What kind of stroke happens?
There are two main types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Both cases are extremely dangerous because when brain cells stop receiving oxygen, they die.
Hemorrhagic stroke
- occurs due to bleeding in the brain. Vessel rupture can occur due to a sharp jump in blood pressure, the presence of an aneurysm or atherosclerosis. In most cases, a person experiences a sharp headache, suddenly loses consciousness, and sometimes there may be convulsions. If someone near you has lost consciousness, do not waste time, call an ambulance.
Ischemic stroke
– occurs in most cases and may develop over time. Often it occurs due to blockage of a vessel by a blood clot, vasospasm, or compression due to injury or tumor.
A precursor to a stroke can be a transient ischemic attack—a short-term disruption of the blood supply to the brain. Brain cells are damaged but not killed. A TIA significantly increases the risk of stroke and requires medical evaluation.
A stroke has a number of symptoms, which, if noticed, can save a person’s life.
There are two types of stroke:
Ischemic – blood vessels in the neck or brain become blocked. More common, it can be triggered by thrombosis, embolism, or arterial stenosis. More often it occurs at night, while clarity of consciousness is maintained. With a mini-stroke, the blockage of blood flow is temporary, but the condition also requires immediate hospitalization.
Hemorrhagic (intracerebral) - occurs in 10-15% of cases, but 30-60% of them end in death. The blood vessel ruptures completely, allowing blood to flow into the brain. Often a stroke is provoked by an aneurysm, in less than 1% of cases - by an arteriovenous malformation (usually congenital). This type of stroke usually occurs during the day, as a result of excessive physical or emotional stress.
Signs of a stroke
1. Facial asymmetry
The sign that first catches your eye. If you have a stroke, you may experience sudden numbness and tingling on one side of your face.
2. Numbness of the limbs
Most often, muscle numbness occurs on only one side. The muscles do not obey, the person cannot lift an arm or leg.
3. Speech impairment
Speech becomes incoherent, confused, and a person may not understand what is being said to him.
4. Loss of coordination
You need to be wary of sudden dizziness, accompanied by imbalance, loss of balance. The person loses the firmness of his gait and has problems with coordination.
5. Severe headache
It is unbearable and may be accompanied by vomiting. The pain occurs for no reason and does not decrease when taking painkillers.
6. Vision problems
Clarity is lost, objects begin to appear double. One or both eyes can lose good vision at once.
Features of a stroke in an old person
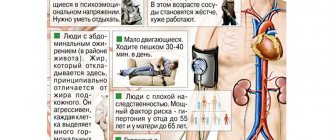
Stroke is a disease that requires emergency medical intervention. At different ages, the consequences of pathology will differ markedly. Patients over 70–80 years of age have a very severe clinical picture of the disease and minimal chances of survival, especially if a major stroke occurs.
It is in old age that 45% of patients who have had an attack are susceptible to subsequent coma in the first few days. After a stroke, an old person's prognosis for restoring the body's functional capabilities will be much worse than that of people under 50 years of age. Even if the patient manages to survive, there is a high chance of remaining disabled, most often bedridden.
Elderly people, fearing to upset their loved ones, often ignore the symptoms of the disease themselves, thereby aggravating their situation during a stroke. When working with such patients, some characteristic features of the course of the disease should be taken into account:
- Stroke increases rapidly and is more severe, since the body of an old person is subject to age-related changes and is burdened by other chronic diseases.
- Elderly people put off visiting a medical facility, citing the fact that this is a common ailment at their age. Unfortunately, age plays a negative role, since at the time of a stroke, brain tissue is affected much faster in an older person.
- In older patients, major ischemic stroke is diagnosed more often than in 30–40 year olds.
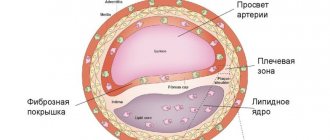
- The most common cause of attacks after 60 years is the presence of atherosclerotic plaques.
We recommend
“High blood pressure in older people: treatment, prevention and traditional methods of combating the disease” Read more
How to provide first aid for a stroke
There is a clear algorithm for providing first aid to a person suffering from a stroke :
- Call a medical team . To do this, you need to dial 103 from a landline phone. If you happen to have a smartphone at hand, then the call is made to the single number 112. The doctor must immediately be informed that the person is unwell and there is a suspicion of a stroke.
- The victim must be laid on a flat surface so that his head is higher than his body. They take off his glasses and remove his lenses. If possible, you need to help him get removable dentures.
- If there is no consciousness, then you need to open the patient’s mouth slightly and turn his head to the side . This is done to prevent aspiration of vomit. It is imperative to listen to the patient’s breathing.
- For better access to fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent..
- Before the arrival of the medical team, it is necessary to prepare documents, if any..
Doctors need to be informed about the person’s illnesses, as well as what medications he is taking. It is prohibited to give the victim any medications. Medication correction should be carried out by emergency physicians. You should not try to give water or food to a person. This may make the situation worse.
If the patient falls and has an epileptic attack, there is no need to unclench his teeth or try to hold him. It is necessary to protect the victim from injury. To do this, place a soft object, such as a pillow, under his head. If a stroke with an epileptic attack happened on the street, then you can use a jacket or other suitable thing. Foam flowing from the mouth is wiped away with a cloth. The head should be elevated at all times.
There is no need to try to bring a person to his senses with ammonia. Until the end of the attack, it should not be moved from place to place.
If breathing stops, resuscitation measures must be started immediately. To do this, perform a heart massage and breathe mouth to mouth or mouth to nose.
Patterns of development of the pre-stroke state
Primary signs of a pre-stroke condition in elderly women may be nonspecific. May appear:
- frequent headaches;
- nausea;
- malfunction of the sense organs.
Similar symptoms can appear with the progression of many diseases, including hypertensive crisis, a drop in sugar levels, and others.
However, despite the nonspecificity of the symptoms, it is still possible to recognize a pre-stroke condition. There are several factors that allow you to determine pathology at an early stage:
- The pre-stroke state was preceded by a long period. It is clear that transient ischemia cannot develop suddenly over a few days or hours. There is always an initial stage from which signs are taken into account. This stage usually takes 14-21 days, but in some patients it can last longer.
- The general condition worsens. In women, pre-stroke is much more severe than in men and often ends in necrosis.
- The manifestations are more pronounced. This factor is directly related to the previous one.
- The likelihood of an emergency occurring is much higher. Most often it is characterized by tissue death.
Treatment of stroke in an old person
If there are signs of a stroke, you should consult a cardiologist. After collecting the necessary information from relatives and the patient himself, the attending physician prescribes blood tests and conducts:
- echocardiography;
- electrocardiogram;
- magnetic resonance (computer) tomography;
- ultrasonography.
All this will allow us to identify the pathology, the location of the lesion, and determine the type of stroke.
The patient also needs examinations by a neurosurgeon and an ophthalmologist, which can identify other affected areas in the body.
It is quite difficult to determine the pathology of hemorrhagic stroke in patients over 75 years of age. Typically, such patients have mild changes in the blood test or they may also indicate other diseases. In such cases, doctors conduct additional examinations, such as electroencephalography and angiography.
Treatment should only take place in a hospital setting under the supervision of a physician. A specialist can prohibit transporting a patient to a hospital only in the case of a severe coma with severe impairment of vital functions.
In order for treatment to benefit an elderly patient, he must follow the sequence of procedures, complete their full course and subsequent rehabilitation measures. Only under such conditions will an old person be able to quickly recover from an attack.
The main goal of treatment after a stroke is to restore the functioning of the cardiovascular system and protect the remaining brain cells. After the patient is recovered from a serious condition, he is prescribed medication and physical therapy.
Medicines for the treatment of stroke in an elderly person are available only by prescription. Among them:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Medicines aimed at reducing blood pressure by reducing vascular tone. A very large group of medications does not affect the presence of cholesterol and does not affect atherosclerosis.
- Class 2 receptor blockers. They have a long period of action, consistently reduce blood pressure, and have virtually no side effects. In conventional therapy, they are often prescribed for chronic hypertension.
- Diuretics. They are used if the first groups of drugs are contraindicated for the patient due to various, most often age-related, reasons.
- Beta blockers. Designed to dilate peripheral blood vessels, lower blood pressure, and help fight arrhythmia.
- Calcium antagonists. As a rule, they are used to treat stroke in old age in the presence of concomitant angina and other heart rhythm disorders. Often prescribed together with ACE inhibitors.
- Adrenergic receptor blockers. Used to reduce blood pressure. Can be used for renal failure and diabetes.
- Centrally acting drugs. With a pronounced effect, contractions of arrhythmias can also lower blood pressure. Used for comprehensive healing of the heart muscle.
- Vascular drugs. In case of a stroke in an old person, they are administered as injections to restore nerve cells and blood vessels in the brain.
- Nootropics. Indispensable during the rehabilitation period of elderly patients for the restoration of brain cells.
- Antihypoxants. Preventative drugs. Prescribed if there is a risk of developing oxygen deficiency.
- Thrombolytics thin the blood, prevent the formation of blood clots and plaques, and are used to restore blood composition.
During the rehabilitation period, various natural supplements and vitamins are included in the patient’s diet.
What treatment does the doctor prescribe depending on the type of stroke?
1. In case of hemorrhagic form, the patient is given intramuscular injections of calcium gluconate, and intravenous injections of calcium chloride. For treatment, Rutin, Vikasop, Dicynon, ascorbic acid with gelatin, Rutamin, and aminocaproic acid are used. If necessary, the lateral hematoma is removed by surgery. In emergency cases, other surgical procedures may be used.
2. For ischemic stroke, vasodilators and nicotinic acid are used. The patient is recommended to use “Trental”, “Stugeron”, “Heparin”, “Phenilin”, “Aspirin”, “Prodectin”, “Complamin”, solutions of diethyphene and cocarboxylase.
We recommend
“Vitamins for elderly people over 70: which ones are needed first” Read more
How to provide first aid for a stroke
There is a clear algorithm for providing first aid to a person suffering from a stroke :
- Call a medical team . To do this, you need to dial 103 from a landline phone. If you happen to have a smartphone at hand, then the call is made to the single number 112. The doctor must immediately be informed that the person is unwell and there is a suspicion of a stroke.
- The victim must be laid on a flat surface so that his head is higher than his body. They take off his glasses and remove his lenses. If possible, you need to help him get removable dentures.
- If there is no consciousness, then you need to open the patient’s mouth slightly and turn his head to the side . This is done to prevent aspiration of vomit. It is imperative to listen to the patient’s breathing.
- For better access to fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent..
- Before the arrival of the medical team, it is necessary to prepare documents, if any..
Doctors need to be informed about the person’s illnesses, as well as what medications he is taking. It is prohibited to give the victim any medications. Medication correction should be carried out by emergency physicians. You should not try to give water or food to a person. This may make the situation worse.
If the patient falls and has an epileptic attack, there is no need to unclench his teeth or try to hold him. It is necessary to protect the victim from injury. To do this, place a soft object, such as a pillow, under his head. If a stroke with an epileptic attack happened on the street, then you can use a jacket or other suitable thing. Foam flowing from the mouth is wiped away with a cloth. The head should be elevated at all times.
There is no need to try to bring a person to his senses with ammonia. Until the end of the attack, it should not be moved from place to place.
If breathing stops, resuscitation measures must be started immediately. To do this, perform a heart massage and breathe mouth to mouth or mouth to nose.
Consequences of stroke for elderly patients
The older the patient is at the time of admission to the hospital, the more severe the pathology will be and the lower the chances of recovery. The following may reduce the likelihood of full recovery after a stroke:
- It is not always possible to dissolve blood clots in blood vessels with medications in elderly patients. Pensioners usually have a large number of contraindications to the insertion of catheters and surgical intervention, so the risk of death increases.
- The younger age of the patient guarantees the restoration of lost functions thanks to an alternative blood supply. Age-related changes in vascular channels (including atherosclerosis) significantly reduce the likelihood of complete recovery in elderly patients.
- Age often goes hand in hand with a variety of third-party chronic diseases. They usually affect the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, heart muscle, respiratory organs, etc. And since a stroke is a huge stress for the body, the progression of all existing chronic pathologies is inevitable. This significantly influences medical prognoses.
- Stroke goes hand in hand with infectious complications. Since one of the consequences of a stroke is paralysis, due to which the patient is forced to constantly lie motionless in bed, the formation of bedsores and congestion is inevitable. Large areas affected by purulent lesions are the best way for infections to enter the body.
Stroke is especially dangerous for older women, because the likelihood of a second attack following the first is extremely high. Usually the consequence of such an illness is loss of consciousness or coma. So you should be especially careful about your health in retirement age, because full recovery of the body after a stroke is almost impossible in the presence of third-party chronic pathologies or predisposition.
Possible consequences, complications
The main danger of a stroke is death. If a person survives, the disease will still make itself felt with certain complications.
Early consequences include:
- Brain swelling.
- Coma.
- Pneumonia.
- Paralysis. It can be partial or complete. Most often, one half of the body is affected.
- Repeated stroke.
- Bedsores.
- Mental disorders. They can manifest themselves in moodiness, irritability, aggression, and anxiety. Sometimes dementia develops.
- Sleep disorders.
- Myocardial infarction, gastric ulcer. These disorders develop against the background of increased levels of stress hormones.
After an ischemic stroke, death occurs in 15-25% of cases. Hemorrhagic damage to the blood vessels of the brain leads to the death of 50-60% of patients. The cause of death is precisely severe complications, for example, pneumonia or acute heart failure. The first 3 months after a stroke are considered the most dangerous.
Arms recover worse in patients than legs. A person's future health is determined by the severity of brain damage, the speed of medical care, his age and the presence of chronic diseases.
Long-term consequences include:
- Formation of blood clots in various parts of the body.
- Depression.
- Speech problems.
- Memory loss.
- Deterioration of intellectual abilities.
After a stroke, you have to deal with the consequences for many months. Sometimes a person never manages to fully recover. For rehabilitation to be as successful as possible, you must strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions.
Stroke is a serious pathology because it affects the brain. Therefore, even the slightest suspicion of a developing vascular accident is a reason to urgently seek medical help.
Treatment and rehabilitation
The patient receives treatment in a hospital. All patients with suspected stroke are hospitalized on an emergency basis. The optimal period for providing medical care is the first 3 hours after a brain accident has occurred. The person is placed in the intensive care unit of a neurological hospital. After the acute period has been overcome, he is transferred to the early rehabilitation unit.
Until the diagnosis is established, basic therapy is carried out. The patient’s blood pressure is adjusted, the heart rate is normalized, and the required blood pH level is maintained. To reduce cerebral edema, diuretics and corticosteroids are prescribed. Craniotomy is possible to reduce the degree of compression. If necessary, the patient is connected to an artificial respiration apparatus.
Be sure to direct efforts to eliminate the symptoms of stroke and alleviate the patient’s condition. He is prescribed medications to lower body temperature, anticonvulsants, and antiemetics. Medicines that have a neuroprotective effect are used.
Pathogenetic therapy is based on the type of stroke. In case of ischemic brain damage, it is necessary to restore nutrition to the affected area as quickly as possible. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that resolve blood clots. It is possible to remove them mechanically. When thrombolysis fails, the patient is prescribed Acetylsalicylic acid and vasoactive drugs.
If a patient develops a hemorrhagic stroke, it is important to stop the bleeding. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that thicken the blood, for example, Vikasol. It is possible to perform an operation to remove the resulting hematoma. It is aspirated using special equipment, or through open access by performing craniotomy.
Relatives and friends should provide support to the patient and not leave him alone with the problem. Psychologists are involved in the work. Sessions with a speech therapist are often required.
The benefits of a boarding house for an elderly patient
Caring for an older person who has had a stroke can be difficult. In order to correctly and effectively help a patient recover, you need to have the necessary knowledge and undergo training. Not every loved one has enough strength, knowledge and time to provide quality assistance to their relative.
Caring for the patient requires monitoring medications, maintaining sleep and eating habits, maintaining regular hygiene, performing physical and cognitive rehabilitation exercises, and observing the prevention of bedsores.
At home, it is difficult to provide full-fledged, high-quality rehabilitation after a stroke. A good option is to go to a boarding house for the elderly, where the person will be surrounded by professional care, and help the relative together with specialists. He needs the support and participation of his loved ones - this is very important for a quick and successful recovery.
How to recover and prevent another stroke for an old person
For older people after a stroke, even in a hospital setting, they offer classes on special simulators and select individual exercises that need to be continued at home. The basis of the rehabilitation period, along with taking medications and physiotherapeutic procedures, is a properly selected diet:
- minimum amount of sugar and salt in the diet;
- reducing the consumption of animal fats (pork, lamb, butter, some dairy products);
- The basis of the diet is lean vegetable soups, vegetable oils, cereals, fruits and vegetables.
It is recommended to steam dishes and eat boiled or baked foods. To avoid difficulty chewing, it is better to eat fairly well-chopped food.
In the post-stroke period, many patients have a deteriorating emotional state, feel morally depressed, and have their usual sleep patterns disrupted. What sedatives does a doctor usually prescribe for an old person after a stroke? As a rule, these are sleeping pills and antidepressants: Doxepin, Mirtazapine, Trazodone. Nicergoline is used as an additional medicine, which not only reduces the symptoms of insomnia and mental disorders, but also helps reduce the tone of the cerebral arteries and improves blood flow. It is worth warning that long-term use of these drugs can be addictive. Beware of this and listen to medical advice.
In recent years, PNF therapy (proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation) has been actively recommended for older people who have suffered a stroke, a technique that allows them to regain the ability to move. Simple physical exercises improve motor functions and prevent the development of complications - paralysis and muscle dystrophy.
Other methods are also effective in treating stroke in older people:
- soft tissue manual therapy - working out all muscles allows you to restore their tone;
- Vojta therapy - through targeted pressure on certain areas of the body, the activity of motor muscles and reflexes is triggered. In some cases, completely paralyzed patients after a course of procedures were able to roll over and crawl on their own;
- The Castillo Morales method is a set of exercises that allows you to restore the breathing and swallowing functions, as well as the speech of the victim. Usually carried out in conjunction with psychological therapy;
- kinesio taping - special elastic patches glued to the patient’s skin not only improve microcirculation and lymph outflow, but provide additional support and strengthening to the joints;
- The Mulligan concept is a type of manual therapy method that has proven itself in the treatment of stroke in an old person. Special manipulations by the doctor alleviate the excessive pain of the actions, and the patient, overcoming the pain, can improve the exercises day by day;
- bobat therapy (neurodynamic rehabilitation) is a practice that helps to correct movement patterns and overcome lack of movement.
All these techniques are usually used to treat stroke in an old person in a rehabilitation center under the guidance of experienced doctors. Additionally, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures, magnetic brain stimulation to restore speech, and transcranial stimulation to improve vascular function.
You can also achieve good results after acupuncture, which helps normalize muscle activity and restore motor functions, improve tissue condition, and form reflexes.
Treatment of a stroke in an old person and the subsequent rehabilitation period is a rather lengthy set of measures that falls on the shoulders of the patient’s relatives and friends. The choice of good doctors, strict adherence to all recommendations, the desire and efforts of the patient himself, the patience and responsibility of relatives help many who have suffered an attack to return to a comfortable standard of living.