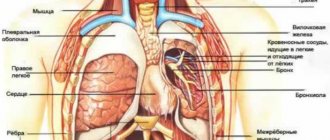
Pain on the right under the ribs from behind from the back is an unpleasant symptom that can appear when the functioning of various organs is disrupted. If unpleasant and painful sensations appear in this area, you need the help of a rheumatologist and other specialists who work at the Yusupov multidisciplinary hospital.
Pain in the right hypochondrium can appear not only with disorders of the musculoskeletal system, but also with other systems. At the Yusupov Hospital, high-precision diagnostics are carried out, aimed at collecting the most detailed information about the patient’s current condition.
Causes
Pain syndrome accompanies various pathologies. If there are disturbances in the functioning of the internal organs, back pain on the right may occur. The cause of this symptom can be determined by diagnostic measures, during which the following diseases can be detected:
- chronic or acute pancreatitis;
- oncological diseases of the lungs or bronchi;
- pneumonia;
- pyelonephritis caused by the activity of pathogenic microorganisms. Pain on the right side of the back with this disease intensifies with sudden movements;
- pleurisy, in which the serous membrane covering the lungs becomes inflamed;
- appendicitis;
- formation of a subhepatic abscess;
- urolithiasis disease.
Localized pain on the right side of the back may indicate diseases such as a herniated disc or lumbar osteochondrosis. In addition, this symptom often occurs in women when carrying a child. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital Therapy Clinic determine the causes of pain and develop a therapy program aimed at eliminating the root causes of discomfort.
Chest pain due to gastrointestinal and respiratory diseases
When an esophageal ulcer worsens, severe pain occurs in the chest, as a result of which in some cases the person may lose consciousness. The pain occurs when eating, and is similar in nature to the symptoms of angina pectoris; it seems as if the heart is stabbing. The same pain occurs with cancerous tumors, Mallory-Weiss syndrome (rupture of the esophagus) and also as a result of chemical burns of the esophagus.
Lung diseases, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, pleurisy, tuberculosis and silicosis, are manifested by aching pain and heaviness in the chest. Symptoms that differ from heart disease are cough, which may include shortness of breath and respiratory failure. As a result of shortness of breath, many people experience heart palpitations.
Classification of back pain
It is impossible to independently determine why back pain occurred in the right hypochondrium, therefore, to determine its causes, you should contact the therapy clinic of the Yusupov Hospital and undergo an examination. Classification of pain by location allows specialists to determine which organs are involved in the pathological process:
- pain on the right under the scapula occurs due to a pinched nerve, damage to the serous membrane of the lungs or during an oncological process;
- back pain on the right under the ribs at the back appears when the pancreas or liver is damaged;
- pain in the center of the back is a sign of kidney disease;
- back pain radiates to the right leg due to a hernia or injury, as well as disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system.
However, laboratory results are required to make a definitive diagnosis. Patients of the Yusupov Hospital can take tests and undergo the necessary diagnostic procedures in one day without queues.
Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Pain and cramps in the right side can be caused by a whole “bouquet” of inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract. “These are, for example, appendicitis, diverticulitis, colitis, gastroenteritis, stomach and duodenal ulcers,” says Bulat Yunusov.
Most often, with these diagnoses, the pain is felt as aching, moderate, with gradually increasing intensity. With appendicitis, pain may increase when walking, coughing, changing body position and decrease at rest. Also with this diagnosis, there is an increase in temperature, nausea, and vomiting.
With a stomach ulcer, the pain becomes more noticeable after eating fatty, spicy or fried foods, alcohol, and intense physical activity. Additional symptoms may include heartburn, nausea, and vomiting.
With colitis (inflammation of the intestines), the pain can be nagging or paroxysmal. The disease is also accompanied by diarrhea, fever, general weakness, headaches, and the presence of mucus in the stool.
With diverticulitis (protrusion of the intestinal walls), acute pain is felt to the right of the navel, the temperature rises, and diarrhea (with blood and mucus) appears.
With gastroenteritis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine), pain in the right side is accompanied by lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, etc.
With pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), the pain begins suddenly and is constant and intense. Sometimes it can “give” to the left side or get worse after eating heavy, fatty or spicy foods.
Symptoms
Back pain in the right hypochondrium is one of the signs of various disorders and diseases. Depending on the cause of its occurrence, the patient may experience other symptoms. The main symptoms accompanying back pain are in the right hypochondrium. Are:
- fever, increased body temperature and chills, indicating the body’s immune system is fighting pathogens;
- attacks of intense headache;
- signs of intoxication of the body;
- decreased blood pressure;
- stool disorders;
- shortness of breath, cough.
When these signs appear, some patients do not consider them serious enough to contact a medical facility. However, in case of diseases of internal organs, self-medication can lead to serious consequences.
At the Yusupov Hospital, patients are treated in comfortable conditions. A friendly attitude towards each client, high professionalism of employees and the use of modern technologies and techniques allow us to provide medical care that meets international requirements. The Yusupov Hospital does not refuse treatment to patients in serious condition; they are offered emergency hospitalization and high-quality treatment.
Abdominal pain on the right side in men
Dull abdominal pain in men most often occurs due to an inguinal or umbilical hernia. The reason is excessive physical activity. A bulge in the groin often develops in boys under 1 year of age due to weakness of the ligamentous apparatus, so babies should not be allowed to cry angrily for a long time. Umbilical and inguinal hernias are eliminated with plastic surgery (suturing the hernia opening or strengthening it with a special mesh). Without timely surgical intervention, strangulation of the hernia is highly likely. The pain increases, spreads to the entire abdomen, patients note frequent vomiting, stool retention and bloating. The surgery is performed on an emergency basis.
Pain in the lower back, radiating to the groin and leg, is characteristic of protrusion and herniation of the intervertebral disc. Patients often complain of weakness and numbness in the legs. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe an effective course of anti-inflammatory drugs. If necessary, a therapeutic blockade or surgery is performed.
Diseases of the genitourinary system in men (cystitis, prostatitis, prostate adenoma) are manifested by pain in the lower abdomen, which subsides after defecation and urination. However, sometimes the pain is worse on the right or left.
With orchitis (inflammation of the testicle) and vesiculitis (an inflammatory process that develops in the seminal vesicles), the temperature suddenly rises, a sharp or dull pain radiates to the groin and perineum, and intensifies when walking down the stairs and physical activity. The damaged testicle swells. Inflammation of the testicles often complicates the course of sexually transmitted diseases and is fraught with infertility.
Varicocele (varicose veins of the spermatic cord) is diagnosed in every fourth man under the age of 30. The disease is often asymptomatic and is diagnosed during clinical examination of adolescents. Only in severe cases does aching pain occur on one side of the scrotum and in the groin. Pain increases with overheating, physical exertion and during sexual intercourse.
When testicular torsion occurs, a sharp pain suddenly occurs in the scrotum on one side, radiating to the groin, perineum and lower back. In young boys, the disease is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Palpation reveals a higher position of the testicle in the scrotum. The pathology is eliminated urgently.
Important! If you suspect prostatitis, prostate adenoma or testicular disease, you should contact a urologist-andrologist.
Muscle pain
People of all ages experience muscle pain in the back. The most common cause of pain is diseases of the spine. So, with osteochondrosis or scoliosis, compression of the muscles located nearby occurs. As the disease progresses, back pain on the right under the ribs may intensify and hinder movement.
One of the methods for eliminating muscle pain in the back is physical therapy. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital Rehabilitation Center select exercises in such a way as to strengthen the muscle corset and reduce the load on the spine, as well as eliminate the resulting pathology. Physiotherapeutic procedures in combination with massages are highly effective for back pain in the right hypochondrium.
Causes of pain caused by pathology of internal organs
Solar plexus pain often occurs during pregnancy
Pain in this area can even appear due to a reflex reaction to pressure that has become higher than normal. This is due to the fact that the nerve plexus is located near the aorta, and from there the baroreceptors can send a signal to all organs. This is how adaptation occurs during stress. The word stress refers not only to mental problems, but also to hemodynamic disorders in the body.
During pregnancy, pain in the solar plexus may also occur, which may be accompanied by nausea and temporary blurred vision. During epigastria, a disorder of the gastrointestinal system occurs, which may be followed by the following diseases:
- Gastritis
- Ulcer (stomach, duodenum)
- Pancreatitis
- Intestinal pathology
- Pathology in the abdominal cavity
If the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, then during a meal you may experience pain in the solar plexus or even in the duodenum. If a stomach or duodenal ulcer occurs, the pain becomes truly unbearable because fluid from the stomach cavity enters directly into the abdominal cavity. Hydrochloric acid hits the receptors, and they send a signal to the center of the nerve plexus. If you take medications, the acidity may decrease and the pain will be relieved.
When inflammation of the solar plexus nerves occurs, the small intestine may begin to ache regardless of the cause of the disease, since it is also close to the plexus. Symptoms of nausea may occur as the central nervous system is irritated. These sensations are similar to the symptoms of seasickness. Pathology of the abdominal cavity is fraught with the following symptoms:
- Peritonitis
- Adhesive disease
- Worm infestation
- Prolapse of internal organs (kidneys and stomach)
In this case, pain in the plexus becomes clearly noticeable during pressing; if the pathology worsens, the pain becomes very strong.
Timely treatment of problems associated with pain in the solar plexus can protect you from such a result.
The solar plexus can also hurt due to injuries. Indeed, pain in the solar plexus area can occur even if there are no inflammatory processes or the presence of pathogens. This can happen due to previous injuries. They usually happen when playing sports, but not only, even wearing a tightly tightened belt can cause painful sensations in the solar plexus. How to determine pain in case of injury:
- Burning sensation in the abdominal cavity
- Severe shortness of breath and difficulty breathing
- Gagging
- Darkening in the eyes
If the problem is not serious, you may be able to get away with a slight clouding of consciousness. If the injury is serious, there is a possibility of losing consciousness. There must be a medical unit on the territory of the sports complex to provide first aid.
Diagnostics
Rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital and other specialists draw patients’ attention to the fact that pain in the ribs on the right side of the back can be a sign of serious disorders, therefore, to establish its causes, a set of diagnostic measures is carried out using European equipment:
- study of symptoms and complaints of patients;
- physical examination of the patient;
- passing biochemical and clinical tests;
- MRI and CT;
- ultrasonography;
- stool analysis;
- performing bronchoscopy.
The diagnostic center of the Yusupov Hospital is equipped with European equipment, which allows obtaining high-precision research results. Cooperation with leading research centers allows us to perform rare and complex studies, so the specialists of the therapy clinic provide assistance even to those patients who were abandoned in other medical institutions.
How to relieve pain at home
- If you experience abdominal pain on the right side for the first time, you should not take analgesics on your own. Anesthesia may distort the clinical picture and make diagnosis difficult.
- If there are signs of an “acute abdomen” (pain, board-shaped abdomen, vomiting, stool retention, fever), cold (a heating pad with ice on the epicenter of pain), hunger, rest (the patient should be placed in a comfortable position) and calling emergency help are recommended.
- If the patient cannot wait until the ambulance arrives, it is permissible to give an antispasmodic tablet.
Treatment
Pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the back, can bother people of all ages, while some patients do not perceive it as a serious symptom. If you seek medical help early, it is possible to stop the pathological process at a stage when it does not cause consequences.
Specialists at the therapy clinic, in particular rheumatologists, treat back pain in the right hypochondrium and the root causes of this symptom. Patients who experience back pain in the rib area on the right may be prescribed complex treatment depending on the type of disorder. Comprehensive therapy programs include the following activities:
- taking medications to relieve pain and inflammation;
- use of physiotherapeutic techniques;
- massages;
- drawing up a nutrition program;
- regular physical therapy classes under the guidance of experienced instructors.
Pre-registration by phone allows you to optimize the work of the Yusupov Hospital and create the most comfortable conditions for patients. Contact the Yusupov Hospital staff by phone and choose a convenient time to visit a specialist.
Pain when coughing
General information
Pain with coughing and inhalation or other respiratory movements usually points to the pleura and pericardial region or mediastinum as a possible source of pain, although pain in the chest wall is probably also influenced by respiratory movements and has nothing to do with heart disease.
Most often, the pain is localized in the left or right side and can be either dull or sharp. The causes of chest pain when coughing can be diseases that a person is not even aware of. The most common causes are diseases in the area near or around the heart or in its middle wall, which manifest as pain. Pain during breathing and coughing can be signs of diseases of the respiratory system, although they can easily be confused with heart disease . Such pain is most often localized on the side of the chest - on the right or left. They can be sharp, piercing or, conversely, dull, pulling
The main causes of pain when coughing
Pain when coughing and inhaling occurs due to inflammation of the membrane lining the inside of the chest cavity and covering the lungs. Dry pleurisy can occur with various diseases, but most often with pneumonia. Pain during dry pleurisy decreases when lying on the affected side. There is a noticeable limitation in the respiratory mobility of the corresponding half of the chest; with unchanged percussion sound, weakened breathing may be heard due to the patient sparing the affected side, and pleural friction noise. Body temperature is often subfebrile, there may be chills, night sweats, and weakness. Restriction of chest movement or pain when coughing, inhaling and exhaling with shallow breathing is observed with functional disorders of the costal frame or thoracic spine (limited mobility), pleural tumors, pericarditis. With dry pericarditis, the pain increases with coughing, inhaling and movement, so the depth of breathing decreases, which worsens shortness of breath. The intensity of pain when inhaling varies from slight to severe. When the interpleural ligament is shortened, a constant cough is observed, which intensifies when talking, taking a deep breath, physical activity, stabbing pain when taking a deep breath, or running.
The interpleural ligament is formed from the fusion of the visceral and parietal layers of the pleura of the root of the lung. Further, descending caudally along the medial edge of the lungs, this ligament branches in the tendon part of the diaphragm and its legs. The function is to provide springy resistance during caudal displacement of the diaphragm . In the presence of an inflammatory process, the ligaments shorten and limit caudal displacement. With intercostal neuralgia, sharp “shooting” pains occur along the intercostal spaces, sharply intensifying when coughing and inhaling. With renal colic, the pain is localized in the right hypochondrium and in the epigastric region and then spreads throughout the abdomen. The pain radiates under the right shoulder blade, to the right shoulder, intensifies when coughing and inhaling, as well as when palpating the gallbladder area. Local pain is observed when pressing in the area of the X-XII thoracic vertebrae 2-3 transverse fingers to the right of the spinous islands. A blow or compression to the chest can cause rib fractures . With such damage, a person feels a sharp pain when coughing and inhaling. Pain when coughing and inhaling may also indicate the presence of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine.
Other reasons
Chest pain that occurs against the background of a cold (flu, ARVI) and is accompanied by a dry, obsessive cough , manifested by a scratching sensation behind the sternum, aggravated by coughing, is a sign of tracheitis - inflammation of the trachea (the breathing tube connecting the larynx to the bronchi). Such sensations go away on their own along with the cold itself. In addition, with prolonged, frequent, “nasty” coughing, pain occurs in the lower parts of the chest, at the level of the lower ribs. It is due to the fact that coughing is carried out mainly due to contraction of the muscles of the diaphragm . Like any other muscle, the diaphragm gets tired after prolonged use and pain occurs with each sharp contraction. This pain also goes away after the cold and cough ends. With lung cancer, the nature of the pain is different: sharp, stabbing, girdling, aggravated by coughing and breathing. The pain can cover a certain area or half of the chest; it can radiate to the arms, neck, and abdomen. The pain becomes especially intense and excruciating when the tumor into the ribs or spine. A cough headache begins immediately after a strong cough, sneezing or straining. It is usually bilateral, pounding, intense and ends quickly when the cough stops. In most cases it lasts less than one minute, only occasionally 30 minutes. In about 1/3 of patients, headache when coughing may be unilateral.
It is assumed that the cause is increased sensitivity to a short-term increase in intracranial pressure (during coughing). For the most part, middle-aged men are affected, and the disease often disappears after a few years. In some cases, it can persist for more than ten years.
A headache that occurs repeatedly when coughing or sneezing may hide a serious illness, mainly when the intensity of the pain increases. You may need to have a magnetic resonance imaging scan of the head to rule out diseases of the posterior fossa (Arnold-Chiari malformation), cerebral vessels, or cerebrospinal fluid dynamics disorders. Pain during pneumothorax is often unbearable, but sometimes it is moderate and, like other pleural pains, increases with coughing and movement. Sometimes spontaneous pneumothorax can occur even without pain. If you often experience pain when coughing , seek help from a therapist, pulmonologist and neurologist to find out the exact causes of the disease.
Symptoms of kidney complications after coronavirus
In severe cases of the viral disease, symptoms of kidney complications appear almost immediately. If you have already had Covid, the first signs of complications resemble a cold: chills, discomfort, headache.
Expressed clinical picture:
- difficulty urinating – difficult or involuntary;
- discomfort when emptying the bladder;
- swelling of the legs and face in the morning;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- the appearance of impurities in the urine;
- increased blood pressure.
Pain syndrome in the lumbar region, aching and shooting pain, which intensifies at times.
At the first symptoms of kidney complications due to coronavirus, it is easier to stop the condition. If you have recently had an illness, monitor your condition carefully and contact your doctor as soon as discomfort occurs.
What complications does coronavirus cause to the kidneys?
Kidney diseases after Covid are associated with inhibition of cell function - traces of viral DNA are found in the urine of patients, which indicates its presence in the urinary system. Most often, the condition is expressed in renal failure - acute, turning into chronic.
Acute kidney damage is one of the factors of mortality from Covid in severe cases of the disease, therefore screening is necessary as quickly as possible. In some patients, sluggish and hidden disorders in the urinary system appear immediately when they become ill with coronavirus.
Risk factors
The risk of kidney complications after Covid is higher in patients with the following conditions:
- renal failure;
- glomerulonephritis;
- pyelonephritis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- strictures;
- cysts, tumors.
It is especially important for such patients to undergo timely diagnosis, even when there are no signs of abnormalities.
Help the liver with Phosphogliv*
If liver problems are detected, the patient is prescribed diet and exercise; if this is not enough, therapy is supplemented with medications. It often includes the use of hepatoprotectors - drugs for treating the liver. One such drug is Phosphogliv*. Phosphogliv* is used as a means of pathogenetic therapy. This product contains 2 active ingredients: glycyrrhizic acid and essential phospholipids.
Glycyrrhizic acid has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antifibrotic effects, which allows the drug to be used both at the stage of treating inflammation and for preventing its development, and essential phospholipids restore damaged liver cell membranes. The use of the drug Phosphogliv* ensures normalization of the patient’s general condition, relief of the inflammatory process in the liver - a decrease in ALT and AST enzymes, and also helps prevent the development of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Signs of liver problems
We have found out where a person’s liver is located and how it hurts; now we should talk about the symptoms. Liver diseases manifest themselves in different ways. There are external and internal symptoms of liver disease. Let's take a closer look at each group.
External manifestations
- The appearance of spider veins
. Spider veins are a pronounced capillary network of dilated small vessels located in the superficial layers of the skin. This symptom is characteristic of serious liver dysfunction associated with intoxication, viral and alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Spider veins most often appear on the lower torso, but sometimes appear on the cheeks and back. - Changes in pigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes
. With liver diseases, regardless of the cause, a person experiences jaundice syndrome. For example, in the acute form of hepatitis, the skin acquires a yellowish tint already 2–3 days after the onset of the disease. The color of the mucous membranes may change even earlier. This occurs due to the fact that the concentration of liver pigment fractions (bilirubin) greatly increases in the blood of an infected person. - Change in color of palms and soles
. A symptom of liver disease is also pronounced pigmentation in places of physiological folds. As a rule, it has a bronze or smoky tint. - Hair loss
. Accelerated hair loss is often observed with liver disease. The liver processes almost all nutrients that enter the body. If liver function suffers, then the body’s supply of “building materials” for growing tissues also suffers. For example, wounds heal more slowly or hair may fall out faster. - The appearance of a rash
. Along with changes in skin color, rashes appear in liver diseases. They can be of a very different nature. Pustular elements (folliculitis and furunculosis) are caused by an immune imbalance due to a decrease in the liver’s ability to synthesize immunoglobulin. An allergic rash (papules and spots) occurs due to a violation of the detoxification function of the liver. This reaction is triggered even to familiar environmental conditions. Hemorrhagic rash (small hemorrhages on the surface of the skin) appears when the synthetic function of the liver decreases. Patients have an increased tendency to form hematomas (“bruises”) even with minor injuries.
Internal manifestations
- Asthenia
. It is characterized by general weakness and lethargy, drowsiness, fatigue, and decreased performance. These symptoms are usually the first to appear when the liver is damaged. Their occurrence is due to the inability of the organ to completely neutralize the products of nitrogen metabolism, which affect the functioning of the brain. - Dyspepsia
. In case of liver diseases, dyspeptic manifestations may be observed in the form of belching, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea or constipation, a feeling of heaviness after eating, and bloating due to increased flatulence. Due to impaired digestion and absorption of fats, qualitative changes in stool occur. Steatorrhea (“fatty stools”) is observed. Any liver disease is usually accompanied by changes in peristalsis (motor activity of the intestines) and the secretion of intestinal glands. - Cytolysis.
The first sign of liver damage is cytolysis—the destruction of hepatocytes. When liver cells (hepatocytes) are destroyed, the level of enzymes such as ALT and AST increases in the blood. If these enzymes are elevated in a biochemical blood test, this indicates an inflammatory process in the liver tissue. - Increased body temperature
. Often, people with constant pain in the liver area experience a slight rise in temperature (up to 37.8 °C). With cirrhosis, thermometer readings can reach 38 °C. In some cases, fluctuations are observed throughout the day, but most often appear in the evening. A higher temperature (from 39 °C) is a symptom of purulent processes in the gallbladder or bile ducts and is not associated with liver disease. Accordingly, treatment is prescribed for another organ.
To learn more about the causes of pain in the liver area and what to do when it occurs, you should consult a specialist. He will conduct an examination, based on which a diagnosis will be made and treatment will be prescribed. In most cases, the main minimum recommendation from doctors is to avoid drinking alcohol and junk food.