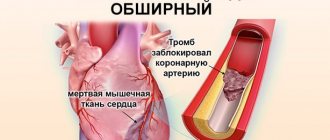
Ischemic stroke has several stages of progression. The first stage is an acute period of ischemic stroke, which lasts up to the 21st day. During the first 3-5 days, perifocal cerebral edema develops, karyoplasmic and cytoplasmic cells shrink.
An important point in the acute period of ischemic stroke is to correctly diagnose. First of all, it is necessary to distinguish any other diseases of the nervous system from a stroke. Next, the nature of the stroke itself is determined, and what caused it (hemorrhage in the cerebral cortex or blood clot). At the last stage of diagnosis, the localization of the lesion is determined, as well as the pathogenesis of cerebral infarction during stroke.
Stages of diagnostics of the acute period
- Stage 1. The victim is urgently hospitalized. The doctor receives basic information from the words of the patient, his relatives or surrounding people. External signs of cerebral circulatory disorders, emotional background, physical stress, and blood pressure levels allow a diagnosis to be made fairly quickly and accurately. The patient's medical history is studied for the presence of other diseases that can provoke the development of ischemic stroke (arrhythmia, atherosclerosis, previous heart attack, etc.). However, the possibility of making an incorrect diagnosis exists in the case of an epileptic seizure, a brain tumor, a head injury, a hypoglycemic state, etc.
- Stage 2. The most important point of this stage is to quickly and accurately determine the nature of the disease. The tactics of first aid and further treatment will depend on this. A computed tomography scan of the brain is performed, since the clinical picture alone cannot provide completely reliable information.
- Stage 3. After a quick history has been collected, the clinical picture has been identified and a CT scan has been performed, the doctor begins to choose treatment tactics. The subtype of stroke is also determined (lacunar, atherothrombotic or cardioembolic, etc.). The correct choice of therapy will help not only provide timely assistance to the victim, including surgery, but also prevent a possible recurrence of a heart attack in the future.
History of rehabilitation after a stroke
My name is Natalya Efratova.
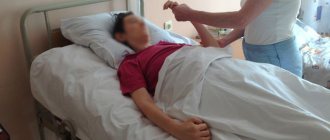
In the summer of 2021, my husband had a left-sided stroke. Almost completely paralyzed. He spent a month in the city hospital. Then, with great difficulty, we transferred him to a rehabilitation center, where he simply lay for a month, and there was no talk of any full-fledged rehabilitation. A month later we were discharged in the same condition in which we were admitted. Sergei didn’t even learn to sit normally. After such treatment, we decided to throw all our energy into recovery and decided to go to a private center. I looked through a lot of information on the Internet and caught my eye. From the very first contact, I felt a desire to help us cope with our problem.
We originally came here for two weeks, but stayed for a month and a half. My husband began to walk. We are not very confident yet and we have not yet achieved the desired result in our hand, but we were told that it will take time. But Sergei is already walking and this is already a big victory for us. Go to the official website {amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;
Therapy for ischemic stroke in the acute period
In the first three weeks (during the acute period), general measures are taken:
- The required oxygen level is maintained;
- Blood pressure stabilizes;
- Cardiac activity is under medical supervision;
- The condition of the bladder and intestines is monitored;
- Passive gymnastics is carried out on all limbs of the victim;
- Prevention of bedsores;
- Antibacterial therapy, including taking antifungal drugs.
Depending on the specifics and subtype of ischemic stroke, special therapy is carried out.
Acute ischemic stroke may recur if the diagnosis is not reliable and not all emergency measures have been taken. In the acute period, secondary hemorrhage into damaged tissue of the cerebral cortex poses a great danger. As a rule, this occurs in the first 10 days after the onset of a stroke. It is almost impossible to detect this complication visually. Only with the help of computed tomography and x-ray examination do they find a new lesion and take action. The reason for this complication is the lack of necessary control over blood pressure, as well as reperfusion therapy. Some patients have serious contraindications for it.
Critical days after a stroke
Stroke is considered to be the most dangerous and severe damage to blood vessels and brain tissue for human life.
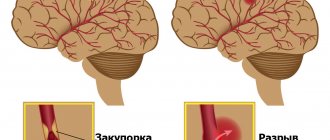
Various parts of the central nervous system suffer, and disruptions in physical activity begin. All this occurs due to the lack of normal blood circulation in the brain, which in turn can be caused by hemorrhages or blockage of blood vessels. The patient’s relatives must be patient in order to help the person get through the critical days after a stroke as easily as possible. Any type of stroke is most often heterogeneous in terms of the nature of its course. At the same time, periods of slight relief may be replaced by a crisis state. It is these periods after a stroke that experts call critical. In the first 3-6 hours of an attack, a critical moment occurs when negative changes in the brain can still be reversible. This is when it is important to promptly recognize an attack and promptly consult a doctor.
It is worth noting that in any of the periods, a hemorrhagic stroke (caused by hemorrhage) will pose a serious danger to the patient’s life, while the ischemic form is slightly less dangerous. Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by a sudden acute period characterized by high criticality. Occurs primarily during the daytime and is associated with hemorrhage.
The symptoms that appear in this case increase very sharply and there may be no precursors before this, unlike an ischemic stroke. A major stroke can cause an initial critical period. May be accompanied by loss of consciousness. Convulsions, vomiting, and uncontrollable urination may occur.
When a cerebral artery ruptures, an extensive hematoma most often occurs. It begins to gradually increase and puts pressure on the brain. It can even cause sudden death. Only modern surgical treatment in the case of hemorrhagic stroke can significantly reduce the risk of death.
Accordingly, in the case of a hemorrhagic type of stroke, it is impossible to single out any individual days that can be considered the most critical. The most risky period may be the first few weeks from the moment cerebral symptoms appear. It is in the first 2 weeks that about 85% of deaths occur in patients who have suffered a cerebral hemorrhage.
Doctors have developed some statistics that have made it possible to determine certain periods of time that are most dangerous to the life of a patient who has suffered a stroke. The most dangerous period is the first two days after the onset of a cerebral catastrophe.
Also, the risk increases significantly on days 7-10 and 14-21 after the pathology has occurred. The percentage statistics for deaths are as follows:
- 1st day – 45.9%;
- 7th day – 24.5%
- 14th day – 17.3%
- 21st day – 12.2%.
That is why back in the 60-70s. The World Health Organization has identified a 21-day period as the most critical period for the life of a person who has suffered a stroke. After active recovery and properly prescribed therapy, the situation begins to improve and the person gets better.
In a situation with ischemic stroke, critical moments often begin to occur less abruptly than with hemorrhages. The onset of the acute period can be characterized by the fact that symptoms increase gradually:
- Harbingers appear;
- Precursors turn into general disruptions in brain function;
- Disorders begin in the musculoskeletal system.
Such ailments can last quite a long time - from a couple of days to several weeks. With a stroke of this type, the critical periods of time will also differ, although the first day for the victim is still always the most dangerous.
Doctors consider the 3rd day, as well as the 7th and 10th days after the primary manifestations of the pathology to appear critical for ischemic stroke. According to statistics, ischemic stroke most affects older people and occurs most often at night or in the early morning.
After primary ischemia has occurred, the risk of a second brain stroke increases significantly. In almost 70% of cases, relapses lead to death. And no matter how much time passes from the moment of the attack, it will not be possible to definitely get rid of the risk of relapse. The most dangerous in terms of the risk of relapse is the 1st year after the attack.
To reduce the risks during critical days and reduce the likelihood of relapse, it is necessary to develop the right behavior strategy. A brain stroke in any form always requires immediate hospitalization in a medical institution that has the necessary diagnostic and treatment equipment. Often, after an attack, it may be necessary to carry out competent resuscitation measures.
After a stroke occurs, the patient often experiences serious changes both physically and psychologically. Most often, during the acute phase of an attack, severe stress occurs, which becomes a serious test for the nervous system. Vision and memory deteriorate, and loss of consciousness is possible. Motor functions may be severely affected.
Independent restoration of the normal functioning of body systems after a stroke can take a very long period of time and sometimes does not occur at all. It is vital for the body to restore such necessary functions as contraction of the heart muscle and the establishment of respiratory movements. If the respiratory area, which is responsible for conscious movements, is affected, the floor of the body may be affected.
It is important to know that the nerve cells that make up neurons are not capable of dividing. Therefore, in the case of any brain damage, the tissue may not even recover. Sometimes their functionality is taken over by unaffected neighboring cells, but full functioning can no longer be ensured.
At critical points after a stroke, the patient’s relatives must completely trust the doctors, and also be as attentive as possible to the well-being of the victim. In case of the slightest change in the patient’s condition, it is necessary to immediately report the information to doctors. In this way, risks can be minimized during critical periods and aid in rapid recovery.
An experienced specialist can, based on the symptoms of each stroke patient, subsequently tell which part of the brain was affected by the attack. This approach will make it possible to predict the subsequent course of the disease and possible critical moments.
The doctor says that after a stroke there are certain critical days when there is the greatest danger to life. What days are these? Are they the same for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke?
There are hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes. Their reasons are different. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when there is bleeding in the brain as a result of high blood pressure or other causes. Ischemic stroke occurs due to spasm or stenosis of blood vessels, increased blood clotting, especially in the heat in summer, due to the formation of blood clots.
Accordingly, the critical periods for different strokes are different. In hemorrhagic cases, the first day after the onset of hemorrhage is considered critical, then the periods between the seventh and tenth days from the start of treatment, after which the fourteenth and twenty-first days are considered critical. In hemorrhagic stroke, the onset of the disease is precisely known. As a rule, after these periods the prognosis is quite favorable.
With an ischemic stroke, it is not always possible to understand when it actually occurred and recording the time is quite difficult. This is due to the fact that with ischemia quite often there are various kinds of precursors, which are not always paid attention to, remembering them only when the thunder has already struck, if they are not very obvious.
For example, an arm may go numb or a leg will twist and a person decides that he was sitting or lying uncomfortably. Only if the warning signs are obvious or there is a knowledgeable person nearby who can recognize the onset of the disease, then sometimes an aspirin tablet can prevent the development of a stroke. Elderly people should definitely monitor their blood clotting.
In case of ischemic stroke, the third, seventh and tenth days after the onset of ischemia are also considered critical. But at the same time, the prognosis is quite poor, unfortunately, ischemia does not just go away, more often it indicates the condition of the blood vessels, any subsequent stroke can become critical.
In general, it is believed that many people experienced a stroke without any symptoms and did not even suspect that it had occurred. Any blow or minor injury can cause a mini-stroke. The brain is large and the manifestations of a stroke are also multifaceted. We are accustomed to the fact that the consequences of a stroke are loss of speech or paralysis, but this is not so.
History of rehabilitation after a stroke
My name is Natalya Efratova. In the summer of 2021, my husband had a left-sided stroke. Almost completely paralyzed. He spent a month in the city hospital. Then, with great difficulty, we transferred him to a rehabilitation center, where he simply lay for a month, and there was no talk of any full-fledged rehabilitation. A month later we were discharged in the same condition in which we were admitted. Sergei didn’t even learn to sit normally.
After such treatment, we decided to throw all our energy into recovery and decided to go to a private center. I looked through a lot of information on the Internet and caught my eye. From the very first contact, I felt a desire to help us cope with our problem.
We originally came here for two weeks, but stayed for a month and a half. My husband began to walk. We are not very confident yet and we have not yet achieved the desired result in our hand, but we were told that it will take time. But Sergei is already walking and this is already a big victory for us. Go to the official website {amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;