Basic information
Susceptibility to this condition is much more common in the female sex, especially during adolescence and menopause, which is due to hormonal instability.
Typically, this code is used in the medical practice of psychiatrists or neuropsychiatrists. In the document of the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, this disease, manifested by increased pressure, is not identified as a separate one, and it is customary to encrypt it under the codes of primary or secondary hypertension, that is, I10 or I15, if there are no pronounced psycho-emotional disorders.
This code defines similar treatment according to local protocols for therapeutic measures of hypertension without target organ damage. Other manifestations of NCD, caused by an emotional state, are usually coded as R45.8. This code implies symptomatic treatment and normalization of the nervous system with the help of appropriate medications and physiotherapeutic procedures.
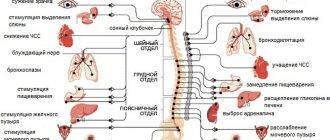
The clinical manifestations of the pathology are based on disorders of the autonomic nervous system and dysfunction of the central nervous system, which regulate vascular tone and heart rate.
Types and tactics of treatment measures
Neurocirculatory dystonia in ICD 10 has code F45.3, which implies the manifestation of certain symptoms and the implementation of diagnostic and therapeutic measures. There are several types of NCD, the clinical signs of which characterize a specific form. Doctors identify the most common types of autonomic disorders:
- NCD of the hypertensive type is characterized by an increase in blood pressure, which is accompanied by panic attacks, headaches, physical inactivity and apathy;
- neurocirculatory dystonia with a predominance of hypotension is manifested by frequent dizziness against a background of low blood pressure, constant apathy and headache;
- NCD of the cardiac type is manifested by attacks of rapid heartbeat or, conversely, bradycardia, which causes constant panic attacks in the patient.
All types of functional disorders need to be treated, starting with the regulation of parts of the central nervous system.
Based on the severity and nature of the manifestations of various symptoms, the doctor prescribes symptomatic therapy.
The NCD code for cardiac type has a similar meaning in ICD 10 to all types of this pathology and the same principles for the treatment of neurological disorders. The best options in the presence of such a problem would be: sanatorium-resort treatment, massages, the use of feasible physical activity in the form of frequent walks, the search for positive emotions, and changing the usual lifestyle to a more active one.
Save the link, or share useful information on social media. networks
Causes
Most often, NCD develops after severe emotional stress or mental trauma; dystonia is inherited and is also the result of hormonal shifts.
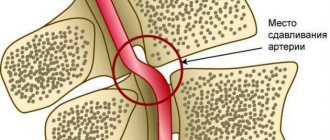
When examining a patient by a doctor, an active “play of the pupils”, rapid pulsation of the carotid arteries is noted, the person is unable to make a forced exhalation. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, areas of pain in the intercostal muscles are detected - especially in the 3rd-4th intercostal space. The disease is classified according to several criteria - by etiology, by severity, by clinical manifestations. According to the etiology, NCD can be essential, psychogenic, infectious-toxic, caused by professional factors, arising from physical stress. Clinical syndromes: myocardial dystrophy, cardiac and tracheocardial, hypertensive and hypotonic, respiratory, asthenic, as well as peripheral vascular disorders.
There are three degrees of the disease - mild, moderate, severe. In general, NCD is divided into hypertensive and hypotonic types, they differ not only in the difference in blood pressure, but also in symptoms.
Thus, patients diagnosed with “neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type” have pale skin and an asthenic physique; they complain of muscle weakness and chilliness. Patients with hypertensive type dystonia are usually overweight. Symptoms of the disease are headaches, fatigue, rapid heartbeat.
Dystonia (G24)
Excludes: athetoid cerebral palsy (G80.3)
ICD-10 alphabetical indexes
External Causes of Injury - The terms in this section are not medical diagnoses, but rather a description of the circumstances under which the event occurred (Class XX. External Causes of Morbidity and Mortality. Heading Codes V01-Y98).
Medicines and chemicals - table of medicines and chemicals that have caused poisoning or other adverse reactions.
In Russia, the International Classification of Diseases
10th revision (
ICD-10
) was adopted as a single normative document for recording morbidity, reasons for the population’s visits to medical institutions of all departments, and causes of death.
ICD-10
introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997 No. 170
The release of the new revision (ICD-11) is planned by WHO in 2022.
Abbreviations and symbols in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision
NOS
- without other instructions.
NEC
— not classified in other categories.
†
— code of the main disease. The main code in the dual coding system contains information about the underlying generalized disease.
*
- optional code. An additional code in the double coding system contains information about the manifestation of the main generalized disease in a separate organ or area of the body.
Neurocirculatory dystonia (NCD) in ICD 10
Neurocirculatory dystonia is a special case of autonomic dystonia syndrome, observed mainly in young people. The article contains a reminder on diagnosing the disease, as well as necessary information for patients
Neurocirculatory dystonia (NCD) is a functional disorder of the circulatory system, the basis of which is violations of its neuroendocrine regulation.
Despite its diversity and subjective severity for the patient, it has minor changes in objective status, a benign type of course and a favorable prognosis.
In patients with NCD, the quality of life decreases and the risk of developing organic cardiovascular diseases increases, which requires high-quality diagnosis, treatment, and medical monitoring.
A doctor’s neglectful attitude towards patients with such a disease can lead to aggravation of the disease, as well as to the development of more serious pathology.
Code in ICD 10
For the diagnosis formulated as neurocirculatory dystonia, the ICD 10 code is not defined; NCD is not an independent nosological unit. But there is a possibility of taking this disease into account.
There are two types of patients. The first ones make general complaints. Additionally, they are not distinguished in the classification.
The latter complain about symptoms that correlate with disruptions in the functioning of one or another system.
In this case, a number of diseases are additionally identified:
- cardiac neurosis;
- da Costa syndrome;
- gastroneurosis;
- neurocirculatory asthenia;
- psychogenic forms (aerophagia, dyspepsia, breathing disorders, etc.).
You will have time to download everything you need using demo access in 3 days
?
There are four types of the disease - cardiac, hypo- and hypertensive, mixed.
Cardiac NCD (ICD code 10 – cardiac neurosis). These are disorders characterized by symptoms from the cardiovascular system.
Hypo- and hypertensive NCD (ICD code - neurocirculatory asthenia) are characterized by lability of blood pressure with a tendency to decrease or increase, respectively.
Clinic of the disease
Most often, at the beginning of the development of a pathology such as neurocirculatory dystonia, symptoms appear weakly and do not directly indicate damage to the autonomic system. The most common nonspecific symptoms are:
- headache;
- severe weakness;
- sweating;
- drowsiness;
- tinnitus and dizziness;
- panic for no reason;
- fainting and a feeling of impending loss of consciousness,
- mood swings;
- anxiety;
- changes in the functioning of the heart, manifested by a decrease or increase in heart rate;
- surges in blood pressure and temperature.
- Sleep disorders
An attack of neurocirculatory dystonia may occur: symptoms will include severe weakness, nausea, hypothermia, headache, abdominal discomfort, hypotension, sweating, etc.
In people over 50 years of age, exacerbation of neurocirculatory dystonia is often more pronounced: symptoms will be more varied and often include signs of existing chronic diseases.
Clinical picture: symptoms and complaints
The most common syndrome is cardiac, most pronounced in NCD of the cardiac type, but one way or another manifests itself in 80-100% of patients.
It is defined by polymorphic pain in the heart area of varying intensity and localization associated with overexertion.
Characterized by a significant decrease in intensity or disappearance of pain when the patient's attention switches.
The most important difference from pain with angina pectoris is the appearance of painful sensations not during, but after physical activity.
Physical activity can reduce the intensity of pain in NCD.
Rhythm disturbances are characterized by increased heartbeat, which is not accompanied by a real increase in heart rate, and interruptions in heart function.
Objectively, the patient’s condition does not cause concern; occasionally a systolic murmur is heard at the apex of the heart.
Changes in blood pressure. Respiratory and asthenic syndromes. Other disorders
NCDs of the hypotonic type and the hypertonic type are characterized by extreme lability of blood pressure.
Changes can be spontaneous or become an inadequate response to emotional stress or a change in body position.
In the hypertensive type, the pressure rises to the borderline values of stage I arterial hypertension.
In the hypotonic type, resting pressure values are normal and decrease with physical or emotional stress.
Respiratory syndrome is characterized by shortness of breath, inability to take a deep breath, frequent shallow breathing, and fainting.
Asthenic syndrome – weakness, increased fatigue, apathy. Characterized by fixation on one's feelings, hypochondria, feelings of anxiety and restlessness, and difficulty sleeping.
In severe cases - depressive states.
Often there are problems with digestion, sweating, chills, headaches, swelling of the face in the morning and legs in the evening, coldness of the extremities, marbled skin tone.
Symptoms
This disease has many faces, it can manifest itself in very different ways. In this condition, the activity of the cardiovascular system is disrupted, which responds with aching or stabbing pain in the heart, interruptions in the functioning of the organ or acceleration of its rhythm, pulsation of the vessels of the neck and head. Pain occurs after suffering stress, overwork, due to weather changes.
The next morning the face is swollen. Asthenic syndrome develops, due to which a person feels weak, quickly gets tired, and his performance decreases.
Disturbances are also observed in the respiratory system: shortness of breath appears when walking quickly, a feeling of incomplete inspiration, a lump in the throat, the condition worsens in stuffy rooms. Sometimes there is a fear of suffocation.
At night, vegetative crises often occur: headaches, sweating, dizziness, and darkness in the eyes. The person may faint or lose consciousness. The duration of such a crisis is 20–30 minutes, but sometimes this condition can last for several hours. Sometimes it is accompanied by excessive urination or loose stools. There are also slight temperature fluctuations in one direction or another.
Diagnostics of NCD
Diagnosis of NCD is the systematic exclusion of organic pathology. For this, first-line techniques, gold standards, are used.
The ECG is most often normal, sometimes nonspecific changes in the T wave, sinus tachycardia, and extrasystole are detected. 24-hour ECG monitoring with blood pressure recording is used.
In the presence of respiratory syndrome, spirometry and a test with bronchodilators are performed. Asthenic syndrome requires laboratory blood testing, because its appearance should lead to increased oncological alertness of the doctor.
Changes in the gastrointestinal system require the appointment of FGDS, stool analysis for occult blood and, in case of any suspicion, FCS.
The main thing in the treatment of NCD is the formation of a correct lifestyle, correction of work and rest schedules, and adequate sleep.
You should refuse overtime and night work, business trips, and if there are occupational hazards, minimize their impact as much as possible or change your type of activity.
It is important to follow a diet, normalize weight, give up alcohol and smoking, take long walks in the fresh air, adequate physical activity, and avoid stress.
Treatment of NDC requires a comprehensive approach and includes psychotherapeutic intervention, physical therapy, physical therapy, and only if absolutely necessary, drug correction of symptoms.
How to inform a patient about a doctor’s mistake and not harm the clinic. The magazine “Deputy Chief Physician” contains a universal algorithm and a set of documents.
Drug treatment
It is important to eliminate foci of chronic infection and correct general somatic disorders. Therapy with multivitamins and adaptogens is prescribed.
Hormonal disorders must be stopped, especially in women.
They use sedatives, often of plant origin - valerian extract, motherwort.
With the participation of a psychotherapist, stronger drugs are prescribed - tranquilizers (phenazepam, diazepam, chlordiazepoxide), which have an anxiolytic and vegetative-stabilizing effect, and a pronounced antiphobic effect.
To relieve sympathoadrenal crises, beta-blockers are prescribed. B vitamins are used in courses.
Non-drug treatment
Therapeutic baths (pine, oxygen), contrast showers, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, thermal procedures, and mud treatment are used.
Acupuncture is prescribed, and massage is extremely effective. Physical therapy is mandatory, as it increases the body’s ability to adapt and trains the circulatory system.
Rational psychotherapy is important to help reduce stress and return to a normal psycho-emotional state.
Relaxation techniques help, which include diaphragmatic breathing, muscle relaxation, training with image building and teaching stress tolerance and problem solving skills.
VKK according to the new order
Accreditation
Our products
© 2006–2019 MCFER LLC
The magazine “Deputy Chief Physician” is a magazine about the organization of the diagnostic and treatment process and medical examination.
All rights reserved. Full or partial copying of any site materials is possible only with the written permission of the editors of the magazine “Deputy Chief Physician”. Violation of copyright entails liability in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
This site is not a mass media outlet. The magazine “Deputy Chief Physician” is registered as a printed media outlet by the Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technologies and Mass Communications (Roskomnadzor). Certificate of registration of mass media PI No. FS77-64059 dated December 18, 2015.
The medical information on this website is provided solely for health care professionals and is provided for informational purposes. They are not intended for use by patients and are not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. The information should not be used by doctors as the sole source of information for making decisions when diagnosing diseases and prescribing treatment.
Treatment
First of all, they eliminate the cause of NCD – stressful situations, by improving the situation in the family and eliminating conflicts at work. If we are talking about an infectious-toxic form of dystonia, then it is necessary to eliminate the sources of infection - sanitize the oral cavity, cure foci of infection, and perform a tonsillectomy. If the impact is caused by physical or professional factors, their influence is eliminated, which sometimes requires a change of place of work. neurocirculatory dystonia, treatment is also carried out in a psychotherapist’s office. Sometimes rational psychotherapy turns out to be a more effective tool than medication. During the session, the nature of the disease is explained to the patient, attention is focused on a favorable prognosis, and he is taught the techniques of self-hypnosis, auto-training and muscle relaxation.
Sometimes psychotherapy sessions turn out to be more effective if the patient’s relatives are present - they are also informed about the cause of the problem and ways to overcome it.
At the same time, the interaction between the hypothalamus, limbic zone of the brain, and internal organs is restored. For this purpose, drug therapy is used, sedatives, antidepressants, tranquilizers, nootropics, and cerebroangiocorrectors are prescribed. They calm the nervous system, relieve feelings of fear and anxiety, and reduce excitability. Also, by taking medications, it is possible to improve the quality of processes and improve blood circulation, improve memory. Cerebral circulation is also normalized, and it is possible to reduce the frequency and severity of angiodystonic headaches, dizziness, etc.
Taking beta-blockers normalizes the tone of the sympathoadrenal system in the hypertensive type of NCD with high sympathicotonia.
Along with pharmacotherapy drugs, herbal infusions are used, which include chamomile, valerian, peppermint, motherwort, lemon balm, etc. Improvement after taking teas, decoctions and tinctures of these herbs occurs within 2–3 weeks, but to achieve a lasting effect it is necessary 6–8 months. Treatment is carried out according to the following scheme: if the treatment has a positive effect, a break is taken after 1–2 months, after which the collection is changed. Even if the disease has subsided, it is good to take herbal preparations for preventive purposes - for 2 months, 2 times a year. Herbal medicines have also proven themselves to be quite good. Thus, neurocirculatory dystonia of the cardiac type can be treated with the drug “Persen”.
Physiotherapy has also proven itself well. The “electrosleep” procedure (session – 20–40 minutes, course – 15 sessions) reduces the manifestations of extrasystole and cardiac syndrome. For hypertensive and hypotensive syndrome, arrhythmic syndrome, and severe symptoms of hypothalamic dysfunction, electrophoresis is useful, and for severe asthenia, a galvanic collar according to Shcherbak.
Water procedures are very useful - showers, douses, wet and dry wraps, as well as therapeutic baths - pine, pearl, nitrogen, radon, iodine-bromine, carbon dioxide, etc.
Recently, aeroionotherapy has become increasingly popular. For a collective session, Chizhevsky chandeliers are used. Such devices ionize the air, during which air ions are formed predominantly with a negative sign. During the session, the patient inhales ionized air. This helps reduce blood pressure by 5–20 mmHg. Art., slow down the heart rate, improve gas exchange, increase oxygen consumption. Aeroionotherapy helps combat symptoms such as insomnia, headaches, and weakness.
Often, patients with NCD are prescribed restorative, acupressure massage. Acupuncture normalizes the state of the central and autonomic nervous system, promotes adaptation of the body, enhances metabolism and the activity of internal organs, and relieves emotional stress. After a course of acupuncture, improvement is observed in 65–70% of patients.
The use of adaptogens helps reduce sensitivity to weather changes, weaken emotional sensitivity, and increase endurance during physical activity. For NCD, sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated, including a rest regimen, nutritional therapy, balneotherapy, and physiotherapy. As holiday destinations, preference is given to regions with a mild climate, which are not characterized by sudden changes in atmospheric pressure. These are resorts in the Baltic states, Leningrad and Kaliningrad regions, Belarus, Crimea, and Sochi.
Lifestyle also matters. If a patient is diagnosed with neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypertensive type, then he is prescribed a hypotensive diet. It involves limiting the amount of fluid and salt consumed. At the same time, the diet should include enough vegetables and fruits, especially those that contain sufficient amounts of magnesium and potassium. In pharmacies you can buy salt substitutes and potassium chloride. The patient is also advised to normalize their weight.
If NDC develops of the hypotonic type, such patients are recommended to drink a cup of strong tea or coffee in the morning or afternoon.
NDC in the International Classification of Diseases: ICD 10
Neurocirculatory dystonia is not defined as a disease by the international medical community. The presence of a symptom complex of unknown etiology is recognized. Therefore, the NDC does not have a code according to the ICD 10th edition. This is explained by the absence of physiological reasons for the present deviations. The pathology has a direct effect on the autonomic nervous system, causing disruptions in the functioning of internal organs and blood circulation. The symptoms cause significant discomfort to the patient, reduce or completely deprive them of their ability to work.
What types are there?
Due to various manifestations, neurocirculatory dystonia is divided into four subgroups. The classification divides pathology according to the type of course:
There is a significant difference between the types of progression, manifested by different symptoms. Since the NDC does not have a separate ICD 10 code, doctors are forced to code the closest disease with similar manifestations. Treatment adjustments correspond to the patient’s complaints, as well as the results of biochemical tests and examinations.
Hypertensive type of development
A distinctive feature of hypertensive type NCD is an abrupt increase in blood pressure. The manifestation is accompanied by a hypertensive crisis that occurs at the slightest change in the environment or other factors. Characteristic symptoms for this type:
- Increased heart rate, attacks of tachycardia
- Facial redness
- When the body temperature is elevated, the extremities remain cold
- Recurrent migraine headaches
- Dizziness, sometimes disorientation
- An inexplicable feeling of anxiety. As the condition worsens, panic attacks occur
- Insomnia
- Intense sweating
- Appetite disturbance
The patient may experience a couple of symptoms or all at the same time. The condition worsens during stressful situations.
Since the patient’s condition is characterized by a constant or periodic increase in blood pressure, the doctor diagnoses “Arterial hypertension.” Considering the severity of the course, the code will be either I10 - primary stage, or I15 - secondary stage. When prescribing treatment, the doctor takes into account individual characteristics and possible causes of the disorder.
Hypotonic type
The difference between this type and hypertensive type is the low blood pressure. NCD of the hypotonic type is accompanied by symptoms such as:
- Low heart rate, accompanied by attacks of bradycardia
- Headache that is intermittent
- Physical weakness, fatigue. The patient wakes up tired
- Loss of orientation in space, fainting
- Drowsiness, inability to concentrate
- Sudden deterioration due to changes in air pressure
- Memory impairment
- Pale skin
- Cold extremities
The condition may worsen intermittently with mild to moderate severity. Severe is accompanied by constant malaise; sudden changes in body position may cause fainting.
For these manifestations, the diagnosis is code F45.3 or “Somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.” As in the previous case, the attending physician takes into account the prevailing symptoms before prescribing treatment.
Cardiac type of development
This variety is more common than others. NCD of the cardiac type is characterized by painful sensations in the chest area. Accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Attacks of tachycardia, bradycardia, alternately replacing each other
- Constant headaches
- Increased irritability, tearfulness
- Insomnia
- Unexplained changes in body temperature
- Fast fatiguability
- Breathing problems
Chest pain can be stabbing, dull or aching in nature. The patient is in a state of inexplicable anxiety, and as the condition worsens, panic attacks appear.
The international classification also classifies this type as somatoform dysfunction with code F45.3 . Considering the fact that the manifestations are periodic, the doctor prescribes additional tests, including a mandatory ECG under stress.
Mixed type
This variety is the most extensive, combining the symptoms of all previous types of development. Individual signs of several types of development, as well as symptoms of each, can appear. Mixed type NCD is one of the most difficult to diagnose and treat. The patient experiences constant discomfort and also suffers from attacks of tachycardia, bradycardia, panic attacks, and so on. According to ICD 10, this type of NDC cannot be initiated with an exact definition. Therefore, doctors often use the designation R45.8 , which stands for "Other symptoms and signs related to emotional state."
Types of pathology
Depending on the prevailing symptoms, several types of NCD are distinguished.
- Cardiac. Symptoms related to the heart come to the fore. A person experiences stabbing or pressing pain in the chest, which is accompanied by an increased or decreased pulse, and a feeling of interruptions in the functioning of the heart. The pain syndrome often spreads to the left arm, completely simulating a serious pathology. At the height of an attack, a person often feels weak, dizzy, and afraid.
- NCD of hypotonic type. This type of dystonia is manifested by a periodic decrease in blood pressure. Insufficient oxygen supply to the brain leads to severe dizziness or even fainting. Against the background of low pressure, a spasm of the capillaries occurs, as a result of which the skin turns pale, the hands and feet become very cold. Lack of oxygen leads to a subjective feeling of stuffiness and shortness of breath.
- NCD of the hypertensive type. Manifests itself with periodic increases in blood pressure. During an attack, a person feels hot, his face turns red, and a severe headache appears. Vomiting often occurs during an attack. Often the trigger is a change in weather. Patients get tired quickly and experience mood swings.
- NDC of mixed type. This type of pathology is the least predictable. Blood pressure rises and falls, which is accompanied by corresponding symptoms. Often there are malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea, flatulence, vomiting), and kidneys (frequent urination). The person becomes emotionally unstable and has trouble sleeping at night.
Depending on the type of flow, the following types of NDC are distinguished:
- mild: symptoms of the disease appear extremely rarely, the person leads a normal lifestyle;
- moderate: manifests itself in single crises, the frequency of attacks affects daily life;
- severe: a person experiences symptoms of NCD almost constantly; against their background, vegetative crises regularly occur.
What is cardiac neurocirculatory dystonia
NCA of the cardiac type is a functional disorder of the cardiovascular system, in which there are no changes in blood pressure levels, but pain in the heart area, shortness of breath, etc. are diagnosed. The disease in ICD-10 (the international classification of diseases) is assigned code F45 - somatoform disorders . Neurocirculatory asthenia of the cardiac type manifests itself in different age groups, but is more often diagnosed in children from disadvantaged families and adults who lead an unhealthy, sedentary lifestyle.
Classification of NCD by cardiac type
This dysfunction of the heart and blood vessels is classified into several types depending on the severity:
- Easy. Symptoms can only appear during intense sports or physical activity, or psycho-emotional shocks. In this case, the person feels a strong decrease in performance.
- Average. Symptoms are extensive and manifest differently in each patient. A person’s performance is reduced by about half and requires taking certain medications to restore it.
- Heavy. The patient needs hospital treatment because his health is very poor and he is not able to work.
Experts also identify the following forms of the disease:
- psychogenic (stimulating factors are stress and nervous shock);
- essential (this form develops in people with a hereditary predisposition);
- NDC physical overexertion;
- infectious-toxic (the body is poisoned by toxins, including alcohol, as a result of which the disease develops);
- professional (determined by factors of professional activity).
The development of cardiac VSD (vegetative vascular dystonia) is caused by various factors, with the exception of organic lesions of the endocrine or nervous systems. As a rule, the causes of dystonia in adolescents and young children are severe mental or physical stress. At any age, the disease can occur under the influence of such negative factors:
- lack of sleep;
- chronic fatigue;
- physical/psycho-emotional exhaustion;
- the presence of acute/chronic infections in the body;
- chemical or physical factors (vibration, hot climate, insolation);
- receiving mental trauma;
- physical inactivity or excessive physical activity;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- poisoning, including nicotine and alcohol intoxication.
Signs of dystonia
The pathology is characterized by many different symptoms: experts today have identified about 40 of the most common signs of vegetative dystonia of the cardiac type. Doctors, as a rule, identify from 10 to 25 symptoms in one patient. The most common signs of VSD are:
- irritability;
- weakness;
- anxiety;
- insomnia;
- Bad mood;
- fast fatiguability;
- chills;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- tachycardia;
- stomach ache;
- heat in the neck, face;
- fainting;
- nausea;
- coldness in the extremities;
- periodic heart pain.
The listed symptoms are universal and inherent in all types of neurocirculatory dystonia. In addition to these, the cardiac type is characterized by pain in the area of the heart. In this case, the pain can be different - pressing, squeezing, stabbing, cutting. The duration and intensity of the symptom is different for each patient. Often, attacks of cardiac VSD develop after emotional shocks, strong experiences, or intense training. In addition to pain, cardiac dystonia is accompanied by:
- dizziness;
- rapid heartbeat;
- anxiety;
- headache;
- high fatigue;
- insomnia;
- weakness;
- irritability.
There are main types of neurocirculatory dystonia:
- hypotonic type (the main disorders in this case are associated with a decrease in blood pressure);
- hypertensive type (characteristic changes in blood pressure with a tendency to increase)
- cardiac type (accompanied by disturbances in cardiac activity, increased or decreased heartbeat, as well as discomfort in the chest, etc.)
- mixed type (when it is difficult to classify changes in the body; in this case, a variety of complaints and symptoms are characteristic).
Diagnosis of NCD
Neurocirculatory dystonia of the cardiac type is difficult to diagnose, due to the variability of symptoms. The doctor may assume the presence of cardiovascular dysfunction during the initial examination and interview of the patient, however, to confirm the diagnosis of VSD of the cardiac type, differential diagnosis with myocarditis and myocardial dystrophy is necessary. The main methods for diagnosing NCD are ECG and blood tests. In this case, myocardial damage or the presence of an inflammatory process will not be recorded.
During the examination of a patient with suspected neurocirculatory dystonia, phonocardiography and radiography are also performed - this makes it possible to exclude other heart defects. To confirm the diagnosis of VSD, ECG tests are performed with stress (physical, medicinal or orthostatic tests are used). Each of the tests determines the negativity of the T wave. EchoCG helps to exclude the possibility of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Diagnostics
Correct diagnosis requires examination by several specialists - an endocrinologist, cardiologist and neurologist. It can be difficult to establish an accurate diagnosis, since the disease has nonspecific symptoms, which are characteristic, among other things, of quite serious and dangerous pathologies. Therefore, it is necessary to exclude neurosis, thyrotoxicosis, ischemic heart disease, heart disease, etc. This is why a number of studies are being carried out. The patient undergoes an ECG, echocardiography, chest x-ray, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring, an orthostatic test, ultrasound of internal organs, and a blood test for hormone levels.
How is neurocirculatory vascular dystonia treated?
Therapy for neurocirculatory (vegetative vascular) dystonia is carried out comprehensively. First, the patient should change their lifestyle, eliminating possible irritating factors that lead to stress. In serious cases, psychotherapy is prescribed. If close people have a negative impact on a person’s psycho-emotional state, they are also involved in treatment. In psychotherapy, as a rule, auto-training methods, relaxation, and self-hypnosis are used. In addition to psychological assistance, the following therapeutic measures are used to combat cardiac VSD:
- Therapeutic treatment of neurocirculatory dystonia. The first condition for a person’s recovery is systematic exercise. The ideal option for therapy is therapeutic exercises. In addition, the patient can jog, swim or play badminton. Physiotherapy is indicated for patients with cardiac neurocircular dystonia. In this case, darsonvalization, electrosleep, acupuncture, balneotherapy, electrophoresis with novocaine, magnesium or bromine, massage, and circular shower are performed.
- Drug therapy for neurocirculatory cardiac dystonia. In severe cases of the disease, tranquilizers are prescribed to relieve feelings of fear and anxiety. If a patient with cardiac VSD is depressed, the doctor prescribes antidepressants. Nootropic drugs are used to improve blood supply to the brain and increase protection against hypoxia. For migraines and dizziness, which often accompany neurocirculatory dystonia, the doctor prescribes cerebroangiocorrectors. In addition, sedatives based on herbal components are used to treat VSD of the cardiac type.
- Traditional medicine against cardiac VSD. For the treatment of neurocirculatory dystonia, herbal decoctions are mainly used. A good therapeutic effect is obtained from the collection of knotweed, yarrow, knotweed, hawthorn and rowan fruits, aralia, licorice root, leuzea and mordovnik, and tansy flowers. In this case, take 20 g of all herbs, except for Echinops, Leuzea and Aralia, of which you need to take 10 g. The ingredients are brought to a powder state, 2 tbsp. l. which is poured with a liter of boiling water and boiled for 10 minutes. You need to take the infusion ½ tbsp. before every meal.