Anal fissure is one of the most common diseases of the anus. About 15% of all patients turn to a proctologist with a similar problem - and only hemorrhoids manage to exceed this figure, with which about 40% of visitors come to the doctor.
Previously, the medical doctor had already described in detail what an anal fissure is, what factors provoke its occurrence, what symptoms it manifests, and also listed modern methods of treating ruptures in the mucous membrane of the anal canal. At the same time, many questions that acutely concern patients with such a delicate disease remain unanswered.
To correct this unfortunate omission, seven of the most frequently asked questions about anal fissures will be discussed in detail below.
How to distinguish an anal fissure from hemorrhoids?
It is extremely difficult to do this without an examination by a specialist, because the symptoms of both diseases are similar: pain and bleeding during and/or after defecation, as well as itching and/or discomfort in the anus.
The presence of external hemorrhoids in a patient does not simplify the task of preliminary diagnosis, since these are not mutually exclusive problems: in some cases, patients have both hemorrhoids and anal fissure.
Conditional pre-medical differentiation will help to compare the distinctive symptoms characteristic of the diseases in question:
| Symptoms | Anal fissure | Haemorrhoids |
| Pain | Acute, occurs at the beginning of the act of defecation and quickly subsides after its completion. | Most often dull, pressing and constant, slightly dependent on the nature of defecation. |
| Blood color | Always bright scarlet. | Scarlet, dark red or dark cherry. |
| Bleeding volumes | More often it is scanty - a few drops, up to 1 teaspoon. Rarely - abundant. | May vary in intensity. |
| Nature of bleeding | Only after defecation. | It does not always directly depend on going to the toilet. |
| Itching or discomfort | May be observed. | May be observed. |
| Anal spasm | Often present. | Absent. |
| Mucus discharge | None. | May be observed. |
Anal fissure: symptoms, causes and treatment from experienced doctors at the MEDSI clinic
Table of contents
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Anal fissure in children
- Chronic fissure
- Consequences (complications) of anal fissures
- Diagnostics
- How to treat anal fissure?
- Prevention
- Advantages of treatment at MEDSI
An anal fissure (anal fissure) is a tear in the lining of the rectum. As a rule, pathology develops in people who suffer from chronic constipation or lead a sedentary lifestyle. Fissures are diagnosed in approximately 20% of patients who consult a doctor with the problem of discomfort in the rectal area. The pathology can be either independent - arising from exposure to traumatic factors, or secondary - a consequence of a number of concomitant diseases (external hemorrhoids, peptic ulcers, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract).
Causes
An anal fissure is caused primarily by trauma to the rectum or constipation and hemorrhoids.
Damage may result from:
- Gastritis, peptic ulcer, colitis
- Congestion in the rectum and pelvis caused by disruption of the cardiovascular system
- Pregnancy during which the uterus puts excessive pressure on internal organs
- Childbirth associated with prolonged pushing
Don't think that an anal fissure will heal on its own. If the patient does not change the nutritional system and eliminate traumatic factors, nothing will change. In addition, acute pathology often becomes chronic. In this case, the patient suffers from severe discomfort and often experiences not only physical, but also psychological problems. If you contact a specialist immediately after detecting signs of pathology, treatment will be carried out quickly using conservative methods. In advanced cases, treatment of chronic anal fissure is often only possible through surgery.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of anal fissure that require consultation with a doctor and treatment are:
- Discomfort after defecation
- Pain
- Minor bleeding
Over time, these symptoms are often accompanied by:
- Sphincter spasm
- Unpleasant sensations when sitting
- Constipation
The patient becomes irritable, sleeps poorly, and fears bowel movements.
Anal fissure in children
Children suffer from anal fissures less often than adults, but in some cases the pathology occurs even in newborns. To prevent the disease from becoming chronic and causing complications, treatment should be started as early as possible. Any self-medication is strictly prohibited, since it only relieves symptoms, but does not eliminate the problem, starting the course of the pathology.
Young children cannot report signs of pathology to adults, so you should monitor:
- Baby's behavior when excreting feces
- Stool density
- Child's behavior before going to the toilet. Children often become irritable and nervous and do not want to sit on the potty.
If a child cries before and during bowel movements, is afraid of going to the toilet, or suffers from constipation, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Chronic fissure
The acute form of anal fissure often becomes chronic. Especially often, pathology develops rapidly in the absence of adequate therapy. It develops into a chronic form mainly in women who have recently given birth. This is due to physiological changes in the body of a young mother. With pathology, the patient suffers not only during bowel movements, but also after it, with prolonged sitting and walking. Constant discomfort, itching and bleeding are added to the standard symptoms. The process is often aggravated by self-medication, taking laxatives, using suppositories and enemas.
Consequences (complications) of anal fissures
If an anal fissure is not treated, the following complications arise:
- Constant bleeding
- Infectious processes in the intestinal mucosa
- Prostatitis
- Rectal fistulas
- Colitis
- Acute paraproctitis
All of them are dangerous not only for health, but also for the life of the patient, and also lead to the development of a number of psychological problems.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, a comprehensive examination of the patient is performed.
It includes:
- Examination of the anus
. An anal fissure is diagnosed fairly quickly, as the mucous membranes lose their integrity and become swollen - Finger examination
. With such a study, the proctologist can determine the size of the crack and feel its edges - Sigmoidoscopy
. Allows you to examine the rectum to a depth of 20 centimeters
Laboratory diagnostics, colonoscopy and irrigoscopy may also be prescribed.
How to treat anal fissure?
Conservative therapy
Treatment of anal fissure is always carried out comprehensively. It is important to eliminate not only the symptoms of the pathology, but also its cause. The underlying disease must be eliminated. Treatment will be useless if the patient suffers from constipation and hard stool constantly damages the anus.
Typically therapy includes:
- Treatment of the anus with emollient compounds
- Relaxation of anal muscles in warm baths
- Preventing constipation
- Using ointments and suppositories for pain relief, wound healing and inflammation relief
Treatment is determined by the form of the pathology, the factors that provoked its development, and the individual characteristics of the patient. It can only be prescribed by a doctor after a comprehensive diagnosis.
Surgery
Surgical interventions are resorted to when conservative therapy does not give the desired result.
All methods used are divided into 2 types:
- Minimally invasive
. Usually the crack is removed using a laser. Its edges are simply sealed. Recovery after such an intervention does not take much time. Within a few days the patient returns to his normal lifestyle and does not experience discomfort. - Standard
. The sphincterotomy technique is used. During this intervention, the doctor makes an incision and separates the layers of sphincter muscle. Thanks to this, the existing spasm is eliminated, which allows you to reduce tension during bowel movements. Also, suturing of the walls and excision of the mucous membranes on which scars have appeared are carried out.
The choice of surgical intervention technique is made by the doctor.
Prevention
There is a set of preventive measures to prevent the formation of an anal fissure.
This includes:
- Healthy lifestyle. You should completely stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, eating fatty, fried and salty foods, which stimulate problems in the cardiovascular system and digestive tract. It is important to consume foods rich in fiber, vitamins and valuable microelements in sufficient quantities.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules. You should wash regularly and prevent the development of inflammatory and infectious processes.
- An active lifestyle, including regular, but not excessive or tiring physical activity. It is enough to walk at least 20-30 minutes a day
- Proper drinking regime. You need to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of fluid every day
- Avoiding eating foods that are too hot or cold
It is important not to restrain the urge to defecate and promptly treat any diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Advantages of treatment at MEDSI
- Use of current treatment methods. Our clinics use drug blockades, excision of anal fissures and other procedures and interventions.
- Experienced doctors. MEDSI proctologists constantly improve their qualifications and master modern methods of conservative therapy and surgical interventions
- Comfortable conditions. All examinations and treatment are carried out by experienced specialists whom our patients trust. There is no fear or embarrassment during the procedures
- No queues. You can consult a doctor at a convenient time
- Compliance with confidentiality rules
If you want to make an appointment with a proctologist at MEDSI, call +7 (495) 7-800-500.
Is it possible to get rid of an anal fissure forever?
Proctology considers anal fissures as a recurrent pathology, but this statement is not unconditional.
If a rupture of the mucous membrane of the anal canal occurred as a result of mechanical impact (anal sex, diagnostic procedures, etc.), then the likelihood of relapse is regarded as minimal - provided that the patient undergoes the full course of appropriate therapy.
The prognosis is significantly worse if the main cause of the fissure is degeneration of the mucous membrane of the anal canal, which has arisen as a result of neglected internal hemorrhoids, untreated atherosclerosis, etc. In this case, the rupture may occur again if the patient does not follow the recommendations for the prevention of anal fissures: bowel movement regulation , avoidance of physical activity, treatment of the underlying disease.
What is the best method to operate on an anal fissure?
In total, there are three main methods of surgical treatment of rupture of the mucous membrane of the anal canal:
1. Scalpel
: the crack is excised and the edges of the wound are sutured. As of today, the method is practically not used anywhere due to its high invasiveness and low efficiency.
2. Laser
: using a laser beam of a given power, the edges of the crack are skinned, and the gap itself is coagulated. This method is quite painful and practically useless for treating old cracks.
3. By radio wave
: the gap is removed non-contactly using the Surgitron device, which generates a focused “beam” of radio waves that allows you to cut tissue and coagulate wounds. The method is painless and has a minimal risk of subsequent relapse.
Thus, if the patient has a choice, it is best to give preference to the radio wave method of therapy.
Rectal fistulas
According to statistics, approximately 95% of patients with rectal fistulas associate the onset of the disease with a history of purulent inflammation (acute paraproctitis). It is not advisable to postpone radical surgical treatment for a long time, since exacerbation of paraproctitis can recur and the inflammatory process can lead to deformation of the surrounding tissues, including the development of anal muscle insufficiency. For most rectal fistulas, excision of the fistula is performed (with or without suturing the wound). Surgical treatment of simple fistulas leads to a permanent cure in approximately 95% of cases and is not accompanied by any serious complications. Complex fistulas (so-called deep trans- and extrasphincteric) can also be cured without functional impairment.
Epithelial coccygeal tract
In proctological practice, every 10 patients (in men, on average, three times more often) are found to have fistulas in the coccyx area. This is a congenital anomaly - the epithelial coccygeal duct. Patients are often unaware of their illness, or their complaints are limited to a small constant discharge above the anus, wetness of the skin between the buttocks, and itching. In other cases, often after an injury, suppuration suddenly occurs in the coccyx area, after opening which a non-healing fistula remains. Prolonged course of the epithelial coccygeal tract without proper treatment or self-medication leads to the formation of secondary fistulas; the entire sacrococcygeal region is affected by the inflammatory process. The prognosis for radical treatment of the epithelial coccygeal tract at any stage of the disease is favorable, complete recovery occurs.
Perianal genital warts
Pointed perianal condylomas are gray-pink papillary formations between which unaffected skin is visible, sometimes in the form of papillae that merge and form whole conglomerates that can cover the anus. Sometimes there are giant condylomas up to 20 cm or more in diameter. It has now been established that condylomas are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) types 6 and 11. The disease is usually sexually transmitted. They must be distinguished from flat condylomas, characteristic of syphilis and lesions in patients with AIDS. Surgical treatment is most often undertaken in the presence of large nodes and damage to the anal canal. Excision is performed with a scalpel, or an electric knife, or a laser. Sometimes, in the presence of large condylomas, surgical removal is not performed at once, since the resulting extensive wounds can lead to deformation in the area of the anus.
Patient consultations in our department are free and are held daily on weekdays. You can pre-agreed the time of your visit by phone. Read more on the website: https://www.surgery-future.ru/proktologiya
Can an anal fissure heal on its own?
This is possible subject to the following conditions:
- switching to a dietary diet that excludes foods that tend to irritate the rectum and anal fissure in particular (spicy, salty, smoked foods, marinades);
- normalization of stool - achieving regularity and softening of stool;
- decreased physical activity, especially weight lifting.
All of the above conditions must be met within the next 5-7 days, otherwise independent healing is regarded as unlikely.
Diagnosis of the disease
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis; a person without a medical education cannot do this on his own, since a full examination is needed. For that? To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will examine the patient and also prescribe tests:
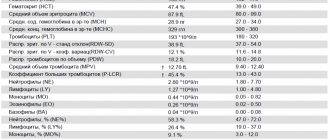
- A general blood test, the main purpose of which is to identify anemia, which directly indicates the presence of bleeding from a fissure
- General analysis of stool, the main purpose of which is to exclude inflammatory processes in the intestines, identify pathogenic flora, exclude bleeding, as well as the presence or absence of worms
Along with the above tests, the doctor may send the person for the following procedures: