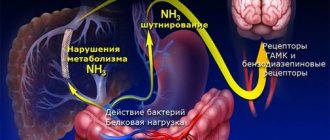
Almost any problem in the human body affects the composition of the blood, so its biochemical analysis serves as the basis for diagnosis. As a result, many patients are interested in ALT and AST levels. Liver enzyme tests are the most important method for detecting severe liver diseases.
CONSULTATION ON THE RESULTS OF ANALYSIS AND ULTRASOUND — 500 rubles. (at the patient's request)
CLICK TO SIGN UP
These substances are representatives of the enzyme group, which normally have low levels in the blood. In diseases accompanied by cell destruction, the indicators of these enzymes in analyzes increase several times and even tens of times, which confirms the presence of a pathological process.
Importance of liver enzymes
The content of the article
A separate class of enzymes are transferases, catalysts for the transfer of molecular residues and functional groups from molecule to molecule.
Transferases are involved in the transformation of nucleic acids and amino acids, lipids and carbohydrates. The most significant liver enzymes are considered to be ALT and AST, which perform several tasks at once.
- Molecular intracellular synthesis ensures sufficient liver functionality.
- Enzymatic diagnostics, carried out by measuring the degree of enzyme activity in the blood. The reliability of this method is based on the fact that liver enzymes in a healthy person are contained inside the cell, leaving it only after the death of the cell itself.
- The prognostic role of enzymes is associated with the characteristics of their dynamics in the blood, which directly depends on the nature of the course and severity of the disease.
- The medicinal role of enzymes is to use special enzyme preparations when they are deficient in the body.
What is alanine aminotransferase (ALAT)
The functioning of the human body is ensured by multiple chemical processes that are both cyclical and interconnected, continuous and consistent. Enzymes play a major role in blood filtration and digestion systems. Alanine aminotransferase (ALAT) is the main liver enzyme involved in amino acid metabolism. Most of the enzyme is found in the liver, with small amounts in the kidneys, cardiac and skeletal muscles.
Alanine itself is important as a source of rapid glucose production to nourish the brain and central nervous system. Studying the level of ALT and AST in the blood greatly facilitates the diagnosis and prognosis of severe diseases and damage to the liver, heart and pancreas.
The specificity of ALT makes it possible to differentiate diseases according to the degree of excess of standard values, which is very important when symptoms are weak and the manifestations of various diseases are similar. Using ALT readings in combination with other tests, the doctor can determine the extent of organ damage and make a prognosis for the course of the disease.
Peptides in blood tests
One of the convenient options for checking blood biochemistry for normal values is the corresponding table. If the C-peptide is higher, then there is a suspicion of excessive insulin synthesis, the development of tumor formation or pancreatitis. A decrease compared to the standard may occur, this is possible during inflammation or diabetes (only the first type).
Content of glucose and carbohydrate metabolism metabolites
In diabetes mellitus, glucose increases, other reasons: problems with the central nervous system, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, brain injuries. If normal blood biochemistry levels for glucose in adults are underestimated, it is worth checking the endocrine system, liver and pancreas.
Why is an ALT test done?
The endogenous enzyme ALT serves as a reliable marker of liver tests - liver pathologies in diagnostic laboratory practice. Alanine aminotransferase is formed due to intracellular synthesis, so it is present in the blood in small doses.
Blood test for ALT
in a healthy person it shows a minimum value. Diseases or damage to the liver cause the death of its cells, and the intracellular liver enzyme ALT is released into the blood, which, along with other indicators, is a fairly informative indicator of disease processes. Any deviation of the enzyme indicator from the standard range, especially upward, is an indisputable sign of an incipient liver disease or an extensive process of its destruction
Elevated ALT levels may also be observed in pregnant women, during a heart attack, and in certain pathological conditions. An increase in the dose of ALT in the blood is observed before the manifestations of jaundice, which allows for early diagnosis of liver diseases.
Detailed description of the study
The study allows you to determine the activity of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in blood serum using a UV kinetic test. The analysis is used to diagnose liver pathologies.
Alanine aminotransferase is one of the liver enzymes, most of which is found in hepatocytes (liver cells). Normally, ALT activity in the blood is low.
When liver cells are damaged, the enzyme enters the vascular bed. In this case, its level in the blood increases, as the test results will show, so the enzyme is considered the main marker of liver pathologies. Since ALT is found in small amounts in the cells of the heart muscle, when it is damaged, the activity of the enzyme can also increase.
ALT activity in viral hepatitis is directly proportional to the degree of damage to hepatocytes. An increase in the level of the enzyme occurs even before the development of jaundice, so the analysis can be used for early diagnosis of viral hepatitis and examination of persons contacted by the disease.
Who is prescribed an ALT test?
An ALT test is prescribed in the presence of certain symptoms and factors:
Symptoms of liver disease:
- weakness, lack of appetite, nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal pain, jaundice;
- dark urine and light-colored feces.
Risk factors for liver disease:
- previous hepatitis,
- alcohol addiction,
- diabetes and obesity,
- hereditary reasons
- taking medications that have an aggressive effect on the liver.
ALT blood test is carried out for the following purposes:
- checking for possible liver damage due to injury;
- identification of drug and alcohol addiction within the framework of a set of interrelated indicators;
- assessment of the effect of anticholesterol therapy and a number of other drugs that are relatively toxic to the liver;
- Finding out the cause of jaundice in a patient - liver disease or blood dysfunction.
A patient who is prescribed an ALT test should inform his doctor about the presence of reasons that could reduce the accuracy of the test results:
- taking certain medications, dietary supplements and herbal infusions (oral contraceptives and aspirin, warfarin and paracetamol, infusions of valerian and echinacea);
- possible pregnancy;
- presence of allergies;
- completing a course of intramuscular injections;
- rehabilitation period after cardiac surgery or cardiac catheterization;
- active physical activity before the test.
The test is performed on the patient's venous blood and results can be available in approximately 12 hours.
ALT analysis
An analysis to determine the concentration of this substance in the body is used to diagnose liver disease and monitor the effectiveness of prescribed therapy. The main indication for the study is suspicion of acute or chronic hepatitis of viral or toxic origin, cirrhosis of the liver, primary malignant neoplasms of the organ or secondary metastatic lesions.
The growth of this substance in the body during hepatitis begins much earlier than the disease enters the icteric stage. In this way, it is possible to diagnose the disease at an early stage and begin treatment in a timely manner.
The analysis is also carried out as part of a comprehensive screening examination in order to assess the condition of the liver. The study is carried out before planned hospitalization for surgical treatment. The analysis is prescribed in conjunction with an aspartate aminotransferase test.
The level of ALT must be assessed together with other enzymes in pathologies of the pancreas and gallbladder - pancreatitis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis. An analysis may be prescribed if the patient complains of general weakness of unknown etiology, fatigue, icteric skin and sclera, abdominal pain, a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting.
This analysis should also be performed in case of myocardial infarction and myocarditis. But in case of heart damage, assessing the ALT level is of secondary importance. The study is prescribed if the patient is suspected of myositis, myodystrophy, pain in the heart muscle, which cannot be explained by excessive physical exertion or another objective reason.
All donors are required to undergo this test.
The concentration of the level of this substance in the body must be assessed in case of chronic diseases, before prescribing medications - antitumor, antituberculosis. The study is also prescribed to assess the condition of the liver over time to assess the tolerability of a particular drug.
ALT elevation levels
The standard ALT indicator as part of the diagnostic complex “blood biochemistry” may differ slightly in different laboratories, but on average the limits of this indicator for men are 10–40 U/l, for women – from 7 to 35 U/l. The criteria for differentiating diseases are levels of excess of the ALT norm:
Minor:
- taking medications and chemicals (antibiotics and barbiturates, chemotherapy and drugs),
- cirrhosis of the liver,
- fatty liver disease;
Moderate and medium:
- alcohol poisoning,
- some forms of hepatitis,
- growth problems in adolescents;
High:
- cancer tumor necrosis,
- viral hepatitis,
- state of shock.
Complexes with this research
Fitness control of sports nutrition Assessment of liver function, hormone levels and metabolism when taking sports nutrition 2,810 ₽ Composition
Expanded hospital complex Expanded infectious screening for prevention and hospitalization 4,270 ₽ Composition
Biomarkers of liver functional capacity RUB 1,920 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- For those at risk of COVID-19 RUB 2,430
- Biomarkers of liver functional capacity. Extended examination RUB 2,560
- Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 9,770 RUR
- Male anti-aging diagnostics RUB 7,900
- Advanced anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause RUB 19,860
How does the level of alanine aminotransferase in hepatitis depend on gender?
Russian scientists, having examined 320 people, including both sick people and healthy people (control group), found that in women with chronic hepatitis, the ALT indicator in 78.6% of cases does not correspond to the severity of the disease. Some patients even had normal alanine aminotransferase levels.
In men, the number of cases of hepatitis not accompanied by an excess of the concentration of this enzyme was only 21.4%, that is, the difference between the sexes is 3.7 times. Moreover, even with approximately the same severity of the disease, in women this figure was 1.5 times lower.
The female body has great potential to combat liver pathology, so if a representative of the fairer sex has clear signs of “liver problems,” then one test
for alanine aminotransferase is not enough - it may not be informative. At a minimum, you still need to undergo an ultrasound of the liver.
In order to get a real picture of the functioning of the liver, it is necessary to carry out other liver tests, then it is possible to more accurately say whether a woman has this pathology or not. Representatives of the fair sex often experience a latent course of chronic hepatitis, when symptoms of liver damage appear later, in the presence of pronounced, sometimes irreversible, changes. In addition, they are characterized by a more rapid restoration of normal ALT levels after Botkin’s disease, which is also associated with the physiological characteristics of the female body.
All these factors must be taken into account when examining men and women for the presence of liver pathologies.
Dependence of alanine aminotransferase levels on gender in viral hepatitis
ALAT norm
with various types of hepatitis it can increase 20 or even 100 times. In this case, the cause of this pathology (viruses, poisoning, hemolysis of red blood cells) does not play a role.
- In Botkin's disease, an increase in this biochemical indicator can be observed even before the appearance of jaundice and other clinical symptoms. Also, the level of ALT in the blood
may be increased for some time after recovery, returning to normal (women - 31 U/L; men - 45 U/L) after two to three weeks. - With “syringe” viral hepatitis , especially those with a chronic and protracted course (CVH), this indicator can constantly fluctuate either down or up. Sometimes it depends on the stage of the infectious process, and in some cases such jumps are difficult to explain.
- Mechanical (obstructive) jaundice also causes sudden changes in ALT concentration. With this pathology, the level
of alanine aminotransferase in the blood can rise to 600 U/L in one day, and then spontaneously return to normal within about two days.
If obstructive jaundice is due to primary liver cancer, the concentration of alanine aminotransferase remains consistently high.
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is an enzyme that is found in all cells of the body, but mainly in the cells of the heart and liver and to a lesser extent in the kidneys and muscles. Normally, AST activity in the blood is very low. When liver tissue or muscles are damaged, it is released into the blood. Thus, AST is an indicator of liver damage.
Synonyms Russian
Serum glutamine-oxaloacetic transaminase, serum glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (SGOT), aspartate transaminase, AST/ALT ratio.
English synonyms
Aspartate aminotransferase.
Research method
UV kinetic test.
Units
U/L (unit per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous, capillary blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress for 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before donating blood.
General information about the study
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is an enzyme that is found in all cells of the body, but mainly in the heart and liver and to a lesser extent in the kidneys and muscles. In healthy patients, AST activity in the blood is very low. When the liver or muscles are damaged, AST is released into the blood. In this regard, the activity of this enzyme is an indicator of liver damage.
The liver is a vital organ that is located in the upper right side of the abdominal cavity. It is involved in many important functions of the body - it helps in the processing of nutrients, the production of bile, the synthesis of many important proteins such as blood clotting factors, and also breaks down potentially toxic compounds into safe substances.
A number of diseases lead to damage to liver cells, which increases AST activity.
Most often, an AST test is prescribed to check whether the liver is damaged due to hepatitis, toxic drugs, or cirrhosis. However, AST does not always reflect only liver damage; the activity of this enzyme can also increase in diseases of other organs.
What is the research used for?
- To detect liver damage. Typically, an AST test is ordered along with an alanine aminotransferase (ALT) test or as part of a general liver function test. AST and ALT are considered the two most important indicators of liver damage, although ALT is more specific than AST. In some cases, AST is directly compared with ALT and their ratio (AST/ALT) is calculated. It can be used to find out the causes of liver damage.
- AST is often combined with the results of other tests, such as alkaline phosphatase (ALP), total protein, and bilirubin, to determine the specific form of liver disease.
- To monitor the effectiveness of treatment of liver diseases.
- To monitor the health of patients taking medications that are potentially toxic to the liver. If AST activity increases, the patient may be switched to other medications.
When is the study scheduled?
- For symptoms of liver disorder: weakness, fatigue,
- loss of appetite,
- nausea, vomiting,
- abdominal pain and bloating,
- yellowing of the skin and eye whites,
- dark-colored urine, light-colored stools,
- itching.
- If there are factors that increase the risk of liver disease: previous hepatitis or recent contact with hepatitis infection,
- excessive alcohol consumption,
- hereditary predisposition to liver diseases,
- taking medications that can damage the liver,
- overweight or diabetes.
- On a regular basis throughout the treatment process to determine its effectiveness.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
| Age, gender | Reference values | |
| 0 - 1 year | ||
| 1 – 4 years | ||
| 4 – 7 years | ||
| 7 – 13 years | ||
| 13 - 18 years old | ||
| > 18 years old | men | |
| women | ||
Normally, AST activity in the blood is low.
Excessively high AST activity (more than 10 times normal) is usually caused by viral infections. It can also increase significantly as a result of taking medications or other substances that are toxic to the liver, as well as due to diseases that slow blood flow to the liver (ischemia).
In chronic hepatitis, AST activity usually exceeds the norm by no more than 4 times. It fluctuates between normal and slightly elevated, so an analysis is often prescribed to determine the extent of the disease. Diseases such as bile duct obstruction, cirrhosis, and some types of liver cancer contribute to moderate increases in AST. After a heart attack or muscle damage, AST activity may also increase, usually much higher than ALT.
In most liver diseases, ALT activity is higher than AST activity, so the AST/ALT ratio will be low. However, there are a few exceptions: alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis and muscle damage.
Important Notes
- During pregnancy, AST activity may decrease.
- Intramuscular injections of drugs, as well as intense physical activity, help increase AST activity.
- In some patients, liver damage and, as a result, an increase in AST activity may be caused by taking dietary supplements. Therefore, it is necessary to inform your doctor not only about all medications you are taking, but also about nutritional supplements.
Also recommended
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Total alkaline phosphatase
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT)
- Serum albumin
- Total protein in whey
Who orders the study?
Therapist, cardiologist, hepatologist, gastroenterologist, general practitioner, surgeon, pediatrician.
Features of ALT norms in pregnant women
In a healthy woman, the ALT norm does not change during pregnancy and should coincide with the values before conception. In cases where ALT is slightly increased during pregnancy, causes not related to diseases can be considered:
- course of intramuscular injections;
- physical activity that is excessive for a pregnant woman;
- addiction to fast food;
- uncontrolled intake of dietary supplements;
- obesity;
- fetal pressure on the biliary tract, preventing the outflow of bile.
Normalization of nutrition, moderation of physical activity, weight control and choleretic drugs normalize enzyme parameters.
How to prepare for donating blood for an AST level test?
It is not difficult to remember how to prepare for donating blood for an AST level test. This is a standard blood test taken from a vein using a vacuum tube. It must be taken on an empty stomach in the morning. At least 8 hours must pass after the last meal. It is important to avoid the use of alcohol and certain medications a week before donating blood, as well as limit physical activity the day before the test.
It is best to donate blood to determine AST levels with the direction of a general practitioner. Before sending you for analysis, the doctor will review your medical history and clarify the details of your well-being. With the results, which will be ready within 1 day, you need to return to the doctor and get an accurate diagnosis, made up of the results of the AST level and other indicators, as well as other symptoms and examination results.
Dependence of ALT level on age and other indicators
During a person's life, the level of ALaT changes. You need to know this in order to correctly decipher ALT in a biochemical blood test.
- In healthy full-term newborns, the alanine aminotransferase rate ranges from 10 to 17 U/l.
- If the baby was born prematurely, then this figure can be 13–26 U/l, and the level of this substance in the blood of such babies changes almost daily.
- From the sixth day of life to six months of age, the upper limit of alanine aminotransferase increases slightly and amounts to 30 U/l. This is explained by the fact that in the first six months all biochemical mechanisms are gradually “launched” in the baby’s body, because the child adapts to existence outside the mother’s womb.
- From seven months to a year, this figure fluctuates between 13–29 U/l. At this time, the indicators for boys and girls do not yet differ.
- From one year to 14 years, the concentration of alanine aminotransferase in boys and girls is different. Moreover, in the female body it will be lower than in the male body. For girls of preschool age, the norm will be considered a concentration of 13–18 U/l, and for boys the upper limit is already 22 U/l. This trend will continue throughout your life.
Alanine aminotransferase levels in adults
- Before reaching the age of 60, the normal alanine aminotransferase level in men is 10–45 U/L, while the normal ALT level in women during this period is only 10–31 U/L.
- The level of this substance in the blood can only change during pregnancy, and then not in all women. In some cases it remains unchanged. If the expectant mother's ALT level is slightly elevated and is 35 U/L, this is not a cause for concern. An increase in ALT during pregnancy is caused by the fact that the enlarged uterus may slightly compress the bile ducts or a slight bend has appeared in the bile ducts. There is no need to be afraid of this state of affairs - after childbirth, the uterus will shrink and the indicators will return to normal. However, if the increase in ALaT in the blood during pregnancy continues, and the concentration of this substance reaches high levels, additional examinations should be performed, as this may be associated with impaired functioning of the liver, kidneys and heart.
- When people “step over” the 60-year barrier, the level of alanine aminotransferase in the blood also changes. Normally, ALT in men of this age ranges from 10 to 40 U/l, and for females it will be 10–28 U/l. The concentration of alanine aminotransferase remains at this level until the end of life.
However, a normal blood level of this substance does not always indicate that a person is healthy. In some cases, even with severe pathology of the liver and kidneys, the indicator does not change, especially for the fairer sex. That is why an isolated study of the concentration of this enzyme in the blood is very rarely prescribed. Most often, other biochemical indicators are analyzed in parallel, which allows a much more accurate understanding of the state of the body.
Blood chemistry. Decoding the main indicators
5. Total protein. Total protein in the blood is the total amount of all protein fractions in the blood. The normal level of total protein in the blood in adults ranges from 65 to 85 g/l.
Total protein consists of albumin, fibrinogen and four globulin fractions (alpha1, alpha2, beta and gamma globulins). The level of protein in plasma allows you to assess the condition of organs such as the liver, kidneys, pancreas, identify disturbances in carbohydrate, lipid or protein metabolism, determine micronutrient deficiency, etc.
Urea and creatinine will tell you about the function of the kidneys: 6. Urea. Creatinine. They are indicators of kidney function. A urea test is usually ordered in combination with a blood creatinine test. To assess kidney function in a range of conditions (in conjunction with a creatinine test). For the diagnosis of kidney disease and for checking the condition of patients with chronic or acute renal failure.
Generally, 2.2 - 7.3 mmol/L is considered normal urea level and any value higher or lower means that there is some abnormality in the body and it is necessary to pay attention and find out the reason for the change in urea level.
Creatinine is a chemical waste product created when muscles function. Its increase is affected by the consumption of large amounts of protein or liver pathology.
Creatinine levels may also temporarily increase with intense exercise or with the use of certain medications such as sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, or chemotherapy drugs (such as sports supplements). Other causes include conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure or thyroid disease.
7. Iron. It's also worth checking regularly. Iron is one of the most important microelements in the body. It is part of the hemoglobin of red blood cells and thus participates in the transfer of oxygen. The normal level of iron in the blood is one at which the body can fully function. If hemoglobin is low, this is a reason to consult a doctor and conduct the necessary research. Typical reasons for low iron levels include:
- improper diet;
- heavy blood loss;
- impaired absorption of iron;
- increased need for microelements.
8. C-reactive protein (CRP) is an informative indicator of the current inflammatory process in the body. This protein is synthesized by the liver and is one of the markers of the acute phase of inflammation.
The level of CRP in the blood may increase within several hours after the onset of an infectious disease, injury, or in the first hours after surgery. CRP quickly responds to changes in the dynamics of the disease and quickly returns to normal upon recovery.
9. Uric acid. Normally – up to 428 µmol/l. Uric acid is a waste product from the metabolism of nucleic acids and purines in the body. The latter are formed mainly in the process of natural cell death. Uric acid enters the body from meat products (liver, red meat, legumes, fish) and from liquids (beer, wine) and is formed in the body. A uric acid test is necessary to determine the cause of gout. When the content of this compound in the body exceeds the norm, its salts begin to be deposited in the joints, causing acute arthritis and the formation of nodules called tophi. In addition, this acid promotes the formation of kidney stones.
During the Middle Ages, gout was often called the “disease of kings.” This is explained by constant large meals without any measure, as well as the tendency to illness in men over forty years of age. The kidneys of those who abused food and wine could not cope with the huge concentration of uric acid. Ordinary people ate a limited diet, and could not afford so much meat and alcohol, which contain the most purines, so they got sick less often.
The material was prepared with the direct participation of N.V. Degtyareva, a doctor of laboratory diagnostics of the highest category at the Botkin Hospital.
Thank you for your assistance and information!
What is aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
The endogenous enzyme aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is responsible for accelerating the release of ammonia from amino acids for its subsequent processing in the urea cycle. AST is found not only in the liver, but also in the heart muscle and brain, kidneys and spleen, lungs and pancreas. Due to the intracellular nature of synthesis, AST is successfully used in diagnosing the condition of the myocardium and liver. Using a biochemical blood test for AST and ALT, as well as their ratio, doctors are able to predict a heart attack even before the appearance of the main symptoms.
AST is also used as a marker in the differentiated diagnosis of a number of diseases:
- Cirrhosis and hepatitis;
- Metastases in the liver;
- Jaundice of various origins.
If, according to the results of the study, high ALT levels are much greater than the excess of the norm for AST, this is a characteristic sign of liver damage. If AST is increased more than ALT, the possibility of myocardial cell death should be considered. Excessive activity of alanine aminotransferase is also possible during the period of taking certain medications. Reduced values of AST and ALT are possible during pregnancy, renal failure or pyridoxine deficiency.
What can tests say about the heart?
What are tests? Tests are a confirmation or exclusion of a particular disease about which an opinion was formed after a clinical examination of the patient. With their help, the doctor will find out what exactly is preventing your body from living and working normally, and what is the condition of its individual organs and systems.
So, what do these same tests say if there is pain in the heart area? The determination of enzymes contained inside cells is important in the diagnosis of diseases associated with myocardial damage. And depending on which and how many cells die, their values will change.
Biochemical blood test indicators:
ALT (alanine aminotransferase): up to 68 U/l, when assessing the level of this enzyme, it is worth considering that it is contained not only in the myocardium, but to a greater extent in the liver, therefore AST and ALT are always determined together, which helps in distinguishing between heart damage and liver. The timing of ALT increases is similar to AST.
AST (aspartate aminotransferase): up to 45 U/l, this enzyme is found in large quantities in the myocardium, and its increase, in most cases, indicates damage to cardiomyocytes - the muscle cells of the heart; An increase in AST in the blood serum is observed in myocardial infarction (95-98%) cases within 6-12 hours from the onset of the disease. The maximum increase is observed on days 2-4, and on days 5-7 the enzyme level returns to normal. There is a clear relationship between AST numbers and the size of the focus of cardiac muscle necrosis. Therefore, if the necrosis is less than 5 mm in diameter, it is possible to maintain the level of this enzyme within normal limits, which also must be taken into account.
LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) and the fractions that make up this indicator: up to 250 U/l, is considered a specific marker for AMI; an increase in the activity of the LDH1 and LDH2 isoenzymes, even with normal levels of general LDH activity, indicates the presence of minor necrosis in the heart muscle. With AMI, its level increases quickly on days 2-4, and normalizes only at 2-3 weeks. LDH levels provide valuable information about MI throughout the course of the disease. Other fractions LDH3 and LDH4 are enzymes of the lung tissue, LDH5 is of the liver.
CK (creatine phosphokinase) and the fractions that make up this enzyme: up to 190 U/l, creatine phosphokinase - is considered a specific marker (especially an increase of more than 10 times) in acute myocardial infarction. It increases in the acute period (in the first 4-8 hours from the onset of the disease), much faster than the activity of the above enzymes and is a marker for early diagnosis of AMI, especially the CPK-MB isoenzyme. After 8-14 hours, the CPK value can reach its maximum value, and normalization can occur after 3-4 days. Also, the CPK value may increase with myocarditis;
Troponin test: up to 0.4 mcg/l. Troponin is a specific contractile protein that is part of the structure of the heart muscle and skeletal muscles. This test is a diagnostic marker for suspected acute damage to myocardial cells and is one of the key results in diagnosing “acute myocardial infarction”;
myoglobin: 12-92 µg/l. A protein in muscle tissue involved in the process of cell respiration. If it appears in the blood, it is regarded as a product of the breakdown of the muscle tissue of the heart or skeleton, with the appropriate clinic, it may indicate necrosis (necrosis) of the heart muscle tissue, therefore it is also considered a specific marker of this pathology.
The indicators of ALT, AST, CPK, CPK-MB, LDH, myoglobin and troponin test closely correlate with the size of the necrosis focus in the heart muscle, and therefore have not only diagnostic, but also prognostic significance.
Acid phosphatase: 67-167 nmol/(s·l), increases in activity in patients with severe, complicated MI, mainly transmural;
C-reactive protein (CRP): up to 0.5 mg/l, its detection indicates the presence of a pathological process in the body, in particular inflammatory or necrotic. It belongs to the so-called “acute phase” proteins. A sharply positive reaction to CRP indicates the severity of the inflammatory process.
sialic acids: 2.0-2.36 mmol/l, the content of sialic acids may increase with endocarditis, MI;
electrolytes are mainly represented by K+ ions (normal 3.6 – 5.2 mmol/l), Na+ (normal 135 – 145 mmol/l), Cl- (normal 100 – 106 mmol/l), Ca2+ (normal 2, 15-2.5 mmol/l). An increased amount of potassium in the serum may be accompanied clinically by cardiac arrhythmia, which is confirmed by an ECG. Atrioventricular blockade of the conduction system of the heart may develop, the syndrome of premature excitation of the ventricles, ventricular fibrillation, and such a serious disorder as cardiac arrest may develop. Therefore, patients with heart rhythm disturbances need to monitor the content of K+ ions in the body. On the other hand, a decrease in potassium in the blood can also lead to adverse consequences in these patients - myocardial hyporeflexia. A decrease in the level of sodium ions may be accompanied by the development of cardiovascular system failure, since the ratio of K+ and Na+ ions, as regulators of processes in the cell, is in constant interaction and a decrease in one leads to an increase in the other ion. Hyperchloremia occurs in patients with kidney disease and may also lead to the development of cardiovascular disease;
lipid spectrum, is associated by the common person with the word “cholesterol”. In this case, substances (lipoproteins of various densities, triglycerides) that are involved in the metabolism of cholesterol (CH) are determined (normal blood levels are 3.1 – 5.2 mmol/l). In addition to the value of total cholesterol, an important indicator is the atherogenicity coefficient (norm up to 4), which shows the ratio of “good” and bad” lipids involved in the metabolism of fats and cholesterol, and the threat of development or progression of atherosclerosis and all the ensuing consequences. An increase in the fractions of lipoproteins and triglycerides can be either a physiological condition (of a nutritional nature) or a pathological condition. Increased lipids are characteristic of widespread atherosclerosis, obesity that accompanies and causes arterial hypertension. But it would be more accurate to say that this disruption of the functioning of internal organs and intermediate links in the metabolism of lipids and triglycerides, expressed in an increase in the atherogenicity index, causes the deposition of cholesterol in vessels of various diameters, the deposition of “spare fat,” which leads to the above diseases. Therefore, with widespread atherosclerosis, in this blood test, you can see increased values of ß-lipoproteins and total cholesterol. At the same time, a decrease in phospholipid concentration can be seen. But it is also necessary to take into account that there are age-related fluctuations in blood fats.
coagulogram is an analysis by which you can look at the “viscosity” of the blood, or in other words, whether there is a threat of blood clots, which can lead to the formation of blood clots with different localizations, which in turn can be complicated by pulmonary embolism, which causes instant death. Or, on the contrary, see how high the probability of bleeding is and whether it can stop on its own after surgery, for example, heart valve replacement.
Any analysis or research provides the doctor with additional information that helps to more accurately make a diagnosis, determine the stage of the disease, and prescribe treatment. Tests also help to monitor the course of the disease, the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment, and ensure the safety of therapy. But sometimes additional research is required to confirm or complement the results of past analyzes.
Fedorova Lyubov Alekseevna – doctor of the first category, therapist, medical cardiologist.