What is pathology
Atrophy of the ventricle of the heart, what it is, is not known to everyone.
The left ventricle, which has a cone shape, with walls three times thicker than the walls of the right ventricle, is one of the four chambers of the heart. It begins a large circle of blood circulation, and, accordingly, nutrition of the whole body. Under the influence of certain factors, hypertrophy of the muscles of the organ occurs: thickening of the walls, loss of elasticity of the septum between the right and left ventricles, which leads to atrophy of the organ. The development mechanism is as follows. More blood begins to flow into the cavity of the left ventricle of the heart. Muscles overcome more resistance. Overload begins due to the resulting pressure and volume. Response to overload: lengthening, increasing muscle mass, increasing the total mass of the myocardium.
As muscles increase, they become denser and their need for oxygen increases. But the body is no longer able to provide the organ with the required volume. Oxygen starvation develops, further modification of the structure.
Types of atrophy
The disease has several types, regardless of the reasons for its development:
- Fat atrophy. Occurs against the background of lipid metabolism disorders, hypoxia, cardiovascular pathologies, alcohol intoxication or blood diseases.
- Dishormonal. When the hormonal system malfunctions. Often develops during menopause.
- Ischemic. Result of the coronary crisis. The condition is dangerous and provokes heart failure.
- Diffuse. Appears against the background of frequent inflammatory processes.
- Grainy. Provoking atrophy is a disorder of protein metabolism.
Left ventricular atrophy is a common occurrence in people who play sports professionally. Systematic physical activity and unbalanced nutrition lead to muscle wasting.
Causes of atrophy
Pathology develops for the following reasons:
- abnormalities of heart development;
- heredity;
- food and industrial poisoning;
- excessive physical activity;
- metabolic disease;
- anemia (low hemoglobin content in the blood);
- thyroid diseases;
- avitaminosis;
- myopathy (chronic progressive hereditary muscle disease associated with metabolic disorders in muscle tissue);
- stressful conditions;
- malnutrition (diet, fasting with lack of normal amount of protein food);
- obesity;
- alcohol abuse;
- cardiosclerosis (characterized by oxygen starvation of tissues, metabolic disorders).
- high blood pressure;
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (a hereditary disease in which the myocardium thickens);
- mitral valve stenosis (a disease characterized by narrowing of the left atrioventricular valve);
- aortic stenosis (during the disease, the passage of the aorta narrows, preventing the free flow of blood);
- pathologies of the respiratory system: lead to impaired lung function;
- cardiac ischemia;
- hypertension in late stages.
All of the above factors cause changes in the muscles of the left ventricle, which, in turn, causes organ dysfunction. Left ventricular atrophy is a dangerous disease that can result in death if not treated promptly.
Prevention
Treating left ventricular atrophy is extremely expensive and ineffective, so it is better to prevent it.
Prevention of the acquired form of the disease consists of the following rules:
- rejection of bad habits;
- playing sports;
- correction of diet;
- good sleep;
- prevention of stressful situations;
- elimination of excess body weight.
Atrophy of the left cardiac ventricle is a severe and incurable pathological process. Due to its development, a person may experience various complications that can be fatal. However, if you start a course of maintenance therapy in a timely manner, you can prolong your life. To improve the effect, drug treatment must be combined with compliance with the rules of prevention.
How is atrophy different from hypertrophy?
To understand why atrophy of the left ventricle of the heart is dangerous, it is necessary to understand the features of this disorder. Many people do not understand the differences between atrophy and hypertrophy, thinking that they are the same pathology. In reality, these are two completely different phenomena in which different changes occur.
Hypertrophy
With this process, thickening of the walls of the ventricle is observed, and the septum between the sections is modified and loses its elasticity. This happens due to increased blood flow, which increases the resistance of the muscle walls. This leads to overload of the ventricle with pressure and volume, followed by the development of a compensatory function. At the same time, the heart cells elongate, which increases the mass of the myocardium.
- What is heart dilatation
As the tissue increases in size, it becomes denser, requiring more oxygen. As a result, oxygen starvation begins and pathological changes in the cardiac structure are triggered.
Atrophy
What is left ventricular atrophy? In this case, there is a decrease in the ventricle, which causes a decrease in its functions, up to complete loss of capacity. A similar phenomenon also occurs due to oxygen starvation, when circulatory disorders provoke the development of cellular atrophy. As the disease progresses, ventricular function decreases significantly.
Causes
Changes in the functioning of the heart occur for several reasons related to sports activities. This:
- Frequent stress on the body due to training and preparation for serious competitions. Usually people, wanting to win, do not spare themselves and their bodies by exercising too much time. If we take into account not very good nutrition and lack of sleep and rest, then everything goes to the point that sooner or later the heart will begin to “protest” against this way of life. To prevent this, you should not torture yourself before the competition, exhausting yourself with back-breaking exercises without proper rest. Still, health is more important and should always come first. The healthiest and most resilient win, so it makes sense to take care of yourself before a serious event.
- Intense sports activities in physically unprepared people. If the body has not previously received such loads, then immediately excessive training can seriously damage the heart, since it will not cope with such rapid changes. The same applies when a person changes his sport and immediately begins to actively train in something in which he is still weak. To prevent overload on the heart, any vigorous activity should be started gradually, increasing the intensity.
- A combination of intense sports with strenuous work or other intellectual activities. A direct blow to the physical and mental areas of the human body can lead to malfunctions and even an emotional breakdown. The same applies to playing sports immediately after an infectious disease, such as tonsillitis, flu, etc.
Symptoms of pathology, complications
At the initial stage of development, there are usually no symptoms.
Important! The lack of timely diagnosis and treatment will lead to the steady progression of the pathological process, which will cause heart failure!
The atrophic process can develop over a long period of time: over several months or years. Symptoms will appear, gradually increasing. At the same time, a person feels:
- general weakness, increased fatigue;
- shortness of breath even with slight physical exertion;
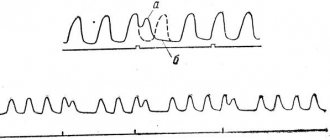
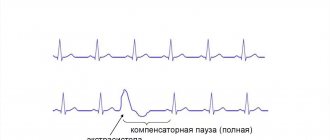
- moderate tachycardia (increased heart rate);
- dull, aching pain in the heart area;
- increased blood pressure;
- dry cough, worse at night, when lying down;
- pallor of the skin, swelling of the lower extremities;
- causeless muscle weakness.
Oxygen starvation, which occurs not only in the left ventricle, but also in the brain, leads to a disturbance in the psycho-emotional state. Headaches, sleep disturbances, memory disturbances, and mood swings develop.
Complications
Atrophy is more than dangerous: symptoms may not appear in both adults and children. This is the insidiousness of pathology. The organ responsible for the systemic circulation, with atrophic changes - dystrophy or hypertrophy - cannot function normally. The blood flow will be disrupted, which means that organs and tissues will not receive sufficient nutrients and oxygen. This will lead to other diseases. Without oxygen, the left ventricle cannot function. Against this background, acute heart failure (AHF) may develop.
Important! On average, heart failure is the cause of death in 90% of older people. Pathology is getting younger every year. Statistics show that the number of deaths from AHF among young people has increased.
It is impossible to remain inactive with such a pathology. If a person has at least one of the above symptoms, they should immediately visit a cardiologist for a diagnostic examination.
Danger to the patient's life
Atrophy of left ventricular tissue causes serious malfunctions associated with lack of nutrition. The degree of danger to humans depends on the severity of dystrophic changes. Often this pathological process leads to complications of the cardiovascular system such as:
- atherosclerotic changes;
- death;
- heart attack;
- angina pectoris;
- arrhythmia;
- pulmonary edema.
As the disease progresses, atrophied areas of muscle are replaced by connective tissue, which is presented in the form of scars. Blood flow in this place becomes difficult and against this background the heart’s ability to contract weakens.
Kinds
In modern medicine, there are several varieties of this pathology, depending on the reasons for its development:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy - signs on the ECG. Treatment of myocardial hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart
- Fat. The disease is provoked by impaired fat metabolism, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, alcohol poisoning, hypoxia, etc.
- Ischemic, occurring during a coronary crisis. This condition can cause heart failure.
- Dishormonal. It is observed when there are hormonal imbalances. Very often occurs in women during menopause.
- Diffuse. Occurs in the presence of an extensive inflammatory process.
- Grainy. The cause of the pathology is protein metabolism disorders.
Left ventricular atrophy often occurs in professional athletes. One of the main factors leading to the development of this disease is regular physical activity. The second reason is an unbalanced diet.
Permissible physical activity for myocardial dystrophy
Myocardial dystrophy requires partial rest so as not to overload the heart muscle.
After all, this can lead to serious complications and even death. But no one says that you need to give up sports completely. To treat the heart muscle, special physical therapy is provided, which allows you to develop the organ and thereby quickly treat it from the disease. At the same time, the “dosage” of such physical education should be prescribed on a strictly individual basis, since what is suitable for one person can be dangerous or even fatal for another. They use gymnastic exercises that exclude strength exercises, so as not to strain the heart. In addition to gymnastics, it is recommended to walk every day and gradually increase the walking time. The duration of gymnastics should not be more than half an hour, since patients need rest. The exercises used are those aimed at intense movements of the limbs. Breathing exercises are required to develop and train the diaphragm. All exercises must be done so that the load on parts of the body is distributed evenly.
In addition to therapeutic exercises, you can go on walking excursions, play volleyball, but no more than half an hour. Bathing and swimming will also be useful, but in moderate doses. In winter it is permissible to skate and ski. With myocardial dystrophy, it is advisable to spend the day actively, alternating physical activity with rest. One-time intense workouts that put the heart at risk by forcing it to work at full capacity should be avoided. Moderate body training will be beneficial if the disease has not taken an acute form, which requires only rest with limited movement.
Treatment of myocardial atrophy
Today, the main treatment strategy for atrophic changes in the myocardium is to prevent its further progression. Unfortunately, as practice has shown, there are currently no effective drugs that can restore myocardial cells. Trimetazidine (preductal) did not live up to the hopes placed on it. The effectiveness of mesidol and riboxia has not yet been proven. And according to a number of notes in the official medical literature, it can be considered controversial
Therefore, now all therapy comes down not to treating the disease muscle atrophy, but to correcting its consequences. The first known drugs that significantly stop the processes of dystrophy and subsequent atrophy of cardiomyocytes are diuretics and beta blockers. They have been successfully used for more than 50 years in different countries of the world. Currently used ACE inhibitors are able to stop the atrophy process only in a number of patients. Sartans and calcium blockers have been used quite successfully over the last decade. But this period is not enough to decide which treatment for heart muscle atrophy is most appropriate at a particular stage.
Dystrophy of the heart muscle and its causes
All causes of atrophy, muscular atrophy of the heart, like all other similar pathologies, are divided into two large groups.
Congenital causes. They consist in the disorganization of myocardial cells. First of all, this group includes congenital defects and cardiomyopathies. Although with heart defects, the connective tissue component of the myocardium and the valvular apparatus of the heart is primarily affected. Dystrophy of muscle cells is secondary. However, they are classified as congenital pathologies. Cardiomyopathies are largely unexplored, as doctors often deal with their consequences.
Acquired causes greatly prevail. They account for more than 2/3 of all cases of myocardial atrophy:
- Infections. Most often these are viral infections such as influenza and Coxsackie. The mechanism of dystrophic changes in the heart muscle is associated with the direct influence of viruses on myosymplast. Since these muscle cells have several nuclei, the probability of their survival after an “attack” of viruses is almost close to 100%. But after the virus has entered the cell, its genetic apparatus may be disrupted, which will affect its metabolism for the worse. And the more cells are affected, the greater the likelihood of developing dystrophy in the muscle. Among bacterial infections, scarlet fever is of greatest interest to medicine, since its causative agent has a genome similar to cardiomyocytes. As a result, the immune system can “attack” it.
- Chronic myocardial ischemia. This is the main reason among the adult population. In fact, IHD and its variant ischemic cardiomyopathy are nothing more than a disease of muscle atrophy. Only this atrophy affects the heart muscle.
- Intoxication. For example, alcohol abuse in just a few years can lead to significant degenerative changes in the myocardium.
Causes of atrophic changes in the heart
All the reasons why cardiac muscle dystrophy can develop can be divided into two categories - congenital and acquired. A direct change in the cellular structure of heart cells is observed in congenital cardiomyopathies, the origin of which has not yet been sufficiently studied.
There are also a number of pathological processes underlying the development of myocardial dystrophy, which arise in the process after birth. These include:
- Intoxication. Occurs as a result of acute or chronic poisoning of the body with tobacco, alcohol, drugs, medications, poor-quality food products, industrial substances and other toxic compounds that enter the body.
- Infection. Often, atrophy of the heart muscle occurs against the background of an acute viral (influenza, Coxsackie virus) or chronic infection. Especially often, heart complications result from constant inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx.
- IBS. It occurs as a result of chronic myocardial ischemia against the background of severe coronary atherosclerosis.
- Excessive overload (in athletes and people with physical labor). Appears as a result of constantly increased load on the heart, which it cannot cope with. This is expressed in impaired oxygen metabolism, including in cardiomyocytes.
- Deviations in the functioning of endocrine organs (thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism).
- Chronic anemia, vitamin deficiency, starvation.
- Metabolic disorders and obesity.
- Physical inactivity.
- Pathological processes in the liver and kidneys.
- Psychosomatic abnormalities.
- Disorders of the digestive system (liver cirrhosis, hepatitis, pancreatitis).