A headache in the back of the head is a very unpleasant phenomenon, causing a lot of inconvenience and often limiting performance. The causes of pain in the occipital part of the head can be very different, from diseases of the cervical spine to neuralgic pathologies.
If you don’t know why the back of your head hurts, then this article is for you. It collects the main causes and describes methods of treating headaches in the back of the head. In any case, you must remember: if you have a headache in the back of your head, you should not self-medicate, you need to seek medical help. Of course, we are not talking about isolated cases of pain in the occipital region. As a rule, they are caused by prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position, stress, extreme hunger, and also due to excessive consumption of foods with caffeine or chemical additives.
Causes of pain in the back of the head
A severe headache in the back of the head never occurs without a reason. It can be a signal of diseases:
- spine;
- vascular system;
- neurological system.
Depending on the cause of the headache in the back of the head, it can be of a different nature and be accompanied by certain clinical manifestations, which must be clearly described to the doctor.
Pain in the back of the head due to osteochondrosis
If the neck and back of the head hurt, the reasons may be the presence of a disease such as osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The disease manifests itself in the destruction of the discs of the cervical vertebrae, and pain appears constantly and is felt not only in the neck and back of the head, but also in the temples. They become more intense with head movements and may be accompanied by:
- tinnitus;
- nausea;
- coordination disorders;
- veil before the eyes and double vision.
More about osteochondrosis
Pain in the back of the head with hypertension
Hypertensive attacks are characterized by the appearance of bursting pain, which is accompanied by pulsation. They may appear when waking up after a night's sleep. In addition, it is observed:
- general weakness;
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased pain when trying to tilt your head;
- reduction of pain after sudden vomiting.
Pain in the back of the head with increased intracranial pressure
Increased intracranial pressure is characterized by:
- pressing, bursting pain in the occipital region or throughout the head;
- increased pain in bright light and loud sounds;
- heaviness in the head and pain in the eyeballs;
- vomiting, which does not reduce pain syndromes.
Pain in the back of the head due to cervical myositis
Inflammatory processes in the neck muscles caused by hypothermia or injury are characterized by pain symptoms that spread from the neck to the occipital, shoulder and interscapular areas. It appears when you move your head and is asymmetrical.
More about myositis
Pain in the back of the head due to occipital neuralgia
Neuralgia of the occipital nerve, resulting from hypothermia or accompanying osteochondrosis, is characterized by very strong shooting pains. They occur periodically, like attacks with any attempt to change the position of the head.
During rest, a slight pressing pain is felt in the occipital region.
Read more about occipital neuralgia
Pain in the back of the head due to vascular diseases
Spasms of the cranial arteries cause throbbing pain, which becomes stronger when trying to move the head and subsides somewhat at rest. The pain begins in the back of the head and eventually spreads to the frontal area. It is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the head and begins in the morning after waking up.
Diagnostics
First of all, you should contact a therapist and describe the disturbing symptoms. The doctor will immediately be able to:
- measure blood pressure, because such complaints may be the cause of the onset of a hypertensive crisis;
- determine the pulse rate and decide to take an electrocardiogram to exclude cardiac arrhythmias;
- palpate paravertebral points and spinous processes, identifying painful sensations in the spine.
If pressure and heart rate are within normal limits, and changes are detected in the spine, further diagnostic measures are necessary and consultation with a neurologist is necessary.
In the absence of signs of cardiovascular disorders, to accurately determine the causes of a headache in the back of the head and select effective remedies to eliminate it, you need to consult a neurologist. A doctor’s appointment includes clarification of the complaint, collection of a history of the development of the disease, as well as clarification of the presence of a hereditary predisposition to certain disorders. At the first consultation, the neurologist will set the level of pain on a visual analogue scale (VAS), check pain points in the paravertebral areas and along the peripheral nerve trunks. A detailed neurological examination is also required, during which the following is assessed:
- patient position;
- level of consciousness;
- presence of signs of injury;
- breathing rhythm;
- eye movement and pupil size;
- muscle tone of the face, tongue, pharynx;
- hearing level;
- stiff neck;
- the amount of muscle tone on both sides of the body;
- presence of limited active and passive movements;
- tendon reflexes;
- coordination of movements;
- presence of sensory disturbances.
The examination will allow us to make a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe those research methods that will most help establish the final diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Despite the fact that the main cause of headaches in the back of the head is diseases of the spine, changes in the brain itself cannot be ruled out. Therefore, electroencephalography (EEG) and even MRI of the brain are sometimes indicated.
X-ray of the cervical spine
X-ray of the cervical spine is a routine diagnostic procedure and does not require a long time. As a rule, the study itself lasts no more than 3-5 minutes.
X-rays of the cervical spine are taken in an upright position with the patient sitting or standing. This is necessary to obtain images under natural physiological stress.
A functional x-ray examination of the spine is often indicated. It allows you to register disturbances in the motor function of intervertebral discs at earlier stages of pathological processes, and to identify forward or backward displacement of the vertebrae. The essence of the study is to take radiographs of the cervical spine with maximum lateral tilt in the direct projection or maximum flexion and extension in the lateral projection.
Displacement of the vertebrae indicates a loss of the fixation ability of the disc, that is, the initial manifestations of osteochondrosis.
MRI
MRI diagnostics are carried out in specially organized rooms. No special preparation is required to carry it out. However, the research procedure itself will take more time than, for example, x-ray diagnostics. To do this, you will need to set aside about an hour in your schedule.
This study has become widespread due to its high information content and the possibility of making a diagnosis in the early stages of the disease. When examining the cervical spine, it is possible to assess the condition of the cervical vertebrae, intervertebral discs, adjacent soft tissues, nerves, blood vessels and the spinal cord. The area of study can be examined down to a millimeter, which helps identify pathology in the early stages. The changes revealed by this diagnostic method coincide with the X-ray ones: a decrease in the height of the vertebra and intervertebral foramina, changes in the intervertebral discs, protrusion and hernia.
Ultrasound of head and neck vessels
Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck is a common diagnostic method that does not require special preparation. It takes about 20 minutes and the result is given by the ultrasound doctor immediately after the procedure.
The method allows you to assess the condition of the inner wall of the vessel, the speed of blood flow and makes it possible to conduct functional tests. Most often it is used to identify developmental anomalies, the presence of atherosclerotic plaques leading to narrowing of their lumen, the presence of external compression, including intervertebral hernias or deformed vertebrae. Ultrasound results complement MRI.
Diagnosis of pain in the back of the head
If you suffer from constant or regular pain in the occipital region of the head, contact the CELT clinic. Our specialists will conduct the necessary research and find out the reason why you are experiencing pain. In order to become our patient, you do not need Moscow registration.
In addition to obtaining a history of the nature, timing and intensity of pain, diagnosis may include:
- examination by a doctor;
- blood pressure measurement and monitoring;
- ultrasonography;
- electroencephalography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- examination of the fundus by an ophthalmologist.
If there is a suspicion of a brain tumor, a consultation with a neurosurgeon will be required.
What to do if you have a headache in the back of your head
As you can see, there is a reason why you have a headache in the back of your head. And if you can deal with the cause of overwork or stress on your own, then other diseases are an urgent reason to consult a doctor. Timely diagnosis of the disease and adequate treatment will not only relieve you of pain, but also keep you healthy and active for many years.
It is better to start the examination with a visit to a therapist. Book a consultation with a doctor right now by calling our clinics' multi-line number 8 or using the online appointment form.
Administrators will select a convenient time and day for your appointment. You don’t need to take anything with you, we will give you everything disposable both for your appointment and for undergoing additional studies, such as tests or ultrasound of blood vessels. #Doctor therapist headache neurology
Prevention measures
Preventive measures will eliminate pain for a long time. The basic rules are:
- proper combination of rest and physical activity;
- morning exercises and exercise throughout the day;
- adjusting the diet (adding fresh vegetables and fruits);
- reducing the consumption of alcoholic beverages and tobacco.
See also: Difference in pressure readings on the right and left hands
Experts recommend contacting medical institutions for systematic pain localized only in the back of the head. In addition, it is recommended to conduct routine diagnostic testing to avoid the development of various pathological conditions and diseases.
Treatment of headaches with high blood pressure
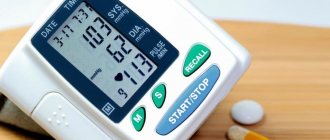
Treatment of headaches with high blood pressure is resorted to when diastolic pressure figures rise above 120 mmHg, or there is a sharp jump in blood pressure (pressure rises by 25% of the normal value and above). If there are problems with blood vessels, the headache will have a bursting, pulsating character, localized in the temples and back of the head. With nervous and physical stress, cephalalgia slowly increases and also subsides, and may be accompanied by nausea and dizziness. A sharp jump in blood pressure causes a severe bursting headache, which intensifies with any movement. With spasm of the cerebral arteries, the patient complains of “floaters before the eyes” and a dull pain in the head.
Treatment of headaches with high blood pressure always begins with measuring blood pressure. If the numbers are elevated, you should first bring the blood pressure back to normal, and then eliminate the headache with other drugs if it does not go away.
To normalize high blood pressure, the following means are used:
- calcium channel blockers - Cordafen, Nifedipine, Verapamil, Phenigidine, Corinfar, Felodipine;
- a new generation of selective beta blockers (reduce heart rate) - Metoprolol, Tenoric, Bisoprolol, Egilok;
- myotropic antispasmodics (prescribed at the beginning of the development of hypertension) - No-shpa, Dibazol, Magnesium sulfate, Papazol, Spazmalgon;
- diuretics (reduce blood pressure by reducing blood volume by removing water from the body with urine) - Lasix, Furosemide, Trifas;
- sartans (without affecting the heart, they reduce blood pressure) - Candesartan, Eprosartan, Irbesartan, Telmisartan;
- ACE inhibitors (dilate blood vessels, reduce blood pressure well) - Renitec, Enam, Captopril, Enalapril, Ramipril, Trandolapril;
- nitrates (sharply reduce blood pressure, used mainly for angina pectoris, myocardial infarction) - Cardiket, Sustak, Perlinganite, Erinit, Isoket;
- ganglion blockers (eliminate spasms in arterioles) - Phentolamine, Benzohexonium, Ebrantil.
If you don’t know how to relieve a headache with high blood pressure, when it has already returned to normal, then you can choose a drug from the list below, but you should first consult with your doctor.
The following will help you get rid of this cephalalgia:
- Ascopar;
- Acetylsalicylic acid;
- Has;
- Paracetamol;
- Solpadeine;
- Citramon.
When taking these medications, you should keep in mind that they should not be taken for more than 10-15 days in a row.
The text was checked by expert doctors: Head of the socio-psychological service of the Alkoklinik MC, psychologist Yu.P. Baranova, L.A. Serova, a psychiatrist-narcologist.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 798-30-80
Call! We work around the clock!
Why is cervical osteochondrosis accompanied by headaches and dizziness?
Headaches are a very common complaint with cervical osteochondrosis. It is often accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness, poor coordination, and blurred vision. Let's consider how changes in the spinal column during cervical osteochondrosis lead to similar symptoms.
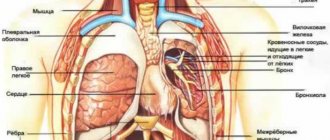
In the transverse processes from the VI to II cervical vertebrae there are canals through which the vertebral arteries pass, supplying blood to many parts of the brain and the so-called “Frank’s nerve”. Due to degenerative changes in the joints of the spine and directly in the vertebrae, the formation of osteophytes (bone growths) occurs, which leads to a narrowing of the spinal canal and compression of elements of the neurovascular system.
Osteophytes directed to the muscles irritate them, this causes a reflex muscle spasm, which leads to compression of the intervertebral discs, aggravating the course of the disease. Osteophytes, irritating the nerve roots at the exit of the spinal column, cause pain and spasms, the localization of which depends on the affected area.
Osteophytes directed to the canal of the transverse processes irritate Frank's sympathetic nerve, which leads to spasm of the vertebral artery, and also mechanically compress this artery, provoking a violation of cerebral circulation.
An acute disturbance of cerebral hemodynamics (brain circulation) leads to the development of an ischemic attack of the brain, which leads to the appearance of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis such as dizziness, nausea, headache, loss of coordination, and blurred vision.
Another reason for compression of the Frank nerve and the vertebral artery is displacement of the disc in the posterolateral and lateral directions, protrusion of the disc into the intervertebral canal during a hernia or protrusion (protrusion of the disc without violating its integrity).
The cause of compression of the nervous and vascular structures in the cervical spine can also be subluxation of the cervical vertebrae, their confusion relative to their natural position.
In addition, muscle spasm caused by psycho-emotional fatigue, excessive physical exertion or an uncomfortable position during sleep also leads to poor circulation in the cervical region and, as a consequence, headaches and dizziness.