The mammary glands, like the rest of the body, consist of many veins, blood vessels and capillaries. Protruding veins are usually associated with some kind of medical condition. But this doesn't always happen. For example, people with fair and thin skin are known to have prominent veins throughout their lives. They do not cause discomfort and do not cause any diseases.
A revolutionary way to lose weight based on the ketogenic diet
⭐ Start active fat burning immediately after taking it. ⭐ Fights the most “harmful” fat – visceral. ⭐ Up to 10 kg of weight loss per month without diets or exercise. ⭐ World hit in the field of nutrition.
To learn more
Venous networks are visible not only on the chest, but also on the arms and legs. Prominent capillaries on the chest are considered the safest because they are in the part of the body where the veins are close to the skin and therefore can see through it. Also, dishes can stick out after playing sports or excessive stress.
If they swell and protrude too much under the skin, consult a doctor.
This problem can occur not only in women, but also in adolescents and men. They have breast veins that dilate when levels of the hormone estrogen increase.
Protruding vessels: what is considered normal
Protruding veins on the chest are considered normal if a person experiences strong emotions for a long time, cries or laughs. This is the first reason for the appearance of veins.
The second reason could be any physical activity. As you tense, your muscles increase in size and bring your veins closer to your skin.
The third reason for venous imaging is external factors. One of them is constant exposure to the sun. Sun exposure is contraindicated for people suffering from vascular diseases. Increased body temperature in the sun causes increased blood pressure, which leads to prominent veins.
The fourth reason for blue veins can be any changes in the female body. This could be a delay in menstruation, PMS or inflammatory processes. The most common change is pregnancy.
Let's sum it up
The main causes of bruising and increased fragility of blood vessels are listed above, but not all of them. There are quite a few of them, and treatment tactics in each specific case can differ radically. Moreover, completely different specialists can treat pathology: vascular surgeons/phlebologists, dermatologists, rheumatologists, infectious disease specialists. It is impossible to give any general recommendations without seeing the patient and without knowing the entire clinical picture. From a relatively harmless, which can have an effect, and in most cases does not harm, we can recommend eating more foods rich in vitamin C, vitamins P, or taking their synthetic analogues. But even here, allergic reactions to these drugs and food are possible, and there are also restrictions for certain groups of patients (for example, pregnant women).
Venous network during pregnancy
The body is completely rebuilt in the early stages of pregnancy. The mammary glands change shape and size, their growth is observed, and preparation for feeding the baby begins. The skin stretches and thins. The size of the breast and nipple increases.
Hormonal changes in the body occur, resulting in the formation of venous networks. They are also called spider veins.
Aesthetically, it looks ugly, but after the baby is born, the hormonal levels will normalize and all symptoms will go away. The cause of spider veins may be the activation of the hormones progesterone and estrogen, which help increase breast tissue for feeding the baby. This causes the blood vessels to dilate and create a venous network.
The appearance of veins on the nipples is also not uncommon. For medicinal purposes, a pregnant woman may be prescribed medicinal ointments or gels, and therapeutic exercises. The main thing is that the treatment does not put the fetus at risk.
Sometimes this pattern also appears in men who like to be in places with high temperatures - baths, saunas, in the sun.
If the problem does not disappear after childbirth, then it is necessary to use vasoconstrictor drugs to strengthen the walls of blood vessels. Sometimes doctors perform laser operations to remove small vessels, use ultrasound treatment, and sclerotherapy. The latter procedure involves the introduction of a special sclerotic agent into the vessels, which glues the walls of the vessels.
This is a safe and popular procedure. After it, bruises and swelling may appear, but they go away over time. Unlike sclerotherapy, laser therapy does not leave bruises and is effective after the first session. If the procedure is not carried out properly, minor skin burns may occur, which will resolve quickly.
Spider veins during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a special physiological state of a woman, in which the course of most processes changes. First of all, this concerns hormonal levels, as well as metabolism (metabolism). Spider veins during pregnancy are a consequence of the influence of certain hormones, the level of which increases, on the functional state of the walls of the microcirculatory structures. After childbirth and normalization of hormone levels, telangiectasias do not disappear on their own, but require treatment.
What diseases can blood vessels in the mammary glands tell you about?
If venous threads on the chest do not appear due to pregnancy or other physiological reasons, then most likely this is a harbinger of some kind of disease. Only a specialist doctor can say this. It could be a blood problem, breast inflammation, an infection in the body, or lumps forming.
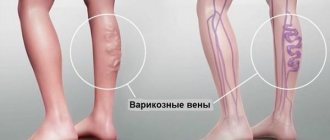
The most common diseases of the blood system include varicose veins and thrombophlebitis.
Most often, the lower limbs are affected; if the disease has spread to the mammary glands, it means it is already in an advanced stage.
Blue spider veins are symptoms of varicose veins in the breast. They bring not only aesthetic, but also physical problems; the disease can be accompanied by pain. Treatment of varicose veins leads to untimely swelling of the capillaries and their green color. Complex treatment is required.
The inflammatory process in the mammary glands occurs during mastitis and mastopathy. During these diseases, lumps in the chest, increased temperature, and deterioration in general condition occur. Infectious diseases may cause inflammation of the lymph nodes, followed by swelling of the veins. Another pathological cause of protrusion of the venous network onto the mammary glands can be neoplasms: adenoma, cyst or lipoma. They are also accompanied by lumps in the chest, high fever and weakness.
Spider vein removal
The basis of radical therapy for telangiectasias is their removal using various methods of physical or chemical influence, as well as taking measures to prevent re-exposure to the provoking factors of their development. High-quality removal is carried out in our medical center using the following methods:
- Sclerotherapy is the introduction into the lumen of the affected vessel of a special chemical compound (sclerosant), which leads to its gluing.
- Laser therapy is exposure to laser, which leads to “evaporation” of the tissues of the inner surface of blood vessels, followed by gluing.
- Electrocoagulation is the destruction of telangiectasia using local point exposure to electric current of a certain strength and frequency.
- Radio wave surgery – excision of the formation is performed, in which radio wave radiation plays the role of a scalpel.
The choice of method for removing telangiectasia on the chest is carried out individually by a phlebologist-mammologist.
Non-dangerous causes of bulging veins on the chest
Dangerous causes of protruding veins include the following:
- The period of adolescence, hormonal changes (in adolescence, girls develop mammary glands, the skin stretches and thins).
- Long-term exercise (saturation of blood with oxygen causes vasodilation).
- Breast changes after miscarriage (pregnancy also affects changes in the breasts, which can thin the skin on the breasts and veins and red blood vessels begin to appear).
- Sharp weight loss (the fat layer under the skin disappears, the skin becomes thinner, and veins appear under the skin).
- Visiting patients with infectious diseases.
- Mood swings (strong emotions cause an active rush of blood to the vessels);
- Taking hormones (many of them have side effects in the form of blood clotting, which worsens the condition of the veins).
- Menopause (hormonal imbalance causes protruding veins).
- Abrupt cessation of breastfeeding.
Non-surgical breast lift
The choice of techniques should be made taking into account contraindications to the method itself and limitations associated with the area of the procedure. The high percentage of detection of benign breast tumors justifies strict requirements for the safety of the treatment methods used. It is not recommended to carry out procedures associated with warming up, both deep and superficial, the prescription of current influences (especially using milliampere currents), darsonvalization, etc. The most severe restrictions are imposed when patients have breast implants, but they need to undergo preventive measures to activate lymphatic drainage and enhance skin turgor. In addition to safety and study, technologies must have the ability to have a multifaceted and multi-level effect in order to restore and strengthen not only and not so much the pectoralis major muscle, but also replenish the volume of glandular tissue, reduce the area of a stretched skin flap, raise the nipple line - preserve subcutaneous fat tissue and simulate the shape of the mammary gland. These tasks are complicated due to the significant mass of the glandular tissue itself and pronounced gravitational ptosis of the skin flap, as well as the need to preserve and restore the volume of fatty tissue and the volume of the gland, which regress with age in women who have given birth.
WHAT IS IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER: AN EXCURSION INTO ANATOMY.
The mammary gland, mamma, glandula mammaria, is a paired organ, in origin it is a modified apocrine sweat gland. In men, the gland remains underdeveloped. The mammary gland is located at the level of the III to VI ribs on the fascia covering the pectoralis major muscle (m. pectoralis major), for which reason it is also called the mammary gland. The mammary gland is loosely connected to the pectoral fascia, which ensures its mobility. On the medial side, the mammary gland approaches the edge of the sternum. Approximately in the middle of the gland there is a nipple, papilla mammaria, with pinholes at its top, which open 10-15 milk ducts (ductus lactiferi) to the outside. The area of skin around the nipple - the areola mammae - is pigmented, just like the nipple; in girls it is pink, in women who have given birth it is brown (brown). The skin of the circle is uneven, tubercles are visible on it, on the surface of which the ducts of the glands of the isolae areolares open, next to which the sebaceous glands are located. In the skin of the nipple and isola there are bundles of smooth muscle cells, partly oriented circularly, partly longitudinally in the thickness of the nipple. The contraction of these muscles tightens the nipple. The body of the mammary gland, corpus mammae, consists of 15-20 lobes (Iobi gl. mammariae), separated from each other by layers of adipose tissue, penetrated by bundles of loose fibrous connective tissue, called ligaments supporting the mammary gland (Iigamenta suspensoria mammaria). The lobes, which have the structure of complex alveolar-tubular glands, are located radially in relation to the nipple; with their excretory ducts (one from each lobe), they open at the top of the nipple of the mammary gland. On the way to the nipple (at its base), each duct has an extension - the milky sinus (sinus lactiferi).
The most important function of the mammary gland is the synthesis and secretion of milk during feeding of a newborn baby.
The structure of the mammary glands changes significantly at different age stages, during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and lactation. These changes are regulated by the activity of the endocrine glands.
In childhood, the mammary gland is underdeveloped, its maturation is confined to the period of puberty. In a pregnant woman, the glandular tissue grows, the mammary gland increases in size. The nipple and nipple circle darken. Dilated blood vessels (veins) are visible through the thin skin of the gland. Iron development reaches its maximum at the end of pregnancy. After lactation, the size of the gland decreases. During menopause, the gland undergoes partial involution: its size decreases, and the glandular tissue is gradually replaced by fibrous and fatty tissue. The function of the mammary gland is closely related to the activity of the gonads (Human Anatomy / Edited by Sapin M.R.)
EXTREME ATTENTION! OR PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE BREAST GLAND.
Mastopathy is a pathological condition of the mammary gland associated with compaction, diffuse focal hypertrophy and/or atrophy of its tissues. The disease is caused by dysregulation of the functions of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, ovaries, adrenal glands and thyroid gland. Against this background, women often experience problems with menstrual and reproductive functions. Artificial termination of pregnancy (abortion) stops physiological proliferative processes, and hyperplastic glandular tissue undergoes reverse development. But often these processes take on a perverted character and become a trigger for the development of degenerative changes (mastopathy).
The main symptoms of mastopathy are: the appearance of lumps in the mammary gland or its diffuse engorgement. Often these changes are accompanied by pain or tenderness, which may be constant or appear before menstruation (mastodynia). Some types of mastopathy are characterized by discharge of grayish fluid from the nipples. Similar discharge appears in a number of other diseases, for example, excessive levels of prolactin in a woman’s body, and intraductal papillomas.
Mastopathy is a disease characteristic of women of reproductive age. Various forms of mastopathy occur in 20-60% of women over 30 years of age. From a clinical point of view, it is customary to distinguish two main forms of mastopathy: diffuse and nodular.
The nodular form of mastopathy is characterized by the presence of clear limited compactions: single or multiple, in one or both mammary glands. Nodular forms of mastopathy are subject to cytological examination and surgical treatment.
Fibrocystic diffuse mastopathy is characterized by the presence of areas of compaction in the form of strands, granularity, enlargement of glandular lobules, pain on palpation, and the appearance of discharge of a different nature (such as colostrum, serous, greenish) from the nipple. Histological studies reveal fibrous changes in connective tissue, fluid cysts, epithelial proliferation, and regression of ductal tissue. Diffuse forms of mastopathy require not only systematic observation, but also treatment, since they are the initial stage of proliferative precancerous processes in the mammary gland (Dymarsky P.Yu., Zolotarevsky V.G.).
PHYSIOTHERAPEUTIC TREATMENT
When a diagnosis of mastopathy has been established, radon and iodine-bromine waters and pulsed ultrasound from 0.2 to 0.6 W/cm2 (6 minutes per mammary gland every other day) are recommended as methods of physiotherapeutic treatment. The course of treatment is 8-10 procedures. To prevent the progression of mastopathy, iodine-bromine baths and iodine electrophoresis are used.
Localized exposure to therapeutic mud, peloid-like substances, supratonal frequency current, inductothermy, microwaves in the centimeter and decimeter range, vibration massage, heliotherapy and all methods that have a deep warming effect are contraindicated.
Insist on an urgent consultation with a mammologist if your patient: 1. has any change in the mammary gland; 2. there was pain in the mammary gland not associated with the menstrual cycle; 3. the skin in the area of the nipple or around it is retracted, the color of the skin has changed, swelling has occurred; 4. a “lemon peel”-shaped seal appeared on the skin; 5. a lump has appeared in the axillary area; 6. there is discharge from the nipple.
HELP AND DO NOT HARM: COSMETOLOGICAL CARE IN A MEDICAL CENTER
The most popular procedures in medical centers for the problem of breast lifting, based on statistical data, are myostimulation, biostimulation and care procedures associated with the use of cooling plasticizing masks. The second most common procedures are microcurrent lifting and cosmechanical procedures. And a very small place is occupied by biocybernetic therapy procedures. The last of these are rarely used due to the insufficient number of devices in medical centers and the lack of awareness of patients and cosmetologists about the latest technologies.
Myostimulation is a technique prescribed for decreased muscle tone, based on the use of milliampere currents (from 0.5 to 20 mA). The strength of the current is selected according to the patient’s sensations (from slight tingling to pain): when exposed to tension, twitching, and contraction of the muscle fiber are observed; currents with rectangular, trapezoidal and H-shaped waves are used. In relation to breast lifting, it is advisable to prescribe myostimulation only to strengthen the pectoralis major muscle, increasing its (i.e. muscle) volume; Such an effect does not affect the gland itself, therefore the results of the procedures are assessed as mediocre (there is no effect of modeling, strengthening the skin flap and restoring the volume of glandular tissue). In addition, this type of exposure can only be prescribed to actually healthy people, as it has many contraindications. CONTRAINDICATIONS
General absolute: • malignant neoplasms; • diseases of the cardiovascular system in the stage of decompensation (acute inflammatory processes in the myocardium, endocardium, pericardium, heart defects, myocardial infarction in the acute period, frequent attacks of angina, acute cardiovascular failure); • stage III hypertension; • pronounced sclerosis of cerebral vessels; • systemic blood diseases; • bleeding or predisposition to it; • cachexia; • general serious condition of the patient; • fever (body temperature over 380C); • mental illness (epilepsy, hysteria, psychosis); • varicose veins stage 111; • active symptoms of phlebitis; • severe vascular sclerosis with a tendency to thrombosis and hemorrhage; • dysfunction of the kidneys, liver and thyroid gland; • condition after a course of radiotherapy for less than 2 weeks; • active form of pulmonary and kidney tuberculosis.
General relative: • hypotension; • vegetative-vascular dystonia; • taking diuretics; • hypoglycemia; • menstruation; • pregnancy.
Local: • violation of the integrity of the skin in the affected area; • skin diseases in the acute stage in the area of the procedure; • purulent and fungal skin lesions; • stones in the kidneys, gall bladder and hepatic ducts (when working in the appropriate projections).
ADDITIONAL CONTRAINDICATIONS TO PRESCRIPTION OF CERTAIN TREATMENT METHODS Contraindications to galvanization (electrophoresis), pulsed and alternating currents, electromagnetic effects:
General: • presence of a pacemaker; • individual intolerance to current; • individual intolerance to the drug; • mastopathy; • pregnancy.
Local: • tooth sensitivity (during procedures in the facial area); • dental cysts (during procedures in the facial area); • diseases of the thyroid gland (during procedures in the face, neck, décolleté); • sinusitis, frontal sinusitis in the acute stage (during procedures in the facial area); • gold and platinum reinforcement (when performing procedures in the facial area); • severe skin irritation after the procedure; • the presence of metal structures in the area of the procedure (large pins, plates, prostheses, etc.); • acute intra-articular injuries; • acute form of herpetic infection.
The course of myostimulation consists of 10-15 procedures, 2 times a week; The duration of the procedure is 20-40 minutes. The effect of the procedure is noticeable (strengthening the pectoralis major muscle) after 2-3 procedures, the result after the course lasts up to 1 month, then maintenance procedures are required once every 2 weeks.
Biostimulation is an innovative and highly effective technique based on stimulating the biological activity of body tissues in order to activate natural physiological processes.
Biostimulation uses more modern equipment and improved waveforms. For example, (England) 44 combinations of different waveforms were developed for an effective complex effect on connective, fatty and muscle tissue, circulatory and lymphatic systems, and skin in order to activate the basic, reserve and compensatory capabilities of the body. Thanks to various waveforms, sequences and signal speeds, biostimulation makes it possible to obtain fast and high results, achieving an optimal biological effect with minimal exposure time. Thus, 30 minutes of a biostimulation program on the Futura Pro device can be compared with two hours of a conventional electrical stimulation program.
However, when prescribing this technique, taking into account contraindications (see myostimulation) and indications: muscle training, increasing their tone, increasing efficiency and strength, skin lifting, breast lifting and increasing the tone of the pectoral muscles, we can conclude that this technique does not allow achieving the effect of modeling the breast.
Biostimulation is prescribed in a course of 10-12 procedures, 2 times a week; The duration of the procedure is 20-30 minutes. The effect of the procedure (to strengthen the pectoralis major muscle) is noticeable after 2-3 procedures, the result after the course lasts up to six months, then maintenance procedures are required once a month.
The technique of three-dimensional tissue stimulation - cosmechanique (Cosmecanique) - developed the idea of pinch plastic massage according to Jacquet. Cosmechanics technology takes into account the anatomical and histological features of the skin, which require dosed atraumatic effects, uses a particularly delicate mechanism for capturing folds and a pulsed vacuum mode to avoid stretching and displacement of the skin relative to the underlying tissues.
The manipule of a specially designed device “Lift 6” (France) captures the skin fold with parallel plates due to pulsating vacuum and initiates mechanical vibrations in the skin and underlying tissues in several planes: vertical, horizontal and in the direction of movement of the manipule.
The cosmechanics procedure is prescribed in a course of 15-20 procedures and is carried out twice a week. The duration of the procedure is 30 minutes. According to the subjective feelings of clients, it is characterized as pleasant and relaxing.
Thanks to the powerful, but at the same time, very delicate effect in three mutually perpendicular planes, there is an increase in vasomotor activity of microvessels, a decrease in blood stasis in various parts and an improvement in all trophic processes in tissues.
Due to volumetric stimulation of fibroblasts with a complex of physical effects, it is possible to renew and strengthen the connective tissue framework of the dermis and activate regeneration processes in the skin. At the histological level, this is manifested by an increase in collagen content and a harmonious reorganization of collagen fibers in the papillary dermis.
Visible physiological effects and the possibility of physiological activation of tissue regeneration when using cosmechanics technology occur due to the following factors: • increase in venous outflow (4-5 times according to research results), unloading of the venous bed, strengthening of the venule wall; • increase in lymphatic outflow (2-3 times); • increased arterial inflow and increased blood perfusion (more than 5-6 times); • activation of fibroblasts, which leads to renewal of the collagen structure (from 30 to 120%) and reduction of the skin flap (by 20% or more).
The above results are confirmed by clinical studies using thermography, Dopplerography, histology, and elastometry methods.
The recommended course is 10-20 procedures, performed 2 times a week; The duration of the procedure is 30 minutes. The effect of the procedure for lifting the gland is noticeable after 7-10 procedures, after the first session the skin in the chest area becomes more elastic and smooth, the natural lines of the chest are restored, the result after the course lasts up to six months, then maintenance procedures are required once a month (provided that body weight).
In addition to effectively toning the bust skin, the cosmechanics procedure provides real psychosensory pleasure.
However, as practical observations show, the results of lifting and modeling the mammary gland are determined only by strengthening the framework of the epidermis and dermis and improving the condition of the vascular bed, without affecting the tissue of the gland itself.
When prescribing this technology, it is necessary to take into account the volume of the gland (if the breast size is 3 sizes or more, the technique is not effective) and the stability of the patient’s weight, since at the first symptoms of weight loss, the activity of blood flow in the breast area decreases, and the result again leaves “much to be desired.” "
Microcurrent therapy (MTT) - Bio Therapeutic Computers, USA - restores the functional activity of tissues at the cellular level. MTT simultaneously acts on all layers involved in the pathological process. For example, in rejuvenating procedures on the mammary gland, microcurrent pulses affect the epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous fat, muscles, glandular tissue and blood vessels.
The advantage of MTT when affecting tissue is its special pulse shape, which is similar in shape to pulses generated on the cell membrane. Thus, the microcurrent impulse is physiologically integrated into the work of the cell, without injuring it and keeping the “resting potential” and “action potential” phases unchanged.
Under the influence of MMT, the state of the tissue returns to the original physiological norm, the muscles are shortened, the skin flap is strengthened and the volume of the glandular tissue is restored. Thus, the shape of the mammary gland is modeled.
The MTT therapy procedure is safe to perform on the breast area and is recommended in courses of 12 to 15 procedures. The result is noticeable after 5-7 procedures, although with significantly weakened tissues the effect may be noted after 2-3 appointments. The result after the course increases over six months and lasts for a long time. The procedures are carried out 3 times a week; it is possible to additionally introduce biologically active drugs (phoresis) at the end of the procedure to enhance skin turgor.
The latest unique technology, biocybernetic therapy, presented in the “Beauty Tek” device from (Germany) has a similar multifaceted and safe effect.
Biocybernetic technology (BT) is an integral complex between diagnostics and therapy, enclosed in a biocybernetic circle, ensuring an inextricable connection between the patient and the computer diagnostic program, which is based on the symbiosis of the achievements of traditional medicine (the highest technical achievements and modern algorithms for research and treatment) and centuries-old experience of Chinese traditional medicine (acupuncture).
The purpose of this technique is to correct the energy balance of cells, tissues and the entire organism. Within a closed loop control system, the device recognizes an energy deficit, which is then restored using complex computer algorithms.
Using a series of algorithms, BT reads and interprets the physical and chemical state of tissues several hundred times per second, the device takes readings, processes the data and makes corrections.
As soon as a state of energy balance is achieved in the area under study, the device stops the treatment. Thus, exactly the impact that is required to achieve balance occurs. Then the next stage of reading the resulting tissue modifications, counting and new adjustments begins.
This work is extremely complex, because it includes thousands of pieces of information and cannot be implemented without computer technology. Obviously, it is inconceivable for the human brain to integrate a mathematical model, solve it, apply an adjustment, and then evaluate the results of that adjustment.
Each real-time adjustment of tissue state represents thousands of calculations carried out by the system in a fraction of a second, since the polarization state of any type of cell covers a wide range of compensatory physical, biochemical and humoral reactions.
The statistical database underlying the diagnostic algorithm used in biocybernetic technology was created taking into account the research developments of EEG, NMR, ECG, CT and other modern research methods. High-precision measurement indicators and a digital multi-frequency digital analyzer, which allows assessing and correcting the bioelectrical state of tissues up to 900 times per second, ensure the creation of individual bioregulation of processes in the human body. Today, biocybernetic technology is the only method in aesthetic medicine that operates on the principle: first diagnosis, then treatment, and all this on-line. This leads to the multifaceted use of BT: “anti-age” therapy, restoration of energy potential, regulation of metabolism, acceleration of regenerative processes, restoration of skin turgor (including in complex therapeutic areas: chest, abdomen, inner third of the shoulder, etc.), cellulite treatment, figure modeling programs, anti-stress therapy and relaxation, rehabilitation programs after plastic surgery, etc. The use of BT in the practice of dermatologists, physiotherapists, gynecologists, surgeons and doctors of other specialties has proven itself.
Unique technologies, safe effects, a small number of contraindications (pacemaker, pregnancy, oncology), the presence of multiple studies and the highest efficiency allow us to speak of biocybernetic therapy as the latest scientific direction.
One of the popular programs for a huge range of therapeutic options is the restoration of the volume and shape of the mammary gland, strengthening the underlying muscular and ligamentous apparatus, restoring skin turgor and raising the nipple line.
The technique has undergone multiple clinical trials confirming the safety of its effects, and has received positive medical reviews for use on the breast area. Efficacy was measured using the following methods: measurement of firmness and elasticity (cutometer), measurement of skin ultrastructure (B-Scan scan), measurement of capillary skin perfusion and oxygen saturation, infrared thermography, LTS test (living skin assessment), photo documentation and profilometry.
When undergoing a course of BeautyTek therapy procedures, the patient is recommended to drink at least 2.5-3 liters of liquid per day. Our body consists of 80-85% water, and it is the liquid that ensures the penetration and conduction of microampere impulses into tissues. Immediately before each procedure, the patient is required to drink 250-300 ml of water or herbal tea.
Recommended course: 12-15 procedures, 2 times a week, maintenance therapy once a month. One procedure takes from 30 to 90 minutes, depending on the chosen form of treatment and the desired result. The result of the procedures is noticeable after 5-7 procedures; with significantly weakened tissues, the effect can be noted after the first appointments. The results from the course increase over six months and last for a long time.
Thus, today it is the “BeautyTek” therapy procedures that are the most effective and safe. Cosmetologists can recommend this therapy not only to patients with breast ptosis, but also as a prophylactic agent for diffuse mastopathy, when placing implants and in the postoperative period. We can only hope that such high-tech treatment methods will soon become available to both patients and cosmetologists, and will delight everyone with excellent results and safety. * “The Art of Beauty Professionals” is a specialized publication for professionals (No. 1/2008). Author of the article: E.V. Sokolova, physiotherapist, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist. Head of the scientific and methodological direction of the St. Petersburg Institute of Beauty.
Alarming causes of swollen capillaries on the chest
If the bulging vessels on the mammary glands do not subside over time, have a bright color and become very bulging, you should consult a doctor. A mammologist deals with this problem. If a patient develops lumps or nodules, he is referred to a phlebologist, a specialist who studies vein diseases. He will refer the patient for additional tests, ultrasound, ductography and sonography.
Thrombosis has alarming symptoms with varicose veins. The skin turns blue, a feeling of heaviness appears in the chest, the mammary glands swell and enlarge. This requires urgent intervention from a medical specialist.
Subjective first signs of pregnancy
Often the first changes in the body that a woman differentiates as signs of pregnancy may turn out to be symptoms of PMS. However, if you have never suffered from premenstrual syndrome before, you should pay attention to these:
- Feeling of weakness, malaise and increased fatigue even with usual exercise.
- The appearance of drowsiness during the day and insomnia at night.
- Unstable emotional state. A woman’s mood can change dramatically in a matter of seconds without good reason.
- A feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, lower back and pelvic area.
- Constant headache and dizziness.
- Change in libido. Moreover, it can either decrease or increase.
- Periodic sensations of heat or chills that replace each other.
- Increased sensitivity of the mammary glands to the point that any touch to the breast results in extremely unpleasant sensations and even pain.
- Increased appetite or change in eating habits. From the first days of pregnancy, a girl may want to eat more or eat dishes that she did not like before.
- The appearance of an unreasonable feeling of nausea. In some cases, heartburn and vomiting occur. This condition is called toxicosis.
- Increased sensitivity to odors and distortion of the sense of smell.
All of the above signs cannot accurately answer the question: has pregnancy occurred or not? However, they allow us to suspect it and move on to more accurate and reliable diagnostic methods.
Treatment with folk remedies
If protruding venous threads are a sign of varicose veins, you can add the use of folk remedies for treatment.
These include: apple cider vinegar, hazel leaf tincture, nutmeg tincture, hop cones. Some of the available remedies help with varicose veins: sea salt, potatoes, lemon.
There is also a set of exercises that help thin thick blood and improve blood circulation in the vessels to avoid stagnation.
Prevention of venous disease
You can prevent such troubles with protruding veins by following certain preventive measures:
- A proper, nutritious diet with vegetables and fruits containing vitamins.
- Regular fluid intake.
- Avoid bad habits.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Temporary restriction of sports activities.
- If you have high blood pressure, avoid saunas.
- Normalization of the emotional background.
- Protecting the mammary glands from hypothermia.
If you have a sedentary lifestyle, exercise more often to avoid blood embolism in the vessels. All these preventive measures will help prevent the appearance of veins on the chest in the future.
Laser therapy
This measure is considered the most successful method of combating venous diseases to date. The laser, as if by magic, destroys all small blood vessels without damaging the skin. As a rule, after one session of laser therapy the result will be visible; in some cases the procedure is repeated.
Laser therapy is absolutely safe and does not cause any pain. In rare cases, complications occur, for example, burns may appear. But there will be no bruises or swelling, like from sclerotherapy.