Low hemoglobin is not an independent disease. It is the result of an underlying disease, therefore, if anemia is detected in a patient, the doctor is obliged to prescribe a comprehensive examination.
Concepts of pseudoanemia and hidden anemia
Pseudoanemia is the entry of tissue fluid into the bloodstream during the resorption of edema.
Hidden anemia is the result of the loss of a significant part of the fluid composition of the blood due to dehydration (can be caused by diarrhea, vomiting, hyperhidrosis). In this situation, the blood begins to thicken, so laboratory analysis shows that the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin is normal, even if this is not the case.
Severity of anemia
Based on severity, anemia is classified into:
- light. Hemoglobin level is more than 100 g/l, erythrocytes - more than 3 T/l;
- average Hemoglobin level from 66 to 100 g/l, erythrocytes - from 2 to 3 T/l;
- heavy. Hemoglobin level is less than 66 g/l.
Classification of anemia
All anemias manifest themselves differently. Taking into account the cause of the pathological condition and its symptoms, there are four main types:
- posthemorrhagic anemia (caused by chronic/acute blood loss);
- hemolytic anemia (develops due to the destruction of red blood cells). This group includes hereditary hemolytic anemias: - with a lack of glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase; - thalassemia; - sickle cell; — Minkowski-Shoffar;
- deficiency anemia (caused by a deficiency of microelements/vitamins/iron, that is, any elements that play an important role in the process of hematopoiesis);
- hypoplastic anemia (results from impaired hematopoiesis in the bone marrow, the most dangerous form).
According to the color indicator of blood, anemia can be:
- normochromic (hemoglobin is normal). This group includes hemolytic and posthemorrhagic anemia;
- hyperchromic (hemoglobin increased). These include folate deficiency and B12 deficiency anemia;
- hypochromic (hemoglobin is low). This refers to thalassemia, iron deficiency and chronic posthemorrhagic anemia.
Based on the diameter of red blood cells, anemia can be:
- normocytic (almost all hemolytic and acute posthemorrhagic anemia);
- megaloblastic (B12-deficiency anemia);
- macrocytic (folate deficiency, hemolytic disease of the newborn);
- microcytic (chronic posthemorrhagic anemia).
Based on the iron content in the blood serum, anemia is divided into:
- normosideremic (acute posthemorrhagic anemia);
- hyposideremic (chronic posthemorrhagic and iron deficiency anemia, thalassemia);
- hypersideremic (hemolytic and B12-deficiency anemia).
Why is hemoglobin needed in the blood and what does iron have to do with it?
Hemoglobin is a special complex protein that is formed in red blood cells when iron atoms enter there. It is hemoglobin that colors blood red. It is entrusted with the most important mission: it transports oxygen from the lungs to organs and tissues. And vice versa: it transports carbon dioxide back to the lungs to be removed from the body. This important protein is also involved in DNA synthesis, maintaining acid-base balance, and organizing proper metabolism.
This is why low hemoglobin is so dangerous: it reduces the efficiency of all internal organs and systems, the vitality and emotional state of a person. And therefore it must be increased to normal.
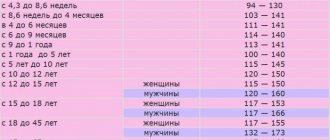
Normal hemoglobin levels in men, women and children
The level of hemoglobin in a person’s blood depends on gender, age and various physiological characteristics of the body. In men, hemoglobin is normal at values of 135–160 g/l. For women, 120–140 g/l are allowed. In pregnant women, the level of hemoglobin decreases noticeably - up to 110 g/l.
Hemoglobin standards for children vary significantly depending on age. The maximum protein level in newborns in the first month of life is from 140 to 200 g/l. Then it declines quite quickly. In the first six months, the norm is considered to be from 90.5 to 140 g/l. In children under 18 years of age, hemoglobin should be in the range of 110–150 g/l, and then equal to the norms of adults.
How to decipher the units of measurement of hemoglobin in the blood?
Hemoglobin is measured in grams per liter (g/L) or grams per deciliter, i.e. 10 liters (g/dL). To convert g/dl to g/l, simply multiply the first figure by 10.
The level of hemoglobin in the blood is influenced by both the innate characteristics of the body and the person’s lifestyle: level of physical activity, environment, type of diet, and the presence of bad habits.
Why does hemoglobin fall?
Hemoglobin cannot decrease, much less drop sharply, without reason. They can be serious illnesses or situations that cause blood loss: operations, injuries, wounds, internal and external bleeding. In women, a short-term decrease in protein is possible during menstruation, which lasts 5 days or more. The most common causes are lack of iron, folic acid and vitamin B12. However, low hemoglobin can also be a consequence of serious pathologies.
Causes of low hemoglobin:
- failure of the endocrine system;
- gastrointestinal diseases, intestinal pathologies;
- kidney disease;
- problems with the circulatory system;
- pneumonia, tuberculosis, hepatitis and other serious diseases;
- gastritis and neoplasms in the digestive organs;
- oncological diseases;
- exhausting long-term diets, unhealthy diet;
- vitamin deficiency and lack of vitamins and minerals;
- severe stress or prolonged depression;
- multiple pregnancy.
As you can see, the causes of low hemoglobin can be extremely serious and dangerous to health, and therefore this indicator must be monitored regularly and, if necessary, quickly increased.
How to find out without tests whether you have low hemoglobin: symptoms of deficiency
Many people are accustomed to ignoring a decrease in hemoglobin. Often, even from doctors, you can hear the phrase: “I have lived with low hemoglobin all my life, and nothing.” However, this does not mean that there is no need to look for the cause of the decrease in hemoglobin and eliminate it.
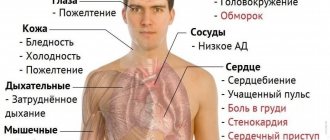
A low level of hemoglobin in the blood gives very specific symptoms, so even a layman can notice them. Here are some of the most common signs of its decline.
Signs of low hemoglobin:
- constant feeling of fatigue, drowsiness, fatigue;
- shortness of breath during physical exertion and normal climbing of stairs;
- regular headaches;
- low blood pressure;
- dry and brittle nails;
- dryness and active hair loss;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pale dry skin, possible peeling;
- tinnitus and dizziness;
- decreased appetite or perverted taste preferences: desire to eat chalk, raw dough or meat, smell paint or gasoline;
- muscle pain, freezing hands and feet;
- regular menstrual irregularities in women;
- decreased potency in men;
- frequent colds and viral diseases.
These symptoms, especially if there are several of them and they are observed for a long time, indicate that the hemoglobin in the blood is already quite reduced. In severe cases, the person may even lose consciousness. This means that you need to look for a solution and take action quickly.
What does low and high hemoglobin levels mean?
When the amount of hemoglobin decreases, a person develops anemia. The main reason for this is considered to be iron deficiency.
Photo: istockphoto.com
Anemia can also be associated with a deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid.
In addition, a decrease in hemoglobin levels can be caused by premature death of red blood cells and an increase in the rate of their destruction. This condition is observed in some immune disorders, long-term infectious diseases, as a result of exposure to drugs and chemicals of oxidative action, poisons, burns and frostbite, infectious factors, etc.
Finger on the pulse: what should be the heart rate at different ages
An increase in hemoglobin above normal may indicate dehydration or a high number of red blood cells. Increased hemoglobin is observed in congenital and acquired heart defects, lung diseases, and some cancers. Also, the level may be higher than normal after physical exercise and in general among residents of high mountains, which is associated with a compensation reaction: high mountain air is poor in oxygen, and in this way the body increases its content in the blood.
When to donate blood for hemoglobin
The reason to consult a physician or hematologist and take a blood test for hemoglobin level may be the detection of the above symptoms - one or more, a serious deterioration in health after an illness, significant blood loss due to injury or during surgery, adherence to a strict diet, an identified disease blood from close relatives, pregnancy.
A slight decrease may not be noticeable to humans. To prevent changes in hemoglobin levels from becoming a surprise, it is better to keep the situation under control: get your blood tested 1-2 times a year, and if necessary, consult a hematologist.
Prevention of anemia
To prevent the development of anemia, it is necessary:
- avoid contact with poisons and toxic substances;
- refuse to visit areas contaminated with radiation;
- do not contact with sources of ionizing radiation;
- do not take medications uncontrollably;
- to harden;
- eat right, include meat, greens, fruits and vegetables in your daily diet;
- spend more time outdoors.
Secondary prevention of low hemoglobin includes:
- blood test once a year;
- seeking qualified medical help in the event of acute infectious and viral diseases;
- annual medical examinations;
- pregnancy planning (for women).
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
What is anemia and how to diagnose it
Anemia (or anemia) is a decrease in hemoglobin and a decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood. This condition leads to the fact that organs and tissues do not receive the required amount of oxygen, metabolic processes and the general well-being of a person worsen. The first symptoms may be fatigue, shortness of breath, loss of appetite, dry skin, brittle hair and nails and other signs that are not always immediately linked into a single picture.
This is why it is extremely difficult to diagnose anemia on your own, and it is impossible to do this based only on laboratory test results. To make a diagnosis, doctors not only look at the level of hemoglobin and iron, but also check the level of cholesterol, glucose, creatinine, uric acid and electrolytes, assess the general condition of the patient and his internal organs, and conduct a comprehensive diagnosis.
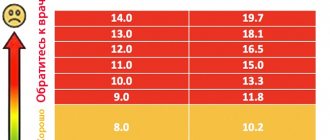
Severity of anemia:
- Mild anemia:
the level of hemoglobin in the blood is less than normal, but more than 100 g/l. The symptoms are subtle, so a person rarely turns to specialists at this stage of the disease. - Moderate anemia:
hemoglobin level in the blood is from 66 to 100 g/l. Frequent dizziness, nausea, drowsiness appear, dryness and cracks in the skin become noticeable. - Severe anemia:
hemoglobin level in the blood is less than 66 g/l. Critical condition, clouding and loss of consciousness, cold hands, fainting. Emergency hospitalization is required as there is a serious threat to life.
However, it is worth consulting at least with a therapist when the indicator drops below 120 g/l in women and below 135 g/l in men, without waiting for the condition to worsen.
How dangerous is anemia for humans?
This disease can be considered both dangerous and relatively harmless at the same time. On the one hand, mild anemia occurs quite often and can be treated without problems. On the other hand, long-term iron deficiency and low hemoglobin levels place a serious burden on the body. Severe anemia can have serious consequences:
- malfunctions of the kidneys, liver and other internal organs;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- cognitive impairment;
- increased risk of falls and, as a result, injuries and fractures;
- oxygen starvation (hypoxia), risk of myocardial infarction and stroke;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- deterioration of the reproductive system;
- anemic coma or death.
However, there is no need to panic. Pathologies and complications tend to develop if hemoglobin is greatly reduced for several years. Regular monitoring and testing of tests 1-2 times a year will be sufficient prevention and will help to quickly identify the problem and begin treatment.
It is important for pregnant women and young children to monitor the level of hemoglobin in the blood and prevent it from decreasing. Otherwise, there is a risk of pregnancy complications, premature birth and impaired fetal development - a malfunction of the brain, nervous and respiratory systems. In young children, a lack of hemoglobin can cause delayed intellectual development.
Reduced hemoglobin
The first symptoms of low hemoglobin are general weakness, constant drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness and headaches, low blood pressure, and irregular heartbeat. In some cases, the patient faints.
If the amount of protein decreases due to lack of iron, then the patient experiences dystrophic symptoms:
- hair and nails become brittle and grow poorly;
- microcracks appear in the corners of the mouth;
- the skin becomes dry;
- Possible hair loss.
In some cases, the patient's sense of taste and smell are impaired.
Most often, reduced hemoglobin is a sign of some disease. The most common ones are:
- blood loss;
- iron deficiency anemia in chronic form;
- thinning of the gastric mucosa;
- dysbiosis, chronic intestinal inflammation;
- iron deficiency anemia that occurs in the postoperative period;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- lupus;
- glomerulonephritis;
- long-term course of infectious diseases;
- malignant tumors, especially of the digestive system;
- malignant blood pathologies.
How to increase hemoglobin
It is quite difficult to quickly increase hemoglobin levels. This process usually takes about a month. You should not assume that self-prescribed vitamins or increased nutrition with meat will work miracles.
The most important thing in the process of normalizing hemoglobin is not to throw iron into the body, but to look for the causes of the malaise. It is important to promptly and correctly diagnose the disease that causes a decrease in hemoglobin, and work with it first. In case of severe blood loss or blood diseases, the patient is given a transfusion of blood or its individual components. This helps replenish its volume.
And already in combination with professional treatment, taking iron-containing medications and adjusting the diet will give a good effect, help avoid complications and improve the patient’s condition.
Important:
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to undergo a medical examination, do a blood test and obtain consultations from all specialized doctors, depending on the diagnosis. Self-medication is unacceptable. All procedures and prescriptions must be agreed with a doctor and regularly monitored by him.
And to prevent iron deficiency and decrease in hemoglobin, it is recommended to adjust your diet and include iron-containing foods. Approximate norms for iron consumption per day are 10–12 mg for men and 20–30 mg for women. More precise figures depend on the person's condition.
Treatment of anemia in children and adults
To get rid of the symptoms of anemia, you need to eliminate the factor that provoked the decrease in hemoglobin. So, if the pathological condition is associated with the presence of parasites in the body, you need to get rid of them, if with poor nutrition, start following a diet, if with a malignant/benign tumor, it should be removed.
In other words, treatment of low hemoglobin in men, women and children may be conservative or require specialized surgical procedures. Usually, in order to improve the condition of patients and reduce the severity of negative symptoms, doctors adhere to the following therapeutic regimen:
- drugs are prescribed that can compensate for the resulting deficiency - B12 for B12-deficiency anemia, iron for iron deficiency, B9 for folate deficiency, etc.;
- normalize the level of red blood cells. This can be accomplished by transfusion of red blood cells or washing of red blood cells. However, these measures when providing assistance to people with low hemoglobin levels are extreme and are carried out only if the resulting disease is life-threatening.
Treatment of acute and chronic posthemorrhagic anemia
Treatment of the acute form of posthemorrhagic anemia is carried out in a hospital or hematology clinic
. The medications prescribed to the patient help normalize the amount of blood and the level of formed elements, and are also aimed at preventing relapses of the disease. Taking into account the amount of blood lost, the patient may need a transfusion, the introduction of blood substitutes or red blood cells.
As for the chronic form of this type of anemia, it is impossible to get rid of its symptoms without eliminating the cause. After the factor that provoked the pathological condition has been eliminated, the patient will be prescribed a diet that includes eating foods rich in iron. Medicines that can be used are Sorbifer Durules, Ferrum-Lek, vitamins B12 and B9, etc.
Treatment of sickle cell anemia
The main goal of therapeutic measures when it comes to a patient with sickle cell anemia is to prevent the development of hemolytic crises. To do this, the patient must avoid being in places with low oxygen levels. In parallel, blood substitutes and red blood cell infusions can be used.
Elimination of iron deficiency anemia
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia includes eating foods rich in iron and treating existing gastrointestinal diseases. The patient should regularly eat:
- cheeses;
- porridge;
- chicken eggs;
- meat;
- dairy products.
Iron supplements can also help quickly get rid of the symptoms of anemia. The tablets usually used are “Ferrum-Lek”, “Totem”, “Sorbifer Durules”, etc. Injections are prescribed only for severe forms of the disease. It is important that the medicine used does not cause problems with the gastrointestinal tract. If constipation or flatulence occurs, the product needs to be replaced.
Treatment of B12 deficiency anemia
Complex therapy of gastrointestinal diseases and adherence to the principles of proper nutrition help eliminate the manifestations of B12-deficiency anemia. Most often, patients are prescribed vitamin B12 injections. They allow you to quickly restore hematopoietic processes in the bone marrow.
How to get rid of folate deficiency anemia
Folate deficiency anemia is treated by taking vitamin B9 and following a diet. The patient should include foods that contain high amounts of folic acid in their diet. This means citrus fruits, vegetables, herbs, asparagus, nuts, seeds, tomatoes, watermelons, corn, avocados, eggs, animal liver, cod liver, cereals, grain bread.
Treatment of hypoplastic anemia
A hematologist treats hypoplastic anemia. Depending on the age, gender and condition of the patient, he can use different methods - bone marrow transplantation, stimulation of hematopoietic processes, blood transfusion, etc.
Which foods contain a lot of iron to increase hemoglobin?
- Dried mushrooms.
A product that can significantly increase iron levels in the body. Just 50 g of dried mushrooms per day will help replenish the iron content in the blood. Not everyone can eat them every day, but periodically including mushrooms in your diet is very useful.
- Red meat.
The dark color of the product indicates a high iron content. For example, a steamed beef cutlet weighing 100 g contains approximately 2.7 mg of iron - almost 15% of the daily requirement. For comparison: in the same turkey cutlet the amount of iron is about 0.7 mg.
- Pumpkin seeds.
An excellent source of iron: 200 g of the product easily covers the daily requirement. But you shouldn’t get carried away with pumpkin seeds: they are very high in calories and can cause disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract. But a small handful of seeds in a salad or hot dish will be very useful.
- Offal.
In terms of the content of iron and other useful microelements, offal easily surpasses meat. 100 g of cooked beef liver contains 36% of the daily iron requirement.
- Buckwheat and rolled oats.
A couple more important foods that can boost your iron levels. A 100 g serving of buckwheat or rolled oats will provide the body with approximately 25% of the beneficial element.
- Legumes.
An essential part of the diet for vegetarians and vegans, legumes are not only rich in iron, but also very filling. A cup of boiled lentils, for example, will cover approximately 35% of the daily requirement for iron, and a glass of boiled beans will cover 20%.
- Dark chocolate.
Perhaps the favorite product of those who seek to increase their hemoglobin levels. The main thing is to choose chocolate with a cocoa content of at least 70% and eat at least ¼ bar (25 g) per day. This will help compensate for about 17% of the daily iron requirement and give you a good mood due to the “happiness hormone”.
For iron deficiency and low hemoglobin, the following foods are also recommended: eggs (especially the yolk), quinoa, almonds, walnuts, peeled apples, pomegranate, grapes, raspberries, rose hips, beets, freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juices, seafood - caviar, fish, oysters It is important that the diet is balanced and that foods contain a variety of nutrients and vitamins.
How to undergo a proper examination to make the correct diagnosis
As practice shows, when examined by most specialists, the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia is established only by the level of iron in the blood. But even this indicator is taken into account within the reference value. This approach is fundamentally wrong, and here's why.
A normal hemoglobin level does not always have a normal ferritin level. Ferritin is a biomarker of iron deficiency conditions. This is a complex protein complex that acts as the main intracellular iron depot in the body.
If you want to find out the level of iron in your blood, in our clinic you can undergo a comprehensive test, which will allow you to make the correct diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe effective treatment.
How to make iron better absorbed
To increase hemoglobin, it is not enough to simply include iron-containing foods in your diet. It is important that the nutrients are absorbed as much as possible and are beneficial. To do this, you should know which products can and cannot be combined with each other.
Iron is best absorbed in the presence of vitamins C and A. That's why seafood with lemon is not only tasty, but also incredibly healthy. A few drops of lemon can be added to salads and other dishes. Almost all fresh vegetables and fruits, such as bell peppers, are rich in vitamin C. Vitamin A is found in fish, oil, vegetables and orange fruits.
It is important to ensure that the body receives folic acid, which takes part in the synthesis of red blood cells. Therefore, you should regularly eat beef, green salad, avocados, legumes, rice, peanuts and other foods high in folic acid.
But calcium and casein (milk protein) reduce the absorption of iron, so you should not consume dairy and fermented milk products and cheeses along with vegetable and meat dishes. Wheat and other grains have a negative effect on the absorption of iron. So it’s better to eat meat without bread, and use vegetables rather than pasta as a side dish. Among the foods that can provoke hemoglobin deficiency: tea, coffee and persimmons (contain tannins), bread, soy, canned food, soda, processed cheese. Therefore, you should not abuse them.
What foods increase hemoglobin
It is advisable for a person who has reduced hemoglobin to include foods containing a lot of iron in their diet. This element stimulates the production of red blood cells and proteins involved in gas exchange.
The foods richest in iron are:
- meat and fish;
- eggs;
- broccoli;
- soy products, including tofu;
- spinach, kale and other green leafy vegetables;
- liver;
- nuts and seeds;
- green bean;
- peanut butter.
Folic acid is a type of vitamin B. It plays a very important role in the production of hemoglobin. Folate is used by the body to produce heme, a component of hemoglobin that helps carry oxygen.
If the body does not receive folic acid in sufficient quantities, red blood cells will not mature. This leads to a decrease in hemoglobin levels and can cause folate deficiency anemia.
Folic acid is found in large quantities in the following foods:
- peas;
- beans;
- spinach;
- rice;
- avocado;
- liver;
- fatty fish.
How to increase the absorption of iron from food
The more varied a person's diet, the less likely he is to become deficient in iron or other essential microelements and vitamins. But if there is a lack of iron, then the diet should have certain restrictions. The fact is that certain foods impair the absorption of this element.
It is better not to consume foods rich in iron at the same time as red wine, tea and coffee. These drinks reduce the body's ability to absorb micronutrients. It is also not recommended to consume chocolate.
In addition, if you have iron deficiency, you should not eat fermented milk products or drink milk. They contain a lot of calcium, and calcium slows down the absorption of iron. Sesame, bran and wheat germ contain a large amount of magnesium, and magnesium is also not friendly with iron.
If it is necessary to increase the iron content in the blood, then all of the listed foods can be consumed only 4 hours after foods with a high iron content.
With a proper and varied diet, hemoglobin deficiency usually does not occur. This is a fairly serious pathological condition. An acute deficiency can have a bad effect on the condition of the entire body. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly take blood tests so that you can adjust your hemoglobin level in the early stages.
Can there be too much iron in the body?
Maybe. An excess of iron is just as harmful to the body as its deficiency. It causes fibrosis of organs and tissues. The pancreas, liver and heart are most often affected. However, it is impossible to achieve an excess of iron through diet alone. The pathology is often due to genetic predisposition and improper or uncontrolled use of iron-containing drugs.
What is an increase in hemoglobin called?
An increase in the number of red blood cells and an increase in hemoglobin is called erythrocytosis. Its characteristic symptoms: nosebleeds, headaches and dizziness, fatigue. Erythrocytosis, in turn, can be a sign of various diseases, which only a doctor can determine.
What does it mean if hemoglobin is elevated?
High hemoglobin levels can be caused by dehydration, smoking, lung cancer, heart disease and other pathologies. Elevated hemoglobin sometimes indicates the presence of a rare disease - polycythemia. When this happens, the body produces too many red blood cells, which can lead to blood clots, heart attacks and strokes. This is a very serious disease that is important to identify and control early throughout your life.
Increased hemoglobin
An increased level of hemoglobin in the blood can be due to various reasons, but often it is due to an excess number of blood cells in the body. This condition is called erythrocytosis. It can lead to a number of disruptions in the functioning of the body, since increased hemoglobin leads to poor blood clotting and circulation.
The main reasons for the increase in the number of red blood cells:
- Decrease in blood plasma volumes.
- Bad habits. Smoking can cause high hemoglobin due to lack of oxygen in the body.
- Moving to a mountainous area. The reason is the same as with smoking.
- Dehydration. Lack of water also leads to an increase in hemoglobin. But when the water balance in the body normalizes, the level will return to normal.
- The use of anabolic agents and certain medications can also lead to an increase in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
How to maintain normal hemoglobin levels
For a healthy person without congenital pathologies, it is important to monitor the daily routine, drink enough water, eat a balanced diet, include foods rich in iron and vitamins in the diet, lead an active lifestyle and periodically undergo general and biochemical blood tests.
These tips may seem obvious and even banal to you, but they will help prevent a decrease in hemoglobin, the development of anemia and other diseases, and improve your well-being and quality of life.
This material summarizes the best research on evidence-based medicine over the years. However, it is for informational purposes only, is not intended to prescribe treatment, and cannot be used as a direct guide to action.
When should you increase your hemoglobin level?
If your hemoglobin level drops below the specified standards, you should consult a doctor. It is corrected taking into account the cause of anemia. An important goal of treatment is to eliminate the underlying disease. Therefore, when determining low hemoglobin in the blood, it is necessary to undergo a number of examinations.
Maximum from nature: why add greens to your diet?