Trunk stroke, ischemic and hemorrhagic: causes, symptoms, diagnosis
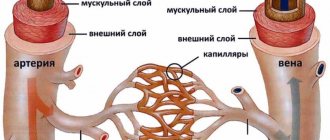
Physiological blood supply is provided by strong but elastic vessels.
There is a layer of smooth muscle around the arteries. Propulsive contraction of smooth muscles ensures that blood moves forward. Brain tissue is sensitive to oxygen. Blockage of the artery lumen by atherosclerosis, scar changes in the wall, and neurological spasms impair microcirculation and create conditions for chronic ischemia.
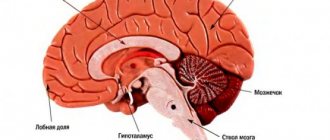
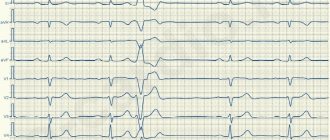
Arterial ruptures and ischemic conditions occur in different parts of the brain tissue. Lack of blood supply to the brain stem leads to multifactorial clinical symptoms from the thalamus, pons, cerebellum, medulla oblongata and spinal cord. The pathology is called brainstem ischemic stroke. Atrophy of the trunk leads to disruption of the functioning of all internal organs. Diagnosis of initial changes is carried out using MRI and CT.
MRI scans of brainstem stroke
Classification, risk factors
Paying attention to the causes, the following types of brain strokes are distinguished:
- Ischemic - lack of blood supply due to the fact that blood does not flow to the brain tissues, as a result, the cells “starve” and then die from “hunger”.
- Hemorrhagic - damage to brain structures due to hemorrhage.
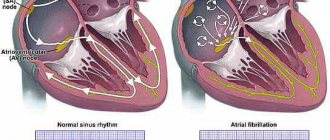
Hemorrhagic stroke, according to statistics, occurs less frequently than ischemic stroke, but is many times more dangerous, and its course is more severe.
Ischemic stroke of the brain stem occurs due to the following factors:
- Increased blood viscosity (with congenital pathologies of blood clotting, excessive use of certain medications).
- Constriction of blood vessels in patients with hypertension.
- Vasoconstriction in experienced smokers.
- Accumulation of cholesterol on the inner lining of blood vessels.
- Blockage of blood vessels by blood clots that are “born” in the cavities of the heart due to atrial fibrillation along the bloodstream to the brain.
The onset of hemorrhagic stroke is expected due to reasons such as:
- Sharp jumps in blood pressure.
- Overdose of anticoagulant drugs.
- Long-term chronic pathologies of cerebral vessels (arteritis, aneurysms).
If changes in the blood vessels of the brain are not very pronounced, a microstroke develops, rehabilitation for which and the previous therapy give faster and more effective results.
Causes of brainstem ischemic stroke
The irreversibility of the pathology is due to multiple etiological factors. The main causes of brain stem stroke are:
- Pathology of the coagulation sphere;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Smoking;
- Excess cholesterol;
- Prolonged psychological experiences;
- Poor nutrition.
Violation of intracerebral circulation can be traced against the background of secondary conditions:
- Diabetes;
- Vascular atherosclerosis;
- Rheumatism;
- Hypertension.
Each nosology increases the permeability of the vascular wall and creates conditions for impaired intravascular patency.
An important criterion for diagnosing a brainstem stroke is its sudden occurrence. Clinical symptoms develop depending on the extent and depth of the damage:
- Speech and motor disorders;
- Paralysis of intraocular muscles;
- Increased intracranial pressure;
- Excessive sweat production;
- Pale skin;
- Dizziness;
- Strabismus.
Extensive bleeding in the trunk area leads to paralysis, loss of mental activity, and memory loss. When specific symptoms appear, neurologists determine the functionality of the respiratory and cardiovascular areas. Changes are assessed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT).
Treatment of brainstem stroke
The main therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of the lesion - a blood clot or hemorrhage. Hematomas are removed surgically. If blood clots form, therapy is used to dissolve and prevent their formation. Drugs that thin the blood, regulate cholesterol levels, and control heart rate are administered. If respiratory function is lost, a special tube is inserted into the person's trachea to provide oxygen.
In most cases, a brainstem stroke leads to death, since most of the vital functions of the human body stop working. In order to avoid such a serious disease as a brainstem stroke, it is important to be regularly examined by doctors if you have other diseases of the cardiovascular system. It is also necessary to give up bad habits, lead a healthy lifestyle, and eliminate stressful situations from your life as much as possible.
Main symptoms of brain stem stroke
The development of signs of the disease is noticeable to surrounding people. Brainstem ischemic changes lead to clinical symptoms:
- Increased temperature (hyperthermia);
- Paleness of the face;
- Increased breathing, the appearance of wheezing during auscultation;
- Dizziness;
- Loss of speech clarity;
- Hypertension (increased blood pressure);
- Weakness of pulse.
Symptoms are determined by ischemic or hemorrhagic changes inside the trunk. The first form is irreversible and deadly. The second name for the pathology is “cerebral infarction.” Cell death is caused not only by a lack of oxygen supply, but also by concomitant metabolic disorders in the pathological focus (lack of nutrients, formation of tissue breakdown products).
Acute disruption of intracerebral blood supply, if persisted for a long time, leads to tissue death. In older people, the most common cause of ischemic stroke is atherosclerosis. Impaired fat metabolism causes the deposition of atherogenic lipids. The condition takes many years to develop, but the changes are irreversible.
Brainstem infarction develops suddenly. Symptoms begin with either impaired blood supply or breathing. Some people experience “unlocked brain” syndrome. Hemorrhage into the stem structures causes disturbances in the transmission of impulses from the central parts to the peripheral extremities. The person's intellectual sphere is completely preserved, but paralysis of the limbs can be observed. Rehabilitation after a stroke can restore some of the lost functions.
The death of 70% of patients after a brainstem stroke occurs in the first two to three days. Timely assistance improves the prognosis. You should seek medical help immediately after the first clinical signs appear.
Causes of pathology
Brainstem stroke occurs due to bleeding in the brainstem or blockage of blood flow. With increased load on the vessels of the brain stem, their walls become thinner and weaken. A vessel rupture can occur at any moment, and then a brainstem stroke is inevitable.
There are several reasons why blood vessels can become weak and brittle, among them the most common:
- Atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes.
- Hypertension 2,3,4 degrees.
- Rheumatic vasculitis.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Excess weight.
In addition, the risk of stroke increases if you have bad habits. Alcohol and smoking have a detrimental effect on the condition of the vascular wall, causing its fragility and fragility. Also at risk are elderly patients, whose vessel walls change due to old age. Doctors advise women in climatic periods to pay special attention to their health. The first warning sign of a stroke is high blood pressure.
Features of brainstem hemorrhagic stroke
Rupture of an artery with hemorrhage causes an acute clinical picture. Hemorrhagic stroke of the brainstem contributes to the formation of extensive symptoms:
- Loss of balance;
- Painful sensations inside the eyes;
- Numbness of the skin of the face;
- Paralysis of limbs.
In comparison with the ischemic type, brainstem hemorrhages provoke severe hemiparesis and paralysis of the muscular sphere. The accumulation of blood (hematoma) provokes an increase in intracranial pressure at the beginning of development. Brain stem coma gradually develops. The person loses consciousness. Even if it is possible to get a person out of the condition, negative consequences remain:
- Muscle paralysis and paresis cause disturbances in gait and swallowing, and difficulties with eating persist. Parenteral nutrition provides the necessary nutritional components;
- Speech disorders make it difficult to communicate with other people. Preservation of consciousness and intelligence allows for rehabilitation after a stroke;
- The cause of death in most patients is swelling of the stem structures with strangulation of the structure in the area of the foramen magnum;
- Hematoma and cerebral infarction are treated on an inpatient basis under the supervision of specialists.
Recovery after a stroke takes a long time. Experts do not guarantee a complete return to health, but some of the lost functions return.
Signs of a brainstem stroke
The pathology is accompanied by destruction of the conductive tracts between the brain and spinal cord. Infringement of cranial nerves leads to disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
First signs:
- Occipital pain;
- Bradycardia or tachycardia;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Significant daily fluctuations in body temperature;
- Dizziness.
Manifestations of brainstem infarction resemble ischemic stroke with cerebral and focal symptoms. Alternating syndromes are formed due to the involvement of accompanying cranial nerves.
Signs of cerebral symptoms:
- Tongue shift to the side;
- Ocular nystagmus;
- drooping eyelid;
- Paralysis of the facial muscles on the side opposite to the lesion;
- Hemiplegia of body parts.
The symptoms of the pathology are more extensive, but the described signs are leading.
Recovery forecasts
Doctors' forecasts directly depend on what symptoms the patient has. The most favorable prognosis is for those patients whose symptoms are not pronounced, motor activity is preserved and speech is not impaired.
Poor prognosis. Doctors are hesitant to allow patients to fully recover if they experience the following symptoms:
- Speech impairment.
- Breathing problems.
- Low blood pressure.
- Fluctuations in body temperature.
Uncertain forecast:
- Swallowing dysfunction.
- Paralysis of limbs.
- Dizziness.
- Eye movement disorder.
It is worth noting that the prognosis for the patient also depends on his age and physical condition. The younger the patient, and the fewer concomitant diseases he has, the greater the chance of recovery. Also of particular importance for the subsequent condition of a patient who has suffered a cerebral infarction is the speed of hospitalization. The sooner a person is taken to the hospital, the greater the chance doctors have to prevent extensive pathological changes in the stem cells.
Prognosis for stroke
Dead stem brain cells are not restored. Rehabilitation and complications depend on the area of localization, the extent of ischemia or hemorrhage.
The prognosis in most cases is unfavorable. Most patients die from complications. Even timely provision of medical care does not always save a person’s life. Research institutes with neurosurgical departments perform decompression operations when a person is admitted several hours after an ischemic or hemorrhagic infarction. Elimination of cranial hypertension in the first hours after pathology prevents a significant part of complications.
Forecast of complications of brainstem stroke
There are unfavorable consequences in patients with “trunk infarction with speech impairment.” Speech therapists will partially restore speech, but weak innervation of the muscles of the tongue and pharynx will make complete correction impossible.
It is possible to rehabilitate after paralysis of the limbs during the first two months after the onset of the pathology. A positive prognosis regarding partial restoration of the functions of the arms and legs can be guaranteed during the first year.
Uncertain prognosis for patients with swallowing pathology. In approximately 65% of people, truncal infarction is accompanied by swallowing pathology. Complete or partial dysphagia leads to difficulty swallowing food. Through a special diet with crushed foods, it is possible to achieve an optimal nutritional balance.
Loss of coordination of movements is combined with dizziness. Prognosis unknown. In old people, headache gradually joins neurasthenia, despite the treatment.
Damage to the center provides a disappointing prognosis. Complete destruction of the zone creates the need to be on an artificial respiration apparatus for the rest of your life. Partial damage to the respiratory center contributes to the development of sleep apnea, in which patients stop breathing at night.
Instability of the hemodynamic system in patients provokes increased heart rate and increased blood pressure (hypertension). Lethal outcome develops due to concomitant changes.
The pathology of thermoregulation is accompanied by a constant temperature curve with hyperthermia above 39 degrees Celsius. Unstable stem cells cannot optimally control balance.
Eye pathology is varied:
- Spontaneous movement on one or both sides;
- Involuntary abduction of vision;
- Loss of ability to concentrate;
- Strabismus.
The prognosis for brainstem infarction is disappointing. Full recovery is impossible to achieve, but saving a life is already a great achievement in treatment.
Risk factors for the disease
There are certain conditions under which the risk of having a brain stem stroke is higher:
- Representatives of the stronger half.
- Over 50 years of age (equal for men and women).
- Blood pressure surges over many years.
- Increase in body weight.
- Diabetes mellitus of any existing type.
- Accumulation of cholesterol on the membrane covering the inside of the brain vessels.
- Experienced smokers.
- Presence of strokes in the family.
You can get detailed answers to questions about risk factors, manifestations of the disease, how hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke of the brain differ, whether the treatment of these two types of pathology is similar or not, and so on, on the pages of our website Dobrobut.com.