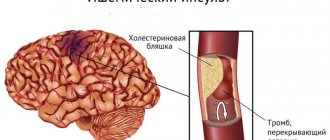
High blood pressure (hypertension) is observed in a number of pathological conditions. This can be either essential hypertension or symptomatic in diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, adrenal glands, hormonal disorders and endocrine pathology.
With such diseases, normal blood pressure for a hypertensive patient will be considered increased numbers of 130/90 and 140/90 mm Hg. Art. In such patients, blood pressure may drop sharply. In such cases, high blood pressure readings are replaced by hypotension.
Hypertensive patients endure such changes more severely than usual!
A sharp drop in pressure is called a hypotonic crisis. A decrease in systolic blood pressure to 90 and 100 mmHg is considered dangerous. This condition can lead to impaired blood flow and tissue ischemia, up to the appearance of necrosis.
Symptoms
A sign of a decrease in indicators may be cold hands of the patient. High blood pressure causes a characteristic state of the body, to which a person gradually gets used. When blood pressure levels decrease, a hypertensive patient does not immediately pay attention to this, attributing all the signs to his underlying disease. Therefore, every person with high blood pressure should know the signs of a hypotensive crisis:
- pale skin;
- bluishness of the lips or skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle;
- sticky sweat;
- cold extremities (upper and lower);
- veins collapse;
- There is a tingling sensation in the arms and legs;
- noise in ears;
- hearing loss;
- darkens and swims in the eyes;
- orientation in space is disturbed;
- speech is confused.
The norm for pathologically low blood pressure is different for each hypertensive patient. But if characteristic symptoms are present, and the pressure has dropped to 100 to 60 or lower, you should urgently call an ambulance.
Return to contents
What to do if your blood pressure drops significantly
If this happened on the street, the patient should be taken to the shade. It's better to plant or put it down. In a horizontal position, you need to raise your legs. This will ensure increased blood flow and oxygen to the brain.
Algorithm of actions to help the victim:
- Call an ambulance! Before her arrival, try to provide assistance yourself.
- Unfasten the collar, remove the belt, belt, tie, loosen all existing elastic bands.
- Open a window if the victim is indoors. It is important to provide a flow of fresh air.
- Constantly talk to the patient to avoid loss of consciousness.
- If the victim has difficulty speaking, then you need to bring a cotton swab with ammonia to his nose.
- Wipe your face with a wet handkerchief.
- If you faint, splash water on your face, wave a newspaper in front of your face, and pat your cheeks.
- If you have a chill, cover with a warm blanket.
- When vomiting, it is better to lie on your side so that the vomit does not enter the larynx and trachea.
- You can increase your blood pressure with the drug Cordiamin.
- If you have a headache, you can give a tablet of Citramon or any other product with caffeine.
If the pressure has not dropped critically, then you can:
- Drink hot sweet tea or coffee. Give a piece of dark chocolate (if you don't have diabetes).
- Massage the ears, back of the head and neck.
- Rub the calf muscles, hands, feet, lower back and stomach.
- Press on the acupuncture point located under the nose.
- Take a contrast shower or rub it completely with a wet towel.
Reasons for decreased blood pressure
The main reason for low blood pressure in hypertensive patients is considered to be drug overdose. Most often this occurs due to a lack of knowledge and taking medications without a doctor’s prescription.
Among the secondary reasons are:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system (coronary heart disease, heart failure, endo- and myocarditis, pulmonary edema).
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Infectious diseases.
- Diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Reduced blood sugar levels.
- Mental illnesses – depression, severe and prolonged stress.
- Taking antidepressants, analgesics.
- External and internal bleeding (perforated ulcer, hemorrhoids).
- Anaphylactic shock.
- Severe pain syndrome (attack of pancreatitis, renal colic, peptic ulcer, periodic pain in women).
Provoking factors
Not only the above conditions, but also a number of other provoking factors can lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
Common risk factors include:
- Prolonged bed rest.
- Pregnancy.
- Fever.
- Elderly age.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Orthostatic collapse when abruptly getting out of bed (especially in old age).
- Exposure to elevated temperatures that cause vasodilation (thermal springs, baths, saunas).
- Errors in nutrition.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun and tanning can cause blood pressure to drop. When tanning, adrenaline turns into the tanning hormone melanin and very little of it remains to maintain blood vessels in tone. Hence - weakness and hypotension after prolonged exposure to the sun.
A decrease in blood pressure due to hypertension always manifests itself with characteristic symptoms.
The most notable ones include:
- General weakness, lethargy, asthenia.
- State of depression.
- Headache.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Dizziness.
- Possibly frequent loose stools.
Some symptoms are characteristic of both hypertensive and hypotensive crises. Therefore, you should pay attention to the totality of other manifestations.
| Hypotonic crisis | Hypertensive crisis |
| Skin | |
| The skin is pale, cold. Often - cold sticky sweat. Cold hands and feet. | The skin is pink and warm. The face is hyperemic. Extremities are warm. |
| Headache | |
| The pain is aching in nature, often diffuse. | The pain is pulsating in nature, often localized in the back of the head. |
| Heartbeat | |
| Weak, pulse is poorly defined. | Strong, often rapid. The pulse is frequent and well filled. |
| State of mind | |
| Depressed, increased sleepiness is noted. | Excited. |
| Other manifestations | |
| Nausea, single vomiting. Unsteady gait. Darkening in the eyes. Possible loss of consciousness. | Nausea, repeated vomiting, which does not bring relief. Flashing of flies before the eyes. |
A sharp decrease in blood pressure in a hypertensive patient is much more severe than in an ordinary person. And prolonged hypotension leads to negative changes in organs and tissues.
- When your nose bleeds, is your blood pressure low or high?
Prevention of hypotonic conditions
These simple tips will help avoid spikes in blood pressure in people predisposed to hypertension:
- Regular monitoring of blood pressure in the morning and evening, recording the results for subsequent analysis.
- Avoid acute and chronic stress, states of nervous tension - take mild sedatives: Valerian and Motherwort in tablets.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle: ensure a good night's sleep for at least 8 hours. Go to bed before midnight. If possible, rest during the day for an hour and a half. Follow a diet with sufficient protein, fat, carbohydrates and vitamins. It is possible to take pharmaceutical multivitamin preparations.
- Do morning exercises, move more, walk in the fresh air. Avoid muscle strain and fatigue.
- Exercise therapy as prescribed by a physiotherapist. According to indications – hyperbaric oxygenation.
- In spring and autumn - preventive therapy to avoid the appearance of negative manifestations when exposed to unfavorable environmental factors (changes in weather and atmospheric pressure).
- Observation by a therapist or cardiologist in compliance with all necessary instructions. Do not self-medicate.
Hypertensive patients should choose the right therapy, lead a correct and active lifestyle, control themselves independently and not neglect the advice of a specialist.
And then you will definitely be able to maintain your working condition, optimism and avoid sudden drops and surges in blood pressure. Author of the article Svetlana Anatolyevna Ivanova, general practitioner
Reasons for the sharp decline
The variety of reasons for decreased blood pressure in a person with hypertension makes it difficult to determine it independently.
A sudden drop in blood pressure is a warning sign. There are several reasons for this change in hypertension:
- Heart failure. Violation of the pumping function of the heart is accompanied by a decrease in pressure in the blood vessels.
- Neurocirculatory dysfunction or VSD. Disturbances in the autonomic nervous system appear as a result of psycho-emotional stress. These conditions cannot be treated; rest helps relieve them.
- Kidney pathologies. Two hormones: adrenaline and acetylcholine control the tone of the vascular walls. They are produced by the adrenal glands. Adrenaline increases blood pressure and excites, acetylcholine lowers and depresses the general condition. Due to functional disorders of the adrenal glands, a jump occurs: blood pressure was high, and suddenly it became low.
- Intense bleeding. It is difficult to notice internal bleeding. The upper limit of blood pressure decreases significantly, the heart begins to beat faster. You can suspect a problem by severe pain in the upper abdomen.
- Medications. With drug treatment, a decrease in blood pressure is a side effect of certain medications (antibiotics, heart and pain medications).
- Infectious pathologies. Severe intoxication and an increase in body temperature provoke a decrease in blood pressure.
- Blood glucose level. Its decrease below normal provokes pathological abnormalities in the body.
- Depressed psychological state. Depression, which is accompanied by weight loss, indifference to everything, and lack of a sense of joy, serve as a source of changes in indicators.
Return to contents
How to behave in such a case?
It is necessary to maximize the blood supply to vital organs. To do this, you need to extract the blood volume deposited in the vessels of the extremities and move it to the central parts of the human body.
If the symptoms of hypotension are pronounced, it is necessary to call an ambulance, and before it arrives, alleviate the condition of the victim on your own.
Tactics at home and with improvised means
| Action | The essence | Mechanism of influence on blood pressure |
| Place the victim in the correct position | The person is placed on his back, his straight legs are raised 20-30 cm above the ground. You can put a cushion or folded clothes under them. The fixator can be the knees of the person providing assistance. | Redistribution of blood from peripheral vessels to the central parts of the bloodstream |
| Remove reason | Do not take antihypertensive drugs, restore water balance if dehydrated | Leveling the effect of the pathological factor |
| Let me drink if my condition allows. | You can drink strong tea, coffee or plain water | The fluid deficit in the body is restored, and invigorating drinks activate the sympathetic part of the nervous system (which is responsible for increasing blood pressure) |
| Taking medications | Alpha adrenergic agonists | Stimulation of vascular tone and cardiac muscle activity |
| Anticholinergics | Blocking the influence of the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system (responsible for lowering blood pressure) |
First aid algorithm, or what an ambulance does upon arrival
- Placing a person with hypotension in a horizontal plane with the lower end of the body elevated (the pelvis and legs are positioned above the head, this is called the Trendelenburg anti-shock position).
Catheterization of a peripheral vein (two if the condition is unstable).- Removing the cause that caused hypotension (if possible).
- Infusion (infusion) of saline solution or other drug capable of filling the volume of the vascular bed. This will raise blood pressure and help prevent the development of shock due to hypotension.
- Administration of drugs that constrict blood vessels (adrenergic agonists: adrenaline, mezaton).
- Stimulation of cardiac activity (dopamine, dobutamine).
What is the blood pressure of a hypertensive patient?
Doctors recognize normal blood pressure levels as 120 to 80 mmHg. If it is higher than normal, a diagnosis of hypertension is made, and if it is lower, hypotension is diagnosed. Blood pressure in hypertensive patients can change throughout the day, and short-term increases are caused by physical activity and poor lifestyle. Blood pressure can also rise sharply due to nervousness.
Hypertension is a pathology in which elevated blood pressure levels depend on physiological and pathological factors:
- Emotional stress
- Mental fatigue
- Genetic predisposition,
- Age,
- Hormonal changes
- Overweight,
- Concussion and other brain injuries
- Pathologies of the endocrine system,
- Chronic, infectious diseases,
- Exceeding the permissible cholesterol level.
The normal blood pressure of hypertensive patients depends on the degree of the disease:
- 1st degree or mild: systolic blood pressure from 140 to 160 mmHg, diastolic from 90 to 99 mmHg,
- Grade 2 or moderate: systolic blood pressure from 160 to 180 mm. Hg, diastolic - from 100 to 110 mmHg,
- Grade 3 or severe: blood pressure remains stable above 180 to 110 mmHg.
Folk remedies for increasing blood pressure
If blood pressure has decreased slightly, then you can use old and proven folk remedies.
For example, you can use:
- One tablespoon of honey sprinkled with cinnamon on top, washed down with hot tea or coffee. Even people with diabetes can afford honey in small quantities.
- St. John's wort decoction reduces the effect of calcium blockers.
- Aromatherapy with mint or rosemary.
- Massage the scalp, back of the head and neck. Apply gently, without pressing, with your fingertips.
Other useful tools:
- Pharmaceutical stimulant preparations to relieve drowsiness and fatigue: tincture of Eleutherococcus, Ginseng or Chinese Schisandra under the supervision of pressure and the attending physician.
- In case of severe hypotension, to narrow the lumen of blood vessels, take Norepinephrine (a synonym for norepinephrine, which increases blood pressure) and cholinergic drugs under the supervision of a physician.
Competent therapy to maintain working condition is not enough. A number of measures should be taken that will help not only eliminate, but prevent unwanted drops in blood pressure.
What is the danger?
The cardiovascular system of a hypertensive patient is constantly tense. A sharp drop in blood pressure in such a situation threatens the health and functionality of the entire cardiac mechanism and the body as a whole. Therefore, it is prohibited to sharply reduce high blood pressure in hypertensive patients, otherwise the following dangerous processes will develop:
This condition in the patient provokes a narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain.
- The rapid expansion of blood vessels leads to a lack of blood flow, since it cannot increase in a short period of time.
- As a result of the current difficult situation, a narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain occurs.
- The blood supply to the brain is disrupted, as a result of which it gives the command to reduce the pressure. Oxygen starvation occurs, which leads to the death of its damaged areas. The occurrence of hemorrhage ends in instant death.
Return to contents
- Low blood pressure - what to do, first aid. Causes of low blood pressure and treatment at home
Why is low blood pressure dangerous?
It leads to insufficient blood supply, depression and oxygen starvation of vital organs.
With a prolonged hypotonic state, symptoms of a neurotic nature appear: increased irritability, memory impairment, inability to concentrate and decreased performance.
The presence of constant headaches, decreased vitality and performance is a strong negative irritant. This leads to a decrease in optimism, paints the entire environment in a gray color and causes a constant bad mood.
There is increased sensitivity to excessively loud sounds and bright light.
Possible consequences:
- If the pressure rises sharply during hypotension, this can cause a rupture of the vessel with possible hemorrhage (stroke, heart attack).
- Injuries from a fall during loss of consciousness.
- Impaired cardiac conduction up to cardiac arrest.
If your health worsens and the above symptoms appear, you should first measure the victim’s blood pressure. It is important! So that, guided only by symptoms, do not mistake hypotension for a normal hypertensive crisis and begin to reduce blood pressure using medications available at home. If low blood pressure is detected, you should try to normalize it yourself.
How do coffee and tea affect blood pressure?
Photo from tolowerbloodpressure.com
Contrary to popular belief that coffee increases blood pressure, there is no convincing evidence for this. In 2012, American medical analysts collected and summarized the results of all studies on this subject and came to the conclusion that there is no scientific basis for recommending coffee to increase blood pressure or prohibiting it for those suffering from hypertension.
So if you don’t notice a real deterioration in your well-being after a cup of coffee, drink to your health.
But black tea, as it turned out, affects blood pressure if consumed regularly, and in the direction of reducing it, albeit slightly.
Green tea significantly reduces both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, so it should be avoided by hypotensive people. For hypertensive patients, 1-2 cups of green tea per day significantly reduces the risk of developing heart disease.