One of the symptoms of acute cerebrovascular accident is dizziness. In case of a stroke, the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital begin treating this subjective sensation by determining its cause. Complex treatment at the rehabilitation clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, including pharmacotherapy, vestibular gymnastics, and stabilization training, leads to a decrease in the intensity and duration of dizziness, a decrease in coordination disorders, and an increase in the stability of the vertical posture.
Causes of dizziness during stroke
Dizziness is divided into true, associated with damage to the vestibular analyzer, and non-systemic, which occurs outside the vestibular apparatus. In turn, vestibular vertigo is divided into three groups:
- peripheral (damage to the labyrinth);
- intermediate (occurs in the vestibular nerve);
- central (occurs in the central nervous system).
There are the following causes of central vertigo:
- acute ischemia in the brain stem (stroke, transient ischemic attack);
- chronic cerebral ischemia;
- whiplash injury to the cervical spine;
- brain injuries and tumors.
The most common causes of peripheral vertigo include Meniere's disease, vestibular migraine, and head injuries.
Dizziness during a stroke and after an acute cerebrovascular accident in 95% of patients is associated with damage or disruption of the blood supply to the cerebellum, which is responsible for a person’s balance and coordination in space. Disruption of the recovery process after a stroke (alcohol abuse, insufficient sleep, smoking) contributes to the persistence and recurrence of dizziness.
Poor nutrition, high levels of lipids, table salt, and simple carbohydrates in the diet slow down the process of recovery of brain cells. Physical and emotional stress, fear, and depression can cause dizziness as a result of autonomic dysfunction after a stroke.
A drop in blood pressure in stroke patients also causes dizziness and blurred vision. Diseases accompanying stroke (compression of the carotid arteries, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine) contribute to impaired blood supply to the brain and the occurrence of neurological symptoms.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke
With hemorrhoidal stroke, symptoms most often appear suddenly, mainly during the daytime and during very heavy physical activity. The following symptoms are typical:
- convulsions;
- Strong headache;
- sudden loss of consciousness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- serious depression of a person's consciousness, similar to or leading to a coma
In addition, general symptoms of a stroke appear:
- decreased facial expressions and muscle strength affecting any part of the body;
- the occurrence of speech disorders and problems with visual perception;
- loss of coordination of movement with impaired ability to move.
During an attack, the patient's skin becomes cold and sometimes acquires a purplish-bluish tint. Breathing becomes more frequent, noisy, with wheezing. Sometimes, on the affected side, the pupil dilates, diverges, or chaotic movements of the eyeballs occur.
An important indicator of the severity of the patient’s current condition is comatose status with loss of consciousness, which can last several days. This makes the prognosis very unfavorable.
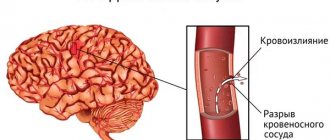
Subarachnoid hemorrhage most often results from rupture of a cerebral aneurysm. As a result, the patient experiences severe headaches localized in the back of the head and forehead. Then it spreads to the rest of the head. Later, other symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke appear.
In case of extensive cerebral hemorrhage, neurosurgical microtechnical operations are performed. In this case, removal of the hematoma leads to a decrease in pressure on the brain tissue and prevents the development of brain edema. But surgery is performed strictly for medical reasons.
In case of an aneurysm, surgery is performed to stop bleeding, and the patient is prescribed hemostatic drugs. Often with subarachnoid lesions, narrowing of the vessel occurs and the development of ischemic stroke. In this case, calcium channel blockers are necessarily prescribed to prevent narrowing and spasm of the vascular walls.
In the first 3 weeks after the attack, the patient’s condition remains the most severe due to progressive cerebral edema, as well as a gradual increase in cerebral symptoms. If there are any chronic pathologies in the body, aggravated by a hemorrhagic stroke, the patient may die. A month later, the patient begins to experience regression of cerebral symptoms and blood pressure stabilizes.
This is interesting! It is recommended to always have glycine in your home medicine cabinet. Many qualified doctors classify this drug as a neuroprotector or a substance that protects brain tissue.
If unpleasant weakness in the limbs or speech disorder occurs, you should immediately put 5 glycine tablets under your tongue. To some extent, such prevention can prevent acute brain damage and the development of hemorrhagic lesions.
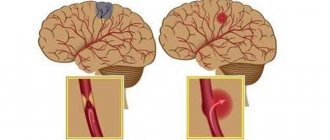
Many people are interested in the difference between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Two such lesions have almost identical symptoms, but have different reasons for the development of such a serious pathology. With ischemic stroke, the prognosis is favorable and mainly depends on the degree of brain damage that has occurred.
The following symptoms are characteristic of each type of this disease:
- suppression of speech ability;
- partial or complete paralysis of the body and limbs;
- impairment of visual sensitivity or its complete loss;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- complete loss of hearing in a hemorrhagic condition;
- • serious inhibition of the functions of the cerebral cortex;
- • increased blood pressure.
The consequences of a stroke mainly depend on the location and extent of the existing lesion. A hemorrhagic attack has an acute onset and progresses rapidly. The onset of coma in this case is possible within the first few minutes or hours. With ischemic stroke, the symptoms are less severe.
Damage to the left hemisphere leads to paralysis of the right side of the body. Hemorrhage in the cerebellar area deprives the patient of sensitivity, the ability to swallow, see and speak. Often the consequence of a hemorrhagic stroke is the gradual development of dementia or dementia.
Dizziness during stroke. Treatment
To treat dizziness, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital take measures to eliminate the cause that caused it. This is of particular importance when dizziness occurs during cerebral stroke, which develops as a result of arterial hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, and diabetes mellitus.
For dizziness in patients with arterial hypertension, the underlying disease is treated. For this purpose, cardiologists individually select drugs for antihypertensive therapy. With the development of cerebral stroke, dizziness is caused by a transient or persistent disruption of the blood supply to the peripheral or central parts of the vestibular system. Most often it occurs as a result of ischemia of the vestibular nuclei of the brain stem. During a stroke, dizziness is accompanied by the following neurological symptoms:
- ataxia (impaired coordination of movements of various muscles in the absence of muscle weakness);
- oculomotor disorders;
- bulbar disorders (with damage to the glossopharyngeal, vagus and hypoglossal nerves);
- paresis (partial impairment of motor function) and paralysis;
- sensory disorders.
Dizziness increases the possibility of falls, injury to patients, limits their functional activity, and reduces the quality of life. In this regard, vestibular rehabilitation, stability training, and improvement of postural control are important tasks in the rehabilitation treatment of patients with stroke.
Comprehensive rehabilitation treatment for dizziness during stroke, which is carried out at the Yusupov Hospital, includes:
- pharmacotherapy;
- vestibular and oculomotor gymnastics;
- use of exercise therapy methods (biomechanotherapy);
- stabilization training with biofeedback effect.
In order to reduce dizziness in patients with stroke, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use drugs from the following groups:
- neuroprotectors, which include inhibitors and antagonists. They help improve cerebral circulation and also protect the brain from repeated damage;
- Betaserc, a drug that helps cope with disorders, has proven itself well, regardless of the duration of dizziness;
- dizziness decreases with regular use of anticoagulants.
After stopping an acute attack of dizziness, rehabilitation specialists gradually begin vestibular gymnastics. It is a type of therapeutic exercises aimed at accelerating the adaptation of the vestibular system to damage caused by acute cerebral ischemia. When carrying out this method of rehabilitation treatment, the ability of various parts of the central nervous system to reorganize due to structural and functional changes is used. The patient is asked to perform a series of exercises that have a mild irritating effect on the vestibular structures. Repeatedly performing them leads to the patient getting used to the irritation and the dizziness subsiding.
To treat patients with dizziness after a stroke, biofeedback specialists at the Yusupov Hospital include stabilometric training in a comprehensive rehabilitation program. The technique is based on biofeedback, in which specialists use the parameters of the projection of the general center of mass onto the plane of support as a feedback signal. During special computer “stabilometric games”, patients learn to voluntarily move the center of pressure with varying amplitudes, speeds, degrees of accuracy and direction of movements without losing balance.
Dizziness 2 months after stroke
Julia, Balashikha
August 15, 2021
Hello dear doctors!
I will attach all my mother’s diagnoses, she is 68 years old. She suffered a stroke on her legs (she didn’t realize it was him); after 2 weeks they took her to the hospital. She stayed there for 10 days. Then we took her to a sanatorium for rehabilitation after a stroke. I took all the medications that were prescribed. There was a sea of them. Now he only drinks Telzap + (80/12.5 mg), Noocil for the third month, Cardiomagnyl and rosuvastatin. The pressure has always been under 200. For more than 20 years. I started taking Telzap after a stroke. He lowered her blood pressure well for 2.5 months - to 110-150. With a pressure of 110-125, she felt dizzy and a neurologist from the sanatorium advised her to keep the pressure no lower than 130. Mom was with us in Moscow for the entire 2.5 months. Her condition became good, she underwent super rehabilitation, her head stopped hurting and dizzy. As a result, 5 days ago she went home - to Samara, where the climate is dry and hot, 33-38 degrees there every day. And during the entire 5 days there, her blood pressure became 180 in the mornings and evenings, and dizziness appeared. Objects do NOT rotate, dizziness is exactly like weakness and shaking. As mom says, for a couple of minutes, then she lets go. And this often happened for 5 days. Please tell me what this could be connected with? The fact is that she lives in a village, we specially took her to Moscow to a sanatorium - since there are no doctors or even a clinic in the village. We talked to the doctors here and they told us everything is fine, take your medications, and check your tests again in six months (monitoring and checking your condition). Mom left and I’m worried that it’s THERE that her bad health returns. Could this be related to climate? What can you do to help her now? Thanks in advance for your help!!! The photo from June 14 is a discharge from the hospital. She had a mini-stroke (not a heart attack!). The sanatorium just wrote the diagnosis. From June 14 to June 24, she was in the neurological department. Next, until July 9, in a Moscow sanatorium for complete rehabilitation after a stroke. There she was checked again with all the tests. They didn’t give any bad prognoses, they said that everything was recovering very well and there was no major damage. Because of this, I got severe neurasthenia, panic attacks, stress and depression. I’ve been in remission for 22 days now, I’m taking Zoloft, and now I’m very afraid for my mother again. After all, it was precisely on this basis that I fell ill too. I beg you to help me, I will thank you more than I indicated in the price of the question. Thank you ! And please write, are there any chances that my mother will not have another more deplorable stroke??? What should I do to avoid this? Like children, we did everything we needed and everything that the neurologists from the sanatorium advised on presidential affairs. Have we really missed something???? She also began to drink little water. Here in Moscow we forced her directly, but at home now she drinks a maximum of half a glass. We didn’t want to let my mother go home to the Samara region in such heat; in Moscow it is cool and the humidity is higher and she always feels good here... but unfortunately my mother misses home very much, we had to take her (((now I regret it. Chronic diseases:
Endometriosis, IDA, nervous exhaustion June 2021, low D, folate, high B6 (before the analysis I drank magnesium b6 and glycine with b6).
The question is closed
stroke
unsteadiness of gait
dizziness
Caring for patients with dizziness after stroke
An important component of the rehabilitation treatment of patients with dizziness after a stroke is the organization of care and nursing. Impaired coordination of movements with preserved muscle strength in the limbs causes loss of self-care ability and a decrease in the functional activity of patients. They can cause injury and recurrent stroke.
In order to improve the quality of life of patients with dizziness, the latest technologies used in care are being introduced. Proper care is not opposed to treatment, but is organically included in it as an integral part and involves the creation of a favorable everyday and psychological environment at all stages of treatment. Due to the decrease in functional activity of patients with dizziness, he is recommended to use absorbent products (diapers for sedentary patients and absorbent panties for patients who have retained mobility).
After determining the cause of dizziness, an individual treatment regimen will be selected for you to get rid of the unpleasant consequences of a stroke. The use of modern recovery techniques allows specialists at the Yusupov Hospital Rehabilitation Clinic to improve the quality of life of patients suffering from dizziness after a stroke. Make an appointment with a neurologist by phone in advance.
Vertigo syndrome
Dizziness, or vertigo (from the Latin “vertigo”), is a condition in which a person in a stable position notices the illusion of movement of objects around him. In young people, vertigo may be the only symptom; in older people, it is usually accompanied by other symptoms: hearing loss, ringing in the ears, nausea, vomiting, and weakness in the legs. The severity of vertigo varies significantly - from insignificant to catastrophic. Severe dizziness in an elderly person, if left untreated, can lead to complete disorientation, incoordination, falls and injuries, and panic disorders.