Liver diseases + high blood pressure
Many hypertensive patients with liver disease try to take as few pills as possible in order to “spare the diseased liver.” But hypertension is a disease no less dangerous than hepatitis or fatty liver.
Article on the topic How to help the liver after a vacation? Suitable treatment can be found. You just need to carefully develop a tactic together with an experienced doctor. Now there are a number of drugs for hypertension that have virtually no effect on the liver.
Hypertensive patients must also take hepatoprotectors in courses. This class of drugs protects the liver from drug load.
See also: Medicine for the liver →
With this combination of diseases, herbal medicine is useful. Raisins, chokeberries, cherries, black currants, dried apricots, and watermelons will be useful both for the liver and for normalizing blood pressure. Instead of regular tea and coffee, it is advisable to drink decoctions of rose hips, hawthorn, as well as teas from peppermint and lemon balm leaves.
Major liver diseases: pathology and distribution
- Hepatitis is liver damage, the appearance of which is triggered by viruses and infections. Experts distinguish several forms of the disease:
- Hepatitis A - occurs due to improper preparation of food or exposure to unsanitary conditions.
- Hepatitis B and C - infection occurs after contact of the body with untreated needles and other medical instruments, as well as during unprotected sex with an infected person.
- Hepatitis D - spreads in the same way as the previous type of disease.
- Hepatitis E occurs after contact with contaminated food or liquid.
- Cirrhosis is a disease whose main cause is considered to be alcoholism. Due to severe poisoning and intoxication, scars form on the liver. Organ tissues begin to harden, and basic functions slow down. The disease is fatal, the damage is irreversible and leads to liver failure.
- Fatty liver disease – cholesterol and triglycerides accumulate in the body. This disrupts the functioning of the organ and causes irreversible pathological processes.
- Autoimmune liver diseases are diseases in which the body independently destroys healthy cells. The immune system protects our body from viruses, bacteria, infections and other malignant microorganisms. In autoimmune diseases, the body begins to attack itself. Damage to healthy liver tissue leads to inflammation and tissue scarring.
Autoimmune organ diseases include:
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Primary biliary cholangitis
- Genetic lesions of the organ
Some people are predisposed to liver disease. Experts include such ailments as:
- Wilson's disease is an excessive accumulation of copper in the body.
- Hereditary hemochromatosis is excessive accumulation of iron in the body.
- Alpha-antitrypsin deficiency is a disease in which our body is unable to produce sufficient quantities of substances necessary for life.
- Infections that cause liver disorders
Such ailments include:
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Adenovirus
- Toxoplasmosis
- Cytomegalovirus
Liver disease + gallstones
| Important | |
When combining liver diseases with any other ailments, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
| |
Gallstone disease is a direct threat to liver health. After all, if a small pebble moves out of place and clogs the duct, the bile will have nowhere to go. Jaundice will appear, and liver cells will begin to quickly deteriorate. So you shouldn’t delay deciding on surgery to remove stones.
In some cases, the problem can be dealt with without the help of a surgeon. In recent years, drugs with dual action have appeared. They dilute bile, dissolving sand in the gallbladder, and at the same time protect the liver from damage.
In addition, when hepatitis is combined with cholelithiasis, it is advisable to avoid herbal preparations with a choleretic effect. They force the liver to work with redoubled force, producing bile. But overloading liver cells can lead to their death, and the likelihood of small pebbles getting into the ducts also increases.
Article on the topic
Alcohol, drugs or overeating? What leads to fatty liver With this combination of diseases, proper nutrition is very important. You need to eat often, 4–6 times a day. Dinner should be light - no more than 20% of the total food. All products are best consumed warm. It is undesirable to eat fatty pork, caviar, goose and duck meat, egg yolk and fatty dairy products. Buckwheat, oatmeal and other porridges, low-fat cottage cheese and kefir are useful both for the liver and for the composition of bile.
aortic aneurysm
An aneurysm is an abnormal, localized dilation of an artery.
In the aorta, aneurysms and diffuse ectasia are distinguished, which is a generalized, but no less pronounced increase in the diameter of the aorta. The term “aneurysm” is used when the diameter of a section of the aorta is increased by 50% or more or if the diameter of a section of the abdominal aorta is increased to 3.5-4 cm or more. A true aneurysm is an expansion of all three layers of the aorta with the formation of a large protrusion of the vascular wall. A true aneurysm can be either fusiform or saccular. Unlike a true aneurysm, a false aneurysm (pseudoaneurysm) has a rupture of the vascular wall. A pseudoaneurysm develops when blood leaks from the lumen of the vessel through an opening in the intimal or medial layer and is simply surrounded by a layer of adventitia or a perivascular thrombus. Pseudoaneurysms are extremely unstable and prone to rupture.
The etiology of true aortic aneurysms is multifactorial and varies depending on the location of the lesion. About 90% of cases of abdominal aortic aneurysm are associated with atherosclerosis. Aneurysms of the ascending thoracic aorta are not usually associated with atherosclerosis. An important role in this case is played, rather, by degenerative changes in the media (cystic degeneration of the media or cystic necrosis of the media). Median degeneration can be caused by connective tissue diseases (for example, Morphan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome) or develop in response to arterial hypertension. More rare causes leading to the formation of aneurysms include a number of infectious diseases (syphilis, bacterial endocarditis), systemic vasculitis (Takayasu’s aortoarteritis, giant cell arteritis).
Aortic aneurysm often develops asymptomatically, but sometimes patients complain of a pulsating formation, especially if the abdominal aorta is affected. More often, when symptoms of the disease appear, they are due to the fact that the enlarging aneurysm puts pressure on adjacent organs (vertebral erosion, compression of the esophagus, compression of the recurrent nerve). An aneurysm of the ascending aorta can cause dilation of the aortic annulus and the development of aortic insufficiency.
Methods for detecting aortic aneurysms include chest x-ray, computed tomography with intravenous contrast, MRI, or conventional arteriography.
Surgical treatment is recommended in most cases of abdominal aortic aneurysms whose diameter exceeds 4.5-5 cm, or in cases where the rate of increase in diameter is more than 1 cm per year. As for thoracic aneurysms, their surgical replacement is recommended if their diameter is more than 6 cm or if there are symptoms of compression of adjacent organs. In patients with Marfan syndrome, surgical treatment is often recommended when the diameter of the thoracic aortic aneurysm is more than 5 cm.
Liver diseases + back and joint pain
With exacerbation of arthrosis and osteochondrosis, painkillers from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often required.
But these drugs are not safe for the liver. Therefore, the fewer of these painkillers you take orally, the better.
To reduce the use of pain medications, consider physical therapy treatment. Properly selected courses of procedures provide both analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Well, in cases where non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs cannot be avoided, take them “under the guise” of tablets to protect the liver - hepatoprotectors.
Instructions for travelers: how to save your liver on vacation >>
Information for patients on liver cirrhosis
M.N. Mayevskaya, Lapshin A.V.
Clinic of Propaedeutics of Internal Diseases, Gastroenterology and Hepatology named after. V.Kh. Vasilenko MMA named after. THEM. Sechenov. Director of the clinic V.T. Ivashkin.
Why do we need a liver?
The liver is the largest organ of the human body; it is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen and covered by the ribs. Its mass reaches 1500 g, which is approximately 1/50 of the mass of the entire body. Anatomically, the liver has two lobes - right and left. The right lobe is almost 6 times larger than the left.
The liver is a very important organ for life; it acts as a filter for the human body. Please note how many functions it performs:
- Synthesis of proteins, blood coagulation factors, hemoglobin, components of the immune system.
- Participation in the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, water, vitamins.
- Participation in the functioning of the endocrine system (hormone processing).
- The production and secretion of bile, without which normal digestion is impossible.
- Accumulation and storage of useful compounds: glycogen (a substance that provides a supply of glucose in the body), fats, microelements.
- Neutralization of various compounds entering the body from the environment (including drugs)
What is cirrhosis of the liver?
Cirrhosis (cirrhosis: Greek: kirrhos lemon yellow), meaning orange or tan color. Due to the death of liver cells under the influence of various damaging factors, normal liver tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue with the formation of nodes and restructuring of the entire structure of the liver. Violation of the liver structure leads to disruption of all its functions.
Causes of liver cirrhosis
Most often, cirrhosis of the liver develops as a result of a long course of chronic viral hepatitis, which is caused by viruses B and C. The second very important reason for the development of cirrhosis is alcohol abuse. Unfortunately, often the cause of cirrhosis cannot be identified, in which case it is called cryptogenic (i.e. with an unknown cause).
Less commonly, cirrhosis is formed due to a violation of the outflow of bile, metabolic disorders of certain elements (copper, iron, etc.), as a result of heart failure, autoimmune disorders (when the body perceives its own cells as foreign).
How does liver cirrhosis manifest?
Signs of cirrhosis do not depend on what caused it, but are determined by the stage of the disease.
At the initial stage of cirrhosis (according to the international classification this is class A), there are still no complications of the disease.
It is at this time that it is very important to eliminate the cause of the disease, which will allow you to preserve the remaining healthy liver tissue and lead a normal lifestyle. The fact is that the liver has very great regeneration (restoration) capabilities, and healthy cells can work for themselves and their injured comrades.
The liver's ability to regenerate is described in the ancient Greek myth of Prometheus.
Every day an eagle flew in and pecked out his liver, and by morning it was restored again.
An increase in the volume of the abdomen, the appearance of changes in consciousness and behavior, bleeding gums, and nosebleeds indicate complications of the disease (according to the international classification, these are classes B and C).
Cirrhosis does not always progress; treatment can stop its further development.
What can a patient with liver cirrhosis complain about??
- Increased fatigue
- Weight loss
- Various disorders of consciousness and behavior (decreased concentration, daytime sleepiness, disturbance of night sleep, etc.)
- Decreased appetite and abdominal discomfort (bloating, feeling quickly full while eating)
- Jaundice (yellow coloration of the skin and sclera).
- Lightening or discoloration of stool, dark urine
- Stomach ache
- Swelling of the legs and (or) increase in the size of the abdomen due to free fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites)
- Bleeding: nasal, gastrointestinal, gum, hemorrhoidal, and subcutaneous hemorrhage
- Frequent bacterial infections (respiratory tract, etc.)
- Decreased sex drive
- In men, gynecomastia (enlarged mammary glands) is common.
Complications of liver cirrhosis
A patient with liver cirrhosis and his relatives should be well aware of their disease, its complications and be able to provide first aid.
Hepatic encephalopathy
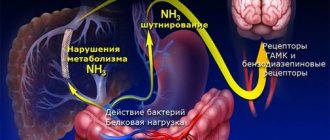
Hepatic encephalopathy is reversible damage to the brain from toxic products that are not neutralized by the liver as a result of its damage.
Hepatic encephalopathy is characterized by various disorders of consciousness, intelligence, behavior, and neuromuscular disorders.
Hepatic encephalopathy can be latent (unnoticeable to the patient and others), and then it can only be detected by a doctor when conducting special tests.
The extreme degree of hepatic encephalopathy is coma (unconscious state), it is based on acute or chronic liver failure.
What can lead to the development or worsening of hepatic encephalopathy?
- Uncontrolled use of diuretics, vomiting and diarrhea. Why? They are accompanied by the loss of large amounts of fluid and disturbances in the composition of blood electrolytes.
- Bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach, ulcers of the stomach and/or duodenum, ruptures of the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus during vomiting. Why? When bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract, blood enters the intestinal lumen, where it is processed and absorbed. This leads to the formation of a large amount of toxic substances, in particular ammonia. Toxic substances are not completely neutralized by the liver and enter the brain. In addition, in such conditions the brain suffers from a lack of oxygen.
- Infections of the respiratory tract, urinary system, etc.
- Constipation (increased absorption of toxic substances in the intestines).
- Protein-rich foods. Why? Proteins are the main source of ammonia formation in the intestines. Ammonia is a major toxic product for the brain.
- Alcohol consumption (suppression of the central nervous system and additional damaging effects on the liver).
- Taking drugs that depress brain activity (sleeping pills, etc.)
Bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract
With cirrhosis of the liver, normal blood flow through the blood vessel is disrupted. This occurs due to disruption of the normal structure of the liver and the formation of nodes. The nodes compress the blood vessels and force the blood to make its way through bypass paths (anastomoses). As a result, blood pressure increases in those vessels that are not suitable for this. For example, veins along the esophagus and in the upper third of the stomach, veins around the navel and rectum. A constant increase in pressure in these vessels leads to their varicose expansion and the threat of bleeding.
What can cause gastrointestinal bleeding?
Bleeding can begin with a sharp rise in pressure in the abdominal cavity, so patients with varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach are not recommended to lift weights or do abdominal exercises. Ascites (fluid in the abdomen) and vomiting also increases the risk of developing this form of bleeding.
If gastrointestinal bleeding is suspected:
- Keep calm
- Put the cold on your stomach
- Get into bed
- Call an ambulance
- Ask your relatives to notify your doctor.
Every patient with cirrhosis of the liver should know that gastrointestinal bleeding is manifested by vomit that looks like “coffee grounds” and loose stools that look like “raspberry jelly”; weakness appears or sharply increases until loss of consciousness.
Infectious complications of liver cirrhosis
Patients with liver cirrhosis are more susceptible to bacterial and viral infections than healthy people. Most often, such patients experience infections of the respiratory tract and urinary system. Sometimes it happens that the body temperature can rise without a specific reason. This is due to the increased absorption of “harmful” (toxic) microorganisms in their intestines. This condition is called endotoxemia.
How to behave at home
General tips:
- Rest as soon as you feel tired.
- Don't lift heavy objects. A sharp rise in pressure in the abdominal cavity can provoke gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Bowel control is extremely important in patients with cirrhosis. The optimal stool frequency is 2 times a day.
Patients with liver cirrhosis are recommended to take lactulose to normalize intestinal function and the composition of the intestinal flora in favor of “good” bacteria.
To improve digestion, patients with liver cirrhosis are prescribed multienzyme drugs. Your attending physician will help you choose the optimal drug.
If there is fluid retention in the body (edema, ascites), it is necessary to limit the intake of table salt to 0.5 g per day, liquid intake to 1000 - 1500 ml per day.
Every morning you need:
- measure body weight, abdominal volume at the level of the navel (an increase in abdominal volume and body weight indicates increasing fluid retention);
- count the fluid balance per day (diuresis): sum up all the liquid taken orally (tea, skin, water, soup, fruit, etc.), sum up all the liquid released during urination. Our common goal is positive diuresis, i.e. a patient with edema or ascites should excrete approximately 200 ml more per day than ingested: the amount of fluid excreted in the urine per day - the amount of fluid taken orally per day = 200 - 300 ml. Do not forget that large loss of fluid in the urine can provoke encephalopathy.
Agree on the dose of diuretics with your doctor. If you are passing too much urine, notify your doctor immediately.
To monitor the level of consciousness (degree of encephalopathy), we recommend using a simple handwriting test. Keep a diary in which you write a short phrase every day. Show your diary to your relatives. As soon as your handwriting changes, contact your doctor. Show your diary to your loved ones every day!
Basic Dietary Recommendations
For most patients with liver cirrhosis, 80-100 g of protein and 2500 kcal per day are sufficient. Food should be prepared in such a way that it stimulates the appetite. It is advisable to avoid drinking mineral waters containing sodium.
In patients with chronic hepatic encephalopathy, the protein content in food is limited to approximately 50 g per day, with preference given to plant proteins.
Alcohol is absolutely contraindicated for patients with liver cirrhosis!!!
- Food must be prepared without adding salt. There should be no salt on the table!
- Salt-free bread, crackers, cookies and crispbreads, as well as salt-free butter are consumed.
- Seasonings such as lemon juice, orange zest, onion, garlic, salt-free ketchup and mayonnaise, pepper, mustard, sage, cumin, parsley, marjoram, bay leaves, cloves and yeast extract (low salt) help enhance the enjoyment of dishes. to taste.
- Any products containing baking powder and baking soda (cakes, biscuits, cakes, pastries and regular bread) are excluded.
- Excluded are pickles, olives, ham, bacon, corned beef, tongues, oysters, mussels, smoked herring, canned fish and meat, fish and meat pate, sausage, mayonnaise, various jarred sauces and all types of cheeses, as well as ice cream.
- Salty canned foods are excluded.
- Allowed is 100 g of beef or poultry, rabbit or fish and one egg per day. One egg can replace 50 g of meat.
- Milk is limited to 1 glass per day. You can eat low-fat sour cream.
- You can eat boiled rice (without salt).
- Any vegetables and fruits are allowed, fresh or in the form of dishes prepared at home.
Approximate daily ration for a salt-free diet
Energy value 2000 - 2200 kcal.
Protein content up to 70 g.
Table salt content 380 -450 mg per day
Breakfast
Semolina porridge with cream and sugar or baked fruit. 60 g of salt-free bread, or crispbread, or salt-free crackers with unsalted butter and marmalade (jelly or honey). 1 egg. Tea or coffee with milk.
Dinner
60 g beef or poultry or 90 g white fish. Potato. Greens or lettuce. Fruits (fresh or baked).
Afternoon snack
60 g salt-free bread or crispbread. Unsalted butter, jam or tomato. Tea or coffee with milk.
Dinner
Soup without salt or grapefruit. Beef, poultry or fish (as for lunch). Potato. Greens or lettuce. Fruit (fresh or baked) or jelly made from fruit juice and gelatin. Sour cream. Tea or coffee with milk
Conclusion
Liver cirrhosis is not a fatal disease; it needs and can be effectively treated.
The treatment results are both disappointing and encouraging. The impaired architecture of the liver in liver cirrhosis is never restored. But liver cells retain such a significant ability to regenerate that even with cirrhosis of the liver, compensation of its function can be achieved.
If possible, the cause of the disease is eliminated, for example, in case of alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver, alcohol is excluded; in case of viral cirrhosis, antiviral treatment is prescribed.
Only a doctor can choose the optimal treatment regimen for a particular patient.
It has been proven that alcohol contributes to the decompensation of liver cirrhosis and its progression, so drinking alcohol in any form or quantity is prohibited.
If conservative (drug) treatment is ineffective, patients are included on the waiting list for a liver transplant.
Success in treating a patient with liver cirrhosis can only be achieved if the doctor’s advice is strictly followed.
The patient's behavior at home determines the course of the disease.
What cases from practice related to liver disease do you remember?
— Severe liver damage occurs with viral hepatitis, when a person for a long time did not know that he had a virus, for example, hepatitis C. This hepatitis can be asymptomatic for many years, ultimately leading to cirrhosis of the liver.
That is, a person lived a normal life and suddenly he began to develop symptoms of cirrhosis. Upon further examination, it turned out that the patient’s liver functions were impaired, the disease was already at a serious stage, and the person was on his way to the operating table for a transplant. We have to fight such cirrhosis, and we are talking about survival, not about cure.
What is the treatment?
— One of the most common causes of liver disease is viral hepatitis. In this case, antiviral therapy is prescribed.
If it is toxic, alcoholic hepatitis, then you need abstinence from alcohol, medication support and diet.
In case of fatty hepatosis associated with excess body weight, measures aimed at reducing excess body weight, diet, drug treatment, and surgical intervention if necessary are prescribed.
In the case of cirrhosis, that is, more severe liver damage, treatment is more difficult, but it is possible. First of all, therapy is aimed at eliminating the causes of cirrhosis.
The next step will be treatment with various medications that allow the liver to function more optimally. Well, the last resort treatment for cirrhosis is liver transplantation.
Types of alcoholic liver damage
Fatty degeneration. At this stage, the process is reversible even without special treatment - just stop drinking alcohol. Steatosis occurs under the influence of ethanol, which disrupts the functioning and structure of hepatocytes. Fat accumulation begins inside them, which displaces the cell nucleus. Gradually the size of the liver increases.
Steatohepatitis. This is hepatitis, caused by regular alcohol consumption and developing against the background of fatty degeneration. When an inflammatory process occurs, hepatocytes continue to increase in size and their structure changes. If the damage is severe, the cells die, and a necrotic process may begin. This affects the structure of the entire organ and disrupts its functions.
Cirrhosis. Fat accumulation continues, fibrous tissue changes appear. The regeneration process is disrupted - attempts at self-healing lead to the formation of tissue nodules. The size of the organ decreases. Fibrous tissue grows, forms wide stripes, and divides the tissue into large nodes.
Order alcoholism treatment
We work around the clock, experienced doctors, 100% anonymous.
The sequential development of these three conditions can lead to death: the liver ceases to perform its functions and the person dies.
The main cause of alcoholic liver damage is regular drinking. The disease can appear even with a small daily dose (from 10 g of pure alcohol, which corresponds to 0.5 liters of beer or 0.2 liters of wine). The process can be accelerated by taking drugs metabolized in the liver, decreased immunity, damage by hepatotropic viruses, malnutrition, and weakened immunity.