The atria are separate cavities in the structure of the heart that provide a suction effect for blood flowing through the venous vessels due to negative pressure. The pumping function causes the chambers to fill, increasing their volume to the limit, and then decrease as blood contracts and passes into the ventricles.
This feature requires the myocardium to have sufficient strength and elasticity. Dilatation of the left atrium and the similar mass on the right implies excessive dilatation without thickening of the walls. The term is used to describe any hollow organs. But it should be borne in mind that the size of the stretch must exceed physiological standards.
Norm and pathology in abbreviation
The normal diastolic volume of the right atrium at 18–25 years of age is about 105 cm3, the left atrium is 90–135 cm3. By the age of sixty it increases by 5–10 cm3. In women it is usually 3–6 cm3 more. When contracted, the cavities are reduced by almost half. Any volumes above the norm are defined as atrial dilatation.
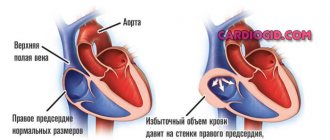
The right atrium receives blood from the vena cava, coronary sinus of the heart and many small veins, and the left atrium receives blood from the lungs. There are no valves at the confluence of the pulmonary and vena cava. The reverse flow of blood is stopped due to the contraction of the ring-shaped muscle formations.
Overdistension of the chambers is caused by difficulty in the passage of blood flow through the atrioventricular openings located between the ventricles and atria. A mechanical obstacle can cause dilatation due to impaired functioning of the valve apparatus and endocardial diseases.
Myocyte cells are responsible for the ability to contract in the atria. The process of contractility is ensured by the mechanism of connection of actin and myosin fibers with the participation of electrolytes and energy production. Any heart disease associated with myocardial damage necessarily affects the supraventricular formations.
Forms of the disease
Enlargement of the left atrium is classified according to the group of bases. Based on the origin of the pathological process, there are:
- Congenital form. The share of this condition in the total number of recorded clinical situations is 35-40%, which is a minority.
Pathological processes are diagnosed already at advanced stages, since a small patient is not able to formulate his complaints until he grows up, and parents interpret objective manifestations incorrectly due to inattention or lack of experience. The prospects for treatment are therefore somewhat worse.
- Acquired form. Caused by the course of a particular disease. An attentive patient can draw a cause-and-effect relationship between the condition suffered and the development of dilatation symptoms, which are quite pronounced from the second stage.
Association with arrhythmias
An important component in the pathology is a violation of the correct formation of the rhythm. The fact is that the main node (pacemaker), which sets the correct rhythm for heart contractions, is located in the right atrium. And in the interatrial septum there is the supraventricular part of the second most important - the atrioventricular node.
Changes such as right atrium dilatation or left atrium dilatation contribute to the loss of muscle mass, replaced by small foci of fibrosis, which leads to the appearance of ectopic foci of excitability
Arrhythmia is expressed in extrasystolic contractions and attacks of paroxysmal tachycardia.
An increase in atrial volume is most often not an independent disease, but reflects a general lesion of the heart, its congenital or acquired pathology.
Symptoms
Moderate dilatation of the left heart is not accompanied by any symptoms. But with strong expansion, the following signs already appear:
- dyspnea;
- change in heart rate;
- fatigue;
- decreased ability to cope with mental stress;
- constant feeling of weakness;
- swelling of the limbs.
People who engage in professional sports or heavy physical labor have an enlarged left atrium. This is considered normal and does not require treatment. Sometimes patients learn that the chambers are dilated only during a routine examination and do not attach any importance to it because they feel well.
If such a pathology continues to progress, then the person feels not only shortness of breath in a calm state, but also a cough, pain in the chest, increased sweating and surges in blood pressure.
What causes dilatation?
For reasons of dilatation, it is customary to distinguish 2 types of pathology:
- tonogenic - occurs when there is increased pressure in the chambers of the heart due to their overflow with blood;
- myogenic - depends on the pathology of the muscle layer (myocardium).
The most illustrative example of a tonogenic type is dilatation of all parts of the heart during hypertension, when a wave of overstretching from the left ventricle passes to the atrium.
The reasons for the increase in the volume of the left and right atria are different. In dilatation of the left atrium and both at once, an important role belongs to:
- severe physical overload in work and sports, which leads to a constant need for increased blood circulation;
- persistent increase in blood pressure;
- various heart defects of a congenital nature (ventricular septal defect, aortic stenosis) or acquired, often of rheumatic etiology (mitral valve insufficiency);
- atrial fibrillation in paroxysmal form;
- heart rhythm disturbances such as fibrillation, atrial flutter;
- development of alcoholic and autoimmune cardiomyopathy.
Stretching begins from the left ventricle when:
- organic changes in the myocardium caused by necrosis, scar, aneurysm after acute infarction;
- infectious myocarditis against the background of viral infections, measles, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, typhus, sepsis;
- severe ischemia;
- hypertension.
There are diseases with unknown causes.
Dilatation in the right atrium occurs with an increase in pressure in the pulmonary circulation. Here the reasons may be:
- chronic diseases of the lung tissue and bronchi, occurring with impaired patency (obstruction);
- congenital heart defects (patent ductus ductus, narrowing of the pulmonary artery, atrial septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot);
- rheumatic heart defects (tricuspid valve insufficiency and stenosis of the right atrioventricular orifice).
The onset of the disease from the right ventricle occurs when:
- rheumatic attack;
- bacterial endocarditis;
- formation of pulmonary hypertension;
- heart failure of the “cor pulmonale” type;
- arrhythmogenic dysplasia of heart tissue.
Inflammation of the myocardium affects all parts and chambers of the organ. The most common reasons are:
- tonsillitis;
- childhood infections;
- viral diseases;
- fungal infection;
- parasitic infestations;
- negative effects of medications;
- various poisonings.
Dilated atria are less commonly diagnosed with:
- thyroid diseases;
- autoimmune systemic processes;
- tumors.
Treatment
Mixed therapy.
Conservative methods are used at an early stage, a combination of surgery and medication in the advanced phase of the pathological process. The following medications are prescribed:
- Antiarrhythmic. Like Amiodarone, it is the safest. They are used to restore an adequate, correct heart rate.
- Antihypertensives if high blood pressure occurs. Enap, Diltiazem, Perindopril will do. The combinations are different.
- Diuretics to normalize the evacuation of fluid from the body.
- Cardiac glycosides. Stabilize myocardial contractility.
- Antithrombic drugs of various types.
Surgical intervention is aimed at stopping the root cause or installing a pacemaker for severe arrhythmia.
Excision of pathologically altered tissues against the background of tumor lesions is possible. Specific techniques are determined by a specialist based on the underlying disease.
The last resort if the heart is significantly changed is transplantation. However, this is not an easy undertaking.
In addition to the fact that finding an organ is almost impossible in the conditions of Russian reality, the operation requires the highest qualifications, which only a few have.
During the treatment process, also during the recovery period, which lasts a lifetime, you need to minimize the amount of salt in the diet (6-7 grams), give up smoking, alcohol, and normalize physical activity (maximum: walking in good weather).
Clinical signs
Symptoms of dilatation do not appear with moderate dilatation. Retrospective analysis shows slight tachycardia during walking, agitation, or physical activity. Signs of dilatation are clinically manifested by general symptoms of heart failure. It is impossible to detect patient complaints or characteristic abnormalities specific only to the atria during examination of the patient.
The doctor should suspect atrial dilatation when registering arrhythmia and conducting a comprehensive examination. You need to pay attention to:
- shortness of breath of the patient when moving, talking;
- arrhythmia of heart contractions during auscultation;
- swelling on the feet and legs.
In their complaints, patients talk about:
- the appearance of unclear weakness, drowsiness;
- fatigue;
- reduced performance.
Diagnostics
The examination of patients is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist, as necessary, a group of other specialists.
- What is dilatation of the left atrium cavity: causes, symptoms, treatment and prognosis
Approximate list of events:
- Oral questioning of the patient and collection of anamnestic data. It is necessary to establish many factors that would play a role.
- Measurement of blood pressure (possibly an increase or decrease), heart rate (tachycardia is typical, flowing in parallel with various types of arrhythmias).
- Daily monitoring. Registration of blood pressure levels for 24 hours. Used for early diagnosis.
- Electrocardiography. Plays the same role. Shows the degree of deviations from the cardiac structures.
- Echocardiography. Basic technique. It makes it possible to identify organic defects at first glance, determine their degree, and predict complications.
- MRI if there is a suspicion of a tumor process in the heart.
Stress tests are not performed due to the possible cessation of muscle function and sudden death.
How to diagnose atrial stretch?
In diagnosing enlarged or stretched atria, the main method is ultrasound examination of the heart.
Modern equipment allows you to display and observe in color images the process of blood filling the chambers of the heart, the direction of blood flow
Objective data on measuring dimensions, wall thickness, and functional indicators are provided taking into account the patient’s age, gender and weight. This helps determine the phase of heart failure. For example, detection of dilatation of the left atrium with the first degree of backflow of blood from the ventricle (regurgitation) indicates a sufficient compensatory mechanism of the heart.
Electrocardiography has:
- signs of atrial hypertrophy in the form of a high P wave;
- detects arrhythmia;
- establishes the localization of extrasystoles;
- determines rhythm characteristics (flickering, fluttering, paroxysm).
With the use of Holter monitoring, it became possible to observe and record changes during the day, during sleep, and at work.
The x-ray shows an increase in the volume of the atria and other parts of the heart, signs of hypertension in the pulmonary circle, impaired structure of the lung tissue, and congestion are important.
Coronary angiography is performed to resolve the issue of surgical treatment of ischemia and elimination of paroxysmal fibrillation through surgery.
For better visibility of the left atrium (LA), lateral and direct radiographs are taken with contrasted esophagus
Development mechanism
LA dilatation is not an independent process. It is not considered a nosological unit. How does such a state form?
Normally, cardiac structures function continuously, acting as a large pump. The release of blood is ensured by alternating synchronous contraction of all chambers of the heart.
Liquid connective tissue moves in one direction: from the upper to the ventricles, no reverse flow is observed.
As a result of congenital genetic defects, acquired sclerosis of active tissues (replacement of affected areas with scars), a long inflammatory period, etc., blood is retained in the left atrium longer than it should be. Or regurgitation is observed (return of liquid connective tissue from the ventricle).
Over a long period of time, the chamber becomes stretched and the normal dimensions of the organ are disrupted.
This leads to a decrease in release into the systemic circulation, and general and local hemodynamics decrease.
Removed tissues and systems suffer from a lack of oxygen and nutrients. The process of development of organ defects and functional failure begins.
Forecast
Every patient with left ventricular dilatation, already knowing what it is, must follow all medical recommendations. With this diagnosis, early diagnosis and initiation of treatment are important. In advanced forms, there is a high probability of developing heart failure. In these same patients, the valve apparatus is deformed, which leads to mitral insufficiency. This diagnosis significantly affects the quality of life and reduces its duration. The prognosis for patients is unfavorable.
The average survival rate for left ventricular dilatation is 10 years. If the course is asymptomatic, then life expectancy is on average 5 years. Patients with chronic heart failure observed in the hospital survive up to 50% of those admitted.
It is important for each patient to remember that the first symptoms are not considered normal and require a set of diagnostic procedures. Timely treatment will reduce the risk of complications, and treatment will prolong life for many years.