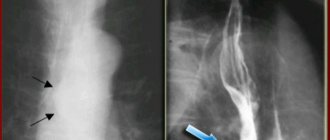
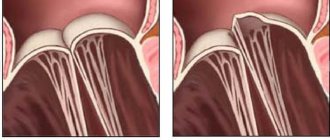
Symptoms of hypertrophy
In the early stages, there are no pronounced symptoms, while when the process is advanced, a whole variety of signs can be observed, among which experts identify:
- headache;
- pain in the left side of the chest, which can radiate to the back, left arm or neck;
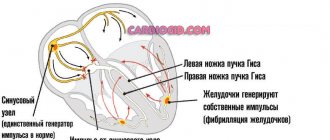
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- pressing pain in the chest;
- sleep disorders;
- cachexia;
- increased fatigue.
Also, people with a hypertrophied left atrium may experience periodic loss of consciousness, which is caused by a lack of oxygen. The same deficiency provokes shortness of breath. In the first stages of the disease, it can be observed in patients during sports or heavy physical activity, while in advanced cases it occurs in a state of complete rest.
Left atrial hypertrophy is dangerous because in the early stages it may not bother a person at all and may not cause him discomfort. The patient knows nothing about hypertrophy until it reaches significant proportions.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to severe, irreversible consequences that can result in death. Therefore, if you detect any signs, you need to contact a specialist as quickly as possible, because only he can help as effectively as possible.
In this case, the patient will retain his ability to work and will be able to enjoy a full life.
Enlargement of the left atrium cavity
Enlargement of the left atrium is not a separate disease. Doctors consider it as a secondary disease that occurs as a result of a number of pathological processes.
Doctors call this deviation hypertrophy. It occurs as a result of a violation of blood flow in the left side of the heart, a decrease in the contractile function of the myocardial muscle. Without timely treatment, pathology can lead to complex consequences.
Diseases are either congenital or acquired. Left atrial hypertrophy is no exception. If it is not hereditary, it develops gradually, depending on the factors that provoke such an anomaly. There are many reasons why the atrium may become enlarged.
The most common are the following:
- Excess body weight. This is one of the most common factors leading to left atrium enlargement at a young age. Obesity often provokes hypertrophy in children.
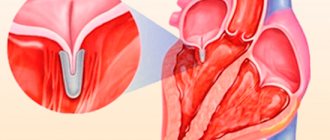
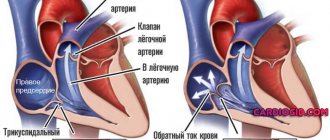
- Stenosis, mitral insufficiency. The mitral valve regulates blood flow between the two chambers of the heart (blood flows from the left atrium to the ventricle). Stenosis and mitral insufficiency can provoke hypertrophy. In the first case, due to the narrowing of the opening between the sections, the heart needs to exert more force to pump the required amount of biological fluid into the left ventricle. Hypertrophy occurs as a result of excessive stress. In the second option, the inability of the valve to close normally allows blood to flow back, which can provoke inflammation and, as a result, enlargement of the atrium.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The pathology is congenital in nature and is usually manifested by thickening of the left ventricle (sometimes the right).
- Hypertension. As a result of increased blood pressure on the walls of blood vessels, the load on the heart also increases. As a result, the atrium becomes enlarged.
- Constant stress, emotional instability. Such factors significantly increase the load on the organ, which leads to the gradual formation of pathology.
- Great physical activity. This reason most often provokes the disease in athletes. Excessive stress is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure in the arteries and, accordingly, increased work of the heart.
- Aortic stenosis. Since the aortic vessel is connected to the left ventricle, if the opening is narrowed, the organ exerts too much force to push out the next portion of blood.
- Lung diseases. Infectious diseases of the respiratory system, which reduce the functionality of the lungs, can lead to enlargement of the left atrium.
Hypertrophy may progress.
But the symptoms are not always pronounced. Therefore, it is very important that such a deviation is diagnosed on time. Otherwise, a myocardial infarction or stroke is possible.
The manifestations of the anomaly primarily depend on the degree of compaction of the septum and myocardium, its uniformity and symmetry.
In such cases, patients practically do not pay attention to this sign, since it does not interfere with normal life activities.
More pronounced manifestations of hypertrophy include:
- regular pain in the heart area;
- labored breathing;
- angina pectoris;
- sudden changes in blood pressure;
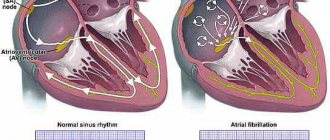
- atrial fibrillation;
- insomnia;
- frequent headaches;
- general weakness;
- very easy fatigue.
If the heart “fades”, fainting is possible. This manifestation is a consequence of insufficient nutrition of the heart muscle. At the beginning of the development of pathology, the patient may experience shortness of breath during heavy exertion. This symptom should not be ignored, as it can be a harbinger of complex illnesses.
Development mechanism
LA dilatation is not an independent process.
It is not considered a nosological unit. How does such a state form? Normally, cardiac structures function continuously, acting as a large pump. The release of blood is ensured by alternating synchronous contraction of all chambers of the heart.
Liquid connective tissue moves in one direction: from the upper to the ventricles, no reverse flow is observed.
As a result of congenital genetic defects, acquired sclerosis of active tissues (replacement of affected areas with scars), a long inflammatory period, etc., blood is retained in the left atrium longer than it should be. Or regurgitation is observed (return of liquid connective tissue from the ventricle).
Over a long period of time, the chamber becomes stretched and the normal dimensions of the organ are disrupted.
This leads to a decrease in release into the systemic circulation, and general and local hemodynamics decrease.
Removed tissues and systems suffer from a lack of oxygen and nutrients. The process of development of organ defects and functional failure begins.
Causes
Factors are always pathological. Some of them are brought to life by the patient himself.
Excessive exercise
Lead to the formation of the so-called athlete's heart. This is a combination of dilatation of several chambers with an increase in mass in the muscle layer.
- What is heart dilatation
Truncated options are possible. Both professionals and outdoor enthusiasts suffer. In principle, this is a relatively normal condition. The body adapts to changes.
But more often, gross asymmetry occurs, since physical activity and its mode are selected incorrectly. Inadequate loads result in dysfunction.
Any pathology of the mitral valve
Accompanied by reverse reflux of blood (regurgitation of the MV). Usually these are congenital malformations of the anatomical structure: prolapse, stenosis.
Slightly less often, the condition turns out to be secondary, acquired as a result of inflammatory pathologies, rheumatism and other similar ones, associated with gross tissue destruction over a long or short period of time (heart attack).
Burdened heredity
A predisposition to cardiac pathologies is transmitted. The more relatives suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system are present in the history, the higher the likelihood. At the same time, no one gives a guarantee of pathology.
Perinatal developmental disorders, genetic syndromes
They are formed at the time of the formation of cardiac structures. The latter are more often characterized by generalized disorders of many organs and systems.
Recovery is very difficult, and in some cases it is completely impossible.
- Left ventricular hypertrophy - signs on the ECG. Treatment of myocardial hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart
Arterial hypertension
It provokes an increase in the load on the heart and blood vessels, leading to a decrease in tissue elasticity and gross organic defects.
Classic anatomical changes in cardiac structures are left ventricular hypertrophy (proliferation of the muscle layer without increased activity), as well as dilatation of the corresponding atrium.
The guarantee of preventing such an outcome is determined by early treatment of the underlying disease with the use of antihypertensives and protectors.
Neoplastic processes in cardiac structures
Relatively rare, but possible. More often, tumors of this localization turn out to be benign, but this characteristic is very conditional: compression and a decrease in the intensity of the work of cardiac structures are observed. Dilatation of the left atrium chamber is a relatively late complication.
Long-term dangerous forms of arrhythmia
From fibrillation to atrial extrasystole. The development of the pathological process is associated not with the violation of the frequency of contractions itself, but with organic tissue defects.
Narrowing of the aorta
Congenital forms of deviation or an acquired process are possible.
It is characterized by insufficient release of blood into the main artery of the body. Hence the congestion in the ventricle.
At an advanced stage of the process, there is so much liquid connective tissue that it puts pressure on the atrium valve and eventually flows back into the previous chamber, stretching and increasing its volume.
This is a chain process that needs to be stopped at an early stage.
- Why does dilatation of the left ventricle of the heart occur?
Inflammatory pathologies of the heart
Usually the myocardium is affected, less often other structures. They are of infectious origin, and to a lesser extent autoimmune. Both options are dangerous and require hospital treatment.
“Bonus” are pathological factors of a subjective, controllable kind: smoking, consumption of alcoholic beverages, coffee, excessive stress on a long-term basis, drug addiction, improper treatment with certain drugs.
The causes of left atrium dilatation are eliminated by preventive methods: management of the underlying disease or elimination of an addiction as a priority.
A paradoxical phenomenon is often observed: the pathological process starts for a specific reason and aggravates itself.
Diagnostics
The examination of patients is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist, as necessary, a group of other specialists.
- What is dilatation of the left atrium cavity: causes, symptoms, treatment and prognosis
Approximate list of events:
- Oral questioning of the patient and collection of anamnestic data. It is necessary to establish many factors that would play a role.
- Measurement of blood pressure (possibly an increase or decrease), heart rate (tachycardia is typical, flowing in parallel with various types of arrhythmias).
- Daily monitoring. Registration of blood pressure levels for 24 hours. Used for early diagnosis.
- Electrocardiography. Plays the same role. Shows the degree of deviations from the cardiac structures.
- Echocardiography. Basic technique. It makes it possible to identify organic defects at first glance, determine their degree, and predict complications.
- MRI if there is a suspicion of a tumor process in the heart.
Stress tests are not performed due to the possible cessation of muscle function and sudden death.
Treatment
Mixed therapy. Conservative methods are used at an early stage, a combination of surgery and medication in the advanced phase of the pathological process.
The following medications are prescribed:
- Antiarrhythmic. Like Amiodarone, it is the safest. They are used to restore an adequate, correct heart rate.
- Antihypertensives if high blood pressure occurs. Enap, Diltiazem, Perindopril will do. The combinations are different.
- Diuretics to normalize the evacuation of fluid from the body.
- Cardiac glycosides. Stabilize myocardial contractility.
- Antithrombic drugs of various types.
Surgical intervention is aimed at stopping the root cause or installing a pacemaker for severe arrhythmia.
Excision of pathologically altered tissues against the background of tumor lesions is possible. Specific techniques are determined by a specialist based on the underlying disease.
The last resort if the heart is significantly changed is transplantation. However, this is not an easy undertaking.
In addition to the fact that finding an organ is almost impossible in the conditions of Russian reality, the operation requires the highest qualifications, which only a few have.
- Features of left atrium dilatation, types of pathology
During the treatment process, also during the recovery period, which lasts a lifetime, you need to minimize the amount of salt in the diet (6-7 grams), give up smoking, alcohol, and normalize physical activity (maximum: walking in good weather).
What can hypertrophy lead to?
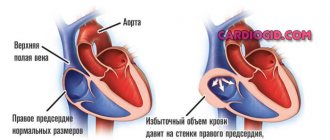
The disease cannot be ignored, because a significant enlargement of the ventricle can greatly change the structure and function of the heart. An enlarged ventricle may weaken and lose elasticity, increasing pressure in the heart. Hypertrophied tissue can also compress blood vessels and restrict blood flow directly to the heart muscle.
On the left is a normal heart, on the right is an enlarged ventricle
As a result of these changes, the following complications may occur:
- complete interruption of blood supply to the heart;
- inability of the heart to pump enough blood around the body (heart failure);
- abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia);
- irregular, fast heartbeat (atrial fibrillation);
- insufficient oxygen supply to the heart (coronary heart disease);
- enlargement of the aorta (dilatation of the aortic root);
- stroke;
- unexpected deterioration in cardiac function (sudden cardiac arrest);
- sudden loss of consciousness.
Hypertrophy is fraught with a significant deterioration in heart function
The consequences of hypertrophy can be called catastrophic for health, so if the patient has identified the reasons for the development of the disease, it is necessary to consult a cardiologist.
Degrees of dilatation
Another basis for classification is the degree of pathological abnormalities. Accordingly, they talk about 3 or 4 stages of disease development.
Lightweight
It is formed as a result of a genetic factor, intrauterine defects and acquired conditions.
It is characterized by a complete absence of a clinical picture, which makes diagnosis a matter of chance.
It is possible to identify the initial deformation of the organic plane using echocardiography. It doesn't take much qualification to state a fact.
Determining the root cause falls on the shoulders of the cardiologist and is carried out with the help of a group of measures.
Moderate dilatation
At this stage, the process is diagnosed much more often.
- What is heart dilatation
A bright nonspecific picture is typical: shortness of breath, chest pain, arrhythmias. These are common signs of any condition associated with impaired functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
However, the chances of early diagnosis are high, which is good news for the patient.
The prospects for a complete cure are already vague, but with a well-thought-out combination of therapy, the patient will not notice the difference. You can keep the process under complete control.
Marked dilatation of the left atrium
Considered extreme in some national classifications.
It is defined by a vivid clinical picture with a significant decrease in tolerance to physical activity, the inability to adequately work and perform household duties.
Organic defects are gross and are observed not only on the part of the heart; remote systems are also changed.
The prospects for a cure are minimal. At the same time, life expectancy during therapy rarely exceeds 3-4 years.
Therapeutic methods
Treatment of dilatation is necessary only in cases where the disease makes itself felt with characteristic symptoms. If there are no manifestations of pathology, and as a result of the diagnosis, no disorders in the cardiovascular system or other parts of the body are revealed, then regular examinations and consultations with a doctor are enough - such patients do not need anything else.
When deciphering diagnostic data has shown the presence of diseases that affect the occurrence of dilatation, it means that they need to be eliminated; this is the only way to improve the person’s condition. Sometimes dilatation of the atria occurs due to infectious diseases, leading to inflammatory processes in the muscle tissue of the organ and provoking changes in its chambers. In these situations, anti-infective treatment is needed, and the doctor also decides whether it is advisable to replace the valve. When high blood pressure levels become the culprit for the development of dilatation, then antihypertensive therapy is necessary. Endocrine disorders require the prescription of drugs that normalize hormone levels.
Medicines used:
- diuretics;
- beta blockers;
- antiarrhythmic drugs;
- ACE inhibitors;
- cardiac glycosides;
- antiplatelet agents.
The actions of doctors should be aimed not only at eliminating the causes of the disease, but also at reducing the risk of complications, of which there can be many. Sometimes the use of medications is not enough, in this situation doctors decide to install a pacemaker. With the help of this device it is possible to increase the systolic function of the ventricles, as well as to increase hemodynamic processes in the organ.
Possible complications
When the expansion of the atrium cavity does not stop, this leads to serious consequences, in particular, dilated cardiomyopathy, which is characterized by pathological disorders in the myocardial muscle tissue.
What complications may there be:
- attacks of arrhythmia that occur suddenly;
- failure of the main organ;
- atrial fibrillation;
- infectious processes in the fibers of the heart muscle;
- blood clots form in the lumen of the arteries, which impedes blood flow;
- mitral valve insufficiency;
- thromboembolism (closure of the lumen of a vessel by a detached blood clot).
The majority of such consequences become the reason for installing a pacemaker on the organ. In rare cases, it is necessary to completely transplant a donor heart into a patient - this is the only way to save his life.