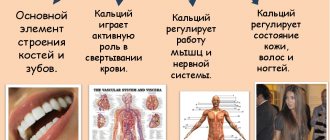
How to understand that there is not enough calcium in the body
The first symptoms of macronutrient deficiency are increased fatigue and general weakness. Signs of hypocalcemia:
- deterioration of hair, teeth, skin and nails;
- numbness of limbs, convulsions;
- sleep disorder;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- blood clotting disorder;
- weakening of the immune system.
With prolonged deficiency of the substance, osteoporosis, heart failure, and changes in mineral metabolism develop. Emerging pathologies require immediate treatment.
Form question
Not only the dose of calcium is important, but also the form in which this mineral is found in a particular drug.
calcium gluconate does not have any advantages. It has a very low percentage of absorption in the intestine, and causes inflammation of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and constipation, as well as other complications already mentioned. Calcium chloride is usually used by injection or intravenously, but is difficult to tolerate and is not suitable for everyone (contraindicated in atherosclerosis, a tendency to thrombosis, or hypersensitivity). When taken in tablet form, it causes heartburn, cramps and even ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract.
Calcium lactate (food additive E327, added to juices, canned fruit, bread and pastries) is well absorbed only by the child’s body, and adults, due to the lack of a special enzyme, can absorb it only in small quantities.
Article on the topic
The magic of magnesium. Why is this mineral important for women?
Calcium carbonate (or simply chalk) is suitable only for short-term use. If you use it for more than two weeks, the acid-base balance may be disrupted. Calcium chelate is an easily digestible form. This is physiological, but, alas, the most expensive of all options.
Calcium citrate is a safe, affordable and highly absorbable calcium compound that does not contain natural impurities. Absorbed by 44%, which is 2.5 times higher than that of calcium carbonate. Moreover, its absorption does not depend on the level of acidity. Good absorption of this form of calcium reduces the risk of its deposition in blood vessels, kidneys and other organs.
Calcium norm, how much should you take
Before you start taking a dietary supplement, you should know your daily calcium intake.
| Age, become human | Norm Ca, mg |
| From birth to six months | 400 |
| From 1 to 5 years | 600 |
| From 6 to 10 years | 800 |
| From 10 to 13 years | 1000 |
| From 14 to 24 years old | 1300-1500 |
| From 25 to 55 years | 1000 |
| Over 55 years old, elderly people | 1300-1500 |
| During pregnancy, lactation | 1500-2000 |
The calcium level can be increased with the use of anabolic steroids, hormones, and excessive physical activity.
3.How is screening carried out?
A CT scan of the body is performed by a technologist and interpreted by a radiologist. Other doctors may also use the resulting images.
You will be asked to remove all jewelry and undress. You will be given a diaper to cover yourself during the procedure. You will need to lie down on a table to which the CT scanner is attached.
The table then slides into the CT scanner and it moves around your body to take pictures. You may hear noises during the procedure. It is important to remain still during the procedure.
If necessary, they can perform myelography, i.e. CT scan using a special dye. The contrast agent is usually injected into a vein in the arm. After this, wait some time for the dye to spread throughout the body.
The procedure takes from 30 to 60 minutes.
How to prepare for coronary calcium screening?
Before a coronary calcium screening, tell your doctor if you may or may be pregnant. You may be asked not to eat or drink anything containing caffeine for a while before the test.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Scientists link physical activity to calcium deposits in arteries
With calcification of the coronary arteries, calcium salts are deposited in the wall of the vessels bringing arterial blood to the myocardium. This is usually asymptomatic, and only a few years after the onset of calcification, heart pain, weakness, and dizziness appear.
Regular physical activity has long been strongly associated with a reduced risk of obesity, diabetes, heart attacks and strokes, and, overall, premature death. However, as new work from cardiologists at the University of Leicester has shown, the most athletic people have calcification of the coronary arteries. Scientists talked about this in more detail in an article in the journal Heart
.
Scientists have previously found signs of coronary artery calcification in physically active people.
Calcification is a serious risk factor for heart attack caused by decreased blood supply to the heart.
Calcinosis is more often observed in older people, mainly men with poor diet. However, it can also occur in people 20-30 years old without any cardiovascular disease.
The researchers collected data from healthy adults who underwent regular comprehensive examinations at two large medical centers in Seoul and Suwon, South Korea, between March 2011 and December 2021. At each health examination, participants completed a questionnaire that included questions about personal and family history, lifestyle, and educational level. Weight (BMI), blood pressure and blood fat levels were also assessed. Physical activity was divided into low, moderate and intense.
Obesity, blood pressure, cholesterol: what spoils the brain from childhood
Obesity, high blood pressure and high cholesterol in children are associated with cognitive decline in adulthood...
11 May 15:06
The scientists then tracked changes in the coronary arteries for an average of three years. The final analysis included data from 25.5 thousand people, mostly men. 47% of them had low physical activity, 38% had moderate physical activity, and 15% had intense physical activity, for example, jogging 6.5 km a day.
Those who were more physically active tended to be older and less likely to smoke. They also had lower levels of total cholesterol, higher blood pressure and more calcium deposits in their coronary arteries.
The relationship between the level of physical activity and the condition of the arteries appeared over time, regardless of their initial condition.
Higher physical activity was associated with faster progression in both those who did not have calcium deposits at the start of the study and those who already had them.
The study does not determine the cause of these changes, the researchers note. They have several guesses.
Physical activity can increase arterial narrowing through mechanical stress and damage to the vessel walls, as well as through physiological reactions such as increased blood pressure and levels of certain hormones. Physical activity also affects the effects of food.
Researchers also do not exclude that, despite calcification, the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases does not increase.
Running from death
The benefits of running have been convincingly proven by scientists. A large study has shown that regular runners...
18 August 18:15
“The benefits of physical activity for the cardiovascular system are undeniable,” they emphasize, recalling national recommendations of 150-300 minutes per week of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity or 75-150 minutes of vigorous activity. “However, patients and physicians need to be aware that physical activity may accelerate the progression of coronary artery calcification.”
Calcification may also have a beneficial effect, the scientists add. Calcified atherosclerotic plaque is more stable and less prone to tearing off, which can cause blockage of the vessel and, as a result, a heart attack or stroke. A similar result is observed, for example, when taking statins.
“The increased rate of coronary artery calcification is a phenomenon that occurs in response to both effective treatment, such as statin therapy, and exercise,” they note. “Assessing the degree of calcification should not be assumed to assess a patient’s cardiovascular risk.”
To assess risks, experts recommend paying attention to non-calcified plaques.
Physical activity remains the best way to control these risks. Those who are concerned about the condition of their blood vessels should consult a doctor to find out if there are any problems.
The authors of the work add that they did not have objective data on the loads of the subjects - the information was obtained through self-reports. In addition, there were no known cases of heart attacks or strokes, so the actual risks to the cardiovascular system cannot be judged.
The bigger, the better?
However, since it is quite difficult to get the required amount of this mineral from food (to do this you will have to drink a liter of milk or eat a kilogram of cottage cheese daily), people switch to preparations containing calcium. And they often drink it in excessive doses, they say, to make sure it is absorbed.
Questions and Answers How to deal with calcium deficiency in the body? It is very dangerous. And not only because with an excess intake of calcium, its absorption not only does not improve, but, on the contrary, worsens, but also because for the body such an excess is almost more harmful than a deficiency. Studies have shown that daily consumption of high doses of calcium increases the risk of mortality in mature and elderly women by 1.5 times over the next 10 years from myocardial infarction, stroke, and other causes. The danger arises due to the fact that unabsorbed calcium settles in the form of deposits on the coronary vessels, heart valves and brain vessels. And taking more than 1,000 mg of calcium per day (in the form of dietary supplements or multivitamins) increases the risk of heart complications even more - by 20%.
The risk exists not only for the heart and blood vessels. With excessive consumption of synthetic calcium, stones (calcium oxalates) form in the kidneys and bile ducts. Scientists also have an assumption that taking large amounts of calcium supplements leads to prostate cancer and the proliferation of pathogenic microflora in the intestines.
Finally, excess calcium interferes with the absorption of other beneficial substances - vitamins and minerals (especially iron), which also increases the risk of many diseases and deficiency conditions.
Test yourself. Are you getting enough calcium? More details
Calcium tablets or eggshells
The shell of an egg is made of calcium carbonate - it is essentially limestone or chalk. It can be purchased in tablets at the pharmacy and is registered as food coloring E170. Eggshells are no better than medicine, because before use they must be dried, disinfected and turned into powder. The product is allowed to be taken if there is a shortage of macronutrients. It is just pointless to try to dissolve calcium carbonate in water since it is insoluble in liquid. In the stomach, hydrochloric acid dissolves the powder from the shell.
Calcium is a macronutrient that takes part in all processes in the body. Its excess or deficiency causes the development of many diseases. You cannot self-medicate; calcium should only be prescribed by a specialist, based on the patient’s condition and symptoms.
Recommended video:
2.Why measure coronary calcium?
Coronary calcium screening is done if you are at risk for heart disease. Coronary calcium screening is not recommended for all people as a routine procedure to test for coronary artery disease (CAD).
Coronary calcium screening is not suitable for you if:
- You are not at risk for coronary heart disease (CHD);
- You have already been diagnosed with heart disease.
This test is also not suitable for men under 40 and women under 50 because... Young people do not have coronary calcium deposits.
Visit our Cardiology page