular joint diseases
. Patients with myofascial pain syndrome, which is associated with disruption of the masticatory muscles and limited mobility of the lower jaw, may also complain of ear congestion. In addition, the disease is accompanied by headaches and facial pain, difficulty opening the mouth, and clicking in the temporomandibular joint.
The root cause of the syndrome is spasm of the masticatory muscles.
A similar clinical picture is also given by diseases of the joint itself caused by malocclusion. Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, increased blood pressure
. Congestion in the ears due to damage or narrowing of blood vessels is explained by a deterioration in the blood supply to all tissues, as well as impaired circulation in the area of the inner and middle ear.
Vasomotor rhinitis, or runny nose during pregnancy
occurs under the influence of hormonal changes and is characterized by impaired vascular tone and the release of mucous secretion. With allergic rhinitis, the clinical picture of the disease is almost the same, but the provoking factor is not hormones, but a specific allergen. Swelling of the mucous membrane and narrowing of the nasal passages lead to obstruction of the auditory tube and cause ear congestion.
Tumors in the area of the auditory canal, auditory tube and inner ear
– the most serious cause of ear congestion. Among them should be called cholesteatoma - a tumor-like formation that consists of epidermal cells impregnated with cholesterol. Cholesteatoma is characterized by slow but steady growth. Forming in the middle ear, it can spread to the outer and inner ear, causing congestion and a feeling of heaviness in the ear, purulent discharge, swelling and redness of the auricle.
Which doctors should I contact if I have ear congestion?
If ear congestion occurs, you should contact an otolaryngologist. In the future, you may need to consult a neurologist, cardiologist, or allergist.
Diagnosis and examinations for ear congestion
To diagnose the disease that caused ear congestion, a careful questioning of the patient, examination of the outer ear and ear canal to the eardrum, and an audiometric examination are necessary. The infectious nature of the disease is determined on the basis of the clinical picture, otoscopy data and culture of the discharge.
Preventive measures
Doctors suggest following a few simple rules so that unpleasant symptoms are not bothered by pressure changes:
- healthy, moderate diet, excluding excess weight;
- Reduce the amount of salt to a minimum;
- physical activity (walking, jogging, physical education);
- Stop smoking and refrain from drinking any alcoholic beverages.
Well-known recommendations will help normalize blood pressure, get rid of tinnitus and ear congestion. Moderate physical activity and proper body weight are the best prevention of cardiovascular pathologies.
What to do if there is wax in your ears?
Often you want to take a cotton swab and just clean out the earwax. You cannot do this if you feel stuffy. It is necessary to make an appointment with a specialist who will assess the degree of congestion and its cause, and then provide professional medical assistance. The ear plug is washed with special tools; this process takes a couple of minutes and does not cause any pain. After rinsing, it is important to follow the rules of ear care; the doctor may also prescribe drops in the ears.
Stuffed ear and won’t go away: what to do
When discomfort and a feeling of stuffiness appear in the ear, you cannot immediately take ear sticks and start clearing the passages. Such measures can lead to a worsening of the situation: the plug is pushed in further, becomes denser over time and can cause the development of infectious inflammation and temporary hearing loss.
The following effective ways to “pierce” the ear are practiced:
- use chewing gum or eat candy;
- yawn, straining your vocal cords;
- take a deep breath, cover your nose and mouth with your hands and exhale slowly;
- sharp tilt of the head with straight shoulders. Pull your ear up.
In parallel with the last technique, you can use the following techniques:
- take a deep breath, cover your nose with your hand and slowly exhale through the closed nose, pushing the air;
- hold your nose with your hand and make a swallowing movement;
- strain your vocal cords with your mouth and nose closed.
Treatment of dizziness and noise in the head
The main principle of treatment for dizziness and noise in the head is its cause and mechanism of development. Therapy should be aimed at relieving the patient of the symptoms of the disease.
Drug therapy
If the patient has dyscirculatory encephalopathy, drugs are prescribed that normalize cerebral perfusion through an effect on the cardiovascular system. These are diuretics, beta blockers and vascular agents, as well as neurometabolites.
If symptoms occur due to high blood pressure, the doctor will prescribe antihypertensive drugs that control blood pressure levels and keep them within normal ranges. In this case, beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel antagonists and diuretics help well.
For cerebrovascular disorders, nootropics, vasodilators, antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are prescribed.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
After suffering injuries, to alleviate the condition, patients are recommended to limit physical activity and emotional stress, as well as symptomatic therapy to alleviate the patient’s condition. For this purpose, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed during periods of deterioration in health.
If the disorder occurs due to a functional cause, such as a tumor, then prompt surgical intervention is necessary.
If a patient has a migraine, the doctor should prescribe preventative treatment to prevent relapses of attacks, as well as medications to stop new episodes of migraine.
To correct anemia and its consequences, a specialist prescribes iron-based antianemic drugs, which can quickly increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood and relieve the symptoms that arise.
During menopause in women, the symptoms of menopause are corrected by menopausal hormone therapy.
Before a long trip in transport, you need to take special anti-motion sickness medications.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures help, in addition to drug treatment, to get rid of the disease. The most common in treatment:
- Magnetotherapy.
- Laser therapy.
- Massage and physical therapy.
- Healthy swimming.
- Acupuncture.
With systematic, course use of these therapeutic methods, there is a decrease in the symptoms of the disease and their complete disappearance.
Nutrition
An important aspect in monitoring your health and well-being is your diet. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, micro and macroelements allows you to maintain normal blood counts, weight and nutrient levels in the body. Excluding easily digestible carbohydrates, sugar, fatty and fried foods from your daily diet will help avoid cardiovascular diseases, which lead to a systematic increase in blood pressure, as well as type II diabetes and surges in sugar levels.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
It is equally important to comply with the daily calorie intake, as well as proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the diet. Daily caloric intake is calculated based on a person’s weight and energy expenditure. With a calorie deficit and abuse of fasting and diets, the body experiences stress, which is accompanied by poor health.