Clinical signs of high blood pressure
A tonometer is used to determine blood pressure readings. Normally, in a healthy adult, the level does not exceed the limits of 120-130 (for systolic) and 80-85 (for diastolic). The limit figures for people over 40 years of age are 145/90 units.
Symptoms of high blood pressure include:
- unreasonable anxiety, irritability;
- rapid heartbeat;
- fatigue, headaches;
- pulsation in the temporal zone;
- swelling, goose bumps;
- chills turning into hot flashes;
- sleep disturbances, dizziness.
The source of unstable blood pressure is due to many reasons, including psycho-emotional and physical stress. With a sudden increase in blood pressure, a hypertensive crisis may occur with irreversible consequences. Its symptoms are presented:
- severe redness of the facial skin;
- nervous excitement;
- painful sensations behind the sternum;
- hand tremors, decreased visual acuity;
- feeling of insufficient oxygen supply.
Calling an ambulance is justified when blood pressure increases to 160/95 units, but there are exceptions. For patients with hypertension, the critical level is 130/85. Referring to specialists is justified by additional factors and the presence of cumulative pathologies. An ambulance leaves for the first or repeated attack, the presence of symptoms of a hypertensive crisis, or the absence of a response to drugs prescribed to a patient with arterial hypertension.
Actions for acute high blood pressure
What is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure (BP) is characterized by two indicators: upper - systolic pressure is determined by the force with which, when the heart contracts, blood presses on the walls of large arteries. Lower - diastolic blood pressure corresponds to the relaxation of the heart, when the pressure of blood inside the arteries decreases.
What blood pressure is considered normal?
Blood pressure below 130/85 mm is considered normal. rt. Art.
What is arterial hypertension?
Arterial hypertension should be diagnosed if systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure exceeds 140/90, obtained as a result of at least two measurements during at least two consecutive visits to the doctor, provided that the patient is not taking antihypertensive drugs.
- You should not smoke or drink coffee for an hour before the measurement; at least 1-2 hours should pass after your last meal.
- Optimal posture: sitting, leaning on the back of a chair, with relaxed and uncrossed legs.
- The hand is free of clothes.
- It is not recommended to talk during the measurement.
What should a patient do if high blood pressure is detected?
If elevated pressure numbers are detected, it is necessary to re-measure, and then twice a day for the next two days.
During this period, it is necessary to keep a self-observation diary, in which to record not only pulse and blood pressure indicators, but also general well-being, the level of physical and psycho-emotional stress, and changes in atmospheric pressure. Registration of elevated blood pressure is a reason to consult a doctor, conduct an examination and, together with the attending physician, develop treatment tactics, control and follow-up.
What is a hypertensive crisis?
A sudden sharp increase in blood pressure is called a hypertensive crisis.
What are the types of hypertensive crises?
Depending on the clinical signs, two types of crises are distinguished. Hypertensive crisis of the first type is characterized by a predominant increase in systolic pressure, agitation of the patient, the presence of chills, palpitations, and feelings of fear. With self-help or medical care, the pressure returns to normal within a few hours.
Hypertensive crisis of the second type is more severe and lasts for 24 to 48 hours. Characterized by increased systolic and diastolic pressure, headaches, nausea, vomiting, and rhythm disturbances. In these cases, the pressure should be reduced gradually, under the supervision of medical personnel.
Actions for acute high blood pressure
An acute increase in blood pressure is a fairly common situation faced by hypertensive patients and practitioners.
Even with correctly selected medications in effective doses (basic antihypertensive therapy) and achieved target blood pressure < 140/90 mmHg. in response to external stimuli (stress, weather changes, “magnetic storms”, overeating, physical overload), as well as skipping medications, it is possible to increase blood pressure to high levels without deterioration or with a slight deterioration in well-being.
What to do in this case? It must be remembered that the higher the blood pressure, the more risk factors, the more pronounced its negative impact on target organs (heart, brain, kidneys), and the greater the possibility of developing complications. Therefore, even an asymptomatic increase in blood pressure cannot be ignored. However, there is no need to go to the other extreme - give in to panic and grab all the medicines available in the house, creating a fuss or immediately calling O3.
Let's learn together how to competently deal with this problem:
1. Try to calm down, “know how to control yourself...”
2. Take one of the following medications under the tongue or orally with 2-3 sips of weak hot tea:
- Anaprillin 1 t (0.04 g or 40 mg) - you should know that this drug is contraindicated in patients with bronchial asthma (used to relieve type 1 hypertensive crisis); or
- Nifedipine (Cordinine, Corinfar) 1 t (0.01 g or 10 mg) or
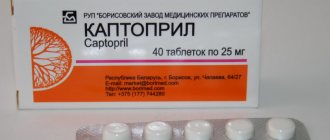
- Capoten (captopril) 1 t (25 mg) or
- Clonidine 1 t (0.075 mg) - provided that you have previously used this drug, and it is recommended for you by your attending physician. Available only by prescription.
- Emotional patients are recommended to take 40-50 drops of Corvalol.
3. Sit comfortably with your legs down. Relax. Close your eyes, think about something pleasant. Convince yourself that you are in control of the situation and are coping with it successfully.
4. Monitor blood pressure no earlier than after 1 hour.
You should not measure the pressure earlier, because... in the first 15-20 minutes after taking clonidine or nifedipine, the heart rate increases and there may be an increase in blood pressure by 10-15 mmHg. from the initial one, which gives rise to panic;
You should not take an additional dose outside of the main dose of basic antihypertensive drugs that you use daily, because Usually these are drugs of medium (up to 12 hours) and long-term (24 hours) action, the effect of their use develops slowly.
5. The result is achieved if after 1 hour your blood pressure has decreased from the initial systolic blood pressure by 20-25% (for example, after 200 mmHg it became 160 mmHg)
Don't try to quickly drop to lower numbers!
6. If you have not reached the recommended pressure, then repeat taking the same drug in the same dose or any other of the above, or take hypothiazide 100 mg or furosemide 40 mg.
For patients with concomitant coronary heart disease, it is advisable to take 1 t of nitrosorbide (0.01 g).
7. Blood pressure monitoring after re-taking medications is also carried out after 1 hour. Usually these measures are sufficient to stop an acute increase in blood pressure.
But if, after 2 hours from the start of self-help, the pressure does not decrease, a deterioration in well-being occurs, or symptoms appear that were not there before, this is a reason to see a doctor or call an ambulance. Every family with a patient with hypertension needs to have an emergency first aid kit for acute increases in blood pressure - place in a small convenient box:
- Anaprillin and (or)
- Nifedinin and (or)
- Kapoten and (or)
- Clonfelline and (or)
- Corvalol, hypothiazide and/or
- Furosemide
As well as a reminder of actions for their correct use (sequence, dose, time of blood pressure control - see above)
Thus, you will always have a reliable assistant at hand who, if necessary, will help you and your loved ones.
We wish you success, health and power over your blood pressure!
Prepared by the head of the RCC of the Partizansky district of Minsk, Mikhalkevich A.D.
Stages of emergency care
The appearance of pronounced clinical signs of hypertension requires the implementation of a certain algorithm of actions:
- Calm the patient - self-hypnosis does not always help a patient with increasing panic. Doctors recommend using tincture of motherwort, hawthorn or valerian root as acceptable medications. For pain in the heart, use Corvalol or Validol, Nitroglycerin. Nervous excitement intensifies the attack; the sick person must calm down.
- Give a comfortable position - regardless of the type, the patient’s head is located above the lower extremities (to speed up the outflow of blood from the brain to the legs). He can lie down, sit - the forced position is determined by his location (house, street).
- Warm up - an attack can cause chills, trembling and a decrease in temperature of the upper and lower extremities. The patient is covered with a blanket and his legs are wrapped. For quick warming, use a heating pad or a hot foot bath. You can pour mustard into your socks or place mustard plasters on the shin area. Heat is a distracting procedure and helps redirect blood flow from central vessels to peripheral ones. Alleviation of the general condition and relief of headaches is carried out by installing mustard plaster on the occipital region.
- Ensure the supply of fresh air - open the windows or expose them for ventilation. You can cool the room using an air conditioner.
- Remove restrictive clothing - unfasten buttons, belt, collar. Remove the tie, sweater and anything that compresses the chest and prevents the victim from breathing.
Medicines are given only to patients who have used them before. It is not recommended to conduct experiments on a person with an attack of hypertension - the body’s reaction to an unknown medication can be anything. In case of primary increased blood pressure, wait for the arrival of the ambulance team, who themselves will select adequate therapy.
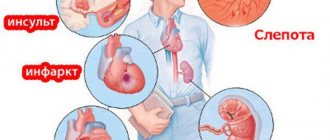
Complications of hypertensive crisis
A hypertensive crisis is dangerous not so much in itself as the influence of high blood pressure on target organs - in the first place. Disruption of blood microcirculation in the brain leads to swelling (hypertensive encephalopathy).
During an increase in blood pressure, the walls of the blood vessels in the brain experience enormous stress, which can lead to hemorrhage in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke).
A sharp increase in blood pressure also affects the function of the heart, not excluding the possibility of angina pectoris - an acute lack of blood supply to the heart muscle with the development of acute heart failure, expressed in the form of shortness of breath, suffocation, and pulmonary edema. The most severe complications of hypertensive crisis
are heart attack and stroke.
First pre-hospital emergency medical care for hypertensive crisis
Hypertensive crisis is a condition that requires urgent measures, because delay can lead to even more severe complications and death. The patient needs to clearly remember the simple rules of independent first aid and not get confused at the right moment.
Independent pre-medical emergency care primarily consists of taking the antihypertensive drugs used (Corinfar, captopril, nitroglycerin, furosemide, etc.) prescribed by the doctor.
During a hypertensive crisis, you need to try not to panic, relax and restore your breathing by taking a series of inhalations and exhalations several times. If an attack overtakes you at home, your loved ones can provide invaluable help: put mustard plasters on your calves, help you take warm foot baths (temperature 30-40 °C, duration of treatment - 10-15 minutes). The measures taken in no case cancel the call to the doctor, because only allow you to stop a hypertensive crisis
rather than eliminating its consequences.
It must be remembered that the main means of preventing hypertensive crises remains the main task - the treatment of arterial hypertension. Do not delay treatment for arterial hypertension
for tomorrow!
GUTA CLINIC specialists will individually select for you the most modern, effective, safe antihypertensive drugs in adequate dosage to achieve the best therapeutic effect, and will also prescribe a set of measures aimed at eliminating risk factors for high blood pressure.