Hemoglobin is a special blood protein found in red blood cells. Performs a vital function. Thanks to it, cells and tissues are saturated with oxygen, and gases and substances are exchanged in the body. Therefore, the importance of hemoglobin cannot be overestimated. If its level drops, health problems occur. This could be due to various reasons. So it is necessary to maintain a normal protein level and know ways to restore it.
Symptoms and causes of low hemoglobin
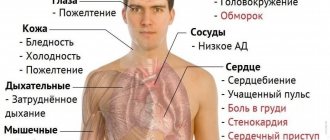
Insufficient hemoglobin content in the blood provokes frequent fatigue, malaise, drowsiness, loss of strength, and bad mood. Patients also complain of constant headache and dizziness. In addition, there is pallor of the skin, poor appetite, tinnitus, cold hands and feet, perversion of taste, pain in the muscles, and the frequent development of colds and viral infections.
In severe cases, the person may lose consciousness. Therefore, in this case, you should definitely visit a doctor and undergo the necessary tests.
Nothing happens for nothing. Including hemoglobin, it cannot decrease without reason. This deficiency in the body is indicated by serious diseases and certain conditions:
- Iron deficiency anemia in chronic form.
- Various bleeding.
- Long-term gastritis.
- Inflammatory bowel pathologies, dysbiosis.
- Time period after surgery.
- Oncology of blood cells.
- Neoplasms in the digestive tract.
- Hepatitis.
- Tuberculosis, pneumonia.
- Iron deficiency.
- Vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiency.
- Destruction of the structure of red blood cells due to severe pathologies.
- Following a diet that involves limiting a large amount of food.
The reasons for a decrease in hemoglobin can be various conditions. However, the greatest impact on protein deficiency is exerted by various blood losses due to surgery, trauma, wounds, and hemorrhoids.
In females, a decrease in hemoglobin most often occurs during menstruation, which lasts more than 5 days.
Hemoglobin in the blood below normal is bad. Above the norm is even worse. Why does its level in the blood fluctuate and what can be done to ensure that this indicator is always normal? 1. The main function of hemoglobin is to transport oxygen to all organs and tissues. The concepts of normal hemoglobin in men and women differ (for women, the normal level of hemoglobin is 120-140 g/l, for men - 130-160 g/l). For pregnant women (whose body works for two) and for infants, the normal hemoglobin level is considered to be 110 g/l. However, expectant mothers need to constantly monitor their hemoglobin levels. Its deficiency can cause premature birth or delayed fetal development, and its excess can cause the death of the child. 2. A moderate decrease in hemoglobin (anemia, anemia) is a common phenomenon, especially in women. This is explained by physiologically determined monthly blood loss. If menstruation is heavy, the hemoglobin level can drop to 90 g/l. Even in healthy women, with a long-term decrease in hemoglobin levels, weakness, dizziness, decreased appetite, drowsiness, decreased performance, dry skin, brittle nails, fragility and hair loss may occur. This is often observed in patients with inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: the inflamed gastric mucosa cannot fully absorb iron. The most dangerous conditions are internal bleeding (ulcers, erosions, tumors, including malignant ones). Pallor is a distinctive feature of patients suffering from these diseases. 3. However, a high hemoglobin level is not a reason to celebrate. Most often this is a symptom of dangerous diseases (erythrocytosis, blood thickening, congenital heart disease, consequences of a burn, intestinal obstruction, heart and pulmonary failure, dehydration). 4. In children, high hemoglobin levels are an indirect sign of blood disease or cancer. Therefore, leaving high hemoglobin unattended is extremely dangerous: it is imperative to find out the cause. 5. Signs of low hemoglobin levels Persistent weakness, loss of appetite, drowsiness, dizziness, perversion of taste, dry skin, brittle nails, hair loss, sticking in the corners of the mouth. 6. Signs of high hemoglobin Similar to signs of hepatitis. Jaundice staining of the skin, sclera, palate and tongue, itching, enlarged liver, heart rhythm disturbances, pallor, thinness. You can take a blood test in the laboratory and quickly get a consultation with a hematologist (adult or pediatric) at our Family Clinic. Receptions for ADULTS and CHILDREN! Sign up by phone. 43-03-03 and 41-03-03.
What is the norm for hemoglobin
As is already known, the protein is found in red blood cells and is responsible for the transport of oxygen in the body.
To maintain a normal level of health, eliminate fatigue, malaise and other characteristic signs of low hemoglobin, it is recommended to regularly take a blood test to determine protein.
The hemoglobin level is different for everyone, depending on age, gender and physiological characteristics of the body. So, for men this figure is 125-160 g/l, for women 115-140 g/l. In newborn babies, the protein level is in the range of 140-195 g/l; for children one year of age, hemoglobin is 110 g/l. And at school age, the blood protein level is at least 150 g/l.
In women, during pregnancy, hemoglobin drops and this is considered normal. At this time its value is about 110 g/l.
As a rule, a low rate is associated with iron deficiency anemia, which occurs in most people, regardless of age and gender.
What level of hemoglobin is considered elevated?
It would seem: if hemoglobin is so important for health, then increased hemoglobin in men should be a good sign. However, it is not. Too high hemoglobin in men signals health problems and can itself cause trouble.
An increase in hemoglobin levels in men by 20 g/l or more is considered a significant deviation from the norm . High hemoglobin in men can be a consequence of heart or pulmonary failure, intestinal obstruction, cancer, or diabetes. Low hemoglobin in men is also observed with dehydration, which can be caused by both insufficient fluid intake and too rapid loss of fluid due to vomiting or diarrhea.
Increased hemoglobin in men makes itself felt with symptoms such as
- loss of appetite up to anorexia,
- weakness and fatigue,
- deterioration of vision and hearing,
- muscle and joint pain.
Some have
- problems with the genitourinary area,
- digestive disorders,
- insomnia,
- dizziness.
High hemoglobin in men is more dangerous than many people think. With an increased hemoglobin content, the blood thickens and moves through the veins with difficulty, which can lead to the formation of blood clots, which can cause a stroke.
Since hemoglobin never increases without reason, it is necessary first to identify the underlying disease and begin treatment. While doctors get to the root of the problem, the patient himself can improve the situation somewhat and reduce the level of hemoglobin. To do this, you need to avoid foods high in iron.
- red meat,
- offal,
- beans,
- eggs,
as well as from fatty and fried foods - such unhealthy foods increase cholesterol, and the risk of blood clots increases.
Both adults and children
With iron deficiency anemia, the balance is disturbed: the loss of iron in the body exceeds its absorption. This happens in children during periods of rapid growth (in the second year of life and adolescence) or due to infection with worms. Anemia is a frequent companion of pregnant and lactating women, whose iron needs increase sharply - after all, they have to “share” it with the child.
But the most common cause of iron deficiency in adults is frequently recurring small bleeding (from 5-10 ml per day). They can be caused by a variety of diseases: from bleeding ulcers and hemorrhoids to stomach cancer. In women, the main cause of iron deficiency is uterine bleeding (caused by endometriosis or other gynecological diseases) and heavy menstruation; in men, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
Often we rob ourselves: fasting days, independent diets are a very short path to iron deficiency.
Below the bar
What is anemia? Nine out of ten people will answer: anemia. This concept has become so common in everyday life that no one even thinks about deciphering it. But “little” does not mean that there is not enough blood in your body. Her quantity is just fine. Problems with “quality”: with anemia, there are not enough full-fledged red blood cells in the blood - red blood cells. And they contain hemoglobin, which is responsible for the “delivery” of oxygen to every cell of the body’s tissues. And if its level is reduced, very unpleasant things happen: organs and tissues experience oxygen starvation, which means they are unable to work at full capacity.
Anemia may be an inherited blood disorder, or it may be a temporary “abnormal” condition. For example, when the body experiences a deficiency of vitamin B12, folic acid, after an injury with large blood loss, etc. But 90% of anemias are so-called iron deficiency: the name itself suggests that the body lacks iron. Why? Let's try to figure it out.
How to compensate for iron deficiency?
A doctor should prescribe iron supplements; you should not buy them yourself at the pharmacy. “It is important to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations. Hemoglobin and ferritin reserves are replenished slowly, up to 6 months, explains Irina Dobretsova. “Therefore, you should not stop taking medications before the end of the course or reduce the dose, even if you feel better. Sometimes, when taking iron supplements, there are side effects, such as belching and bloating. Then you can switch to intravenous administration of the drug, depending on the severity of the situation and the degree of intolerance.”
It is important to remember that preparations containing iron cannot be combined with dairy products. Calcium makes it difficult to absorb iron. It is also undesirable to drink iron supplements with black tea. But orange juice will give excellent results: vitamin C, on the contrary, helps iron absorption.
How to “read” blood tests correctly?
To make sure that the cause of deterioration in health is a lack of iron, you need to take a detailed blood test. Now there are many different laboratories where this can be done.
Article on the topic
Dear, useless, yours. Tests you shouldn't spend money on
Standards may vary. For a man, the norm of hemoglobin is 130-160 g/l of blood, for a woman - 120-140 g/l.
— If a man’s hemoglobin is reduced even slightly, say, to 120-110 g, then this is already a red flag. Even if he does not experience fatigue and has no other symptoms of anemia,” Dobretsova emphasizes, “Reduced hemoglobin may indicate the presence of a polyp, erosion or stomach ulcer. Therefore, you need to go to a gastroenterologist and do a gastrocolonoscopy. There may also be concerns that low hemoglobin is a sign of intestinal or stomach cancer, so this is not something to joke about. With such a result, it is also worth visiting an andrologist.
Women often attribute the lack of hemoglobin to monthly blood loss. But the problem may not only be in the menstrual cycle.
— In a woman, a reduced hemoglobin level may also indicate the presence of polyps, erosion or oncology, so there is no need to delay going to the doctor. Be sure to visit a gastroenterologist and gynecologist, the expert advises.
Well, if a medical examination has ruled out all dangers, reconsider your diet. Get rid of fast food and foods containing dyes and preservatives, eat more lean red meat (beef and lamb) and liver, eat pomegranate, seaweed and pumpkin seeds.
The second important indicator to pay attention to is the mean erythrocyte volume (MCV). Normal MCV is between 80 and 100 femtoliters. If the indicator is reduced (with simultaneously reduced hemoglobin), then most likely the person has iron deficiency anemia. If MCV is normal with reduced hemoglobin, this indicates incipient iron deficiency anemia. It can also signal a chronic disease, such as kidney disease. An elevated MCV is often a sign of a lack of folic acid or vitamin B12.
Yes - to meat, no - to tea. How to deal with anemia? More details
Who is at risk of iron deficiency or anemia?
- Pregnant women, unless taking special multivitamins
- Breastfed infants if the mother was anemic during pregnancy or while breastfeeding
- Babies whose diet was introduced to pureed meat too late (this is usually recommended from 6 months of age)
- Children who actively engage in sports and do not take additional vitamin and mineral complexes
- Teenagers during hormonal changes in the body
- Vegetarians
- Fans of strict diets and fasting.