Leukemia, which is often called blood cancer or leukemia, is a serious cancer. It affects the hematopoietic organs and causes changes due to which the number of leukocytes in the patient’s blood sharply increases. As the disease progresses, the blood gradually ceases to perform its functions in the body, which causes death if left untreated. The disease affects not only adults, but also children, and is found with equal frequency in men and women.
Childhood leukemia
Recognizing the signs of leukemia in a child can be difficult. A child may not be able to describe their symptoms as easily as an adult.
Some of the most common signs and symptoms of leukemia in children are: loss of appetite, bleeding gums, headache, easy bleeding, slight bluish discoloration of the skin, fever without other signs of infection, problems with pain when breathing, rash, swollen lymph nodes that the person may feel under the arms, above the collarbone or groin, unexplained fatigue, unintentional weight loss.
Many of these symptoms may resemble other childhood illnesses, such as the flu, respiratory syncytial virus, or pneumonia.
Leukemia in adults
Symptoms of leukemia in adults can range from a general feeling of unwellness to abdominal swelling due to problems with the spleen, an organ of the immune system. A person may experience the following symptoms.
Nonspecific symptoms
Sometimes a person may experience flu-like symptoms that they do not necessarily associate with leukemia. These symptoms are usually associated with the destruction of blood cells in the body and an increase in the amount of energy the body needs to fight the disease.
Symptoms include: loss of appetite, fever, night sweats, unexplained weight loss. A person may often associate these symptoms with leukemia when a doctor diagnoses them.
Bloating
As the number of leukemia cells increases, they may begin to accumulate in the spleen and liver. The presence of excess cells can cause these organs to become enlarged. As a result, a person may experience a feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdominal cavity.
Bleeding problems
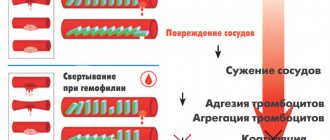
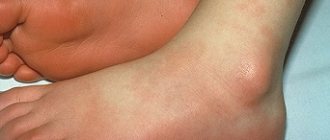
Some types of leukemia can destroy platelets, a type of blood cell that helps stop bleeding. As a result, a person may notice that they bleed longer if they have a cut. He may also have bleeding gums or frequent nosebleeds.
Bone or joint pain
Abnormal cells can accumulate near or inside bones, which can cause unexplained pain in the bones or joints. This pain can range from a dull ache to severe pain and discomfort.
Increasing number of infections
Leukemia can destroy white blood cells, which help fight infections. As a result, people with this condition may experience higher levels of infection and fever due to low white blood cell counts. A person may feel like he is always sick and fighting various viral and bacterial diseases. The temperature may not increase.
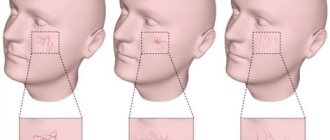
Enlarged lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are a key aspect of the body's immune system as they filter fluid and potentially harmful substances from the body. If leukemia cells spread and multiply, they can reach lymph nodes in the body.
A person or doctor may feel the lymph nodes as fluid-filled lumps under the skin. Common places where swollen lymph nodes can occur include: either side of the groin, sides of the neck, under the arms. Sometimes lymph node swelling does not occur to such an extent that a person can feel the swollen nodes.
Superior vena cava syndrome (SVC)
Some people have leukemia, which affects the T cells in the thymus. The thymus is a gland near the trachea, or windpipe, that acts as an organ of the immune and endocrine systems. If leukemia cells are present in the thymus, the gland may begin to swell and put pressure on the SVC.
This large vein transports blood to the heart from the upper body. Pressure from the thymus gland on the SVC can cause blood to pool in the veins, which can lead to dizziness, headaches, and swelling of the chest, arms, face, and neck.
Some people may even experience changes in thinking and consciousness due to the disruption of blood flow from the vein. SVC syndrome is a serious medical complication of leukemia that requires immediate treatment.
Types of disease
The modern classification of leukemia includes several principles of division into types. First of all, it is worth mentioning the division of cases of the disease according to the nature of the course into:
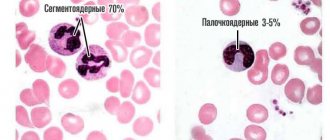
- acute, characterized by rapid development and the formation of a large number of immature blood cells - blasts;
- chronic, which are characterized by a long course and pathological production of mature leukocytes with altered properties.
Another principle for classifying leukemia is based on the level of differentiation of the affected cells, which can be:
- undifferentiated;
- quotational;
- blast.
In addition, oncologists distinguish many types of leukemia according to the types of cells whose pathological changes underlie the disease. According to this principle, lymphoblastic, monoblastic, myeloblastic, lymphocytic, myeloma and other types of disease are distinguished.
Early signs of leukemia
Leukemia does not always cause symptoms in the early stages. Often the initial symptoms are very similar to flu symptoms, but unlike flu symptoms they do not go away.
Examples of common early symptoms of leukemia include: loss of appetite, bone pain, bruising, fever, frequent infections, headaches, heavy bleeding, joint pain, night sweats, shortness of breath. If symptoms do not go away within a few weeks, the patient should talk to a doctor.
Chances of recovery
Currently, the diagnosis of leukemia is not a death sentence, as it was before. The answer to the question whether leukemia is curable depends on certain factors:
- types of disease;
- timely diagnosis;
- the nature of tissue and organ damage;
- age characteristics;
- other possible risks.
Thus, it is important to monitor your health carefully and closely. At the moment, specialists do not have a maximum guarantee that leukemia can be treated, but thanks to modern medicine, there are a considerable number of methods that make it possible to extend the patient’s life by several decades.
Symptoms of acute and chronic leukemia
Doctors may classify leukemia as acute or chronic. Acute leukemia occurs suddenly, and cancer cells multiply quickly. Chronic conditions result from the slow development of cancer cells, and it may take years before a person develops any symptoms.
However, acute and chronic leukemia have some similarities. They both cause flu-like symptoms, fatigue, and a general feeling of ill health. Examples of symptoms of chronic leukemia include: anemia, loss of appetite or a feeling of fullness in the upper left side of the abdomen (where the spleen is), easy bruising or bleeding, fatigue, enlarged lymph nodes that are not painful, night fever, weight loss.
Symptoms of acute leukemia may include: bone pain; cuts that heal slowly; fatigue that does not go away; persistent infections; joint pain; low temperature; fever night sweats; pale skin; small red dots under the skin.
These are just some examples of symptoms of acute and chronic leukemia. A person may experience other symptoms instead of or in addition to those described.
Stages
Separately, it is necessary to consider the main stages of leukemia.
- Initial. Most often diagnosed in patients who suffer from anemia.
- Expanded. All the symptoms are already showing up here.
- Remission. May be complete or incomplete. It is characterized by an increase in blast cells by a maximum of 5% in the bone marrow (in their absence in the blood).
- Relapse. It can develop both in the bone marrow and other organs. It is worth saying that each subsequent relapse is more dangerous than the previous one.
- The last one. In this case, the patient develops ulcerative-necrotic processes, and suppression of hematopoiesis occurs.
Causes and risk factors
Scientists have not yet identified the main cause of leukemia. They suggest that multiple factors may influence the likelihood of this disease.
These factors include: older age, family history (parent or close relative who had leukemia), chemotherapy or radiation after treatment for other cancers, history of cigarette smoking, exposure to chemicals such as benzene, history of exposure to high levels of radiation.
However, just because a person has these risk factors does not mean that he or she will definitely develop leukemia.
Treatment
After leukemia is detected, treatment is selected in accordance with the form and stage of the disease, the level of damage to vital organs, age, and general condition of the body. The treatment method is chosen by a specialist - an oncologist, an oncohematologist, and his goal is to restore the normal hematopoietic process, achieve long-term remission, and ideally, a complete cure.
The choice of method largely depends on the form of the pathology. In acute cases of the disease, chemotherapy has a good effect; in cases of chronic disease, the most effective method is often a bone marrow transplant or stem cell treatment. Adverse symptoms are relieved by detoxification and hemostatic therapy, the introduction of healthy platelets and leukocytes, and courses of antibiotics.
Forecasts
In acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the prognosis depends primarily on the age of the patient. In children, recovery occurs in 80-90% of cases. For adults, the rate is currently 40-45%, with younger patients having significantly higher odds than people over 60 years of age. We should not forget that in recent years, oncologists have made significant progress in the treatment of blood diseases. Every year new, increasingly effective and safe targeted chemotherapy drugs appear.
Reviews
16.11.2021
Oncology clinic NACFF. The real story about “not giving a damn”
In 2021, on August 16, my older sister flew to Lobnya to undergo examination and, if necessary, treatment at the NACFF oncology clinic.
She lives in the capital Kyrgyzstan...
Read full review
27.10.2021
At the clinic, like at home
30.09.2021
Feedback on the treatment of ovarian cancer at the NACFF clinic
07.09.2021
NACFF patient about treatment, quick examinations and attentive attitude
View all reviews
Hospital, hospitalization, emergency medical care - 24/7, 7 days a week
+7 (495) 259-44-44
Book your room today
6 seats
1 local ward
- 4 meals a day
- Bathroom in the room
- Anti-decubitus mattresses
8200 rub.
Book
13 places
2 local ward
- 4 meals a day
- Bathroom in the room
- Anti-decubitus mattresses
5700 rub.
Book
2 seats
VIP chamber
- a guest room
- 4 meals a day
- Bathroom in the room
- Anti-decubitus mattresses
17700 rub.
Book
6 seats
1 local ward
- 4 meals a day
- Bathroom in the room
- Anti-decubitus mattresses
8200 rub.
Book
13 places
2 local ward
- 4 meals a day
- Bathroom in the room
- Anti-decubitus mattresses
5700 rub.
Book
2 seats
VIP chamber
- a guest room
- 4 meals a day
- Bathroom in the room
- Anti-decubitus mattresses
17700 rub.
Book
Diagnostics
Since the disease develops very quickly, when contacting an oncologist or oncohematologist, the symptoms of acute lymphoid leukemia are usually already pronounced. However, to confirm the diagnosis and determine treatment methods, laboratory tests are necessary, as well as instrumental studies:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- myelogram - study of bone marrow cells, cytochemical analysis, immunophenotyping;
- spinal cord puncture with histological and cytological examination of the biopsy;
- Ultrasound of internal organs and lymph nodes;
- chest x-ray;
- ECG and other studies according to symptoms.