Repeated ischemic stroke occupies one of the first places among diseases leading to disability and death. If life expectancy after the first stroke averages eight to nine years, then a second acute cerebrovascular accident can reduce it to two to three years. Therefore, in modern neurology clinics, one of which is the Yusupov Hospital, a large role is given to secondary stroke prevention.
It is proper prevention and treatment that can prevent the recurrence of a vascular accident, because, according to statistics, the probability of a second stroke within a year after the first is about 15%, and after a few years - up to 30-40%.
Who's at risk
After a primary stroke, the body retains mechanisms that provoke the following development of events: intravascular thrombus formation, vascular atherosclerosis. The patient, as a rule, also has a number of concomitant diseases, often in advanced forms: hypertension, diabetes mellitus, arrhythmia, heart failure and others. Preventing recurrent ischemic stroke in such cases is a rather difficult task, but thanks to the efforts of qualified specialists at the Yusupov Hospital, it is feasible.
Repeated ischemic stroke sometimes threatens even patients who are unaware that they have already suffered a vascular accident: patients with short-term disturbances of cardiac or cerebral circulation, the so-called transient ischemic attacks, manifested by the sudden onset of headache, dizziness, numbness of the arm or leg - symptoms which are often ignored, despite the fact that they are the first alarm bells preceding a stroke. The threat of vascular attack increases even more with transient loss of vision, speech, weakness in the upper or lower limb, sudden amnesia and other symptoms.
In this case, the patient should not hesitate; it is recommended to seek medical help as soon as possible at the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital to obtain a doctor’s consultation. You will undergo the necessary examinations: ultrasound examination of large vessels (first of all, it is necessary to examine the carotid arteries), an electrocardiogram, ECHO-CG, detailed blood tests for the lipid profile and the tendency to form blood clots, the level of homocysteine - an amino acid that causes early atherosclerosis and thrombus formation, as well as several times increasing the risk of stroke and heart attack.
A similar examination is also recommended for patients who have suffered a hypertensive crisis, attacks of angina pectoris (pain in the heart area), or arrhythmia. These conditions often precede a stroke and are manifestations of transient ischemic attacks.
Make an appointment
Causes
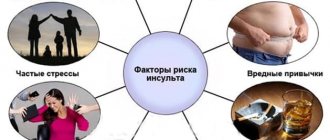
There are several reasons for the development of a recurrent stroke, including factors beyond a person’s control that provoke the development of a recurrent stroke:
- Patient's age
- Hypertonic disease,
- Alcohol, drug addiction, smoking,
- Poor nutrition
- Failure to follow doctor's recommendations
- Stress,
- Obesity,
- Sedentary lifestyle,
- High cholesterol levels
- Increased irritability
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system,
- Improper work and rest schedule, night shifts, disturbed sleep,
- Diabetes.
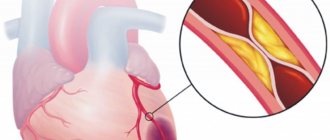
The most common type of vascular disorder is ischemic stroke, which accounts for up to 85% of cases. This type of stroke is caused by blockage of blood vessels supplying the brain or their critical narrowing.
The development of ischemic stroke is caused, first of all, by a person’s destructive lifestyle, which means: alcohol abuse, heavy smoking, poor diet, physical inactivity (lack of physical activity). Such habits lead to a deficiency of oxygen in the brain, associated with inadequate heart function, the loss of the vessels’ elasticity and ability to expand, due to which the blood flow increases, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the central nervous system.
Repeated ischemic stroke occurs due to a number of main reasons:
- psychological and emotional stress;
- excessive stress, heavy physical labor (most often, relapses occur during the summer season, if the patient spends a long time in an uncomfortable position, upside down, and also under the scorching sun, as a result of which dehydration occurs, increasing the risk of vascular accident);
- deterioration in quality of life;
- deterioration of the environmental situation;
- indifferent attitude towards one’s own health (neglect of prevention, poor lifestyle).
Types of stroke
Stroke is classified into three types:
1. Hemorrhagic. Its cause is a rupture of a brain vessel, which causes blood to accumulate in the surrounding tissues. Neurons are deformed and their functionality is impaired. Hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to bleeding in the brain into the white matter area. The disease is provoked by sudden surges in pressure that the vascular walls are unable to withstand. The vessels rupture, and hematomas form at the site of the ruptures. The resulting tumor puts pressure on the diseased area of the brain, causing its functioning to be disrupted. 2. Ischemic. It develops due to poor blood supply to tissues, since arterial blood is difficult to reach certain parts of the brain. This is facilitated by thrombosis of the vessel. Blood circulation stops, the diseased area of the brain loses oxygen and nutrients, and cells begin to die. This type of stroke is common in old age. Vessel rupture can also occur due to a detached plaque or after a myocardial infarction. 3. Subarachnoid hemorrhage. Occurs due to a rupture of an aneurysm or injury to a vessel, resulting in an accumulation of blood mass in the brain cavity.
What types of stroke do older people suffer from? In elderly patients, all three types can occur, but they are most susceptible to the ischemic type.
A stroke can be:
1. acute (symptoms appear sharply and increase); 2. subacute (slower development - up to a week with a gradual increase in symptoms); 3. chronic (the disease develops gradually - from a week or longer, it is rare).
Symptoms and consequences
The symptoms of a second stroke are not always the same as those of the first stroke, and they are sometimes quite difficult to determine. Therefore, at the first manifestations of discomfort, it is advisable to turn to professionals - to the neurology center of the Yusupov Hospital, where the patient will quickly undergo a comprehensive examination and be prescribed immediate treatment, thereby minimizing the risk of developing severe complications. Our specialists will organize transportation of the patient to the hospital.
The main symptoms that should cause alarm in a patient who has previously suffered a first stroke:
- the muscles of the face, body or limbs become paralyzed or numb;
- vision deteriorates sharply, vision decreases, blindness occurs;
- speech abilities are impaired;
- consciousness is disturbed: slight drowsiness is felt, fainting occurs, coordination of movements is impaired;
- Nausea and vomiting occur.
The severity of the attack depends on the volume of the affected part of the brain and the location of the affected area. Among the likely consequences of repeated ischemic stroke in the absence of adequate medical care are the following:
- loss of control over the senses;
- loss of ability to think;
- impairment or loss of motor function;
- death (in patients who have suffered a recurrent ischemic stroke, survival is significantly reduced).
Patients suffer a repeated ischemic stroke much more severely than the first, and it is sometimes impossible to predict what consequences it will accompany. In some cases, the nature of the resulting pathologies becomes irreversible. Therefore, the main role belongs primarily to stroke prevention.
Symptoms
Brain cells that have lost normal blood supply due to a stroke die. Usually this immediately manifests itself in a person’s condition.
The main signs of a stroke are as follows:
• Dizziness and severe headache; • Loss of consciousness, fainting; • Impaired coordination of movements, disorientation in space; • Problems with speech and pronunciation: poor diction, the patient cannot pronounce sounds, speaks slowly; • Absent-mindedness; • Deterioration of vision: darkening of the eyes, blurred vision.
A stroke in an elderly person can happen at any time of the day, but most often occurs in the early morning or evening. The condition may worsen over several days as bleeding in the brain occurs slowly. Symptoms may wax and wane over several days.
There are certain initial signs that indicate an approaching attack. Older people often don't give them the attention they deserve, but they shouldn't be ignored or overlooked. If you find them, be sure to consult a doctor.
Stroke manifests itself differently depending on the type and location.
Hemorrhagic stroke manifests itself clearly:
• Acute and sharp pain; • Foggy consciousness, lethargy, fainting; • Cramps throughout the body; • Nausea and vomiting; • Feeling as if someone had hit the head; • Pupil dilation – on the side of the head where the stroke occurred.
Ischemic stroke manifests itself more easily and develops gradually. A person has a headache and also experiences these symptoms:
• Memory problems; • Numbness of the muscles at the back of the head; • Incorrect speech; • Paralysis, paresis; • Dementia and other mental disorders.
An ischemic stroke may go away on its own over time. Symptoms increase, then gradually weaken, and the person’s health returns to normal.
First aid
When the first symptoms of a stroke appear:
- Place the patient on the bed.
- Call an ambulance.
- Place the patient on his back or side if vomiting begins or he loses consciousness.
- Unfasten clothes and belt.
- Open the window to allow fresh air into the room.
- Place a cold wet towel or ice in a bag wrapped in cotton cloth on your head.
- Measure the patient’s blood pressure, pulse, and monitor blood pressure and breathing until the doctors arrive.
- If necessary, give medications that were previously prescribed by the attending physician.
- Constantly talk to the patient, try to get answers to questions from him, and do not lose contact.
Forecast
As is already known, the five-year survival prognosis is disappointing. Loss of intellectual and motor abilities after a second stroke can be lifelong. Most patients after a relapse suffer from irreversible changes and pathologies in the cerebral cortex.
After lesions, patients usually experience disability. In more than half of patients, after suffering a recurrent stroke, a coma occurs, which does not allow the doctor to give a positive prognosis about recovery from it.
Rehabilitation of patients after repeated ischemic stroke in the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is based on traditional, latest and original methods for the recovery of patients who have suffered a stroke.
Thanks to the extensive practice and rich knowledge of the clinic’s specialists in the field of rehabilitation medicine, comprehensive rehabilitation of patients is carried out at the highest level, meeting international standards.
For optimal rehabilitation, patients are provided with comfortable conditions of stay: cozy rooms, good nutrition and attentive attitude of the staff.
Call by phone and the coordinating doctor will answer all your questions.
Make an appointment
Periods of rehabilitation after a stroke
Modern medicine recommends starting rehabilitation of a patient who has suffered a stroke in the first hours after the attack, as soon as hemodynamic parameters (heart rate, blood pressure) return to normal. This allows not only to restore lost functions as much as possible, but also to avoid various complications that can aggravate the patient’s condition.
The recovery period can be divided into several main stages:
- acute (first 3-4 weeks after the attack);
- early recovery (first 6 months after an attack);
- late recovery (from 6 months to a year);
- remote (more than a year).
Life after ischemic stroke
If the patient experiences an acute period of stroke, then residual disorders are possible in the form of:
- complete immobilization;
- paralysis on one side of the body;
- partial paralysis of a limb;
- paresthesia (numbness with loss of skin sensitivity);
- speech and swallowing disorders;
- vestibular disorders;
- hearing loss;
- pelvic paralysis with inability to control bowel and bladder movements;
- decreased intelligence;
- changes in psyche and character;
- impossibility of self-service.
Recovery of various impaired functions in patients with ischemic stroke occurs at different rates. Thanks to the use of innovative techniques in the rehabilitation clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, movement disorders go away faster, and it may take longer to restore speech. After discharge from the hospital, patients need support from loved ones and continued rehabilitation under the supervision of specialists from the Yusupov Hospital.
Prognosis in older people
In patients with ischemic stroke, age is one of the most important factors that influence the prognosis and quality of life after the acute period of the disease. In older people, ischemic stroke is much more severe than in younger patients. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital take an individual approach to the treatment of elderly patients; when prescribing medications, they use doses recommended for a certain age. When using innovative methods of kinesitherapy, the age characteristics of the body are taken into account.
The prognosis after an ischemic stroke suffered by an elderly person is influenced by the following factors:
- localization of the ischemic focus;
- prevalence of cerebral infarction zone;
- a disease that caused a stroke;
- severity of neurological symptoms.
Coma caused by cerebral edema is the most severe neurological manifestation of a stroke, sharply worsening the prognosis.
Factors that positively influence the results of rehabilitation of elderly patients and improve the prognosis are:
- a small lesion confirmed by computed tomography;
- maintaining the patient's full consciousness;
- minimal number of neurological damages;
- absence of pronounced atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels according to the results of Dopplerography of the arteries of the head and neck;
- the patient's profession requiring constant mental stress;
- normal blood pressure;
- absence of arrhythmias and other heart diseases.
Methods for diagnosing stroke
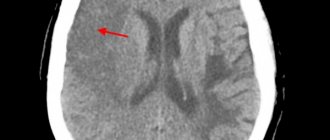
CT scan
(CT) is the "
gold standard
" for detecting cerebral hemorrhage. This study is distinguished by its accessibility, information content and short scanning time. A CT scan performed in the first hours of the disease helps to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI) has greater sensitivity for small foci of hemorrhage and helps to more accurately determine the stage of the process. However, in order to verify the hemorrhagic nature of the stroke, an MRI scan must be done 24 hours after the onset of the disease. Even many years after a stroke, an MRI of the brain will reveal pathology.
To determine the cause of hemorrhagic stroke, MRI is preferable because it shows brain structures in more detail than CT. In any case, each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, so before using them, you need to be examined by a specialist - a neurologist.
Since the patient’s further well-being depends on the time of initiation of treatment, primary diagnosis is usually carried out using CT. Later, after the necessary therapy or surgical treatment has begun, an MRI will help clarify the cause of the stroke.
Treatment
A patient with a recurrent stroke most often ends up in the intensive care unit. At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors begin treatment and early rehabilitation immediately after diagnosis. The prognosis is most favorable when patients are admitted to the neurology clinic within the first 4 hours from the appearance of the first signs of acute cerebral circulation. Doctors at the neurology clinic prescribe adequate treatment, thanks to which the nerve cells around the ischemic site completely restore functional activity.
The use of thrombolysis therapy by neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital for elderly patients significantly improves the prognosis. As a thromolytic agent, doctors at the neurology clinic use the most effective drug - tissue plasminogen activator. After the clot dissolves, blood flow through the affected vessels is restored, the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the ischemic area and the area around the cerebral infarction improves. The outcome of ischemic stroke is improved by the use of ancrod (an enzyme from snake venom) in the first 3 hours after the development of acute cerebrovascular accident and for five subsequent days.
To prevent further formation of blood clots and re-embolism, elderly people are given:
- direct anticoagulants (sodium heparin or low molecular weight heparin);
- antiplatelet agents;
- drug from the thienopyridine group Ticlopidine.
If there are contraindications or a high risk of complications from taking these drugs, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe Clopidogrel to patients. Drugs with neuroprotective and neurometabolic effects improve the plasticity of nerve cells. The tone of cerebral arteries in elderly people increases under the influence of vasoactive drugs.
In elderly people, ischemic stroke often occurs against the background of severe arterial hypertension. During the 7-10 days of the acute period of stroke, cardiologists at the Yusupov Hospital when the patient’s systolic blood pressure is less than 200 mm. rt. Art. do not carry out antihypertensive therapy, since hypotension worsens the oxygen saturation of brain areas susceptible to ischemia. In patients with systolic blood pressure above 200 mm. rt. Art. it is reduced very slowly to numbers of 10 mm. rt. Art. exceeding the pressure to which the patient is adapted. After the acute period, cardiologists select individual antihypertensive therapy.
Stroke treatment
After identifying signs of a stroke, relatives or friends must provide emergency assistance to the victim:
- put the person on the right side (especially when vomiting) to prevent stomach contents from entering the respiratory tract;
- raise the upper half of the body approximately 30 degrees;
- measure blood pressure, help take medications for high blood pressure (in this case, you should not give medications that need to be washed down with water, because a stroke may be accompanied by a swallowing disorder);
- organize air access - loosen collar, tie, belt, free from restrictive clothing.
After the ambulance team arrives, any information about the disease will help in correct diagnosis. The medical worker should report everything that happened to the victim and talk about:
- time of onset of the disease;
- the symptoms with which the disease began;
- the nature of the development of symptoms: the condition worsened sharply or gradually;
- signs of a stroke that occurred later;
- chronic diseases (especially those that could be the cause of the development of a vascular accident);
- constant use of medications;
- blood pressure numbers (if it was measured).
Regardless of the type of stroke, treatment begins with:
- compliance with bed rest;
- eliminating any physical stress; for this purpose, laxatives and other symptomatic drugs may be prescribed, for example, antitussives for severe dry cough;
- organizing patient care to prevent infectious complications and bedsores;
- adequate nutrition depending on the level of consciousness: if the patient can swallow on his own, then give him gentle food through the mouth, if he cannot, through a tube;
- prescribing drugs that regulate blood clotting, which is necessary to stop bleeding or prevent its recurrence;
- the use of neuroprotectors - medications that reduce oxygen starvation of brain cells.
Medicines are prescribed only when they are necessary and not contraindicated.
Rehabilitation
Early rehabilitation significantly improves the prognosis after a stroke. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital begin to carry out rehabilitation measures from the first day the patient is admitted to the neurology clinic. The intensity of the rehabilitation program depends on the patient’s condition and the degree of his disability. At the Yusupov Hospital, the department for seriously ill patients is equipped with special multifunctional beds. Using the devices of a multifunctional bed, medical personnel can periodically change the patient’s position, carry out hygiene procedures, and care for the patient. Changing your posture helps avoid the formation of bedsores and congestion. To reduce the risk of developing contractures, joint pain, pneumonia, and deep vein thrombosis at the Yusupov Hospital, specialists carry out passive rehabilitation from the first days of treatment.
To improve the prognosis of older people, rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital after a stroke use the following innovative methods for restoring impaired functions:
- PNF;
- Voita therapy;
- minor manual therapy;
- Castillo-Morales method;
- kinesio taping;
- Mulligan concept;
- Bobath therapy.
Recommendations after a recurrent stroke
All patients who have suffered a stroke are at risk of relapse of the disease. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital give recommendations to patients on nutrition and prevention of recurrent stroke:
- Dieting. Refusal of spicy, smoked, fatty and sweet foods, alcohol, caviar, eggs, liver. The menu includes more vegetables, fruits, and grains.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Refusal of heavy physical labor, night shifts, and work with high psycho-emotional stress.
- Sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- During the rehabilitation period, measure blood pressure every day, after completion of rehabilitation at least 3 times a week.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor in a timely manner and strictly on time.
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations.
- Do the recommended therapeutic exercises daily.