October 10, 2021
Anemia is a decrease in hemoglobin content and/or a decrease in the number of red blood cells per unit volume of blood, leading to a decrease in oxygen supply to tissues
What is anemia?
Anemia is a decrease in hemoglobin content and/or a decrease in the number of red blood cells per unit volume of blood, leading to a decrease in the supply of oxygen to tissues. The diagnosis of anemia is made when hemoglobin decreases below 130 g/l in men and below 115 g/l in women.
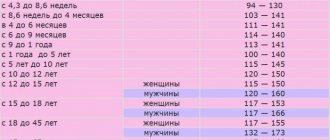
In children, the age of the child is taken into account when diagnosing anemia. Anemia is classified depending on the cause and mechanisms of occurrence, as well as by color index. The severity depends on the decrease in hemoglobin levels in the blood and is divided into: mild, moderate and severe.
In the initial stages of the disease, a person feels constant fatigue and decreased performance. If you perform a laboratory blood test with these symptoms, it will determine a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells. low hemoglobin is a very common ailment that occurs in both adults and children. This phenomenon can develop for a number of reasons and is a serious disease that must be treated. Otherwise, anemia can cause significant damage to health.
Symptoms of low hemoglobin
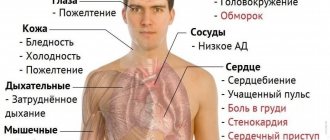
Although different types of anemia have different causes, their symptoms are very similar. Here are the frequent complaints of patients with low hemoglobin, that is, with iron deficiency anemia: fatigue, weakness, fatigue, dizziness, pallor, headache, feeling of cold, numbness of the limbs, shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air, increased heart rate, chest pain.
Most often, anemia manifests itself as pale skin, often with moderate yellowness, weakness and fatigue, and sometimes with decreased concentration. Shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat appear. You can also notice external signs of anemia: a person looks pale and lethargic, he exhibits some “oddities” in behavior: a desire arises to eat chalk, he begins to like unpleasant odors.
In older people, angina attacks may occur and become more frequent, and in young women, menstrual irregularities may occur. The usual explanations for this are: “tired”, “stress in the family and at work”, “lack of sleep”, “overworked”. Meanwhile, quite often these are signs of anemia.
Is it dangerous to exceed the norm?
In some pathologies, the body begins to intensively produce hemoglobin. If the norm is significantly exceeded, the composition of the blood changes and the risk of blood clots increases. This is fraught with blockage of veins, impaired circulation in the extremities, and often causes cardiac ischemia or cerebral stroke. Possible reasons include:
- diabetes;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- intestinal obstruction.
For women, a hemoglobin level above 150 g/l is considered dangerous. A disorder can be suspected by characteristic symptoms: high blood pressure, pale skin on the fingertips, frequent urination, joint pain.
Why does the body need hemoglobin?
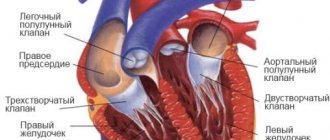
Hemoglobin provides oxygen transport. In the capillaries of the lungs, a maximum of four oxygen molecules bind to one oxygen molecule and form oxyhemoglobin. Then, in the blood stream, red blood cells deliver this ligament to organs and tissues. Here, the oxygen necessary for oxidative processes is freed from bonding with hemoglobin.
Iron is necessary for the normal functioning of the human immune system. A lack of this microelement can lead to problems with potency in men and disrupt the menstrual cycle in women. Low hemoglobin levels can also warn of other serious diseases.
Signs of iron deficiency in the body may include loss of energy, depression, hair loss and dry skin, drowsiness and irritability. However, to determine true anemia and replenish iron deficiency, it is necessary to conduct a detailed blood test.
At risk are vegetarians and fans of strict diets, teenagers during hormonal changes in the body, and child athletes who do not take additional vitamin and mineral complexes. If pregnant women do not take special multivitamins, they are also at risk of developing anemia.
The doctor reminds you that you should not buy drugs to replenish hemoglobin and ferritin reserves at the pharmacy yourself. They are prescribed only by doctors. In addition, the effect of the drugs begins only after six months and therefore the course of treatment cannot be interrupted.
Development of anemia in women
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells. Its main function is to deliver oxygen molecules to tissues and internal organs, remove carbon dioxide and toxic compounds. An indicator of 117–120 g/l in middle-aged women is considered normal for life support. But for various reasons, a violation of healthy levels occurs:
- diseases of the urinary system;
- hidden bleeding;
- malignant neoplasms;
- strict diets or fasting;
- monthly menstruation;
- blood loss due to injury;
- bone marrow pathologies.
Anemia in women occurs due to problems with hematopoiesis and impaired iron-binding ability of the blood. Hemoglobin drops during pregnancy, after childbirth or major surgery. Depending on the severity, there are several stages of the disease:
- Easy. It is characterized by a drop to 90 g/l, does not require hospitalization, and is easily corrected by changing the diet.
- Average. Hemoglobin drops to 70 g/l, health problems and exacerbation of chronic diseases are observed.
- Heavy. The indicator drops below 70 g/l, the patient requires drug treatment in a hospital.
The main signs of anemia in women that require additional diagnostics:
- chronic fatigue, irritability, muscle weakness;
- low-grade fever not higher than 37.3° C for a long time;
- tachycardia;
- frequent ARVI;
- dizziness;
- pressure changes.
The lower the hemoglobin level, the more severe the symptoms. With chronic anemia, women experience pale and bluish skin, shortness of breath when walking or climbing stairs. In 90% of patients, low blood pressure and digestive problems are detected.
Important! During menstruation, hemoglobin levels can drop sharply by 30 units. But with proper nutrition and the absence of chronic diseases, it recovers within 7–10 days without consequences.
Treatment and medications for low hemoglobin
Of course, treatment of anemia always includes the prescription of medications. It is impossible to eliminate iron deficiency anemia without iron supplements, only with a diet that includes a lot of iron. The absorption of iron from food is limited, its maximum is 2.5 mg/day. From medicinal preparations, iron is absorbed 15-20 times more.
However, the food must be complete and contain a sufficient amount of well-absorbed iron and protein. It is better to take iron supplements together with ascorbic acid. The latter improves the absorption of iron in the intestines. Since food significantly reduces the absorption of inorganic iron, taking the tablets before meals is more effective.
There are a wide variety of iron supplements. Experience has shown that organic salts of ferric iron and iron compounds with various organic radicals are most easily absorbed by the body and do not cause side effects. Such drugs are safer, they have less risk of overdose and poisoning than coarser inorganic salts. The gums and teeth do not darken, there is no heaviness in the stomach, and quite rarely there is a need to discontinue the drug.
Iron supplements
Now there are many medicines on the market that can be taken orally: coated tablets, for example Sorbifer Durules, chewable tablets Maltofer and Ferrum Lek, Actiferrin drops, Ferrum Lek and Actiferrin syrups for children, Actiferrin and Maltofer drops for infants, there are also injectable forms : Ferrum Lek, at the moment they are used strictly under the control of blood tests.
During pregnancy, it is especially necessary to carefully monitor the hemoglobin level in the blood. For pregnant and lactating women, there are special forms: chewable tablets Maltofer Fol, long-acting tablets coated with Tardiferon, which contain not only iron salts, but also folic acid, which is necessary during pregnancy in higher doses. Depending on the age of the child, a drop form or syrup (Aktiferrin, Maltofer, Ferrum lek) is selected and treatment is carried out.
Iron deficiency anemia during pregnancy
When carrying a child, a woman's body undergoes hormonal changes and the total blood volume increases. Doctors calculated what level of hemoglobin is considered critical for the expectant mother:
- mild anemia with a reading from 90 to 110 g/l;
- average at 80–90 g/l;
- heavy – below 80 g/l.
At risk are women with multiple pregnancies, patients with severe toxicosis or kidney disease. The interval between previous births and conception of less than 2 years increases the risk of anemia.
The main danger of critically low hemoglobin during pregnancy is disruption of embryo development. The child’s brain and nervous system experience oxygen starvation and lack of nutrients. There is a risk of congenital pathologies and anomalies, cerebral palsy. Therefore, gynecologists do not recommend refusing regular tests, offer vitamin complexes, and prohibit strict diets unless necessary.
Preparation and delivery of glycated hemoglobin analysis
Analysis for glycated hemoglobin does not require special preparation. There is no need to donate blood on an empty stomach. Before blood sampling, the patient does not need to limit himself to drinks or refrain from physical or emotional stress. It will not affect the results of the study and taking medications (except for drugs that reduce blood glucose levels).
The test is more reliable than a blood sugar test or a “load” glucose tolerance test. The analysis will reflect the concentration of glycated hemoglobin accumulated over three months. The form that the patient receives will indicate the results of the study and the norm of glycated hemoglobin. The interpretation of the test results at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out by an experienced endocrinologist.
Normal blood protein level
Blood counts must comply with generally accepted standards. The hemoglobin level may vary throughout life. So, a liter of a man’s blood contains 130-160 g of hemoglobin, for women this figure is 120-155 g. And when the norm turns out to be lower or higher, this affects the well-being of both young and old people. And depending on the results of the analysis, this display should be lowered or increased.
The reasons why hemoglobin drops can be very different. This may happen if:
- the person has lost a large amount of blood;
- his diet is monotonous and incomplete;
- he abuses alcohol;
- suffers from an illness such as chronic enteritis or various infectious diseases;
- underwent long-term treatment with droppers, etc.
Diagnostics
If the symptoms described above appear, especially if this is accompanied by the presence of factors predisposing to a decrease in hemoglobin, you should take a general blood test and consult a physician with its results. To confirm anemia, a repeat clinical blood test is usually prescribed. This eliminates the possibility of mistakes being made in the laboratory.
If a decrease in hemoglobin levels is confirmed, treatment for anemia is immediately prescribed. And in parallel with this, a comprehensive examination of the body is carried out in order to identify the causes of its development. This is especially important in cases where there are no obvious prerequisites for this, for example, having undergone surgery in the recent past, injuries with large blood loss, etc. For this, the following may be prescribed:
- blood chemistry;
- stool test for occult blood;
- colonoscopy;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys.
What level is considered lethal?
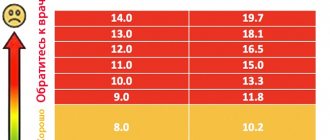
Experts believe that the lethal level of hemoglobin for an adult is below 70 g/l. In fact, the patient dies not from a lack of protein, but from the development of complications due to oxygen starvation:
- metabolic disease;
- drop in immune defense;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases of the kidneys, liver, intestinal tract;
- severe arrhythmia or tachycardia.
With acute and massive blood loss and a drop in hemoglobin below 38 g/l, the patient dies from cerebral hypoxia. But with a slow decrease in iron-containing protein, symptoms appear gradually, the body adapts to the changes. Therefore, in medical practice there are many cases where a person with anemia at a level of 40–50 g/l works productively and leads a relatively active lifestyle. This is due to the individual characteristics of the patient’s cardiovascular and nervous system, his age and health.
What else is worth checking?
Ferritin. This is a protein complex that shows the level of iron reserves in the body; it is responsible for both the storage and release of iron.
- The optimal ferritin range is 50-80 nanograms per milliliter. The figure usually roughly corresponds to our weight,” says Dobretsova. — If the indicator fluctuates between 30-40, then this is a reason for concern, even with a normal hemoglobin level. This indicator is especially recommended for those who take anti-inflammatory or painkillers for persistent headaches, back pain and others. The fact is that these medications can cause erosion of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines and, accordingly, bleeding. Taking antacids (Maalox, for example) can affect the absorption of iron, so such patients should also undergo such testing regularly. Vegetarians, people with frequent bleeding, and those taking blood-thinning medications are also at risk. All of them need to donate blood for this indicator, even in the absence of symptoms of anemia.
Excess ferritin is also dangerous - especially with liver diseases, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. When there is a lot of ferritin, the vessels harden and become fragile. This means that the aging of the body accelerates.
Article on the topic
Iron in the blood. 10 foods that will increase hemoglobin in winter
Increased and decreased levels of glycated hemoglobin
An increased level of glycated hemoglobin indicates a long-term gradual but steady increase in the concentration of glucose in a person’s blood. These data do not always indicate the development of diabetes mellitus. Carbohydrate metabolism may be impaired as a result of impaired glucose tolerance. The results will be incorrect if the tests are performed incorrectly (after meals, not on an empty stomach).
A glycated hemoglobin content reduced to 4% indicates a low level of glucose in the blood - hypoglycemia in the presence of tumors (pancreatic insulinoma), genetic diseases (hereditary glucose intolerance). The level of glycated hemoglobin decreases with inadequate use of drugs that reduce blood glucose levels, a low-carbohydrate diet, and heavy physical activity leading to exhaustion of the body. If the level of glycated hemoglobin is increased or decreased, consult an endocrinologist at the Yusupov Hospital, who will conduct a comprehensive examination and prescribe additional diagnostic tests.