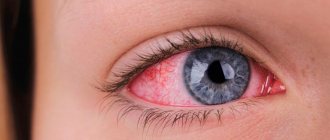
Many of us, at least once in our lives, have been involved in a situation where it was necessary to provide assistance to a person who has fainted, and some have even found themselves in the role of a victim. The most common symptoms that precede the onset of fainting are most often darkening of the eyes, which may be accompanied by tinnitus, general weakness, nausea and dizziness.
Darkening in the eyes occurs quite often in people and can be not only simply a consequence of a person’s overwork, but also a harbinger of serious health-related complications.
Causes
Darkening of the eyes can be a consequence of two main fundamental reasons, the first of which is the lack of oxygen and various nutrients that should have reached the brain. The second may be pathology or disorders of the visual system.
Darkening of the eyes is often the first symptom, followed by dizziness or fainting.
More often than not, most fainting and darkening of the eyes that are common in everyday life are low-risk and do not indicate vital health problems or damage. But sometimes such phenomena indicate the development of quite serious processes in the human body and require urgent contact with doctors, where, after a thorough examination and possible confirmation of negative changes in the body, a serious course of treatment can be prescribed. However, it is worth emphasizing that the treatment will not be the consequence, which is darkening in the eyes, but the root causes that caused this failure.
Content:
- Causes
- Safe causes of darkening of the eyes
- Darkening of the eyes from disease
- Characteristics of diseases
- Local visual problems
- First aid
- Diagnosing the problem
- Preventing dark eyes
Clouding of the lens of the eye: is there a treatment?
Fortunately, today this problem is curable. The treatment for clouding of the lens of the eye is an operation to replace the “native” lens with an artificial one, and it is called phacoemulsification.
Throughout the world today, this operation represents the “gold standard” for the treatment of this disease, relieving a person of a clouded, swollen or wrinkled/liquefied lens. During the operation, an artificial lens with optimally selected refractive power is installed in place of the altered optical structure, which allows the person to completely restore vision. Please note that surgical intervention, whether ultrasound or surgical, should be performed at the mature stage of the process.
There is also drug treatment that can have a positive effect in the initial stages of the disease. But, given the catastrophically low number of visits to an ophthalmologist for minor vision problems, the process is extremely rarely detected at such early stages.
In Moscow, cataracts are treated daily in dozens of patients at the Svyatoslav Fedorov Medical Center.
Ophthalmologists-microsurgeons are improving for your sake and in order to return to you the joy of a full vision of the world. This is a place where competent specialists are gathered, ready to help people with their vision problems. If you have any, do not delay visiting your doctor. Fedorov Medical Center is open for you! Making an appointment Today registered: 21
Safe causes of darkening of the eyes
Overwork and excessive stress, which accompany the lives of most students, athletes, and some workers overloaded with responsibilities, can often lead to darkening of the eyes. With all this, there is also tinnitus, a general deterioration in hearing, loss of orientation in space, but, as a rule, there is no pain. Even with such symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor and conduct examinations for a qualified conclusion to find the cause and source of the problems, as well as draw up a plan for getting rid of the negative consequences and not repeating this in the future. Based on this, relatively negative reasons include overwork and its subtypes, as well as a reduced level of hemoglobin.
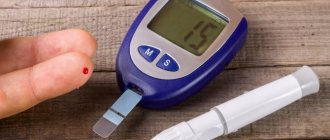
Quite often, darkening of the eyes and malaise occurs due to a drop in blood glucose levels in the case of diet, from overwork and exhausting physical activity, or in the case of strong emotions that a person experiences.
After confirmation of precisely such reasons, a person will need significant time for rest, good nutrition and a transition to a healthy lifestyle. You will also have to give up stress for a while.
Fainting - symptoms and treatment
Diagnosis of syncope includes a thorough history taking and examination of the patient [6]. A history, physical examination, and a 12-lead ECG are among the 2007 American Society of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) Level A (highest level of evidence) recommendations for syncope [5].
Anamnesis
When questioning the patient, the doctor finds out:
- Were there any provoking factors (fear, fatigue, lack of sleep, stuffy room, fasting, drinking alcohol).
- What did the patient do before fainting (was he at rest or was there physical activity), what exactly did he do when he felt unwell. If the attack occurs during shaving, severe coughing, urination or defecation, this indicates the reflex nature of fainting.
- What position was the patient in before fainting (lying, sitting or standing). At rest and lying down, cardiogenic attacks occur more often. Fainting that occurs a couple of minutes after changing body position indicates orthostatic hypotension.
- What were the pre-syncope symptoms (dizziness, blurred vision, nausea, etc.) and how did the patient feel after fainting?
- Does the patient have any diseases or is he taking any medications?
The doctor's increased alertness should be caused by symptoms such as pain in the heart, shortness of breath, tachycardia, severe headache, focal neurological symptoms: weakness, numbness in one half of the body, unsteadiness, instability when walking (ataxia), speech impairment (dysarthria), double vision. in the eyes (diplopia).
Examination and physical examination
Vital signs are assessed:
- A high temperature may indicate an infection as the cause of fainting.
- A high heart rate (tachycardia) may be a sign of acute coronary syndrome or pulmonary embolism (PE).
- A low heart rate (bradycardia) may also indicate acute coronary syndrome and cardiac conduction abnormalities.
- Heart murmurs during auscultation (listening) indicate the presence of valvular heart disease.
Laboratory diagnostics
From laboratory tests, primarily a general analysis of blood and urine, analysis of electrolytes and glucose levels in the blood serum are used.
Diagnostic tests
A number of diagnostic tests are used in patients with syncope:
1. Carotid sinus massage is performed on patients over 40 years of age with fainting of unknown origin, which presumably develops as a reflex. The massage is carried out with the patient lying on his back, the doctor presses the common carotid artery for 5-10 minutes. During the massage, blood pressure measurement and ECG monitoring are mandatory.
Criteria for a positive test result: asystole (cardiac arrest) for 3 seconds or more and a drop in systolic blood pressure of 50 mmHg. Art., which indicates hypersensitivity of the carotid sinus.
The test should be performed with caution in patients with a history of transient ischemic attack and stroke, as well as with carotid artery stenosis > 70%.
2. Active orthostatic test (Schellong test). During this test, the subject independently moves from a lying position to a sitting position. The study includes measuring blood pressure and heart rate in a lying and standing position for 3 minutes.
Criteria for a positive test:
- systolic blood pressure decreases by 20 mmHg. Art. or more or diastolic pressure decreases by 10 mmHg. Art. and more compared to the initial readings;
- systolic blood pressure becomes less than 90 mm Hg. Art.
3. Passive orthostatic test (tilt test). The patient lies on a motorized table that can tilt at angles of 30-60 ° . The table is abruptly transferred from a horizontal position to a vertical one. In this case, the patient’s blood flows to the lower part of the body, which causes a drop in pressure in the right side of the heart.
Criteria for a positive test:
- a significant decrease in blood pressure and heart rate is recorded, up to prolonged asystole;
- the patient's condition worsens to the point of fainting.
The tilt test is contraindicated in patients with heart disease with low cardiac output.
4. The Valsalva maneuver is used to evaluate the autonomic nervous system. The essence of the test is to try to exhale forcefully with your mouth closed, nose pinched and vocal cords closed. That is, straining occurs during maximum inspiration while holding the breath for 30-40 s.
Criteria for a positive test:
- absence of changes in blood pressure and increase in heart rate (typical of neurogenic fainting), pronounced decrease in blood pressure (typical of situational fainting, for example, occurring when coughing)
- the patient's condition worsens to the point of fainting.
5. Deep breathing test (hyperventilation). It consists of deeper and more frequent (about 20 per minute) breathing for 2-3 minutes. The amount of time may vary. A reflex narrowing of blood vessels is provoked due to excessive removal of carbon dioxide and a shift in the blood reaction to the alkaline side. This assesses the body's ability to tolerate reduced blood supply to the brain. Most often, this test is used in electroencephalography.
Criteria for a positive test:
- a characteristic pattern of brain activity (slow waves) when recording an electroencephalogram in the absence of epileptic activity;
- the patient's condition worsens to the point of fainting.
Differential diagnosis
- Coma. Loss of consciousness lasts much longer than fainting.
- Epilepsy. With fainting, unlike epilepsy, there is no focus of constant pathological excitation in the brain, and disturbances in brain activity develop only when exposed to unfavorable factors.
- Fainting in cerebrovascular diseases.
There are several causes of fainting that are associated with cerebrovascular diseases:
1. Movements of the head and neck: when throwing back the head or turning. In the pre-syncope period, there may be short-term dizziness. When fainting, the patient's skin is pale, focal neurological symptoms may appear, which indicates the occurrence of a cerebrovascular accident. Typically, symptoms do not increase to the point of loss of consciousness and are often limited to neurological manifestations. If loss of consciousness occurs, it lasts longer than with normal fainting [3].
After the attack, symptoms of vestibulo-atactic syndrome are revealed (unsteadiness when walking, vomiting, nausea) as well as focal neurological deficit (weakness, numbness in the limbs of one half of the body, double vision, etc.). When questioning the patient, it turns out that he has vascular atherosclerosis according to ultrasound data, anomalies in the development of the main arteries of the head or pathology in the cervical spine: deforming spondylosis, spondylolisthesis of the cervical spine.
2. Hemorrhages in the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid and pia mater of the brain). Subarachnoid hemorrhage can occur when an aneurysm ruptures (pathological dilatation of a vessel) due to hypertension or traumatic brain injury. A severe headache after fainting indicates the cause. Unlike the classical clinic of syncope, loss of consciousness does not occur suddenly, but slowly progresses [3].
3. Subclavian steal syndrome. The syndrome is characterized by reverse blood flow through the vertebral artery due to stenosis (narrowing) of the subclavian artery. Accordingly, blood supply to the brain decreases, which leads to the development of ischemia (lack of oxygen) in the vertebrobasilar region. Unlike ordinary fainting, neurological symptoms are always additionally present [3].
Subclavian steal syndrome occurs when performing hand movements. Clinically manifested by dizziness, loss of coordination, blurred vision, speech, weakness in the limbs and impaired sensitivity. The cause of arterial stenosis can be atherosclerosis, nonspecific arteritis, Takayasu arteritis, rib anomaly (cervical ribs), anterior scalene muscle syndrome.
For differential diagnosis of different types of loss of consciousness , including those that are not related to fainting (PE, epileptic seizure and some others), a certain set of studies is performed:
- If cardiac syncope is suspected - ultrasound examination of the heart (ECHO), ECG monitoring (Holter study, implantable ECG recorders for long-term monitoring), blood pressure assessment, bicycle ergometry (stress test on a bicycle, during which an ECG is recorded and blood pressure levels are measured), analysis for troponin (a heart muscle protein, a specific marker of heart damage), biochemical analysis for adenosine.
- If PE is suspected, test for D-dimer (a marker of thrombosis).
- For neurogenic syncope, tilt test and massage of the carotid sinus.
- For orthostatic syncope - Schelong test, 30-minute standing test, tilt test, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring.
- In case of loss of consciousness of a cerebrovascular nature, MRI and CT of the brain are performed to exclude focal lesions, ultrasound examination of the main arteries of the head, and, if necessary, angiography and radiography of the cervical spine are performed.
- For epileptic seizures - MRI and CT of the brain, video-EEG monitoring, test with hyperventilation during EEG.
- For psychogenic seizures, consult a psychiatrist.
- If orthostatic hypotension is suspected, test for vasopressin (a hypothalamic hormone), endothelin-1 (a vasoconstrictor peptide), natriuretic peptide (normally released into the blood when the heart walls are stretched - a marker of heart failure). An increase in these markers can also be observed in syncope of cardiac origin [17].
- For carotid sinus syndrome or paroxysmal atrioventricular block (slowing or stopping the passage of impulses between the atria and ventricles), a blood test for adenosine. An increase in level is possible, for example, with vasovagal syncope [17].
For all types of syncope, various video recording devices are used to display the overall external clinical picture of the attack.
Darkening of the eyes from disease
Darkening in the eyes can occur in the morning when a person gets out of bed, with sudden movements of the body and turns of the head and torso, and also occur with strong physical stress on the person’s body. Such cases are often accompanied by headaches, nausea and vomiting. The latter signs are more serious and may be a confirmation of the following diseases:
- hypotension;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- all kinds of diseases caused by infections;
- diseases of the nervous system.
Main symptoms
In this regard, we can say with a high degree of probability that if your eyes get dark when you try to stand up, then we are talking about hypotension. This disease, in addition to the above, also has the following symptoms:
- Dizziness;
- Weakness, lethargy;
- A feeling of constant exhaustion, as if at night, instead of sleep, the carriages were unloaded;
- Absent-mindedness;
- Problems concentrating;
- A veil appears before the eyes;
- Shortness of breath even with minimal physical activity;
- Memory impairment.
During hypotensive crises, which are exacerbations of the disease and usually occur in spring and autumn, fainting can also occur.
Characteristics of diseases
The consequence of hypotension is a negative effect on brain cells due to oxygen starvation. With this syndrome, blood pressure drops significantly, because of this the brain does not receive enough oxygen and its cells begin to die, which is precisely manifested by darkening of the eyes, as well as headaches and nausea. Like any other serious health problem, this requires a certain course of treatment and a review of the patient’s lifestyle.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia has similar symptoms. The causes here are extensive and require long-term rehabilitation treatment.
If the problem with darkening of the eyes is caused by an infection in the body, the doctor will prescribe antibacterial drugs, which, along with eliminating the infection, will lead to the disappearance of symptoms associated with vision, headache, weakness and lethargy.
Also, darkening in the eyes is included in the primary list of factors that may indicate diseases such as osteochondrosis, various aneurysms, compression of arteries and nerve endings. In such situations, darkening and pain occur only with certain movements and positions of the body or its parts and will most often be the first symptoms of the emerging disease.
The main types of diseases that lead to darkening of the eyes include diseases of the thyroid gland, malfunctions of the heart valves and disruption of metabolic processes in the body. In the case of such problems, the phenomenon will be only one of a whole complex of symptoms.
Diagnosis of nausea, weakness and noise in the head
When visiting a doctor with complaints of dizziness, headache, nausea, weakness, ringing and tinnitus, the patient first receives a preliminary diagnosis. For this purpose, an examination plan is drawn up, which includes the following studies:
- Comprehensive examination by a neurologist. The doctor conducts special coordination tests that distinguish benign paroxysmal positional vertigo from its other varieties, as well as a neurological examination, checking the condition of the cranial nerves, conditioned and unconditioned reflexes. The specialist conducts a detailed survey of the patient, identifying the main complaints, their location and time of occurrence, and connections with chronic diseases.
- General blood test, biochemical blood test, coagulogram. They are carried out to exclude anemia, acute inflammatory and infectious processes in the body, as well as tumor diseases of the blood and lymph. Also, thanks to these studies, the blood lipid profile, the tendency to thrombosis and vascular atherosclerosis are assessed.
- ECG and blood pressure measurement. Studies reveal a connection between the complaints that have arisen and arterial hypertension.
- X-ray, CT and MRI of the brain and spinal cord. MRI examination has advantages over other diagnostic options, as it shows a layer-by-layer image of all scanned areas. This allows you to minimize diagnostic errors, accurately determine the location and size of the pathological focus, and also conduct an examination in the shortest possible time. Magnetic resonance imaging is the method of choice for formations that do not originate from bone tissue, as well as the gold standard for examination in dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
- Ultrasound of cerebral vessels to identify pathological narrowings and blockages by blood clots.
- An audiogram and examination by an otolaryngologist to rule out problems with the inner ear and vestibular apparatus.
- Electroencephalography. Helps detect areas of epileptic activity.
Local visual problems
Do not forget that sometimes the cause of darkening in the eyes can be problems that are associated only with the visual analyzer itself. Among them are the following:
- visual field defects;
- violations of the integrity of the optic tract;
- optic nerve diseases.
Darkening is caused by pathological loss of visual fields. A sudden movement in this case, or a sharp turn of the head can cause such a reaction in the eye.
Patients with glaucoma and people with farsightedness and myopia also complain of similar problems after prolonged visual strain.
Problems can arise when the signal from the eyes to the brain is disrupted, which occurs when the optic nerve or optic tract becomes spasmed or paralyzed.
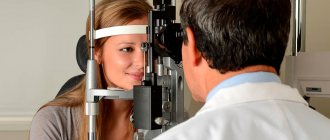
To determine an accurate diagnosis that will reliably show the source of the problem and possible ways to eliminate it, a comprehensive ophthalmological examination will be required, including ophthalmoscopy, refractometry and several other manipulations that the doctor deems necessary in a particular individual case.
First aid
Symptoms of darkening of the eyes appear very quickly, so their manifestation can be noticed and the negative consequences of this type of incident can be minimized, including strong falls, bumping into surrounding objects, and loss of balance. If such symptoms occur, the best solution is to sit or lie down, provide fresh air, drink cold, clean water or sweet tea.
If darkening of the eyes is accompanied by fainting, then it is recommended to lay the person on his side, in order to avoid swallowing the tongue when relaxing, it is better not to raise the head, so as not to interfere with the flow of blood to the brain. It is also permissible to use ammonia or splashes of cold water to try to revive the person.
Prevention methods
Preventive measures in this case require, first of all, treatment of the disease causing darkening .
Remember! Additionally, it is necessary to strive to improve the quality of life, which will reduce the risk of this symptom.
It is advisable to limit alcohol consumption and stop smoking , as well as exclude foods containing high amounts of cholesterol from the diet.
It is important to properly manage your time during the day and
give the body enough time to rest (for an adult this is 6-8 hours a day).
Diagnosing the problem
If you suspect such a problem, you should immediately consult a therapist and ophthalmologist. If this symptom is not a consequence of overwork, then a series of studies are prescribed.
These examination methods include the following four main types:
- MRI of the brain.
- MRI of the orbits.
- Computerized perimeter visual field testing, which can detect scotomas.
- MRI of the vessels of the neck and head, which diagnoses disorders in the circulatory system.
It is worth remembering that after visiting a doctor with a similar problem, a patient complaining of darkening in the eyes must be prepared for the fact that he will have to clearly answer many questions of interest to the doctor. It is necessary to describe in as much detail as possible what exactly the nature and signs of the symptoms are, how often the most serious of them or maximum darkening occur, whether the person has previously experienced injuries associated with damage to the skull and brain, and whether there have been certain diseases recently. Only after listening to a detailed answer from the patient, the doctor can prescribe the necessary examination with research from one or another specialist, and subsequently save the person from this serious problem.
Diagnosis of hypotension
If, when you try to stand up suddenly, your vision becomes dark, you must undergo a full medical examination. In this case, it is worth contacting a neurologist, who, after observing the blood pressure, will draw conclusions about the condition of the blood vessels and the causes of the disease.
You may also need a visit to a cardiologist, whose examination is necessary for a final conclusion and to receive recommendations for treatment and further lifestyle.
Correct diagnosis of the disease is the key to adequate subsequent treatment. It is after an examination by the above-mentioned specialists that it will become clear whether medical intervention is necessary at all and which drugs should be used. Or, perhaps, the situation will improve by changing the usual rhythm of life, diet, and normal physical activity.
Treatment of hypotension using traditional methods
Medications used for hypotension should only be selected by the attending physician. However, very often drug therapy in such cases is unnecessary and the specialist recommends taking regular pharmacy tinctures of medicinal herbs. Particularly effective in the case of hypotension is taking lemongrass tincture. It is recommended to drink 20-30 drops twice a day, half an hour before meals in the morning and evening.
Ginseng tincture also has an excellent effect. The course of its use is 20 days. The tincture is taken twice a day, 5-20 drops before meals in the morning and in the middle of the day.