What are the features of the symptoms of this disease?
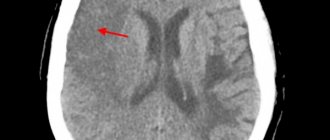
In the presence of an ischemic stroke in the territory of the right middle cerebral artery, it is possible to identify symptoms of lesions of the midbrain and cerebral hemisphere, depending on the location and conditions of collateral blood supply in the clinical pictures. Quite often you can find a combination of damage to the thalamus and the cerebral hemisphere or isolated infarctions of the thalamus. It should be noted that in most cases, the symptoms of the disease in patients can be combined. The most common symptoms include visual damage, neuropsychological damage, and hemiparesis.
Emotional and mental stress
These disorders are quite difficult to eliminate even with the help of a competent psychologist or psychotherapist, since a person perceives reality completely differently. His attitude towards himself as a “burden” for loved ones, a sense of his own inferiority - all this leads to the development of deep depression and apathetic states. In other cases, the patient shows aggressiveness towards himself and the people around him.
Also not least is the fear of a possible future, the likelihood of remaining bedridden for life, and the fear of death from a second stroke.
What are the features of diagnosing ischemic stroke in the territory of the right middle cerebral artery?
It is worth noting that often computed tomography does not allow identifying any ischemic changes in the brain parenchyma for a certain moment after the onset of strokes, precisely the time that is very important as the beginning of the treatment of this type of disease.
Thanks to the use of magnetic resonance imaging, it becomes possible to more accurately determine the presence and nature of any ischemic changes in the main brain during strokes. After obtaining data from magnetic resonance imaging, it becomes possible to identify early ischemic changes. Today it has become possible to combine different modes, which makes it possible to determine more severe, subacute and congenital ischemic changes in the brain parenchyma.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
Treatment
The sooner the diagnosis is made, the better the treatment prognosis. If you hit the therapeutic window, dangerous consequences can be avoided. This is the period from the beginning of oxygen starvation of the brain (the appearance of the first symptoms) until the development of irreversible disorders - 3-6 hours after the attack.
Treatment for stroke can be basic or specific.
It begins in the ambulance and continues in the intensive care setting. The objectives of basic treatment include stabilizing the patient and supporting the functioning of vital organs. Therapy includes the following actions:
- sanitization of the respiratory tract, connecting the victim to a ventilator (artificial lung ventilation) in case of breathing problems;
- control of body temperature and pressure;
- maintaining optimal water-alkaline balance in the body;
- relief of seizures;
- regulation of cardiac activity through intravenous administration of drugs.
Specific therapy helps restore blood circulation and prevent the development of irreversible consequences. Treatment includes the following methods:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical intervention aimed at restoring blood circulation and reconstructing blood vessels.
Drug treatment
To relieve symptoms, eliminate blood stagnation and the consequences of a stroke, the following groups of medications are prescribed:
- Thrombolytics – Actilyse, Gemaza. Used in the first 3-6 hours after an attack to dissolve blood clots and restore blood circulation to the brain.
- Nootropics – Phezam, Semax, Piracetam, Cerebrolysin. Reduce brain swelling and protect neurons from damage. During the recovery period, nootropics improve the processes of concentration and memory.
- Anticoagulants – Heparin, Clopidogrel. Prescribed to prevent recurrent blood clot formation and blood thinning. The drugs are contraindicated in the presence of bleeding and hemorrhagic stroke.
- Diuretics – Furosemide, Torasemide. They remove excess fluid from tissues and help relieve cerebral edema.
- Angioprotectors – Troxevasin. Restore vascular permeability and prevent microthrombosis.
- Vasoactive agents – Cavinton, Vinpocetine. They improve blood circulation in ischemic brain tissues and help restore lost neuronal functions.
- Metabolic drugs – Mildronate, Actovegin. Promotes increased blood circulation and tissue metabolism.
- Volume-substituting agents – Albumin, Reopoliglyukin. They normalize hemodynamics and replenish the missing volume of fluid in the body.
Recovery period after a stroke
Rehabilitation helps patients regain lost motor functions, speech, and other consequences of a stroke. The recovery period is divided into 3 stages:
- Acute – first 3-4 weeks. Rehabilitation is carried out in intensive care conditions. Bed rest and medication are prescribed.
- Early recovery stage – 6 months after the attack. The victim is prescribed a diet. Spicy, fried, smoked foods and salt are excluded from the diet. To restore motor skills, physical therapy (PT) is prescribed.
- Late recovery period – a year after the attack. It takes place on an outpatient basis or in special rehabilitation centers.
The following methods help eliminate the consequences of a stroke and improve the prognosis:
- Kinesitherapy – treatment by position. The affected limbs are temporarily fixed in a splint. Prescribed for pain relief and after operations.
- Massage. The procedure improves blood circulation in tissues and helps remove excess fluid from the body.
- Reflexology. Acupuncture is prescribed for spastic conditions. The procedure speeds up the tasks of therapeutic exercises and has a positive effect on the nervous system.
- Exercise therapy. Exercises help improve muscle tone and strengthen the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. They help restore mobility to the injured arm or leg.
- Working with a speech therapist-aphasiologist. Prescribed for speech restoration. The doctor re-teaches the patient to speak and develops ligamentous-motor skills. Prescribes exercises for articulation and phonation.
- Psychotherapy. A visit to a psychologist helps stabilize the emotional background and avoid depression. Classes are held individually or in groups with other patients.
What is the procedure for treating ischemic stroke in the territory of the right middle cerebral artery?
To begin with, it is worth noting that the healing process is quite long and requires patience on the part of patients. At the very beginning of the healing process, you should normalize your lifestyle and attend rehabilitation events. The motor rehabilitation process includes strength and dexterity in each limb, self-care skills, all of which can be fully or partially rehabilitated. The speech rehabilitation process includes every session with specialists, in particular with speech therapists and neuropsychologists, every exercise necessary to restore common reading or counting disorders. As for the psychological and social healing processes, a healthy climate should be created in families, participation in any cultural event within social circles.
Quite often, specialists in this field of activity prescribe their patients to use various types of antidepressants, which are selected individually for each patient. Great attention should be paid to this, because using your own assumptions about taking antidepressants can only lead to various complications and side effects that can provoke undesirable consequences. That is why only the attending physician can prescribe the period of taking the drugs and the immediate dosage. The use of antiaggregates can reduce the risk of stroke recurrence, and in cases of no therapy, the disease may also return.
Symptoms
There are several stages in the development of the disease. Acute lasts for 21 days. Within this stage, the most acute stage is distinguished, lasting approximately five days and characterized by an increase in the brightness and variety of symptoms.
Next comes the early rehabilitation stage, which lasts up to 5 months. At this time, the blood supply to the remaining cells is restored, and compensation tasks are distributed.
The late recovery stage conventionally lasts from the seventh month to a year. At this stage, the affected tissues become scarred. Cysts and glial formations form at the site of damage.
Beginning of the disease
Many people imagine that during an attack a person falls due to sudden paralysis and loses consciousness. Indeed, such a beginning is very characteristic of a blow. At the same time, a person does not feel any warning signs.
Sometimes symptoms begin to increase in waves. The patient's condition either worsens or returns to normal. The pathology resembles a microstroke. Patients complain that, for example, their arm has temporarily failed.
Approximately a third of patients with intact memory, who are able to speak and express their thoughts after an attack, describe certain symptoms that anticipated the attack.
Visual disturbances are noted. Floaters appear before the eyes, parts of the field of vision fall out. Pain occurs.
Motor functions, the ability to sit and turn disappear. Signs of paresis appear. There is a feeling that an arm and leg are paralyzed on one side or both. The patient loses his balance.
The person notices arrhythmia and feels that the pulse disappears. Dizziness appears. Patients often report pain that is described as very severe.
However, they often do not pay enough attention to a sudden speech disorder, the inability of a loved one to utter simple words or answer an easy question. The drooping corner of the mouth on one side and the fact that one of the arms has failed is ignored. Delay in identifying the disease prevents patients from surviving.
Development of the disease
If the warning signs of an attack can be confused with signs of other diseases and attributed to poor health, then the signs of a blow occurring to a person are unlikely to be confused with anything.
If you notice the following symptoms in others, immediately call an ambulance:
- Impaired consciousness. In this case, several degrees are distinguished. With mild and moderate changes, there is stupor, heaviness in the head, lethargy of the patient, fixation of the gaze at one point, and inability to answer questions. With stupor, it is impossible to establish contact with a person; pain and pupillary reflexes remain intact. The most severe disorder is coma. It is almost impossible to survive with this condition.
- Change in breathing. It becomes superficial, weak, sometimes noisy and rapid.
- Inability to move. With a stroke, paresis and paralysis develop.
- Cramps. The whole body is affected by convulsions, muscles tense, and the person is unconscious.
- Distorted face.
- Stiff neck.
Signs of a left-sided injury
Damage to the left side in a stroke leads to muscle weakness on the right side of the body. There is a loss of memory, analysis, and counting. Left-sided stroke is characterized by speech impairments and inability to understand what is heard.
The arm on the right is bent at the elbow, the leg, on the contrary, is extended, the foot is turned inward. Palms clenched into fists.
The emotional background is characterized by dejection and depression. A person is prone to depression, apathy, and isolation. This mood does not increase the chances of improvement.
After a stroke with paralysis on the right side, recovery is more difficult.
Signs of right-sided lesion
Damage to the right hemisphere leads to left-sided hemiparesis. Characterized by a disorder of sensations. A person thinks that he has several legs and arms. Sometimes it seems as if the limbs do not belong to him at all.
After a stroke, the left side is often completely paralyzed.
Stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation!
A stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation. It is characterized by the sudden appearance of focal or cerebral neurological symptoms. Meanwhile, general cerebral symptoms do not always appear and, as a rule, are typical for fairly extensive, often hemorrhagic, strokes. Translated from Latin “insultus” means attack, attack or blow.
Focal symptoms are characterized by motor, sensory, speech and other disorders. They are also called symptoms or clinical manifestations of the disease. In case of a stroke, such symptoms persist for more than a day!
RISK FACTORS FOR STROKE
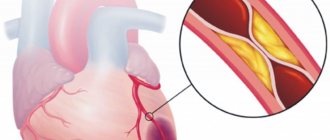
There are two types of stroke – ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic stroke occurs when there is a sharp decrease and cessation of blood flow in a certain area of the brain. Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when there is bleeding in the brain, under its membranes or in the ventricles.
Signs and first symptoms of a stroke. Explicit and implicit.
A stroke occurs suddenly. At the same time, patients often have so-called precursors.
In approximately half of cases, a stroke is preceded by transient ischemic attacks. In everyday life they are called microstroke.
In a transient ischemic attack, acutely developed stroke symptoms persist for no more than 24 hours from the onset of the disease. This:
- weakness, awkwardness in the limbs;
- the appearance of numbness in various parts of the face and limbs;
- speech and vision impairment;
- dizziness, imbalance.
If such symptoms go away within 24 hours, this is a transient ischemic attack. At the same time, it is often a harbinger of a stroke! Such a condition cannot be left unattended! If you react in time, seek medical help and carry out all the necessary diagnostic and therapeutic measures, a stroke in such cases can be avoided!
A transient ischemic attack is a menacing signal of trouble in the cerebral circulatory system. Often this condition can be provoked by hypertensive crises.
Despite the specific “picture” of a stroke, the severity of the first symptoms can be different, sometimes quite erased. Therefore, diagnosing stroke in some cases based only on the clinical manifestations of the disease can be difficult.
Common symptoms of a stroke:
- sudden weakness in the face, arm, or leg, most often on one side of the body;
- sudden confusion, problems speaking or understanding speech (ask them to say something);
- distorted face (ask him to smile, bare his teeth, stick out his tongue);
- sudden vision problems in one or both eyes;
- sudden disturbance in gait, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination;
- sudden severe headache of unknown cause.
Lack of consciousness or any combination of these signs is a high probability of a stroke. It is very important to immediately recognize its symptoms in order to call an ambulance as quickly as possible. After all, the sooner treatment is started, the better a person recovers from a stroke. Failure to seek help in a timely manner leads to severe complications and disability.
Providing first aid for a stroke is not just important, it is vital. And if suddenly you are near a person who has shown obvious signs of a stroke, there are several actions you should immediately take. The life of this person depends on them.
As soon as you realize that a person has all the signs of a stroke, immediately call an ambulance. This must be done immediately so as not to miss time. Cerebrovascular accidents are most effectively treated in the first 3 hours. So don't waste your time.
- Remove unnecessary people from the room if business is taking place indoors.
- If outside, ask everyone to step aside and not interfere with the flow of fresh air. Only those who can help should remain nearby.
- Do not disturb the person under any circumstances. Is it dangerous. The patient must be left where the attack occurred. Do not transfer to the bed.
- Elevate the patient's upper body and head (about 30 degrees). It is best to add several pillows.
- Unfasten or remove all clothing that constricts and interferes with breathing (belt, collar, belt, etc.).
- Provide fresh air.
- If vomiting begins, turn the victim's head to the side and clean up the vomit properly, otherwise the person may suffocate.
- Sometimes it happens that a stroke is accompanied by epileptic seizures. Moreover, they can follow one after another. In this case, turn the person on his side, insert a spoon, comb, or stick wrapped in a handkerchief into his mouth and, lightly holding the patient’s head with your hands, wipe away the foam. The most important thing in this case is not to press the person. You just need to hold it lightly and that’s it. And even more so, you can’t bring ammonia. The consequences can be terrible - cessation of breathing and death.
- It may happen that the victim's heart stops and breathing stops. In this case, you will have to immediately begin chest compressions and artificial respiration until the ambulance arrives.
Effectiveness of first aid and prognosis.
According to statistics, correctly provided emergency care for stroke patients with delivery to a medical facility within the first three hours:
- saves the lives of 50–60% of patients with severe massive strokes;
- in 75–90% it allows people with minor strokes to fully recover;
- improves the recovery abilities of brain cells by 60–70% in case of any stroke (better in case of ischemic stroke).
Stroke prevention is based on the basic principles of a healthy lifestyle.
- Know and control your blood pressure - it should not be more than 140/90 mmHg.
- Don't start smoking or stop smoking as soon as possible.
- Add as little salt as possible to your food and avoid canned and processed foods that contain excess salt.
- Monitor your blood cholesterol levels - the maximum allowable level is 5 mmol/l.
- Follow the basic principles of a healthy diet - eat more vegetables and fruits (at least 500 g per day), avoid added sugar and saturated animal fat.
- Don't drink alcohol. The risk of stroke is highest in the first hours after drinking alcohol.
- Exercise regularly. Even moderate physical activity (walking outdoors for 30 minutes a day) reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including stroke.
- A disease is a process that develops gradually in the body, quietly forming over the years before manifesting itself as sensations and symptoms. Only the sick person himself thinks that the disease arose suddenly. In fact, it takes a long time for painful changes in the body to become apparent. That is why disease prevention and knowledge of the principles of a healthy lifestyle are necessary - the basis of good health.
Remember that a stroke can happen to anyone at any time. Get ready to take the first step to help fight this disease!
Doctor - neurologist
Svetlana Meleshko
Complications, consequences of stroke
With a small area of damage and timely medical care, a full recovery of the patient is possible in a short time.
However, much more often, complete restoration of brain function does not occur. The degree of disability from a stroke can vary greatly. Some people can live a full life, slightly rearranging the rhythm of life to accommodate the existing changes, while others need temporary or round-the-clock help from outsiders.
Problems that arise after an ischemic stroke depend on the location of the necrosis site. For example, if this part of the brain was responsible for coordinating movements or controlling a limb, the patient will not be able to fully/completely use it. If the neurons involved in the formation of speech die, a person will experience problems with its perception and reproduction. Memory impairment, thought processes, loss of orientation in time and/or space, visual impairment, and hearing problems are also possible.
Most deaths are associated with complications of stroke, the deadliest of which are:
- cerebral edema (50%);
- pneumonia;
- heart disease;
- pulmonary embolism;
- renal failure;
- sepsis;
- relapse of the attack.
Less dangerous but common complications include:
- Bedsores are a local disturbance of blood circulation and innervation of soft tissues, which can result in their necrosis. They are typical for bedridden patients. To prevent the development of bedsores, it is necessary to turn the patient over every few hours and place small pads under protruding parts of the body.
- Urinary tract infections are a common complication of stroke that occurs after urinary catheter placement. To reduce the likelihood of infection, it is recommended to change the catheter only if it is damaged. Men can use an external urinal, which is similar in structure to a condom.
- Convulsions are characteristic of large heart attacks. They arise due to the formation of a small area of neurons with abnormal electrical activity.
- Depression after stroke is a complication that is ignored by many patients. Feelings of grief, loneliness, panic, powerlessness. However, if they do not go away, thoughts become predominantly negative - you should consult a doctor. Depression is a disease like pneumonia or infection. It does not need to be tolerated, it needs to be treated.
- Deep vein thrombosis is a dangerous complication that develops in bedridden patients. Due to lack of movement, ideal conditions are created for the formation of blood clots in the large veins of the legs. If one of them comes off, there is a real threat of blockage of a pulmonary vessel and the development of pulmonary embolism.