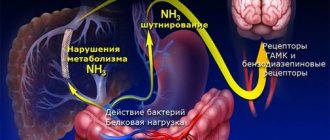
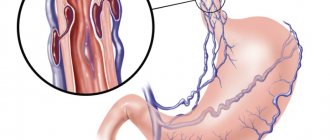
The portal vein collects blood coming from the abdominal organs (intestines, spleen, stomach) and carries it to the liver. The organ ensures blood purification, after which it flows into the general circulatory system. The portal blood vessel is formed by the confluence of the splenic, inferior and superior mesenteric veins. The pancreatic and gastric veins (right and left) flow directly into the portal vascular trunk. The portal blood vessel of the liver ensures the normal functioning of the digestive tract and is an important unit of the circulatory system, the pathologies of which affect the functioning of the entire body.
Normal dimensions of the gallbladder:
- length up to 8-12cm[1,5,7];
— transverse size up to 3.5-5 cm [1,5,7];
— wall up to 3-4mm*[1,5,7].
*All measurements are given on an empty stomach, i.e. when the gallbladder is full. The wall of the gallbladder in a contracted state can be thicker!
When conducting a food test to determine the function of the gallbladder using ultrasound, it should shrink by 2/3 of its original volume by about 30 minutes after eating.
The pancreas normally has an even contour, a fine-grained structure and an echogenicity slightly lower than the hepatic (but may be higher than the hepatic, which, with normal sizes, can also be regarded as a variant of the norm - slight fatty involution, against the background of an “active” lifestyle, in particular abuse fatty foods, smoked meats, alcohol...), measured by transverse scanning, usually three dimensions are measured (anterior-posterior dimensions): head, body and tail; although some authors [5] also suggest measuring the isthmus of the pancreas (the border of the head and body), but in practice this is rarely used.
Diagnostic measures
The main diagnostic technique for detecting changes in the portal vein remains ultrasound. The study can be prescribed to pregnant women, children and elderly patients. Doppler ultrasound, used in conjunction with ultrasound, helps assess the speed and direction of blood flow. Normally, it should be directed towards the organ.
With the development of thrombosis, a hyperechoic (dense) heterogeneous formation is detected in the lumen of the vessel. It can fill the entire lumen of the vessel, or cover it only partially. In the first case, blood movement stops completely.
One of the most common liver vascular pathologies
With the development of portal hypertension syndrome, dilation of the vascular lumen is detected. In addition, the doctor detects an enlarged liver and fluid accumulation. Doppler ultrasound will show a decrease in blood flow velocity.
A possible sign of portal hypertension is a cavernoma. The patient is required to undergo an FGDS to assess the condition of the esophageal anastomoses. Additionally, esophagoscopy and radiology of the esophagus and stomach may be recommended.
In addition to ultrasound examination, computed tomography with a contrast agent can be used. The advantage of using CT is the visualization of the liver parenchyma, lymph nodes and other formations located in close proximity.
Angiography is the most accurate method for diagnosing portal vein thrombosis. Instrumental studies are complemented by blood testing. Of clinical interest are indicators of leukocytes, liver enzymes, and bilirubin.
Normal stomach wall thickness:
- up to 3.5+-1.1mm[6].
Normally, on an empty stomach there should be no liquid contents in the stomach.
Kidneys normally have an oval shape in a longitudinal section, the echogenicity of the cortical layer of the parenchyma is lower or equal to that of the liver/spleen**[4], the echogenicity of the medullary layer of the parenchyma is lower than the cortical layer. The collecting-pelvis system, which is also sometimes called the renal sinus (which often causes antipathy among some urologists), is not normally dilated, which means the size of both the cups and pelvis is on average up to 5 mm; although depending on the type of pelvis and water load (therefore, the kidneys also look on an empty stomach, if the patient drank water before the ultrasound, the size of the collecting system may be larger), the size of the pelvis can normally reach 8-10 mm, with an increase in the pelvis of more than 1- 1.5 cm requires consultation with a urologist and urography (X-ray).
**Except for the neonatal period, in newborns the echogenicity of the renal cortex may be higher than the echogenicity of the liver/spleen!
[8]
The kidneys are usually measured in a longitudinal section, most often two sizes are measured, but sometimes three, and even the volume is calculated. It should be noted that the size of the kidneys may differ even in the same person when measured from different accesses (water load must also be taken into account), i.e. from the side and from the back. The error can reach 1 cm or more. By analogy with the liver indices, the ratio of length and transverse size of the kidney is also sometimes calculated[7], normally this ratio should be within 2:1 (i.e. oval shape). With nephritis of various etiologies, this ratio is smoothed out, i.e. the bud begins to tend to a round shape.
Forecast
Portal hypertension is a complication of underlying liver disease. The disease can often be controlled, and survival depends on the preservation of liver function. The worse the liver performs its functions, the worse the prognosis.
There are higher rates of mortality and morbidity in patients with severe and persistent gastrointestinal bleeding. The mortality rate of patients diagnosed with esophageal varices is 30%.
Patients who have had at least one episode of bleeding due to esophageal varices have an 80% chance of rebleeding within 1 year. In patients with esophageal varices, complications of the immune, cardiovascular and pulmonary systems contribute to approximately 20-45% of deaths.
Normal kidney sizes:
- length 9-12 cm [1,5,7] (length less than 9 cm can be considered as hypoplasia), sometimes in tall people the kidneys can be longer than normal, also when lengthening the kidney, it is necessary to exclude doubling of the kidney, which is often asymptomatic (t i.e. often not dangerous to health) and is detected by chance (i.e. for another reason) on urography;
— transverse size 4-6cm[1,5,7];
— parenchyma thickness 1.3-25 mm[1].
The adrenal glands are normally visible only in infants, usually up to 1-2 months of life. On ultrasound they appear as hypoechoic curved linear structures.
https://www.uzgraph.ru/forum/ugadayka/7/479/nadpoc...
Sometimes you can find a description of the size of the adrenal glands in some literature sources[6] and in reports on adults; most often this is simply a measurement of a piece of fatty tissue in the area of the upper pole of the kidney, because according to classical ideas about anatomy, this is where the adrenal gland should be located (as the name suggests). In fact, in adults, the adrenal glands are not visible on ultrasound (i.e., they are indistinguishable on ultrasound from the fatty tissue around the kidney), and they can be located not only in the area of the upper pole of the kidney. And the main task of ultrasound is to search for formations of the adrenal gland, which are often visible on ultrasound!
Normally, the ureters are also not visible on ultrasound; they become visible when they expand due to diseases. The exception is when the bladder is full. In such cases, the patient should be asked to go to the toilet and look again.
The bladder normally has an oval shape and an anechoic lumen, the thickness of the wall when filled is up to 4 mm [1,7], if the bladder is empty or poorly filled, the wall may be thicker.
Portal vein lesions
The following types of pathologies are distinguished.
Portal hypertension
. This disease is characterized by an increase in internal pressure in the portal vein. The causes of the development of this pathology may be viral hepatitis, hepatic cirrhosis, metabolic disorders, severe heart disease, blood clots in the hepatic, splenic veins and others. Symptoms include dyspepsia, weight loss, heaviness in the right hypochondrium, and general weakness.
Thrombosis
. This severe pathology develops when blood clots form in the lumen of the portal vein, obstructing the outflow of blood. The main reasons for the development of thrombosis are the following: inflammation and malignant formations of the digestive organs, injuries to the liver, gallbladder, spleen, blood clotting abnormalities, cirrhosis, various infections and others. The pathology is manifested by pain in the abdomen, nausea followed by vomiting, fever, dyspeptic syndrome and other symptoms.
Cavernous transformation
. The disease is characterized by the formation of vascular cavities (cavities) filled with blood, and develops as a result of a genetic defect in the formation of veins, which consists in their significant narrowing, partial or complete absence. Cavernous transformation is a congenital anomaly. If it was not detected in childhood, then detected in adulthood indicates progressive portal hypertension caused by hepatitis or cirrhosis.
Pylephlebitis
. This pathology is characterized by purulent inflammation of the portal vein, provoked by peritonitis that arose after acute appendicitis. Symptoms of pylephlebitis are: high fever, abdominal pain with signs of poisoning, jaundice, internal hemorrhage in the venous area of the esophagus, stomach, and others.
What does an ultrasound of the liver show?
Ultrasound of the liver allows you to evaluate the size, structure, location of the organ and its parts, the presence of any formations (cysts, tumors, metastases, etc.), inflammatory changes, pathological foci, traumatic injuries. In addition, ultrasound of the liver makes it possible to evaluate the surrounding tissues, lymphatic and blood vessels. Ultrasound results allow us to identify the following liver pathologies:
- hepatitis (acute and chronic);
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hepatosis (fatty liver);
- pathological foci in the liver (abscess, echinococcosis);
- benign neoplasms in the liver (cysts, tumors, foci of nodular hyperplasia);
- malignant neoplasms in the liver (cancer or metastases);
- changes in the structure and condition of the liver caused by heart disease and heart failure.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment of the disease involves an integrated approach and includes taking medications and surgery. Drug therapy includes the following medications:
- drugs from the group of anticoagulants - prevents the formation of blood clots and improves vascular patency;
- thrombolytics - dissolve existing blood clots, freeing the lumen of the portal vein.
Medicines are prescribed by the attending physician based on current symptoms
If there is no therapeutic result from the selected drug therapy, the person is prescribed surgical treatment. Transhepatic angioplasty or thrombolysis may be performed.
The main complication of surgical treatment is bleeding of the esophageal veins and the development of intestinal ischemia. Any pathology of the portal vein of the liver is a serious condition that requires the appointment of therapy adequate to the condition.
Preparation for ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Ideally, an ultrasound examination when scanning the hollow organs of the digestive system is carried out after special preparation for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, when gas-forming products are excluded from the diet for three days. Otherwise, the air interferes with obtaining a detailed image of the structures.
What foods are prohibited to eat before the study?
Prohibited foods include cabbage, apples, milk, and other fruits and vegetables containing cellulose. Legumes and grains should also be avoided. The day before the study, experts indicate low-fat soup, cottage cheese, and yogurt among what you can eat. For 8-12 hours it is necessary to exclude food altogether.
Is it possible to drink water before the test?
To view the bladder and prostate in men, you need to fill your bladder (drink about 3-5 cups of liquid 1.5 hours before the exam and do not urinate). It is strictly forbidden to drink soda, energy drinks, or coffee.
For women, when asked whether they can drink water before an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, the answer is similar. It is possible and necessary, but only if the water is simple, not saturated with sugar and gases. If a transvaginal ultrasound is performed, it is not necessary to drink water.
It is important that the patient cooperates with the doctor during the examination and assumes the required position or holds his breath when asked to do so. In the event of an emergency, an abdominal ultrasound is performed without special preparation in emergency mode.
Where can I get a paid ultrasound of organs?
If you are interested in where you can get a paid ultrasound of your organs, pay attention to the medical one. We work every day without lunch breaks. You can always see on the map how to find us, as well as check our opening hours, on our website.
If it’s difficult to make a decision, read the reviews of our patients, who speak about the quality of services better than any advertising. Come visit us and see for yourself. We will be glad to see you at the address on the street. Panfilovtsev, 38.