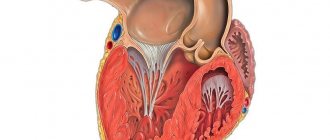
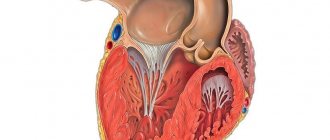
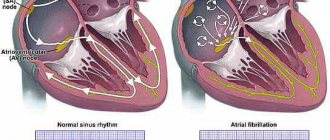
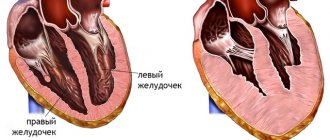
Trabecula is a tendon formation in the cavity of the heart, which refers to minor developmental anomalies not related to the valve apparatus. The presence of an additional trabecula in the left ventricle is not a defect, and in certain situations is considered normal. Typically, the diagnosis is made during a routine examination of the child when a systolic murmur is detected on cardiac auscultation.
This pathology is observed in every seventh person in the world. The connective formation does not pose a serious danger to the life of an adult or a child. Only in rare cases is it possible to develop complications, which usually appear during puberty.
Reasons for appearance
Additional trabecula in the left ventricle is a pathology related to abnormal development of the heart.
In itself, it does not pose a health hazard, because it does not lead to deformation of the heart, does not cause disruption of its performance and is not a defect. Trabecula in the cavity of the left ventricle is a thread that connects the muscle tissue of the left ventricle of the heart with the valve. Most often it is found in newborns, because it can only be congenital.
This topic has been discussed many times by famous scientists and professors at medical universities. Numerous studies have also been carried out in children and adults, as a result of which additional trabeculae in the left ventricle have been attributed to pathologies transmitted genetically from one of the parents to the child. If the baby’s mother has an additional chord inside the heart, then the probability of her giving birth to children with this pathology is 50%.
Healthy mothers also give birth to children with an additional intracardiac chord. This may be due to the following factors:
- Radiation effects on the body of a pregnant woman.
- Alcohol abuse, smoking and drug use during pregnancy.
- Living in an area with a polluted environment.
- Regular nervous tension, depressive states.
- Heavy physical activity.
Additional cardiac chords recorded by researchers are usually classified. This is influenced by the thickness, number of connecting filaments, and their location inside the left ventricle. Therefore, the additional trabecula of the left ventricle in a child may be:
- Multiple, single.
- Muscular, fibrous, mixed.
- Apical, apex, basal.
- Diagonal longitudinal and transverse.
These factors allow us to assess the malignancy of the trabecula, but only in rare cases can it pose a threat to health.
Left ventricular trabecula: what is it, causes
Left ventricular trabecula is a minor cardiac anomaly that does not pose a threat to human life.
Recently, due to the development of technology and more thorough examination of newborns for congenital anomalies, the number of detected trabeculae in the left ventricle has increased significantly.
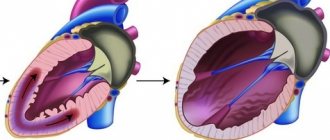
Many people do not distinguish between the concepts of “additional chord” and “additional trabecula,” but doctors say that these are different things. The notochord is a thin thread of connective tissue that extends from the mitral valve to the muscle tissue of the ventricle. By trabecula we mean septa, small outgrowths, cords, that is, the trabecula can sag into the cavity of the ventricle, rather than connecting the valve with muscle tissue. However, not all doctors recognize this difference and sometimes write “chord” instead of “trabecula” in the conclusion.
The left ventricular trabecula does not pose any danger to the child's life.
Most often it is found in children, since it is congenital. The heart, as you know, consists of four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The ventricle and atrium are separated by a valve, which serves as a gate that allows blood into the ventricle and does not release it back into the atrium. This valve is connected to the muscle tissue of the ventricle by peculiar springs, chords, thin threads that stretch and open the valve, and then relax and close it. The valve opens and closes in accordance with heart contractions.
Useful video - Ultrasound of a child's heart.
The left ventricular trabecula is essentially another chord connecting the valve to the left ventricular muscle. This is not dangerous to the child’s health and may not manifest itself in any way throughout life.
Left ventricular trabecula is a minor cardiac anomaly; it is not a heart defect or a fatal disease. Often it does not even require special treatment, but it is recommended that a child with such an anomaly be observed and regularly shown to a doctor. The cause of left ventricular trabecula is heredity (in more than 90% of cases). It appears during embryonic development.
Signs of the disease
Left ventricular trabecula is a hereditary disease
The additional chord itself does not manifest itself in any way. It is quite rare to suspect left ventricular trabecula; most often, the disease is discovered by chance, during examination or echocardiography of the heart.
However, in some cases, left ventricular trabecula is accompanied by complications or occurs against the background of another, more extensive disease, such as connective tissue dysplasia. In these cases, the child will exhibit certain signs that require examination. Most of these symptoms are observed during the period of active growth, in primary school and adolescence.
If there is not one, but several additional chords, a connective tissue disease can be suspected, which will affect the entire body as a whole.
Signs of left ventricular trabecula:
- Pain in the heart area, tachycardia. Pain and rapid heartbeat can be observed during the period of active growth of the child, when there is an increase in the size of internal organs, growth of bones and muscle tissue. As a rule, the child complains of regular tachycardia and pain in the chest after or without physical activity.
- Fast fatiguability. If complications arise and increased stress on the heart, the child begins to get tired quickly, complains of chronic fatigue, causeless weakness, and quickly gets tired. For such complaints, pediatricians often prescribe an ECG and a blood test, which will help identify other disorders and detect trabecula.
- Limb deformity. With connective tissue disease, not only the heart suffers, but also the skeleton and muscle tissue of the whole body. A child with connective tissue dysplasia has abnormal flexibility, scoliosis, a wobbling gait, and a arched back line.
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. Children with dysplasia often experience bending of the gallbladder, as well as gastroesophageal reflux, in which the contents of the stomach enter the esophagus along with gastric juice, causing irritation.
Symptoms
If the disease is found in a benign form, it will not cause pain or discomfort, so the child can live like other healthy children. However, if the trabecula is malignant or complications occur, the following symptoms may appear:
- Pain in the heart area, tachycardia . In infancy, children do not feel discomfort, but when they begin to grow up, the internal organs increase in size, and the child can feel the force of the heartbeat and pain in the chest space, which manifests itself as a result of physical activity.
- Decreased physical activity and chronic fatigue . They arise as a result of the development of an additional chord. This symptom is the most common.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system.
- Musculoskeletal disorders are a complication caused by trabecula. At the same time, changes in the position and shape of the limbs are visually noticeable. As a result, the child may find it difficult to be physically active.
If trabecula in the left ventricle have not been previously detected, but symptoms begin to appear, you should consult a specialist and undergo an examination, which includes an examination by a doctor, an ultrasound scan, an electrocardiogram or a Holter study to assess the current functionality of the heart. As a result, the child will be prescribed treatment and other measures to prevent complications.
Treatment
Typically, additional trabecula in the left ventricle does not need to be treated, but if pain or discomfort is present, it should be.
To support a person with an additional chord, the following measures are used:
- A complex of vitamins is prescribed, which the patient takes in the form of injections, capsules or tablets for 1-3 months. They allow the heart to return to normal functioning and improve the patient’s well-being.
- Medicines containing magnesium and potassium are prescribed. They have a positive effect on the functionality of blood vessels and the heart. It is not recommended to take these drugs without a doctor's prescription, especially for children. An incorrectly calculated dosage can provoke a negative effect, which will affect the well-being and condition of the patient.
- Medicines that stimulate metabolic processes are prescribed. With their help, cardiac performance improves, because these medications improve appetite and myocardial functionality.
Having discovered this disease in a child in a benign or malignant form, it is necessary to undergo an annual medical examination and monitor the course of the disease. This will prevent complications and still lead an active lifestyle.
Diagnostics
Ultrasound of the heart - effective diagnosis of pathology
If the above symptoms occur or as a routine examination, the doctor may prescribe diagnostic methods such as ECG, echocardiogram, etc.
All methods of examining the heart are usually painless, non-invasive and completely safe:
- Examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis. The doctor will carefully examine the child, listen to all complaints, record them, clarify when exactly the symptoms appeared and with what frequency they appear, and also listen to the heart rhythm for murmurs.
- Echocardiography (or ultrasound of the heart). This is the most informative procedure for identifying left ventricular trabeculae. It is a non-invasive, painless ultrasound diagnosis of the heart. The principle of this method is the same as with conventional ultrasound; ultrasonic waves of a certain frequency are reflected from tissues, and an image is displayed on the monitor. Echocardiography is prescribed for patients with complaints of heart function, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, and chest pain. This procedure does not cause discomfort, is absolutely safe and has no contraindications, however, diagnosis can be difficult in women and girls with large breasts and in patients with chest deformation.
- ECG. Electrocardiography allows you to evaluate the work of the heart, but it is almost impossible to notice the trabecula in the heart in this way. An ECG is prescribed to identify complications. The procedure is also painless, non-invasive, performed fairly quickly, and may include physical activity. The essence of this procedure is that electrodes are attached to the chest and limbs, and then the device records heartbeats and displays them in the form of a curve. For more information, you can do a monitoring ECG, when the device is attached to the patient for a day and records heart function throughout the day. There is also such a type of ECG as stress ECG and transesophageal ECG. The latter is carried out in the case when a regular electrocardiogram turns out to be uninformative.
Treatment method
Treatment of pathology depends on individual signs of disease development
The asymptomatic course of the disease does not require any treatment. Left ventricular trabecula can hardly be called a disease in the traditional sense of the word; it is rather an anatomical feature. Additional chorda requires only observation and not treatment.
Treatment of left ventricular trabeculae may be necessary in the presence of complications and the occurrence of trabeculae against the background of connective tissue dysplasia. If the patient has various disorders of the cardiovascular system, the doctor will prescribe medication. Surgical removal of trabeculae is prescribed extremely rarely and only in severe cases.
Features of the treatment of pathology:
- Vitamin therapy. To maintain the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, a sufficient amount of vitamins B1, B2, PP is necessary. Vitamins can be taken orally or given by injection. As a rule, courses of vitamin therapy last at least a month and are repeated several times a year. Adequate supply of vitamins to a growing body is especially important.
- Preparations containing magnesium and potassium. These substances help normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system and improve the conduction of impulses along the myocardial fibers. Magnesium and potassium preparations are taken in courses in the dosage prescribed by the doctor. Such drugs include Magne B6, potassium orotate, Panangin. You should not take these drugs without a doctor's recommendation, as an overdose can cause a large number of side effects, especially in children.
- Drugs that improve metabolic processes in the body. Such drugs include L-carnitine, Elcar, Ubiquinone. They strengthen the body, improve the patient’s condition, increase appetite, and improve the cellular energy of the myocardium.
In addition to drug treatment, the doctor may prescribe a diet containing a minimum of cholesterol, as well as maintaining a daily routine, reducing physical activity and stress, sedatives, and hardening.
At the same time, physical activity is not always contraindicated, but it must be adequate to the patient’s condition.
For example, swimming and yoga can help strengthen your cardiovascular system in some cases. You should consult your doctor about playing sports.
Combating complications
Despite the fact that trabeculae in the cavity of the left ventricle do not pose a threat to the child’s health, with the wrong lifestyle they can go from a benign form (painless) to a malignant one (requiring regular use of medications). Therefore, when a disease is detected, doctors immediately determine prohibitions for the patient. These include:
- Extreme sports, sports career, active gymnastics, excessively active dancing, scuba diving.
- Unauthorized taking of medications. Each drug (even those not related to heart disease), its dosage, must be approved by a specialist. Many pharmacological drugs affect intravascular pressure and increase heart rate, which is unacceptable for this type of pathology.
- Intense physical and emotional stress.
In addition, the doctor issues a certificate prohibiting the child from participating in school physical education competitions and exempting him from certain types of exercises. He develops such a complex of activities so that the child’s additional trabecula of the left ventricle is trained and does not bother him in the future. This shows:
- Easy short run.
- Walking on a tightrope.
- Drill exercises.
- Jumping.
- Gymnastic procedures on a skipping rope, wall bars, bench, with a ball.
In addition to all this, a child with an additional chord will benefit from attending massage courses, eating right, going to slow dances, resting more often and not getting into stressful situations.
The best way to give birth to a healthy baby is to avoid factors that can negatively affect the development of the fetus (for the entire period of pregnancy). If the expectant mother has this disease, it is recommended to take it much more seriously. This way you can reduce the risk of an additional chord. If a child has already been born with such a pathology, you need to carefully monitor the baby’s well-being and listen to every medical recommendation so that the child grows and develops on par with his peers.