Rehabilitation after an ischemic stroke is a set of medical, psychological, social and pedagogical measures aimed at restoring lost functions and returning the patient to a normal lifestyle.
The effectiveness and quality of patient rehabilitation after an ischemic stroke depends on several main factors:
- Active participation in the recovery process, both of the patient and his loved ones;
- The complexity of rehabilitation measures - i.e. comprehensive restoration of functions impaired as a result of a stroke;
- Early start of rehabilitation measures;
- Systematicity and continuity of rehabilitation measures at various stages of the recovery period.
Important aspects of the rehabilitation program for patients who have suffered a stroke are the prevention of complications in the post-stroke period and the prevention of the development of recurrent strokes.
Step-by-step rehabilitation after ischemic stroke
The timing of the start of rehabilitation of patients after ischemic stroke depends on the severity of the cerebrovascular accident. But the fundamental principle is the same - the earlier rehabilitation measures are started, the greater the chances that it will be possible to minimize the risk of developing neurological deficits in the future. For patients in this group, the approach to the rehabilitation process is always individual. For some patients, rehabilitation measures are recommended to begin 24-48 hours after a stroke; for other patients, rehabilitation begins later - after 5-7 days.
An integrated approach to the problem of rehabilitation of patients who have suffered a stroke is the key to the success of the entire complex of treatment measures. The recovery program for stroke patients must take into account many aspects, in particular:
- diet,
- motor, speech and drug rehabilitation,
- social and psychological readaptation.
The process of rehabilitation of a patient after an ischemic stroke requires, in addition to enormous work on the part of the patient himself and his relatives, the efforts of a number of specialists. These include: neurologists, rehabilitation specialists, physical therapy methodologists, speech therapists-aphasiologists, physiotherapists and psychotherapists.
What to do if a person cannot return to his previous position after a stroke?
If it is not possible to return to the job that the patient was engaged in before the stroke, it is often possible to find another activity (paid work or volunteering) or undergo training for a new type of employment. In such cases, you can contact the labor exchange. There are employment consultants for people with disabilities. They help you gain new skills and highlight employers who work with patients with special needs.
Social workers should also be contacted for available support . They will, for example, tell you about services or funds that can help pay for taxi fare to work if the patient is unable to use public transport, or pay for training for the patient's colleagues on disability issues.
Write to us what difficulty you encountered, and we will suggest further steps for rehabilitation or provide the missing information.
Diet of a patient who has suffered an ischemic stroke
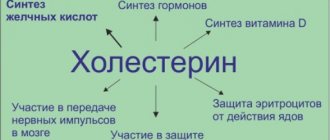
Since the leading cause of ischemic stroke is atherosclerosis, which affects the vessels responsible for the blood supply to the brain, the diet after a stroke should help prevent further progression of atherosclerosis.
- Strong meat broths, high-fat dairy products.
- It is necessary to reduce the consumption of cholesterol, which is found in large quantities in butter and animal fats.
- It is recommended to exclude fatty meats (primarily pork) from the diet.
- Reduce salt intake to 3-5 grams per day.
The basis of the diet of a person who has suffered a stroke should be foods containing large amounts of fiber and complex hydrocarbons. First of all, these are fresh fruits and vegetables.
Regular consumption of foods containing polyunsaturated fatty acids can reduce blood cholesterol levels and, accordingly, reduce the risk of developing a recurrent stroke:
- Liquid vegetable oil,
- Seafood,
- Fish.
Recommended to eat:
- Boiled and baked lean meats,
- Low-fat dairy products,
- Wholemeal bread,
- Bread with bran.
In the first days after a stroke, boiled food is better absorbed. Preferably in pureed form.
Motor rehabilitation
Passive gymnastics. Motor rehabilitation of patients who have suffered a stroke is an integral and one of the most important components of the recovery process. The basic method of motor rehabilitation is physical therapy, which begins as soon as the patient’s condition allows. The objectives of physical therapy include restoration (full or partial) of range of motion, strength and dexterity in the affected limbs, balance function, and self-care skills.
In the early period, immediately after a cerebrovascular accident occurs, passive gymnastics is performed. It allows not only to normalize the tone of the limbs, but also to prevent the formation of bedsores. Passive gymnastics is performed by exercise therapy specialists together with the patient’s relatives.
When performing gymnastics, passive movements of paretic limbs are performed at a slow pace, carefully, slowly, while trying not to cause pain or increase muscle tone. Such gymnastics is first performed on the healthy side and then on the sore side. It is important to start proximally, in isolation at each joint. In this case, 8–10 movements are performed in each joint.
Active gymnastics. The next stage of recovery is the beginning of active gymnastics, which begins with simple movements of the limbs and becomes more complex as the patient becomes more active. The patient is taught to sit up in bed, maintain balance and stand up, then walk, first accompanied or with support, and then independently.
Great importance is given to motor rehabilitation in the affected upper limb, in particular the restoration of fine motor skills, which is the key to full social and everyday readaptation. The patient learns simple self-care skills, in particular eating, personal hygiene, using the toilet and bathroom, as well as dressing independently, in stages.
The duration of the various stages of motor recovery depends, first of all, on the extent of the area of brain damage. An important part of rehabilitation, both motor and psychological, is the early involvement of patients in household work and the preparation of able-bodied patients to go to work.
Massotherapy
Along with physical therapy, positioning of the lying patient and therapeutic massage are important for the recovery of the patient. The purpose of these therapeutic measures is to prevent the development of muscle contractures and maintain normal joint function, prevent bedsores and pulmonary complications, primarily congestive (hypostatic) pneumonia. When conducting massage sessions, certain principles must be observed:
- the extensor muscles are usually massaged on the arm,
- on the leg - the flexor muscles of the leg and the dorsum of the foot.
Massage is carried out throughout the entire recovery period.
Physiotherapeutic procedures, acupuncture, acupressure, cryotherapy, and water procedures are widely used as additional methods that speed up the rehabilitation process.
Fatigue
Fatigue is one of the most common symptoms of stroke. This symptom affects most people who have had a stroke, regardless of its severity, and is usually most noticeable when they return home from the hospital.
This type of fatigue is different from the usual and usual fatigue for us, and it does not depend on your activity or activity. Each of us sometimes feels tired, but this feeling often goes away after rest. However, after a stroke, the fatigue you feel may make you feel like you don't have the energy to do anything. Often you may feel that the feeling of fatigue comes completely unexpectedly and at this moment the only thing you can do is rest until this feeling passes.
Sometimes it takes months or even years for this symptom to go away. Many people after a stroke say they have good days and bad days - days when they feel they can do more things and days when they need to rest more because they feel tired. During the recovery process, good days tend to increase and bad days decrease. Often this fatigue is invisible to other people, so it can be difficult for them to understand what you are feeling. Despite this, you can help yourself in various ways. The key to success is to realize that it is not your fault and it is not your fault. You need to accept the fact that it takes a long time to overcome this symptom of fatigue.
Speech rehabilitation
Speech disorders after a stroke are observed in more than a third of patients who have suffered acute cerebrovascular accident. It is necessary to understand that the concept of “speech impairment” implies not only a violation of one’s own voluntary speech (motor aphasia), but also a violation of the understanding of the speech of others (sensory aphasia), forgetting of individual objects and actions (amnestic aphasia), and there are also combined manifestations of these conditions. Another common type of speech impairment after a stroke is dysarthria - a violation of the correct articulation of sounds while maintaining “inner speech”, understanding the speech of others, reading and writing.
The main factor for success in restoring speech functions is systematic long-term classes on the development of speech, reading and writing, which are conducted by a speech therapist-aphasiologist or under his direct supervision.
It is necessary to begin speech restoration classes in the acute period of a stroke, as soon as the level of consciousness allows. At this stage, classes are short - no more than 15-20 minutes. Subsequently, the duration increases to 30-45 minutes or more. In such a situation, speech isolation of the patient is very dangerous. Relatives and friends of the patient must understand that not only special classes, but also ordinary constant everyday speech contact with the patient and reading books in themselves contribute to the restoration of both his own speech and understanding of the speech of others. Consequently, the timing of the patient’s return to normal life after a stroke depends on the atmosphere created by the loved ones around him.
Working conditions provided for disabled people
If a medical examination has recognized the patient’s limited ability to work and he has been asked to work from home or under easier conditions, then they should be as follows:
- the work place should be located away from temperature changes and strong vibration;
- during the working day, the patient should not remain in one position for a long time - the place should be comfortably equipped;
- activities should exclude excessive stress on the emotional, mental and physical sphere;
- no contact with household toxins.
With severe financial difficulties, many patients earn money not only at their main job, but also at home, completing simple orders according to their profile, taking advantage of a reduced working day. This is a natural need for a person, but it is better to undergo a full rehabilitation course and prove your ability to work for VTE in a year than to expose yourself to the risk of another stroke due to overwork and stress.
Drug rehabilitation
Drug therapy in patients after a stroke is aimed at restoring the functions of the affected areas of the brain that were “inhibited” as a result of the cerebral catastrophe, improving cerebral blood flow, as well as preventing the development of postoperative complications.
Drug rehabilitation includes a range of metabolic drugs and biogenic stimulants. This group includes the following drugs:
- amino acids,
- adenosine triphosphate,
- B vitamins, etc.n
- nootropic drugs,
- Essentiale.
Biogenic stimulants include:
- ginseng tincture,
- aloe extract, etc.
Anticholinesterase drugs are prescribed according to indications, which include:
- oxazyl,
- prozerin,
- improving neuromuscular conduction.
If muscle spasticity is detected, muscle relaxants are used, such as:
- baclofen,
- isopropane,
- mydocalm.
In cases of increased plastic tone, cyclodol and other drugs are prescribed.
In the absence of contraindications, all patients who have suffered an ischemic stroke receive drugs that improve the rheological properties of the blood, in particular, aspirin and new generation antiplatelet agents (Plavix, Tiklid, etc.). Therapy is prescribed and carried out only under the supervision of a specialist.
Stay active and keep in touch with friends and acquaintances
Many people feel weak, have difficulty speaking, or have any other problems after a stroke. This leads to them losing interest in the outside world and not wanting to communicate with friends and acquaintances. An important step in rehabilitation after a stroke is socialization. You may find it difficult to go to places you used to go to before your stroke because of your mobility problems, or you may be worried that you will not be able to cope with your problems outside the home. You may find it easier to stay home, but this can lead to isolation, loneliness and low mood. There is always a solution to problems, you can take the help of others or use a stroller to move around. Try to keep in touch with your close friends, invite them to visit or travel with them. It will help if your friends know your capabilities, what you can and cannot do. Meeting new people may be intimidating at first, but it is likely that meeting new people can be especially beneficial for you. Often people make new friends with people who have also had a stroke, and this helps them share their experiences. A positive mood, an active life and maintaining relationships with friends and acquaintances are the key to your recovery.
Prevention of recurrent stroke
The main goal of preventing recurrent disruption of cerebral blood flow is to reduce the risk of developing this disease by eliminating the factors leading to the development of stroke. The main risk factors include:
- Arterial hypertension,
- Hyperlipidemia,
- Smoking,
- Some heart diseases with heart rhythm disturbances (atrial fibrillation) and/or valve damage,
- Insufficient physical activity
- Obesity,
- Diabetes.
Repeated strokes in the overwhelming majority develop according to the same mechanism as the first ones, so it is necessary to determine the possible genesis of the first stroke. For all types of ischemic stroke, long-term (almost lifelong) use of antiplatelet drugs is recommended. For ischemic strokes that develop as a result of cardioembolism, along with antiplatelet agents, the use of anticoagulants (phenylin) under the control of blood prothrombin is indicated.
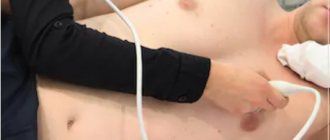
All patients who have suffered a cerebrovascular accident of the ischemic type must necessarily consult a vascular surgeon with an ultrasound examination of the main arteries supplying the brain. Since one of the main causes of ischemic stroke is atherosclerotic damage to the carotid arteries. When their pathology is identified and there are indications, the issue of surgical intervention or stenting is decided.