The peak of popularity of magnetic bracelets occurred in the 80s and 90s of the last century, although the healing properties of constantly wearing metal accessories have been known since time immemorial. At least, the ancient Assyrians, Sumerians and Babylonians constantly wore such bracelets, considering them a kind of amulets. It cannot be said that in those days medicine was at a high level, but even today a pressure bracelet is not considered an absolutely useless accessory, and many doctors recommend it as an alternative to drug therapy. Of course, it is unlikely to help hypertensive patients, but for people whose blood pressure increases not so often and on a non-critical scale, this product can make life easier by preventing the occurrence of a painful situation caused by a variety of factors - for example, weather dependence.
There is no medical basis for treating blood pressure with bracelets.
Metal as medicine
Magnetotherapy as a phenomenon gained worldwide fame in the middle of the last century. A lot of research has been and is being carried out on the influence of magnetic fields on people’s health, and today it is reliably known that there is definitely such an influence. As for the impact specifically on blood pressure, science does not reject the possibility of normalizing blood pressure when using magnetic bracelets, but not within clinically significant limits. Therefore, before going to the store for such a purchase, you should definitely consult with a cardiologist - it is quite possible that the individual characteristics of your body are not compatible with any electromagnetic influence, even if it is weak.
The main operating element of therapeutic pressure bracelets is a permanent magnet, or rather, a magnetic field formed around this accessory. There is no doubt that, when placed on the wrist, the accessory will enhance the effect of the magnetic field characteristic of each individual. This means that it can influence certain physical and chemical processes occurring in our body at the cellular level. Adherents of the therapeutic use of magnetic bracelets are convinced that as a result of exposure to the external environment, a person’s magnetic balance decreases over time, so constant replenishment is simply necessary for most of us.
From a scientific point of view, there is an opinion that the magnetic field created by the bracelet additionally magnetizes the iron present in the blood, increasing the speed of its movement and thereby facilitating more complete saturation of tissues and organs with oxygen.
Methods of application
It is necessary to differentiate invasive magnetic therapy (electrical stimulation), the effectiveness of which has been proven, from non-invasive ones. These two methods are very different in terms of action. In the invasive version, the magnetic field is used only to transmit electrical energy. Magnetic therapy is now also used in animals such as horses to relieve tension, heal injuries, combat allergies or relieve pain. Again, the effectiveness of invasive therapy is scientifically proven.
Allergy
Non-invasive magnetic stimulation methods are not recommended due to insufficient evidence of effectiveness. Zirconium or magnetic bracelets are ineffective methods of treating hypertension.
In what cases is wearing a bracelet indicated?
The healing properties of metal magnetized bracelets have not been studied well, but the positive effects of wearing this accessory are reliably known in the following cases:
- in order to improve blood supply, especially peripheral vessels;
- to improve immunity;
- with rapid fatigue;
- presence of VSD;
- joint diseases;
- to normalize blood pressure.
When diagnosing cardiovascular pathologies, including hypotension and hypertension, metal bracelet therapy should in no way be perceived as a replacement for drug treatment.
Indications for use
The manufacturer indicates the following indications for use:
- Strengthening the immune system;
- Treatment of infections and allergies;
- Improvement of cartilage structure;
- Acceleration of healing of bone fractures;
- Spinal diseases;
- Headache;
- Premenstrual syndrome;
- Hypertension.
According to the manufacturer, the magnet helps with problems with the musculoskeletal system. Magnetic therapy, according to the creator of the bracelets, is also useful for the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatism and osteoporosis.
Varieties
Medical bracelets are divided depending on their purpose and material of manufacture. According to the target factor, the following varieties of this wrist accessory are distinguished:
- anti-arthritic;
- for the treatment of vascular diseases;
- anti-inflammatory;
- for headaches;
- sports.
Based on the type of prevailing material, bracelets are:
- made of medical steel;
- copper;
- zirconium;
- hematite;
- titanium;
- neodymium
Steel bracelets
This is the cheapest and most common option, providing a good effect in the treatment of high blood pressure thanks to the magnetic field created by special inserts.
Copper bracelets
They are more efficient than steel ones, since the effect of the magnetic field is enhanced by the action of copper, which has the ability to affect many human systems and organs. The rules for wearing a copper bracelet for hypertension are standard - the desired effect is achieved with long-term wearing, after about 20 - 30 days you can observe the first positive results.
Zirconia bracelets
This metal, rarely found in nature, is often used for medical purposes, since zirconium, not belonging to the class of noble metals, is absolutely harmless to the human body. Zirconium products have a characteristic white-silver color with a faint golden tint. Worn on the wrists, where a large number of biological points are concentrated.
Hematite bracelets
This type of medical accessories differs from other varieties in that the raw material for production is a mineral that contains a lot of iron. This material does not require magnetic inserts, since hematite can be magnetized artificially. Hematite accessories are preferred by people with an allergic reaction to steel, copper or other metal.
Titanium bracelets
The excellent characteristics of this metal have been known for a long time - it is light, extremely durable, and very rarely causes allergic reactions. Therefore, despite the fairly high cost of titanium products, such accessories are very popular.
Neodymium bracelets
The neodymium alloy used to make healing bracelets consists of a rare earth metal - the lanthanide neodymium, iron and boron (another combination is also popular - neodymium, yttrium and cobalt). Due to its excellent magnetic properties, neodymium products are used very widely in medical practice, allowing normalization of blood flow, helping to saturate tissues and organs with oxygen.
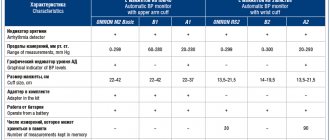
Modern mobile methods for monitoring blood pressure and pulse
There are many portable devices on the market that can measure heart rate, blood pressure and transmit data in real time or save them.
They are often connected to a smartphone or PC through a special application and have a number of additional functions.
These are all kinds of smart watches, fitness trackers, compact cardiac monitors for Holter studies and daily monitoring of cardiovascular system parameters, a bracelet for measuring blood pressure (portable blood pressure monitor).
Smart bracelets
Smart bracelets (smart watches) are a computerized wrist device that has many additional functions (including the ability to monitor a person’s physical condition. The results obtained are transmitted via Bluetooth to a smartphone or PC. The primary task of a smart watch is to receive incoming calls and messages , GPS navigation, checking email, access to social networks... Monitoring the physical parameters of the body is an additional option.
The newest models are actually mini-computers that can replace a smartphone and sometimes a PC.
In addition to measuring heart rate and blood pressure, smart watches can monitor human biorhythms and record physical activity and calories burned. Smart watches can remind the patient to measure blood pressure, blood sugar levels, or take medications.
The disadvantages of such bracelets are their short battery life (maximum 48 hours), high cost, and rather bulky design. The lower the price of such a gadget, the higher the error in measuring blood pressure and pulse.
Fitness trackers
A fitness tracker is a device in the form of a small bracelet that is worn on the wrist and has sensors for recording a person’s daily activity (number of steps, heart rate, biorhythms, calories burned, blood pressure level). The device has a certain degree of protection from moisture and physical impact and is designed for use during sports.
Fitness trackers are low-cost, compact, easy to use and do not require frequent recharging, which has made them popular among people who exercise or want to lose weight. Some models are equipped with a medication reminder function and can signal a person about staying in one position for a long time and the need to move.
Portable heart monitors
Portable monitors are designed for daily monitoring of cardiac performance indicators (cardiograms, for example). They consist of a set of electrodes that are attached to the skin, a cuff for measuring blood pressure and a base that can be worn on the forearm or belt.
Daily monitoring allows the doctor to see a complete picture of the state of the patient’s cardiovascular system, helps to make an accurate diagnosis and assess the adequacy of the prescribed treatment or identify paroxysmal rhythm disturbances that cannot be detected when taking a standard ECG.
The latest models of cardiac monitors also have the ability to record the patient’s body position and motor activity, recording a rheopneumogram (impedance movement of the chest).
Reopneumography makes it possible to diagnose ventilation disorders and periods of sleep apnea.
Some models of cardiac monitors are equipped with a pulse oximeter, which makes it possible to monitor fluctuations in saturation (the degree of saturation of oxygen in the blood).
Hypertension is closely related to obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (it has common risk factors, development mechanisms and similar clinical signs). Sometimes hypertension occurs secondary to sleep apnea, so identifying and treating sleep-disordered breathing can correct the blood pressure problem.
Features of treatment
Like any other alternative therapy method, a magnetic pressure bracelet cannot be considered a complete replacement for traditional drug treatment, but as a preventative measure it can demonstrate quite tangible results. Advantages of using medical accessories with a magnetic therapeutic effect:
- unlike course drug treatment regimens, you can interrupt treatment using a bracelet at any time;
- such therapy is especially useful for weather-dependent people in whom blood pressure surges occur unpredictably - drug treatment in such cases will be post-therapeutic in nature, while the bracelet will be preventive;
- In addition to health benefits, such accessories can serve as stylish decoration.
It is impossible not to note some negative aspects of wearing these products:
- many people who bought a blood pressure bracelet rely entirely on its medicinal properties, forgetting to regularly see their doctor;
- since their effect appears at least a month after the start of wearing them, many patients, without waiting for real results, stop wearing them, being disappointed in the benefits of such therapy.
Wearing a therapeutic bracelet to normalize blood pressure is a procedure that requires patience, perseverance and maintaining a positive attitude throughout the entire period of wearing this accessory.
Ureterorenoscopy (URS) and flexible URS
Ureteroscopy is the preferred treatment for small to medium-sized stones located anywhere in the urinary tract. The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia. During this procedure, a ureteroscope (a long, thin instrument with a tiny camera at the end) is inserted through the urethra and bladder into the ureter or kidney. Once a stone is found, it can be removed using "tongs or a basket", or a laser or pneumatic is used to break the stone into smaller pieces before they are removed using a basket. Ureteroscopes can be flexible, like a thin, long straw, or more rigid. After the stone is removed, a small temporary tube called a stent may be placed in the ureter to help urine flow from the kidney to the bladder. The urinary catheter and/or stent is usually removed soon after the procedure.
You should know!
URS can be accompanied by both intra- and postoperative complications, which in rare cases may require conversion to open surgery or re-intervention.
During the operation the following may occur:
- migration of stones to the kidney (up to 12%);
- infectious complications (up to 6%);
- ureteral damage (up to 2%);
- bleeding that may require blood transfusion (0.1%);
- ureteral avulsion (0.1%);
In the postoperative period, the following may develop:
- fever and sepsis (up to 1.1%);
- persistent blood in the urine (up to 2%)
- renal colic (2.2%)
- narrowing of the ureter (stricture) 0.1%;
- reflux of urine from the bladder into the kidney (0.1%);
- damage to internal organs (up to 0.05%);
You need to return to the hospital immediately if:
- body temperature above 38 °C;
- can't urinate;
- a large amount of blood in the urine;
- You continue to experience severe pain in your side.
Even if you are at low risk of developing another stone, you need to make some lifestyle changes. These measures reduce the risk of recurrence of the disease and improve your overall health.
Rules of care
First, a few words about how to wear these products:
- in order to achieve the maximum therapeutic effect, hypertensive patients or people prone to sudden increases in blood pressure should wear them alternately on the left and right hands (or better yet, change their location during the day);
- In order for the result to appear as quickly as possible and be stable, it is recommended to wear the bracelet without taking it off at night, it is even recommended to leave it on the wrist during water procedures (of course, if it is made of materials that are not susceptible to corrosion);
- do not expect instant results, but to make sure that the magnetic bracelet still works, make it a rule to measure your blood pressure at least twice every day and write down the results in a notepad or on an electronic gadget;
- do not pass on your bracelet to other people and do not change the product yourself - the body is tuned to a certain magnetic field, changes in which with increased pressure will not help solve the problem.
Caring for bracelets is easy - wash the product with warm running water every 20-30 days. After thorough drying, it is again ready to serve you faithfully until the next “rejuvenating” procedure.
Percutaneous (percutaneous) nephrolithotripsy (PNL)
PCNL is most often used when the kidney stones are large, high density, or there are many of them. PCNL is usually performed under general anesthesia. During this procedure, a small tube called a catheter is placed in the bladder. Another catheter is inserted into the ureter. Contrast, or dye, may be injected through this catheter to provide a better view and pinpoint the location of the stone. Once the stone is located, access to the renal collecting system is achieved using a thin needle and a so-called guidewire. The guidewire provides safe access for the nephroscope (an instrument for visualizing the inside of the kidney). Once the stone is visualized, some can be removed using forceps. Large stones must be crushed using a special pneumatic, ultrasound or laser device - nephrolithotripsy. After removing stone fragments from the kidney, a temporary small tube is usually installed in the ureter connecting the kidney to the bladder (catheter-stent), and the working channel through which the operation was performed is inserted into a tube draining the kidney (nephrostomy). After surgery, these tubes are removed after a few days.
You should know!
PCNL can be accompanied by both intra- and postoperative complications.
During the operation the following may occur:
- bleeding, which may require blood transfusion (up to 20%), embolization of the kidney vessels, or removal of the kidney (up to 1.5%);
- pleural damage (up to 11.6%);
- damage to internal organs (up to 1.7%);
- lethal outcome (up to 0.3%).
In the postoperative period, the following may develop:
- fever (up to 32.1%);
- sepsis (up to 1.1%);
- urinoma (accumulation of urine in the perinephric or retroperitoneal tissue, surrounded by a fibrous capsule) up to 1%;
- residual stone fragments (up to 19.4%), in some cases repeated intervention is required;
- aneurysm, arteriovenous fistula;
You need to return to the hospital immediately if:
- body temperature above 38 °C;
- nausea and vomiting;
- chest pain and difficulty breathing;
- a large amount of blood in the urine;
- severe pain on the side of the operation;
- you can't urinate.
Contraindications for using magnetic bracelets
Due to the physical and chemical characteristics of the impact of a magnetic field on the human body, wearing bracelets with magnetic inserts cannot be called an absolutely safe activity. Like any other therapy, it has a number of contraindications that you need to familiarize yourself with before deciding to purchase such an accessory:
- the presence of metal prostheses, implants in the body, the use of a pacemaker and other electrical or electronic devices;
- the product should not be worn during acute infections accompanied by a febrile state;
- open wounds;
- acute inflammatory processes;
- a history of heart failure;
- pathologies of the hematopoietic organs;
- previous heart surgeries (stenting, bypass surgery, prosthetics);
- hemophilia;
- pregnancy period;
- the presence of malignant tumors;
- individual intolerance.
Remember: if you choose to wear a magnetic bracelet as a remedy for blood pressure, such therapy does not oblige you to anything, so there is a possibility that your high expectations may not be justified. However, practice shows that for most people this method is completely justified and can provide quite satisfactory results.
A little history
Hematite is a natural mineral of piercing black, gray, reddish or brown color. In essence, it is iron oxide, by nature it is ordinary iron ore, that is, the rock from which the corresponding metal is mined. Its name comes from the Greek “heme”, that is, blood.
There are many varieties of hematite (or red ironstone), differing in both physical and chemical properties, but they all have one thing in common: a very high iron content. It is this that gives the mineral such a mysterious and bewitching metallic shine.
Despite this, hematite became known to people even before the Iron Age. True, our distant ancestors used it for slightly different purposes: many rock paintings that have survived to our times were made with hematite.
Iron ore has been widely used as a dye since ancient times. The great painters did not neglect this property of hematite, mixing paint from ground iron ore. By the way, this is red lead, which is widely used today.
It is believed that the ancient Sumerians were the first to use hematite for making jewelry and magical amulets (and who knew the difference in those days?). The ancient Chinese, Greeks, and Romans also knew about the amazing properties of red iron ore. And the Aztecs made mirrors from blocks of this mineral!
In Ancient Rus', hematite was known as “bloodstone”. Warriors sewed pieces of it into clothes, because it was considered a powerful amulet against enemy arrows and swords. It was also used in medicinal art. Crushed iron ore was sprinkled on wounds: it not only stopped bleeding, but also prevented inflammatory processes. And this, by the way, is a scientifically proven fact!