Protruding veins are an important symptom of varicose veins: the walls of the veins irreversibly change their structure and lose elasticity, persistent pathological bends and nodular areas appear on them. Valve failure occurs, resulting in the development of chronic venous insufficiency and its complications. Varicose veins are not a congenital pathology; its symptoms appear throughout life. Let's consider the reasons for the visible appearance of veins.
Watch the video!
Phlebologists talk about the causes of varicose veins, the appearance of protruding veins on the legs - information based on evidence-based medicine and real practical experience.
Protruding veins on the legs do not look aesthetically pleasing. Leg injury and lack of treatment pose a serious threat to health. A pathogenetically significant difference between humans and animals is upright walking. The predominantly vertical position of the body in people is the main factor contributing to the development of varicose veins of the lower extremities. The human venous system is located virtually vertically, without obvious bends in the frontal plane. The column of blood flowing to the heart in humans is much higher than in animals. It exerts significant pressure on the walls of the vessels of the distal parts of the venous system, which is explained by the action of gravity. As a result, the superficial veins of the lower extremities and the valves located in them constantly experience increased stress. This situation is aggravated by the lack of an external compensating mechanism: subcutaneous fat and highly extensible skin of the legs are not able to provide sufficient resistance if the superficial veins begin to dilate. In animals, these vessels are pressed against the fascia much more tightly, since they are not characterized by the presence of a fatty layer on the extremities - this reduces the likelihood of pathological dilatation of blood vessels. Almost all people can be considered predisposed to developing varicose veins. But it should be understood that all this in itself does not lead to permanent changes in the walls of blood vessels and the appearance of protruding veins. But the additional impact of other factors can become a destabilizing moment and trigger the process of varicose veins of the lower extremities.
Multicolored legs
Thin and thick, red and blue... veins on the legs. Almost every woman studied them, intently examining her legs and wondering what they were? They appear out of the blue, and every year there are more and more of them. Some try not to notice these defects, others begin to worry when they are not even visible to others. However, the fact remains: this problem affects almost every person. Many patients are very surprised when they find out that they have dilated vessels, because this can mean anything: barely visible veins, or unaesthetic varicose veins. In fact, vessels are tubular organs (channels) of various sizes through which blood or lymph moves. In this article we will only touch on blood vessels, which in one way or another appear externally on the skin. On the skin, as a rule, you can see either thin red vessels with a diameter of less than a millimeter (usually capillaries or arterioles), or vessels of blue and purple shades up to several millimeters thick; quite often much larger vessels appear - the so-called varicose veins. If they begin to change and look like ugly subcutaneous nodes and tangles, then you should think about whether varicose veins have “fell” on your poor legs?
Treatment options
If the veins in your legs hurt precisely because of varicose veins, the specialist will prescribe a whole range of measures to eliminate the disease. The most common methods of treating varicose veins include:
- medical supplies;
- folk remedies;
- gymnastics;
- massage;
- compresses and bandages of the affected areas;
- special diet.
Treatment will be most effective if the patient agrees to a comprehensive rather than selective approach.
Medicines
Medicines for the treatment of varicose veins can be divided into 4 groups:
- external use;
- for oral administration;
- to eliminate symptoms;
- to treat underlying causes;
- operating methods.
To combat the disease, doctors prescribe medications that thin the blood, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, a complex of vitamins, etc. Oral medications can be taken into the body orally or by injection.
Any medications should be used only under the supervision of the attending physician, following the instructions for use and the duration of the course of treatment.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of varicose veins should complement a set of measures to eliminate the disease. You can use them at home.
Among the common folk methods are:
- medicinal baths;
- compresses;
- herbal decoctions.
For effective treatment of varicose veins, baths are recommended 3-4 times a week. The water should be diluted with special sea salt for baths or special herbs prepared in advance. For example, you can use the following recipe:
- Fill the bathtub with warm water.
- Dissolve dry leaves of medicinal herbs in water.
- Take a bath for 20-25 minutes.
Suitable raw materials for baths include chamomile, St. John's wort, oak bark and plantain leaves, which can be purchased at any pharmacy in the city for a low cost. You can also take such baths for preventive purposes, because they help cleanse blood vessels of toxic substances and also stabilize blood flow.
Compresses and lotions can be made using pharmaceutical plant and essential oils, aloe juice or honey. To do this, you need to apply one of the listed components to the areas affected by varicose veins, and then wrap the area of application with an elastic bandage. Such compresses need to be changed twice a day every 2-3 hours.
You can prevent the development of the disease using folk methods by consuming decoctions of medicinal herbs internally. The following herbs are suitable for preparing decoctions:
- hawthorn;
- chamomile;
- hop cones;
- plantain;
- St. John's wort;
- liquorice root;
- angelica root.
You should consult with your doctor in advance about traditional methods. It is possible that some components cannot be used due to allergic reactions.
Gymnastics
One of the reasons for the development of varicose veins is lack of mobility, which causes stagnation of blood in the vessels. Therefore, people who are forced to lead a computer lifestyle should regularly perform gymnastic exercises at home. Eg:
20-25 times:
- Sit on a chair
- Press your legs together
- Tighten your muscles
- Lower your feet onto your toes and then onto your heels
20-25 times:
- Lean on the wall with both hands
- Rise on your tiptoes
- Get down on your heels
15-20 times:
- Sit down
- Stand on tiptoes while sitting
- Sink on your heels
15 times on each leg:
- Sit down
- Raise your right leg parallel to the floor for 7 seconds
- Lower
- Do the same with the left leg
Massage
Massage for varicose veins can be performed independently at home. You will need a special nourishing cream or oil. Sea buckthorn is perfect. Rub the product into problem areas of the legs in a circular motion for five minutes daily. This procedure will also increase the elasticity of the skin and nourish it with moisture.
Diet
The diet for varicose veins involves limiting consumption or completely avoiding the following products:
- broths;
- marinades;
- salty, smoked, sweet, fried food;
- coffee and derivative drinks;
- alcohol and tobacco products.
It is worth diversifying your diet with foods that have a positive effect on strengthening the walls of blood vessels:
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- nuts;
- fish products; seafood;
- greenery;
- fermented milk products.
Operating methods
Varicose veins are also treated through surgery. However, it is used in extremely advanced cases. The operations consist of ligating the veins of the esophagus and stomach with anastomosis or installing a stent in the duct between the hepatic and portal veins.
To avoid varicose veins, you should give your legs rest and carry out preventative home procedures. Effective treatment of already existing varicose veins consists of timely and comprehensive treatment under the guidance of a specialist.
"Spider" entangling your legs
Varicose veins are the most common vascular pathology, affecting up to 40% of the working population, it is a manifestation of congenital weakness of the walls and valves of the veins and in most cases is hereditary.
Aggravating factors, in addition to hereditary predisposition, are prolonged sedentary standing, pregnancy, and obesity.
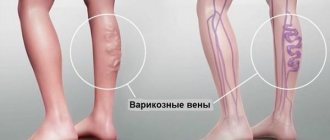
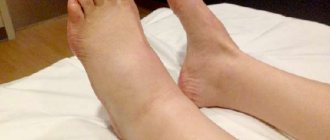
Signs of varicose veins are varied and depend on the form and stage of development of the pathological process. External manifestations may include tortuous and dilated subcutaneous venous trunks and their tributaries, swelling of the feet and legs, darkening and thickening of the skin in the ankle area, fragility of blood vessels and a tendency to hemorrhage, trophic ulcers and bleeding from varicose nodes.
The main complaints with varicose veins include a feeling of fatigue and heaviness in the legs, cramps of the calf muscles at night, dull arching pain and swelling, which intensifies with a prolonged vertical position.
Varicose veins.
Menopause
Climax
3877 March 23
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Varicose veins of the lower extremities: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Directly varicose veins without chronic venous insufficiency is a chronic disease with varicose veins of the saphenous veins of the lower extremities without the phenomena of chronic venous insufficiency (edema, hyperpigmentation, venous eczema, lipodermatosclerosis, trophic ulcers).
According to statistics, about 30% of middle-aged and older people have varicose veins of the lower extremities.
Often the early stages of varicose veins are missed because the ability to work is not yet impaired and the person is only concerned about a cosmetic defect.
Later stages of chronic venous disease significantly reduce quality of life and require long-term treatment.
Causes
There is no exact answer to the question of the reasons for the development of varicose veins, but it has been established that hereditary predisposition plays a significant role. Scientists have identified gene sections that are responsible for changes in the structure of the venous wall.
The development of the disease is based on a violation of the venous outflow in the lower extremities. With healthy hemodynamics, blood moves from the legs to the heart due to the pumping (pulling) function of the heart, contraction of the muscles of the lower extremities and venous valves.
An important mechanism for the development of varicose veins is disruption of the valvular apparatus of the veins.
In this case, a reverse discharge of blood occurs under the influence of gravity down the venous bed, or venous reflux. Gradually, blood stagnation occurs, causing expansion of the saphenous veins.
Classification
Doctors use the CEAP classification of chronic venous diseases. Each letter in the abbreviation indicates a specific section of the classification.
The letter “C” codes for the clinical class of the disease.
- C0 – there are no manifestations of the disease.
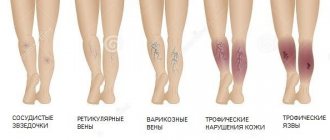
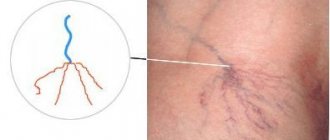
- C1 – the appearance of telangiectasia and reticular varicose veins (reticular veins are medium-sized vessels, larger than capillaries). Telangiectasia is an expansion of venules that are located deep in the skin, and reticular varicose veins are an expansion of veins up to 3 mm in diameter.
- C2 – varicose veins of the saphenous veins more than 3 mm.
- C3 – the appearance of edema of the lower limb.
- C4a – the above symptoms are accompanied by trophic changes in the skin in the form of hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin area) and/or varicose eczema (damaged areas of the skin with blisters and weeping).
- C4b – lipodermatosclerosis (varicose dermatitis) – excessive skin thickening and/or white skin atrophy (formation of small white scars).
- C5 – healed trophic (venous) ulcer.
- C6 – open (active) venous ulcer.
The letter “E” in the classification stands for etiology, or cause of the disease.
- Ec is a congenital disease.
- Ep – primary disease.
- Es – secondary varicose veins as a consequence of another pathology, for example, due to occlusion by a venous thrombus or due to trauma.
- En – the cause of varicose veins has not been established.
The next letter “A” indicates the anatomical localization of the pathological process.
- As – superficial veins are affected.
- Ap – perforating veins connecting the superficial and deep veins of the lower extremities are affected.
- Ad – deep veins of the lower extremities are affected.
- An – changes in the venous system cannot be detected.
The letter “P” denotes the pathophysiological section of the classification, which reflects the characteristics of hemodynamic disorders in the veins of the lower extremities.
- Pr – reflux.
- Po – occlusion, or blockage of the lumen of a vessel.
- Pr, o – a combination of reflux and occlusion.
- Pn – it is not possible to detect changes in the venous system.
Symptoms of varicose veins
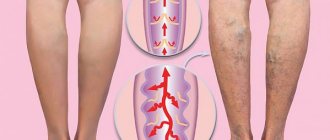
One of the first symptoms that attracts attention is the expansion of small veins and venules in the form of stars (telangiectasia and reticular varicose veins).
Then, a feeling of tightness and squeezing appears in the legs, itching and burning in the legs and ankles, as well as dryness and flaking of the skin of the legs often occur.
These symptoms are caused by gradually developing stagnation of blood, lack of oxygen in the tissues, as well as a delay in the removal of metabolic products from the tissues.
A common symptom of varicose veins is swelling: marks from shoes and elastic socks remain on the skin. With a progressive deterioration in blood outflow, throbbing or aching pain, muscle spasms appear, and leg cramps may occur at night.
In advanced cases, in addition to the indicated symptoms, the color (pigmentation) of the skin in the area of the legs and ankles changes to brownish.
Sometimes local redness of the skin develops and the risk of developing trophic ulcers in this area increases.
A trophic ulcer is an extreme degree of skin malnutrition and often occurs as a complication of varicose veins. The term “trophic” indicates that the ulcer arose as a result of tissue malnutrition and in the affected area the ability to heal independently is sharply reduced. This is why trophic ulcers are extremely difficult to treat, and chronic infection in this area can lead to the development of dermatitis and eczema. In severe cases, the purulent process can spread deep into the tissues, affecting the subcutaneous tissue and muscles.
Trophic ulcers occur in chronic venous insufficiency.
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis of varicose veins of the lower extremities is primarily based on the patient’s typical complaints and external manifestations:
- Heaviness in the legs;
- Rapid fatigue of the legs;
- The appearance of edema;
- Itching, burning, numbness, cramps;
- Enlarged veins visible to the naked eye (“stars”, varicose veins, swollen veins on the legs);
- Changes in skin color and structure;
- Long-healing ulcers.
The diagnosis is confirmed using instrumental examination methods and excluding other causes of dilated veins.
- Ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities (Doppler);
Let's run to the doctor!
Unfortunately, many patients with dilated veins in the legs are in no hurry to see a doctor, since “protruding nodes”, apart from a cosmetic defect, do not cause them any suffering. But this is a misconception!
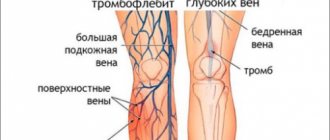
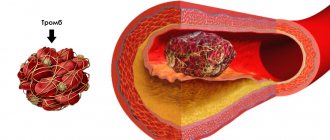
Varicose veins is a disease that sometimes leads to very serious complications - deep vein thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, trophic ulcers, since it disrupts the outflow of blood from the lower extremities. Venous congestion in the legs leads to blood thickening and blockage of blood vessels with a blood clot. As a result of impaired venous circulation in the legs, the nutrition of the skin deteriorates, and long-term non-healing trophic ulcers form.
How to prevent the development of varicose veins?
Primary prevention of varicose veins is the maximum possible correction of existing risk factors, eliminating the causes of the disease that can be influenced (8, English).
Prevention of varicose veins
Main methods of prevention:
- increasing general physical activity, including “physical exercise minutes” in the daily routine, and walking daily;
- normalization of body weight;
- timely treatment of developing dishormonal conditions, careful selection of oral contraceptive and replacement therapy regimens;
- treatment of diseases accompanied by increased intra-abdominal pressure, prevention of constipation;
- detection and treatment of tumor diseases of the pelvis and abdominal cavity.
Body weight control, proper nutrition, and regular physical activity as indicated are the basis for the prevention of varicose veins. If there is a family predisposition to varicose veins, during pregnancy, while taking oral contraceptives, it is advisable to undergo regular preventive examinations to monitor the condition of the veins of the lower extremities.
Author of the article: Letunovsky Evgeniy Anatolyevich
Last update: 09/28/2020.
Let's join hands, friends.
If you find dilated venous nodules, you need to be examined by a phlebologist. A visual examination by a doctor is usually supplemented by the necessary examination - ultrasound duplex angioscanning, based on the results of which the phlebologist will give you the correct diagnosis and will be able to determine further treatment tactics.
Unfortunately, neither drug therapy, nor wearing elastic bandages or compression garments, nor physical therapy can lead to a cure, but only to a temporary slowdown in the progression of the disease, because It is impossible to eliminate the causes of its occurrence in a conservative way. However, conservative measures are indicated and effective in preventing complications when radical treatment is not possible.
Treatment
Traditionally, all methods of eliminating protruding veins - treating varicose veins - are divided into conservative and surgical (7, English).
Non-invasive methods for treating varicose veins:
- taking medications (phleboprotectors, phlebotonics, disaggregants, anticoagulants);
- physiotherapy;
- compression therapy (wearing specialized compression hosiery);
- exercise therapy;
- Normalization of body weight, correction of hormonal levels, elimination of other provoking factors (physical inactivity, constipation, etc.).
Therapeutic measures are not able to relieve the patient of varicose veins, although they can alleviate his condition, reduce the severity of symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. They are also unable to prevent further progression of the disease.
Classic surgical methods are crossectomy, combined phlebectomy, miniphlebectomy. Flaws:
- traumatic;
- use of general or spinal anesthesia;
- hospitalization;
- discomfort in the early postoperative period;
- long-term rehabilitation.
Currently, radical treatment no longer necessarily means the presence of postoperative scars and long recovery. You can safely get rid of varicose veins using cryosclerotherapy, laser obliteration and RFO.
Glue or cut?
Vein sclerotherapy
- Cost: 6,500 rub.
- Duration: 20-60 minutes
- Hospitalization: No hospitalization required
More details
The pages of modern magazines are full of advertisements about the non-surgical treatment of varicose veins, the so-called “sclerotherapy”. However, unfortunately, only rare forms of this pathology are eliminated non-surgically. Surgery remains the radical method. Sclerotherapy (introduction of “gluing” substances into dilated veins) only complements, but does not replace the treatment of varicose veins.
Fear of pain and large postoperative scars sometimes makes patients refuse surgery. Of course, surgery is a certain risk, but the risk of complications if you refuse surgery is much higher. There is an opinion that surgery does not lead to a lasting positive result, and varicose veins reappear even after it is performed. This is not entirely true. The further course of the disease depends on the type of structure of the venous system. There is a group of patients who, after surgery, “forget” about their veins. Another notices the appearance of new dilated ducts. There is no need to be afraid of this. Regular visits to a phlebologist will allow you to get rid of these troubles. And in this case, sclerotherapy takes a leading place.
Causes
Many people call varicose veins a disease of modern society.
In fact, it has been known for a long time. Even in the treatises of ancient doctors there are descriptions of its characteristic symptoms and attempts to rid patients of this disease. But scientists began a targeted study of the etiology and pathogenesis of varicose veins not so long ago. And at present, quite a lot of factors have been identified that play a role in the development of this pathology. But it is impossible to call any one of them unambiguously leading to varicose veins. A person can be exposed to several potentially harmful factors simultaneously, but not suffer from venous pathology. And what led to the debut of varicose veins in one patient may not affect the health status of another. Therefore, even in the presence of several unfavorable factors (in the absence of signs of venous pathology), doctors only talk about predisposition. Such a patient is considered to be at increased risk for the development of varicose veins, and during preventive examinations, special attention is paid to the condition of his legs. All causes of varicose veins can be divided into (1, 2, English):
- external (exogenous);
- internal (endogenous), that is, created in the human body itself.
In the vast majority of cases, factors are combined and complement each other. Some of them are considered irremovable. The majority can still be corrected, which reduces the likelihood of early onset and rapid progression of venous pathology. And the maximum possible elimination of such factors lies at the basis of primary and secondary prevention of varicose veins.
What factors cannot be corrected?
Unavoidable causes are considered:
- Ethnicity. Some races are less likely to develop varicose veins, even if they have other risk factors. For example, this disease has a very low prevalence among indigenous people of Africa, New Guinea, and the northern subpopulations of India. In Europe, about 80% of the population has signs of varicose veins.
- Female. According to world medical statistics, the ratio of men and women of reproductive age suffering from varicose veins is approximately 1:3.
- Heredity. Varicose veins are considered as a genetically determined pathology with a polygenic mode of inheritance. The structural features of the venous system, the number of valves, the composition of the main structural proteins of connective tissue and other factors can be passed on to descendants (3, English). Therefore, if the family history is burdened with varicose veins in relatives of the 1st and 2nd lines of kinship, the likelihood of developing this disease increases significantly. But this does not mean that children from parents with vein pathology will necessarily suffer from the same problem.
- Elderly age. As tissues age, the amount of structural proteins (collagen, elastin) decreases, which is accompanied by a decrease in their elasticity and adaptability to stress. The same changes occur in the walls of blood vessels. Women also have an additional varicose factor - pronounced changes in hormonal levels during premenopause and menopause.
Despite the presence of such fatal factors, not all people develop varicose veins. And the timing of the onset of symptoms in patients can vary significantly. This is explained by the polyetiology of the disease and the great importance of many other factors.
Causes and provocateurs of varicose veins
The main predisposing and provoking causes of varicose veins include (4, English):
- Pregnancy is a powerful provoking factor. The increased risk of varicose transformation during gestation is due to significant changes in hormonal levels and difficult outflow in the inferior vena cava system. Most often, changes in the veins appear in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, when the growing uterus begins to compress the pelvic vessels. A large fetus, polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancies, a combination of pregnancy and myomatosis significantly increase the likelihood of developing varicose veins.
- Taking medications based on sex hormones (in women). Oral contraception, hormone replacement therapy for decreased ovarian function, and hormonal treatment for certain tumors are considered a high risk factor for the development of varicose veins.
- Excess weight and associated metabolic disorders. Excessive body weight is associated with increased stress on the heart muscle. Obesity leads to a decrease in the suction force of the right side of the heart with a tendency to stagnation of blood at the periphery of the venous system. Overweight people often experience a lack of physical activity, which results in insufficient muscle pump performance in the lower extremities.
- Any conditions that lead to obstruction of outflow in the inferior vena cava system. The pathogenesis of such disorders may include mechanical compression of the pelvic vessels and increased intra-abdominal pressure. Chronic constipation, pregnancy, pelvic mass formations, megacolon, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD) with frequent cough and flattening of the dome of the diaphragm are often the causes of varicose veins.
- Venostasis. Inactivity, prolonged sitting - all this slows down the outflow of blood from the lower extremities.
The more pronounced predisposing factors, the higher the likelihood of early onset of peripheral venous pathology and the rapid course of the disease.
A phlebologist will put you back on your feet
In recent years, phlebology has been developing rapidly - new minimally invasive technologies are being introduced that make it possible to obtain a high cosmetic effect, make the operation less painful, without at the same time reducing its effectiveness.
The consultative and diagnostic department of CELT employs highly qualified phlebologists who use the most advanced technologies in their work. An individual type of treatment is selected for each patient, involving a combination of various techniques. It is possible to choose a method of pain relief from various types - local anesthesia to general anesthesia. Gentle methods of treatment involve rapid restoration of working capacity, and in a number of cases, there is no need at all to change the usual lifestyle during the treatment period. Our Center provides treatment for both primary varicose veins of the lower extremities and for relapses of the disease after previous surgery or sclerotherapy. However, we must remember that at the slightest manifestation of varicose veins (and this could be the appearance of “vascular networks” or simply an increase in the venous pattern on the legs), you should immediately consult a doctor, since in the initial stages the treatment is most effective, including from an aesthetic point of view .
Diagnosis and treatment of varicose veins
Accurate diagnosis of varicose veins in the early stages of the disease is the key to quick and effective treatment without negative consequences for the patient. Doppler ultrasound and ultrasound angioscanning are considered one of the most highly informative methods for determining the severity of the situation. Both methods reliably assess the condition of blood vessels, down to the direction of blood flow.
After ultrasound diagnostics of the lower extremities, the doctor prescribes a treatment plan based on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and the stage of the disease. There are 2 main methods effective in the fight against varicose veins:
- Surgical and minimally invasive interventions. These methods are the only way to completely get rid of a damaged vessel. Today, minimally invasive techniques such as sclerotherapy, laser coagulation, and phlebectomy are especially popular.
- Drug treatment. This method is based on the use of venotonic drugs, antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants. They are able to maintain vascular tone, help increase the elasticity of venous walls and dilute blood stagnation. Phlebodia 600 is considered one of the most effective drugs in the fight against varicose veins.
Anyone can get professional advice from a phlebologist and learn about modern methods of getting rid of varicose veins on our website in a special window.
So that the blood runs through the veins...
Finally, we would like to offer you some useful tips:
- Don't sit cross-legged;
- When sitting for a long time, for example at a table, place your feet on a small bench;
- When resting at night or during the day, place a pillow under your feet so that your feet and legs are slightly above heart level;
- When traveling by car, it is advisable to stop every 1.5–2 hours, get out of the car, do several squats and walk around for 10–15 minutes;
- If there is a high probability of illness, do not take hot baths, do not visit the bathhouse or sauna;
- Avoid overheating your feet and sunburn;
- Do not wear tight shoes or tight clothing.