Why does pain occur in the temples?
Physiological reasons
A dull pressing pain in the temples is observed when staying in a stuffy room. If a person cannot go out into the fresh air, the painful sensations increase, sometimes becoming sharp and pulsating. In some people, the symptom is triggered by strong feelings, most often anxiety and fear. May occur against the background of stressful situations. Another possible cause is starvation when trying to quickly lose weight, following strict diets, or eating disorders.
Migraine
The pain is pressing, throbbing, one-sided. The zone of maximum pain is located in the projection of the temple, eye or forehead. Sometimes an aura or prodrome is observed in the form of weakness, impaired ability to concentrate. It is typical for the affected side to change from one attack to another. Migraine symptoms are aggravated by bright light, loud sounds, and any physical activity. Patients try to “lie down” in solitude, silence and darkness.
Cluster headache
Pain occurs during periods of exacerbation, lasting from 2 weeks to 2 months. Appear suddenly, reaching a maximum after 1-3 minutes. The attack lasts from 15 minutes to 1 hour, less often up to 3 hours. Episodes occur at one time, often at night, and can be repeated from one per day to two to four (sometimes eight) during the day. Painful sensations are one-sided, more often on the left.
Localized in the eye, radiating to the temple, ear, cheek and teeth, extremely sharp, unbearable, stabbing or burning. Accompanied by nasal congestion, facial and conjunctival hyperemia. Described by patients as an “eye rupture” or “stabbed in the eye.” Photophobia, nausea and vomiting are observed in 30% of cases. The patient is agitated and rushes about, since physical activity somewhat reduces the intensity of the pain.
Tension headache
The symptom is mild or moderate. The headache is bilateral, non-pulsating, squeezing or squeezing the head with a “hoop”, especially noticeable in the temple area. There is no dependence on physical activity, no nausea or vomiting. The duration of the attack ranges from half an hour to 1 week. Pain increases with strong emotions and decreases with emotional relaxation.
Pain in temples
Primary and symptomatic hypertension
Along with essential hypertension, there are more than 50 diseases that cause high blood pressure. An increase in blood pressure, regardless of etiology, is accompanied by pain in the temples and back of the head. Patients complain of tinnitus, spots before the eyes, shortness of breath, chest pain, restlessness, or a feeling of fear. An external examination may reveal hyperemia of the skin. The symptom is observed in the following pathologies:
- Kidney diseases
: pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, hypoplasia, polycystic disease, amyloidosis, urolithiasis, tumors, diabetic nephropathy, renal tuberculosis. - Endocrine disorders
: pheochromocytoma, Cushing's disease and syndrome, primary aldosteronism. - Pathologies of large vessels
: coarctation of the aorta.
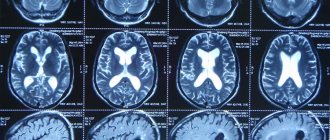
Hydrocephalus
Due to an increase in the amount of fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid system with hydrocephalus, intracranial pressure increases. Along with pain in the temples and throughout the head, intracranial hypertension is manifested by disturbances of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, and sometimes convulsive seizures. The symptom is detected in conditions such as:
- developmental defects: Chiari anomaly, Dandy-Walker syndrome, stenosis of the Sylvian aqueduct;
- intrauterine infections and birth injuries;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- inflammatory processes: encephalitis, meningitis, arachnoiditis;
- vascular pathologies: hemorrhagic stroke, intraventricular hemorrhage;
- neoplasms: colloid cysts, intracerebral ganglioneuromas, germinomas, astrocytomas, etc.
Traumatic brain injury
Headache is a constant symptom of TBI and is observed with injuries of any severity. Accompanied by dizziness, nausea, vomiting, amnesia. Impaired consciousness, paresis, decreased sensitivity, and other manifestations are possible. At first, the pain is usually diffuse. During the recovery period, pain in the temporal areas sometimes prevails.
Temporal arteritis
Caused by autoimmune damage to the temporal artery. Often occurs after viral infections. Horton's disease develops in middle-aged and elderly patients. Accompanied first by aching, then by piercing, burning pain in one or both temples, increasing over 2-3 weeks. The symptom worsens with chewing and talking. Complemented by loss of appetite, sweating, hyperthermia, weight loss, sleep disturbances, myalgia, arthralgia.
Intoxication syndrome
Pain in the temples is one of the possible variants of headache with intoxication syndrome against the background of bacterial and viral infections, local purulent processes. It can be dull, squeezing, aching, pulsating. Increased body temperature, weakness, weakness, dizziness, pain in joints and muscles are observed. Other signs are determined by the cause of intoxication.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Prosopalgia is paroxysmal in nature and is a series of intense, shooting, burning pain impulses that resemble an electric shock and spread from the lateral surface to the center of the face. The duration of the episode is up to two minutes, the attacks are repeated several times. When the nerve is completely involved, the entire half of the face suffers; when the second branch is affected, the pain is localized in the temple area, the outer corner of the eye, the adjacent part of the cheek, and the upper lip.
Damage to the temporomandibular joint
TMJ dysfunction is a problem that can be caused by the following factors:
- Dentofacial pathologies
: trauma, malocclusion, dental defects, poor-quality prosthetics, congenital anomalies. - Muscle overstrain
: bruxism, tonic spasm, overload of masticatory muscles, high speech load. - Psychological factors
: prolonged neuropsychic stress.
Typical symptoms include pain in the temples, eyes, ears, prosopalgia, headaches, difficulty and clicking when opening the mouth. Possible dizziness, sleep disorders, dysphagia, glossalgia, sleep apnea syndrome.
Other reasons
Sometimes hormonal changes become a provoking factor. Girls may experience pain in their temples during the onset of menstruation. Some mature women note the onset of symptoms during menopause. Another possible reason is intoxication. Pain in the temple area is observed in a state of alcoholic intoxication, with an overdose of certain medications, or carbon monoxide poisoning.
How to help yourself with a headache
If a headache radiates to the eyes after hard work, you should rest well, take a walk in the fresh air, and give yourself an acupressure massage. You can take a warm bath with chamomile infusion added to the water. Take a break from working at the computer or watching TV
Give yourself a head massage. Relax, drink warm milk with honey, tea with lemon balm. Do simple exercises to relieve headaches:
- sit on a chair, keep your back straight and your head free;
- without effort, just under the influence of gravity, tilt it towards your chest;
- stay in this position for twenty seconds; take a break for 30 seconds;
- Bend again for 20 seconds.
Repeat the exercise 15-16 times.
The second exercise is done in the following sequence:
- sitting or standing, raise your hands to your head;
- the thumbs of each hand are pressed to the zygomatic arches, with the remaining fingers clasping the back of the head;
- look up;
- while inhaling, try to throw your head back for 10 seconds, while holding it with your hands;
- while exhaling, look down for 6-8 seconds;
- tilting your head to your chest as much as possible, stretch but do not strain the neck muscles.
Repeat the inhale-exhale cycle 5-6 times.
To relieve headaches coming from the cervical spine, rehabilitation experts recommend performing the following exercise:
- sitting on a chair, with one hand clasp your head from above on the side in which the pain is felt more strongly;
- Place the index finger at the level of the beginning of the ear;
- With a little hand effort, turn your head to the “healthy” side;
- Press your free palm from below to your chin and cheek;
- while inhaling for 10 seconds, looking down, press your chin to your lower palm against its resistance;
- As you exhale, relax for 6-8 seconds and look up.
- repeat the exercise 5-6 times, slightly changing the turn of the head.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic program is compiled by a neurologist. If necessary, a maxillofacial surgeon, infectious disease specialist, and other specialists are involved in the examination. To clarify the pathology, the following procedures may be prescribed:
- Questioning and external inspection
. During the conversation, the doctor finds out the time and circumstances of the onset of the symptom. Asks about the nature and duration of pain, other manifestations, as well as the presence of similar symptoms in blood relatives. Upon examination, increased blood pressure, skin hyperemia, renal edema, signs of endocrine pathology and infectious diseases may be detected. - Neurological examination
. With hydrocephalus, vestibular and cerebellar ataxia and nystagmus are possible. In patients with TBI, general cerebral and focal symptoms are determined. With trigeminal neuralgia, pain in trigger points is detected, with fascicular cephalgia - rhinorrhea, hyperhidrosis, drooping eyelid, conjunctival injection (during an attack). - Neuroimaging
. X-ray, CT, MRI, MRA and ultrasound techniques (duplex, Dopplerography) are informative for hydrocephalus, traumatic injuries, and determining the genesis of compression of the trigeminal nerve. They help to establish the cause of hydrocephalus and assess the severity of vascular damage in patients with arterial hypertension. - Lumbar puncture.
Indicated to clarify the cause of increased intracranial pressure, it is performed as part of an examination for traumatic brain injuries and neuroinfections. The resulting cerebrospinal fluid is sent for microscopic, microbiological, and PCR studies.
In addition, ultrasound of the kidneys and endocrine organs, radiography and computed tomography of the TMJ, laboratory tests to assess the condition of the body, determine the causative agents of common infections and purulent processes can be performed. For migraine, cluster cephalalgia, tension pain, additional studies are not very informative; differential diagnosis, carried out on the basis of clinical signs of the disease, comes to the fore.
Neurologist consultation
Flickering in the eyes and headache
The main cause of flicker in the eyes and headaches is retinal detachment and rupture. Sharp flashes of light are the result of tension in the eye membrane. After a rupture of the capillaries and retina, a person sees many black dots.
Vitreous detachment also causes tension on the retina. It comes in back and front. The vitreous body is divided into a gel and a liquid part, which passes under the membrane and “disconnects” it from the retina. The main sign of the pathology is “flying flies”. They can be seen when looking at the sun, snow in sunny weather, or blue sky.
Chorioretinitis is inflammation of the vessels of the retina of the eye. The development of the disease is caused by:
- infectious diseases;
- increased levels of radiation;
- allergy;
- intoxication;
- injuries and damage to the organs of vision;
- autoimmune conditions;
- decreased immunity after long-term treatment or in HIV-infected patients.
Chorioretinitis can be congenital. Symptoms of the disease include darkening of the eyes and decreased visual acuity. The patient cannot determine the size of objects; it is difficult for him to navigate in low light. Ophthalmologists at the Yusupov Hospital use the latest diagnostic equipment from leading global manufacturers to examine patients and apply innovative treatment methods.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
The plan of conservative measures is determined by the etiology of the pain syndrome:
- Migraine
. To relieve attacks, simple and combined analgesics are used, and sometimes therapeutic blockades are performed. To prevent new paroxysms, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and psychotropic drugs are used. - Tension headaches
. Medicinal methods include NSAIDs, antidepressants, muscle relaxants, occipital nerve blocks, non-medicinal methods - massage, manual therapy, acupuncture, biofeedback, relaxation techniques. - Bundle cephalalgia
. Paroxysms are eliminated with the help of triptans; in case of intolerance, oxygen inhalations are prescribed, and local anesthetics are injected into the nasal cavity. Calcium channel blockers are effective for preventive purposes. - Hydrocephalus
. In the case of an acquired variant of the pathology, the causative disease is treated and diuretics are prescribed. - Arterial hypertension
. Etiopathogenetic therapy is carried out. It is recommended to control blood pressure and take antihypertensive drugs. - Temporal arteritis
. The basis of drug therapy is glucocorticoid hormones. If there is no result, they switch to cytostatics. To eliminate symptoms, vasodilators, anticoagulants, and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. - Trigeminal neuralgia
. Anticonvulsants are considered the first line treatment. Additionally, antispasmodics, microcirculation correctors, antihistamines, and therapeutic blockades are used. - TMJ dysfunction
. It may be necessary to eliminate dental pathologies. Soft food is recommended. Pain is reduced with the help of NSAIDs, antidepressants, botulinum therapy, glucocorticosteroid blockades, massage, and physiotherapy.
Eye spots and headaches
The main reason why a person experiences ripples in the eyes, and then a headache, is the compression of the blood vessels. This happens when the weather changes, atmospheric pressure changes, or oxygen starvation. Floaters “fly” before the eyes and a headache appears after stress. The cause of headaches and dizziness is nervous exhaustion, deficiency of essential substances and microelements, and the presence of bad habits.
In this case, the pain goes away after rest. But ripples and flickering of spots before the eyes, a headache may be the first signs of a tumor, diseases of the cardiovascular system, or vegetative-vascular dysfunction. If, after rest, the ripples and flickering of spots before your eyes, the headache does not go away, make an appointment by calling the Yusupov Hospital. In each case of headache, neurologists first determine the type of pain, identify its cause and eliminate it, stop the pain attack and carry out therapy, the purpose of which is to prevent subsequent headache attacks.