Anomalies in the formation of the central nervous system are by no means uncommon. This pathology ranks second in frequency after congenital defects of the heart and blood vessels.
and in most cases is represented by hydrocephalus of various origins. In addition to severe disorders that accompany pathological brain development, central nervous system defects carry a high risk of death, and according to statistics, they lead in the number of deaths in infancy.
Dandy-Walker syndrome is one of the types of disorders of brain formation during fetal development. And although its frequency is relatively low (only 1 case per 25-30 thousand babies), the defect is diagnosed in almost every tenth baby with congenital hydrocephalus, which is one of the main manifestations of the pathology.
The syndrome was first described almost a century ago, and a little later a method of surgical correction was proposed, but after many decades the pathology remains incurable, and even modern medicine is unable to correct the severe consequences of embryogenesis disorders that occur with brain abnormalities.
Dandy-Walker syndrome is a defect of the posterior cranial fossa, with the main structural changes affecting the cerebellum, the cerebrospinal fluid drainage tract, and the fourth ventricle of the brain. The anomaly is diagnosed during pregnancy through an ultrasound examination, after which the woman may be offered a termination of pregnancy for medical reasons.
Of course, any abnormalities in the development of the fetus are always a great stress and worry for parents, but in the case of a congenital brain defect there is no hope for a miracle - the prognosis is serious and the mortality rate is high. Children with combined defects of the brain and other organs die at an early age from both brain dysfunction and associated infection.
Dandy-Walker anomaly is often combined with other disorders and genetic diseases, often incompatible with life - microcephaly (underdevelopment of the cerebral hemispheres), cerebral hernias. The baby may be diagnosed with genetically determined polycystic kidney disease, underdevelopment of the optic nerves and eyeballs with blindness, and abnormalities of the cardiovascular system.
All these unfavorable factors, the possibility of combined pathology of many organs, make Dandy-Walker syndrome a serious problem if the baby is given the opportunity to be born. Treatment of pathology is usually symptomatic, aimed at maintaining the main life support systems and combating infectious complications
. In rare cases, a surgical operation is used, which only alleviates the symptoms of hydrocephalus, but does not eliminate it completely.
Why does Dandy-Walker syndrome occur?
The causes of anomalies in the development of the posterior cranial fossa have not yet been clarified, but a number of factors have been identified that contribute to such congenital defects:
- Infection during pregnancy with cytomegalovirus, past rubella;
- Drinking alcohol, smoking, drug addiction during pregnancy;
- Extragenital pathology, especially diabetes mellitus in the expectant mother.
Under the influence of the listed reasons or in the midst of complete well-being, a spontaneous mutation in genes may occur, predisposing to impaired brain development. The risk of defects is especially high under the influence of unfavorable factors during the first trimester of gestation, when the formation of the main structures of the central nervous system occurs.
In some cases, Dandy-Walker syndrome is hereditary in nature, that is, it occurs due to a gene defect and can be inherited as a recessive trait. If the first pregnancy proceeded with the formation of this pathology, then the risk of repeated defects in the future increases to 25%.
What happens to the brain in Dandy-Walker syndrome?
Anatomically, the classic variant of posterior fossa malformation includes:
- Hydrocephalic syndrome of varying severity;
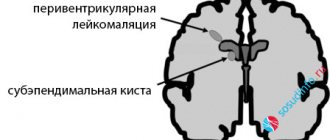
- A cystic cavity in the back of the skull with an enlarged fourth ventricle of the brain;
- Absence or underdevelopment of the cerebellar vermis, underdevelopment of its hemispheres.
The cerebellar vermis is a structure located between its halves and carrying conductive nerve fibers. With Dandy-Walker anomaly, it can be represented by a small gap or a wide space between the hemispheres of the organ. In the incomplete absence of the worm, a slit-like expansion is formed only in its lower part. Against the background of the pathology of this department, insufficient development of the cerebellar hemispheres is observed.
It is the defect of the cerebellar vermis in the form of a cleft that is considered a characteristic sign of the Dandy-Walker anomaly, which makes it possible to distinguish it from underdevelopment against the background of other brain defects.
An obligatory component of the syndrome is a cystic cavity in the back of the skull,
which communicates with the ventricular system or is closed and originates from the fourth ventricle. Excess cerebrospinal fluid and hydrocephalic syndrome are associated with underdevelopment of the openings of this part of the brain (Lushka and Magendie), which provide fluid outflow. If the ventricular cyst has partial communication with the subarachnoid space, the latter will be called open, otherwise the cyst is considered closed.
A cyst of the fourth cerebral ventricle may spontaneously open into the 3rd ventricle or subarachnoid space. In this case, the symptoms of cerebrospinal fluid tract occlusion will be somewhat weakened. The severity of hydrocephalic syndrome is variable - from a slight dilation of the ventricular system to a high degree of occlusive hydrocephalus with the absence of the possibility of cerebrospinal fluid circulation.
Many experts note that most babies with Dandy-Walker syndrome do not have hydrocephalus as such at birth, but it develops progressively
increases during the first few months of life, therefore the fact of the absence of hydrocephalic syndrome immediately after birth in the presence of pathology diagnosed in utero is not a reason to revise the diagnosis and the unreasonable hopes associated with it.
In more than half of the cases of Dandy-Walker syndrome in children, in addition to the described structural abnormalities, other brain defects are also found
- underdevelopment or absence of the corpus callosum, brain cysts, underdevelopment or absence of gyri, displacement of the gray matter relative to its correct localization, which further aggravates the course of an already severe pathology.
According to MRI data, several types of Dandy-Walker syndrome have been identified:
- The classic type of anomaly - the posterior cranial fossa is enlarged, the fourth ventricle is cystically changed, the cerebellar vermis is partially or completely underdeveloped, its hemispheres are hypoplastic, and the tentorium is higher than normal, the ventricular system does not communicate with the subarachnoid space, cerebral cysts and the absence of the corpus callosum are often observed , almost all patients have hydrocephalus, and compression of the stem structures is possible. The defect manifests itself clinically from birth and has an unfavorable prognosis.
- Dandy-Walker variant - the morphological signs are less pronounced than in the classic form, the lower part of the cerebellar vermis is hypoplastic, the ventricles communicate with the cyst and cerebrospinal fluid spaces, ensuring the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, so hydrocephalus is rarely observed. The posterior cranial fossa is of normal size, the stem structures are not compressed.
- Blake's pouch cyst is an enlargement of the ventricular system with hydrocephalic syndrome, the cyst is located under or behind the cerebellum, the vermis is relatively well developed. The fourth ventricle is dilated, but does not communicate with the occipital liquor tank.
- Mega cisterna magna is a variant of focal expansion of the subarachnoid space in the posterior and lower parts of the posterior fossa of the skull with an increase in the volume of the occipital cistern, which communicates with the fourth ventricle and subarachnoid space.
Manifestations of the disease
Symptoms
Dandy-Walker syndrome is varied. Both practically normal development of the child after birth and severe neurological changes leading to severe disability and even death are possible. According to some data, normal development of intelligence occurs in half of the cases of isolated defect; it is even possible that the syndrome is accidentally discovered during examination of adults.
children with Dandy-Walker syndrome
The intrauterine course of the pathology is determined by the degree of brain damage, the increase in hydrocephalus, and the presence of other developmental defects. The prognosis is significantly worse when the syndrome is diagnosed before birth. , hydrocephalic syndrome comes to the fore among other manifestations.
:
- Increase in head diameter;
- Bulging of the fontanel.
The increase in the diameter of the skull occurs mainly due to the occipital region, in which a cyst forms, causing thinning and stretching of the bone base. With severe hydrocephalus, the baby's head actively grows during the first two months, and at the same time, the sutures between the bones in the front or back part separate. In addition, it is characteristic:
- Increased nervous excitability (reflexes);
- Oculomotor disorders - nystagmus, strabismus;
- Attacks of respiratory arrest;
- Facial nerve paresis.
Symptoms of cerebellar disorders in newborns cannot be identified, and even a severe defect in the formation of cerebellar structures does not always cause significant signs of ataxia (motor disorders), which is recorded in only a third of patients.
Much more often than motor disorders, disorders of mental activity and intelligence occur, which manifest themselves against the background of general motor “awkwardness.” 25% of patients with a hypoplastic cerebellum have signs of autism, and therefore experts are trying to find a relationship between changes in the cerebellum and autism in children.
Children with hydrocephalus at an early age are restless, sleep poorly, are characterized by a monotonous cry, increased reflexes, floating eye movements and their rolling, pronounced vessels of the cornea, a noticeable subcutaneous venous network as the size of the head grows. Spontaneous motor activity of newborns may be weakened, convulsions and tetraparesis are possible due to muscle hypertonicity.
At an older age, a lag in mental and intellectual development
, children cannot learn, get tired quickly, and do not assimilate new information well, which makes the adaptation process extremely difficult. In severe cases, learning is completely impossible, and therefore the child needs constant outside help, care and consideration of the issue of disability.
Motor development
noticeably slower. In severe forms of the anomaly, children cannot learn to roll over, crawl, sit up and walk in a timely manner, do not keep their eyes on toys, get tired quickly and often cry. Possible nutritional disorders with malnutrition, a general decrease in immunity, and frequent infectious diseases.
The combination of a defect of the nervous system with other anomalies of organ development predisposes to serious complications, including not only brain dysfunction, dementia, convulsive syndrome, but also heart failure, a tendency to pneumonia with heart defects, chronic renal failure and uremia with congenital polycystic disease, which aggravates phenomena of cerebral edema and can cause the death of the patient.
With severe occlusive hydrocephalus, death can occur in early infancy from cerebral edema, fatal arrhythmias, respiratory arrest due to compression of brainstem structures, severe pneumonia and other infectious complications.
In adults, a gradual increase in hydrocephalus with cranialgia, decreased memory and attention, irritability, a tendency to depression, morning sickness and vomiting at the height of headaches is possible. In severe cases, convulsive syndrome occurs. There may be problems with coordination and performing small movements, uncertainty when walking, and visual disturbances.
Advantages of treatment in Israel
- World-renowned doctors with enormous clinical experience.
- Equipping clinics with high-precision equipment.
- Endoscopic neurosurgical operations.
- Medicines of the latest generation.
- Reasonable prices.
Timely, accurate diagnosis and an adequate therapeutic course will improve well-being and ensure the possibility of normal further development of the child. Don’t waste time, contact an Israeli clinic and trust the health of your baby to world-renowned doctors.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 5 out of 5)
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of Dandy-Walker syndrome is based on the results of an ultrasound examination, and it is important to detect the anomaly during embryonic development. Ultrasound becomes informative after the 18th week of gestation, but in some cases pathology can be suspected earlier - already at 14-15 weeks of embryonic development.
Diagnostic criteria for an anomaly of the posterior cranial fossa are:
- The presence of a large cystic cavity, including the fourth cerebral ventricle, in the back of the skull;
- Absent or abnormal development of the cerebellar vermis;
- Hypoplasia of the cerebellar hemispheres, the presence of a wide gap between them;
- Dilatation of the ventricular system (hydrocephalus).
To make a diagnosis of Dandy-Walker syndrome, you need:
- Ultrasound (neurosonography);
- MRI to determine the anatomical features of the fourth ventricle of the brain;
- Consultation with an ophthalmologist;
- Examination by a neurosurgeon;
- Ultrasound of the heart to exclude congenital anomalies;
- Consultation with a geneticist and determination of the karyotype for possible genetic mutations.
Treatment of the pathology is determined by the symptoms and severity of the manifestations.
If there is no hydrocephalus, and intracranial pressure is within normal limits, then dynamic observation by a neurologist, pediatrician or neurosurgeon is justified; no medications are required.
shunting to level hydrocephalus
With increasing hydrocephalus and intracranial pressure, shunt surgery is indicated to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the skull into the chest or abdominal cavity. Drug treatment includes the use of diuretics (diacarb, mannitol), nootropic drugs (piracetam, pantogam), anticonvulsants (depakine).
In case of hypertonicity, physiotherapeutic and water procedures, massage, and special exercises are indicated. Careful care and constant monitoring of the baby are important, creating a calm environment for restless behavior and sleep disturbances.
In severe forms of pathology with mental retardation, children are advised to work with defectologists-teachers and a psychologist according to an individual program that eliminates excess information and mental overstrain.
The prognosis for Dandy-Walker syndrome depends on a number of reasons:
time of diagnosis, presence of other defects and chromosomal diseases, degree of cerebrospinal fluid duct occlusion. Mortality and morbidity after birth are higher in cases where the anomaly is combined with other defects and is detected before the baby is born.
Hydrocephalus and intracranial hypertension are key points in determining the prognosis
, which affect both the patient’s development and the duration and quality of his life. In the case of isolated brain damage without signs of hydrocephalus, the prognosis is favorable. The child may develop according to age, and sometimes the anomaly is even detected in adults during examination for other reasons.
Due to the fact that the causes of the defect have not been clarified, it is not possible to carry out specific prevention. Of course, you need to maintain a healthy lifestyle, especially for women planning a pregnancy or already pregnant, excluding bad habits and adverse environmental influences. It is important to promptly identify and treat cytomegalovirus infection, herpes, and in the case of rubella, which a woman contracted during pregnancy, doctors will offer abortion for medical reasons due to the high risk of combined defects.
The future mother and her family will have to decide whether to continue pregnancy if the syndrome occurs accidentally in the fetus of an absolutely healthy woman. The decision is always difficult, but you should know that an anomaly of the nervous system and the normal development and growth of a child are rather an exception to the rule.
In the vast majority of cases, children and parents have to deal with hydrocephalus, often requiring more than one expensive and complex operation, while its effectiveness and prognosis may still remain questionable.
Journal "Child's Health" 3 (30) 2011
Malformations of the nervous system overall occupy second place in the structure of developmental anomalies after congenital pathologies of the cardiovascular system, and about 80% of these diseases are represented by hydrocephalus of various origins. In addition, conditions of the perinatal period and congenital malformations have been in first place in the structure of infant mortality for many years [3].
Among live-born children, the incidence of Dandy-Walker syndrome is relatively low - 1 case in 25,000–35,000, however, among children with congenital hydrocephalus, Dandy-Walker syndrome is diagnosed much more often - from 3.5 to 12% of cases and is classified as to malformations of the posterior cranial fossa. Etiology unknown. The syndrome can be a manifestation of genetic diseases, such as Meckel syndromes (autosomal recessive path: microcephaly, polydactyly, polycystic kidney disease, ocular abnormalities - microphthalmia, optic nerve hypoplasia, congenital heart disease, cryptorchidism, occipital spina bifida), Meckel-Gruber syndrome ( the same + encephalocele), Warburg, Turner, various chromosomal aberrations. It is assumed that factors such as viral infection (CMV, rubella), alcohol, and diabetes in pregnant women influence the development of this pathology [1, 3].
The syndrome was first described in 1914 by W. Dandy and K. Blackfun in an article devoted to the study of various forms of hydrocephalus, and in 1921 the work of W. Dandy was published, in which he analyzed the methods of diagnosis and treatment of this defect. After 21 years, J. Taggart and A. Walker proposed the option of surgical correction of the described pathology. Only in 1954, S. Benda combined the names of two scientists in the name of one syndrome - W. Dandy and A. Walker [1, 2].
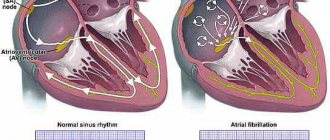
In the classical form, the syndrome includes the following manifestations: 1) hydrocephalus of varying degrees; 2) a cyst of the posterior cranial fossa, including an enlarged fourth ventricle; 3) developmental agenesis of the cerebellar vermis and hypoplasia of its hemispheres (Fig. 1).
The vermis defect can vary in size from a thin gap to a wide canal between the separated hemispheres. In some cases of partial agenesis of the worm, the gap can be traced only in its lower part. Depending on the degree of atresia of the orifices of the fourth ventricle (Lushka and Magendie), cysts are divided into open and closed. In the first case, the connection between the fourth ventricle cyst and the perimedullary subarachnoid space is preserved; in the second case, this communication is absent. Cysts can rupture into the third ventricle or subarachnoid space, which can lead to self-resolution of occlusive manifestations. The degree of hydrocephalus varies from slight dilatation of the lateral and third ventricles to severe occlusive hydrocephalus (Fig. 1).
According to most authors, hydrocephalus in most children with Dandy-Walker defect is absent at birth and develops during the first months of life [2].
In 65% of cases, according to R. McLaurin (1985), the defect is combined with other brain anomalies - agenesis of the corpus callosum, encephalocele, polymicrogyria, agyria, heterotopia of the gray matter, as well as with lesions of other organs and systems (polydactyly, syndactyly, congenital heart defects, polycystic kidney disease, cleft palate, etc.).
Ultrasound studies in children with Dandy-Walker syndrome reveal the following characteristic picture: in the posterior cranial fossa, during coronal and sagittal scans, a large cyst-like formation is observed, including the IV ventricle; the cerebellar vermis is not identified (Fig. 3, 4); the cerebellar hemispheres are sharply reduced in size and moved apart; the cerebellar tentorium is displaced upward; The third and lateral ventricles are dilated to varying degrees.
Differential diagnosis of Dandy-Walker defect is carried out with retrocerebral cysts and expansions of the cistern magna in the presence of cerebellar hypoplasia of another etiology (inflammatory, toxic, etc.). For Dandy-Walker syndrome, a defect in the cerebellar vermis is pathognomonic, which is not observed with its hypoplasia caused by other diseases. Differential diagnosis of arachnoid cysts can be difficult and requires the use of computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
Prenatal diagnosis of Dandy-Walker syndrome is extremely important, which is usually carried out after the 18th week of pregnancy. However, in some cases, diagnosis of Dandy-Walker syndrome is possible at earlier stages of pregnancy. According to some authors, the earliest prenatal diagnosis of Dandy-Walker anomaly was carried out with transvaginal echography at 12–14 weeks of pregnancy.
The prognosis for life and health with Dandy-Walker syndrome depends on the presence of combined developmental anomalies, chromosomal abnormalities and the timing of diagnosis. According to the literature, postnatal morbidity and mortality rates are higher in cases where the syndrome is diagnosed in the prenatal period rather than in the newborn.
We present our own observation of a patient with Dandy-Walker syndrome.
Girl Anna (Fig. 5). Born from the first pregnancy (ultrasound examination revealed a congenital malformation: anomaly of the central nervous system - Dandy-Walker syndrome, hydrocephalus), which proceeded without any peculiarities, pathological (cesarean section), premature birth (35–36 weeks) with premature rupture of amniotic fluid (anhydrous period 7 hours). Body weight at birth was 3000.0 g, body length 48 cm, head circumference 41 cm, chest circumference 32 cm, Apgar score 6–7 points. The severity of the condition is due to respiratory failure and pathological neurological symptoms. After consulting a neurosurgeon in the maternity hospital, the child was given a drainage system to unload the cyst. By the end of the second week after birth, the child was transferred to the neonatal pathology department of the Children's Clinical Hospital with a diagnosis of intrauterine infection of unspecified origin. Congenital malformation of the brain, Dandy-Walker syndrome, cyst of the posterior cranial fossa. Delayed rate of psychomotor development. Tetraparesis. Prematurity of the first degree." The condition upon admission was severe. The child is hypodynamic, spontaneous motor activity is reduced, and the cry is weak. The skull bones are soft, the sutures are open. Large fontanelle 4.0 x 4.0 cm. Palpebral fissures D = S, floating movements of the eyeballs. Multiple stigmas of dysembryogenesis (auricular stigmas, coracoid nose, microglossia). Tetraparesis, crossing the legs in the lower third of the leg. The skin and visible mucous membranes are clean and pale. Soft tissue turgor is reduced. Breathing is rhythmic, weakened over the entire surface of the lungs. Heart sounds are muffled, moderate tachycardia. The abdomen is soft, the liver is 2.5 cm below the edge of the costal arch, the spleen is at the edge of the costal arch.
The girl was admitted to a specialized orphanage at the age of one and a half months in serious condition. The severity of the condition was due to the increase in pathological neurological symptoms: forced position in bed on the side with the head thrown back, monotonous “brain” cry, floating movements of the eyeballs, “setting sun” symptom, horizontal nystagmus. The light does not respond to sound. Reflexes of the newborn period are suppressed. Multiple stigmas of dysembryogenesis are noted - auricular, beaked nose, micrognathia. The cerebral part of the skull is significantly enlarged (head circumference 49 cm), divergence of all cranial sutures, and bulging of the fontanelles. The subcutaneous venous network is prominent. Hypodynamia, spontaneous motor activity is reduced. Muscle tone in the limbs is dystonic, tetraparesis, legs crossed in the lower third. Physical development is inharmonious, the child has low nutrition, tissue turgor is reduced. The skin and visible mucous membranes are pale. There is puerile breathing in the lungs. The boundaries of the heart are within the age norm, heart sounds are muffled and rhythmic. The abdomen is round in shape, soft and painless on palpation, the liver is up to 1.5 cm below the costal margin, the spleen is not palpable.
Neurosonography from 06/04/10. The brain structures do not correspond to the anatomical ones. Echogenicity is increased. The pattern of grooves and convolutions is smoothed. Hypoplasia of the vermis and cerebellar hemispheres. In the posterior cranial fossa there is a cyst 47 x 60 mm. Echo signs of congenital malformation of the brain. Dandy-Walker syndrome.
Examination by an ophthalmologist: OU - the media are transparent, the fundus is within normal limits.
Examination by a surgeon: umbilical hernia.
Complete blood count: Hb - 130 g/l; Er - 4.0 T/l; Tr - 280 G/l (70: 1000); CPU - 0.9; L - 9.6 G/l; reticulocytes - 0.0020 G/l; e - 1; n - 7; s - 72; l - 8; m - 12; ESR - 5 mm/hour.
Urinalysis: normal.
Based on the above, a diagnosis was made: congenital anomaly of brain development, Dandy-Walker syndrome, cyst of the posterior cranial fossa. Tetraparesis. Delayed rate of psychomotor development. Stage I prematurity Umbilical hernia. Hypotrophy stage I
From the moment she was admitted to the orphanage, the girl’s condition remained serious; she received symptomatic therapy. During the second week of stay, the child's condition worsened. Neurological symptoms increased, lethargy alternated with periods of anxiety and monotonous screaming, appetite decreased, and temperature increased. The girl was hospitalized in the intensive care unit of the CSCH.
Despite the treatment, the child's condition progressively worsened and the patient died.
An autopsy confirmed a congenital malformation of the brain in the form of Dandy-Walker syndrome with mixed hydrocephalus and atrophy of brain tissue, which clinically occurred with tetraparesis and a sharp delay in all types of development. Histological examination revealed bilateral focal interstitial pneumonia and serous leptomeningitis, which were regarded as complications of brain malformation that aggravated the swelling of brain tissue with the development of death. The immediate cause of death was cerebral edema. In this case, there is a coincidence of clinical and pathological diagnoses.