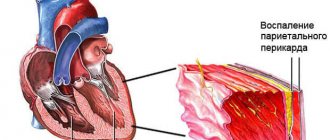
Functions in the body
The pulse refers to the oscillation of the arteries, which is caused by the flow of blood into them. A push or beat indicates a contraction of the heart. As a result, the blood vessels are compressed due to the movement of blood through them. The indicator is measured in beats per minute.
The pulse can be used to determine a person's health status. First of all, the indicator speaks about the functionality of the cardiovascular system. Additionally, it is possible to identify the child’s physical fitness.
The pulse has a classification. The varieties are listed in the table.
| Pulse name | Description |
| Arterial | The walls of the blood vessels contract as blood leaves the heart. The pulse is determined by touching the arteries - in the arm (radial) or neck (carotid). |
| Capillary | The pulse is also called Quincke's pulse. Capillary index means a change in nail color synchronous with arterial waves. The pulse is determined on the nail. If a person is healthy, when the upper part of the plate is pressed, its half turns pale. And there is redness at the bottom of the nail. There should be a clear boundary between these colors until the pressure on the plate stops. This is called a negative Quincke reaction. If the aortic valve is damaged, during systole (contraction of the ventricles and blood flow) the nail turns red. And during diastole (relaxation of the organ), the plate turns white. This is a positive Quincke reaction. |
| Venous | Involves the presence of a pulse in the jugular (neck) or other veins that are close to the heart. If a person is healthy, waves are detected only visually. And during palpation, the pulse is difficult to determine due to low pressure in the veins and weak tension in the walls of blood vessels. The volume of the vein changes due to the pressure difference in the vessel. If the flow of venous blood to the right atrium is normal, the jugular veins in a healthy person are not noticeable in an upright position. Their filling occurs when intrathoracic pressure increases. For example, during straining, coughing, singing. In a horizontal position, the vein should be filled to 1/3 of its length above the collarbone. When a person stands up, the overflow disappears. |
In addition to the variety, the pulse has characteristics. Detailed information is shown in the table.
| Name | Description |
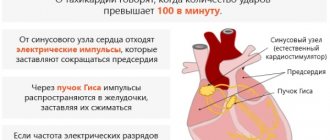
| Frequency | Another name is heart rate (HR). The value reflects the contraction of the artery walls. The following types of heart rate are distinguished:
Rare heartbeats are called bradycardia. And tachycardia is frequent vibrations of the artery walls. Sometimes the pulse becomes less than the heart rate. This is due to the fact that with weak contractions, an insufficient amount of blood enters the aorta, and the wave does not reach the arteries. |
| Rhythm | These are the intervals that appear between pulse waves. Normally, PS should be rhythmic. That is, the waves follow each other at the same time. In case of rhythm disturbance, the pulse becomes arrhythmic. That is, the waves follow each other at irregular intervals. |
| Filling | A value that means the amount of blood leaving the artery at the height of the pulse. The indicator can be moderate, full (exceeds the norm), empty (palpation of waves is impossible). Additionally, there is thread-like filling (barely noticeable). |
| Voltage | Understands the force required to completely stop blood flow. There is moderate, hard and soft tension. The value is related to blood pressure (BP). The higher the blood pressure, the more intense the pulse. For example, with hypertension, force is required to compress the artery and stop pulsation (hard). And with low blood pressure, everything is done easily, the pulse disappears even with little effort (soft). |
| Height | This is a displacement of the vibrations of the walls of the arteries. To determine the indicator, the sum of the tension and fullness of the pulse is determined. There is a large, small and moderate wave. |
| Speed or form |
|
Critical age periods
For young patients, there are critical periods during which an elevated heart rate is often observed. Most often, the child cannot explain exactly how bad he feels and what is the reason for such physiological changes. He feels pressure in his chest, dizziness, sometimes chills, and may even lose consciousness. You should not allow such frequent reactions to occur, and you should visit a pediatric cardiologist in Saratov as soon as you notice the first symptoms. A small patient may be afraid that his body reacted this way to running, watching his favorite movie and the fact that he received a gift that he had dreamed of for so long.
How and under what conditions does it appear?
A normal heart rate for a 15-year-old teenager can range from 61 to 81 beats/min. The indicator appears in the body due to the work of the heart. Its life activity is similar to a pump. That is, the heart pumps blood into the arteries.
Pulse waves are formed at the mouth of the aortic valve when fluid exits the left ventricle into the aorta and then spreads through the vessels at high speed. Stroke volume of blood occurs when systolic pressure increases, that is, the diameter of the arteries expands. And during diastole, the walls are restored to their original size.
The further the vessels are from the heart, the lower the pulse. For example, in capillaries it is impossible to feel the wave at the level of arterioles (small arteries).
Indicator table is normal
Compared to adults, teenagers have a faster heart rate. This is explained by intense metabolic processes and rapid contraction of the heart. The most frequent pulse is observed in newborns. As you get older, the rate gradually decreases.
The normal heart rate in children is shown in the table.
| Age category of the child | Normal heart rate (in beats/min.) | Average value (in beats/min.) |
| Up to 1 month | 71 – 171 | 141 |
| 1 – 12 months | 81 – 163 | 131 |
| 1 – 2 years | 95 – 155 | 125 |
| 24 years | 91 – 141 | 116 |
| 4 – 6 years | 87 – 127 | 105 |
| 6 – 8 years | 79 – 127 | 99 |
| 8 – 10 years | 69 – 109 | 89 |
| 10 – 12 years | 61 – 100 | 81 |
| 12 – 15 years | 56 – 96 | 76 |
| 15 years and above | 61 – 81 | 71 |
When exposed to physical activity, the indicator changes. In teenagers it can be 120 – 150 beats/min. The pulse should be measured not only after sports, but also after 5 – 15 minutes. from the end of classes. Normally, the blows should not become more frequent.
If a child is involved in professional sports, after training the heart rate may increase to 100 - 120 beats/min. That is, there is a general decrease in the indicator, the heart works less to obtain nutrients. During competition, your heart rate may increase. This is due to the combination of physical activity and emotional experiences.
You can roughly calculate the value beyond which your heart rate should not go beyond during sports. To do this, subtract the child’s age from 220. For example, a 12-year-old teenager’s heart rate during physical activity should not exceed 208.
The minimum value of the indicator is calculated according to a different scheme - from 220 it is necessary to subtract the child’s age and the number of heartbeats before performing physical activity, then multiply by 0.5 and add the heart rate before sports.
Using these formulas, it is possible to adjust the activity of athletes and children with excessive mobility. If after sports the child’s pulse is not higher than the upper limit and does not go beyond the lower limit, everything is normal, the load is not maximum.
Symptoms of increase and decrease
The normal heart rate of a 12-year-old teenager is between 55 and 100 beats/min. PS can deviate more or less. A decrease or increase is characterized by certain symptoms.
In the first case, the following symptoms may appear:
- coldness and paleness of the skin;
- increased irritability;
- worsening sleep;
- lethargic state;
- labored breathing;
- changes in blood pressure;
- dizziness;
- cold sweat;
- lack of coordination;
- nausea and vomiting;
- lack of air;
- chest pain;
- darkening of the eyes;
- mood changes;
- loss of consciousness;
- constant fainting;
- cardiac arrest (in critical cases).
When your heart rate is high, the following symptoms may occur:
- discomfort;
- rapid heartbeat - the process may be accompanied by jerking movements in the chest area;
- pain in the chest (symptom may be absent);
- anxiety, especially at night;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- sleep disturbance;
- difficulties with performing the usual load;
- changes in blood pressure;
- increased sweating;
- loss of consciousness.
Why is it important to monitor your heart rate?
When visiting pediatric cardiology in Saratov, the specialist will pay attention to the fact that sometimes too high a pulse rate does not provoke painful sensations. It is extremely important to monitor the child’s behavior and reaction after physical activity, as well as after emotional outbursts. A small patient may complain of shortness of breath, headache, pain in the sternum radiating to the arm, as well as severe fatigue after:
- active physical exercise;
- long walks at a calm rhythm;
- walking up to low floors.
An increased heart rate in a child can also be observed after emotional stress. A pediatric cardiologist in Saratov will explain that laughter, as well as tears, prolonged viewing of cartoons, and strong emotional reactions can cause an increase in heart rate. It is important to measure the indicators after such a condition, and in addition, parents must make a lot of effort to check the frequency of contractions in the usual way.
Reasons for promotion and demotion
The normal heart rate of a 13-year-old teenager is between 56 and 96 beats/min. But there is a deviation of the indicator up or down. An increase or decrease in heart rate is associated with a disease or physiological cause. Detailed information is shown in the table.
| Change in heart rate | Physiological reasons | Possible pathologies |
| Promotion | Exceeding the indicator may indicate the following reasons:
| An elevated rate may indicate the following disorders:
|
| Demotion | Low heart rate may be due to the following reasons:
| A low rate may be associated with the following disorders:
|
Maintains normal heart rate
In order for the pulse to always be within normal limits and rhythmic, you need to maintain the functioning of the cardiovascular system with moderate physical activity, strengthening the general immune system, regular walks in the fresh air, and a healthy/rational diet.
Teenagers are susceptible to emotional overload, and their hormonal levels are often unstable. Therefore, parents should show maximum attention to their well-being, for example, promptly seek help from a psychotherapist, load them with tasks moderately, and give them more time for rest.
In adolescents, a normal pulse is recorded extremely rarely, because the active development of all body systems, hormonal fluctuations, and powerful emotional experiences affect it. Parents should understand that an increase in heart rate at the age of 14-17 years to 100 beats at rest will be the norm if this is recorded periodically and without other symptoms such as dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath.
How to determine
The pulse of a teenager (12 - 18 years old) must be monitored to compare it with the norm.
Measurements can be taken at the following locations:
- wrist;
- ulnar artery (slightly below the elbow);
- elbow bend;
- armpit;
- temple area;
- neck (carotid artery);
- lower jaw and corner of the mouth;
- inner thigh;
- bend of the leg (below the knee);
- foot.
The most common places where the pulse is measured are the extremities (wrist) and neck.
To monitor the indicator at home, the following methods can be used:
- Palpation. You should choose the hand on which the pulsation is better. If everything is the same, then you need a limb close to the heart. You need to find a point that has a pronounced pulsation and press it with your ring finger. Next, count the number of blows in 1 minute, compare the result with the norm. You can use another method - count the number of beats for 6 seconds, then multiply the number by 10. If it is impossible to hear the pulse on the wrist, measurement on the carotid artery is allowed. To do this, you need to sit or lay the person down and press on the artery with your index finger. Next, count the number of beats in 6 or 60 seconds. In the first case, multiply the indicator by 10.
- Using an electronic tonometer . Modern devices can count pulse together with measuring blood pressure. The result is displayed on the tonometer screen.
- Heart rate monitor. The device is designed to analyze heart rate, monitor the load and functionality of the heart. There are different types of heart rate monitors - on the chest, on the finger, on the arm.
Before measuring, you must adhere to the following rules:
- exclude physical activity;
- rest before measurement for 5 – 10 minutes;
- eliminate stress 1 – 2 hours before measurement;
- stop smoking 2 - 3 hours before measuring your pulse;
- do not drink strong coffee or alcohol;
- do not measure your pulse after a hot bath or swimming;
- Do not eat heavily or fast before taking measurements;
- you need to take measurements 1 – 2 hours after waking up;
- remove tight clothing, as it can compress the artery.
How to normalize an elevated heart rate in a teenager
An elevated heart rate in a teenager can be normalized only after the cause of the tachycardia is eliminated. If this is a pathological condition, then full treatment and even surgical intervention is needed. Doctors can prescribe medications from a variety of drug groups:
- beta blockers – Bisoprolol, Metoprolol;
- potassium channel activators – lidocaine;
- cardiac glycosides – Korglykon, Strophanthin;
- sodium channel blockers – Disopyramide;
- calcium channel blockers - Amiodarone, Verapamil.
If the reasons are physiological
But in the case of physiological tachycardia, the following recommendations from doctors can be used:
- Sports activities. You should start with minimal physical activity and actively use target heart rate values during training. This term refers to the heart rate that promotes maximum muscle performance.
Doctors say that for effective exercise it is enough to maintain the heart rate within 50-70% of the permissible maximum. For example, a 16-year-old teenager would have a normal heart rate of 102-143 beats per minute at the time of exercise. But you need to take into account that as you train, this figure will increase - after a year of constant training in the pool, the normal heart rate will already be 143-173 beats per minute.
- Elimination of stressful situations. You need to calm the teenager down as much as possible; if necessary, you can seek help from a psychotherapist - for example, if the child cannot cope with anxiety or emotional stress during the exam period. Parents should not escalate the situation (“if you don’t pass the exam, there will be no vacation,” “you’ll stay for a second year,” and so on), but make it calmer - reassure the teenager, help with classes, give time for proper rest.
- Adjust your diet. It is necessary to exclude coffee, strong black tea, chocolate from the diet, and make the entire menu varied, enriched with vitamins and healthy drinks - fruit drinks, compotes.
First aid at home
If an attack of tachycardia occurs suddenly, then you can quickly normalize the pulse rate with the following “exercises”:
- take alternate deep and quick breaths, then slow, deep exhalations;
- wash your face with cold water, you can put your face in a basin of ice water (only under the supervision of another person!);
- do a light massage of the eyeballs with your fingertips (they are closed), without pressure or strong tapping;
- try to induce vomiting (you can irritate the root of the tongue with the handle of a teaspoon) - if everything works, then vomiting is not critical.
Each action can be performed for no more than 30 seconds in a row, this can reduce the heart rate by 20-30 beats per minute.
Traditional methods
The problem of high heart rate in adolescence can be solved using some traditional medicine:
- Tea with mint. Prepared in the usual way - 1 teaspoon of plant material per 250 ml of boiling water, leave for 15-20 minutes. Can be taken warm or cold; you need to drink 200-300 ml of this drink per day.
- St. John's wort infusion. The dried herb in the amount of 1 tablespoon is placed in boiling water (300 ml) and infused in a closed/wrapped container for 20-30 minutes. The resulting drink is filtered and the entire volume is drunk throughout the day.
Folk remedies should be taken for a long time - at least 2-3 weeks on a daily basis, and if the pulse does not normalize during this period, then you need to seek qualified medical help.
Decoding the results
The normal pulse of a 17-year-old teenager can be found in the table. After the measurement, the value should be compared. If the indicator deviates slightly from the norm, it is impossible to say with a 100% guarantee that the child has some kind of disease.
Normal heart rate in teenagers, children and adults
This may be due to physiological reasons or incorrect measurement.
When to see a doctor
If the pulse constantly deviates from the optimal value or various symptoms appear (chest pain, dizziness), it is recommended to visit a specialist for diagnosis. First you should contact a therapist - this is a general practitioner.
The specialist will conduct a survey, during which it is necessary to talk about the symptoms, if any. Next, important indicators are measured (pulse, blood pressure, temperature). Then the teenager's body is examined.
Next, the therapist can write a referral to another specialist, depending on the cause of the change in pulse. For example, if you suspect endocrine diseases, you should visit an endocrinologist.
After passing through all the specialists, a diagnosis is prescribed. For example, if a heart disease is suspected, a teenager may be referred for an electrocardiogram (ECG), 24-hour monitoring (Holter) and other procedures.
If a person’s well-being rapidly deteriorates or there are serious symptoms (fainting, severe heart pain), an ambulance should be called.
Diagnostics
If a child has a pulse deviation from normal values, the pediatrician will prescribe a general examination to exclude non-cardiac causes of the pathology - anemia, infection, etc. The child is sent for an ECG. This test does not always provide the information you need because the recording lasts a short time and pulse (and heart rhythm) disturbances may be inconsistent.
If rhythm disturbances are suspected, the child is prescribed 24-hour ECG monitoring. This test is completely safe and can be performed on babies from birth. Disposable electrodes are attached to the baby's front chest and connected to a small recording device using a wire. The next day, the electrodes are removed, the recording is deciphered using a computer program and analyzed.
Daily ECG monitoring during changes in a child’s pulse allows you to:
- Heart rate norms for women: Table by age at rest and during training
- determine the maximum, minimum, average heart rate per day, per night, per day and its compliance with the age norm; this, for example, makes it possible to exclude pathology if a child cries during a doctor’s examination or an ECG;
- identify paroxysmal rhythm disturbances, for example, with WPW syndrome, which can lead to a temporary significant increase in heart rate;
- determine the number of pauses in the heart and find out whether there are indications for installing a pacemaker.
In adolescents and young adults, transesophageal electrophysiological testing is also used to diagnose the causes of a sudden increase in heart rate. It consists of stimulating the heart using an electrical signal that comes from an electrode placed in the esophagus. The study is informative for diagnosing sinus node dysfunction, WPW syndrome, and supraventricular tachycardias.
If a heart murmur and complaints of changes in pulse are detected, the child is referred for a heart ultrasound. The main goal of such a study in children is to identify congenital heart defects and determine indications for surgery.
To determine how well a child's heart can cope with physical stress, doctors perform the Ruffier test.
How to get it back to normal
Therapy is prescribed when the pulse deviates from the optimal value.
Treatment includes the following methods:
- medications;
- folk remedies;
- proper nutrition;
- physical activity.
In some cases, surgery is recommended. This happens if a change in pulse indicates a disease. For example, in the case of oncology, surgery may be performed. The need and type of intervention is determined by a specialist depending on the cause of the pulse deviation and the individual characteristics of the body.
If PS was slightly above or below the optimal value and returned to normal on its own, no therapy is required.
Medications
Medicines are not always used to treat abnormal pulses. For example, medications are not used if the situation has normalized with the help of folk remedies, proper nutrition, and sports. When a violation of the indicator indicates a disease, medications are often prescribed.
Specific medications depend on the degree and cause of the pulse deviation from normal. Additionally, the individual characteristics of the body are taken into account. If the pulse is high or low, the medications listed in the table may be prescribed.
| Group name | Action | List of funds |
| Sedatives | The drugs normalize a person’s emotional state and eliminate excessive nervousness. | Afobazol, Tenoten, Novo-Passit |
| Antihypertensive | Medicines lower high blood pressure. | Enap, Amlodipine, Bisoprolol |
| Cardiac glycosides | The drugs normalize the contractile and pumping function of the heart. Additionally, the products in this group restore metabolism, nutrition and cellular respiration. | Digoxin, Korglykon, Strophanthin |
| Antiarrhythmic | The drugs are used for heart rhythm disorders. | Cordarone, Sotahexal, Amiodarone |
| Tranquilizers | Products that have a calming effect. After taking it, anxiety, fear and any emotional stress disappear. This group of drugs is stronger than sedatives. Tranquilizers are sold from pharmacies strictly according to a doctor's prescription. | Phenazepam, Dormicum, Elenium |
| Diuretics | The drugs remove excess fluid from the body and are prescribed for high blood pressure. | Veroshpiron, Hydrochlorothiazide, Diuver |
| Thyroid hormones | Medicines are prescribed for hypothyroidism. | L-thyroxine, Euthyrox |
| Caffeinated | The drugs tone blood vessels, raise blood pressure and pulse. | Caffeine-sodium benzoate, Citramon, Coficil-plus |
| Vitamin complexes | The products restore the lack of vitamins and microelements. | Vitrum, Complivit |
| Immunomodulators | The drugs improve immune defense. | Immunal, Echinacea |
It is possible to prescribe additional symptomatic medications. For example, for pain, analgesics (Analgin, Baralgin) or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nurofen, Ibuprofen) are recommended.
Medicines must be prescribed by a specialist. The doctor takes into account the information specified in the instructions for use of the product. Next, he makes a decision on prescribing the drug.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies have a low likelihood of side effects due to their natural composition. The table shows recipes that can be used when the pulse deviates from the norm.
| Pulse | Herbal Recipes |
| High | Folk remedies include the following recipes: 1. Rose hips. For cooking you need to take 2 tbsp. chopped berries and 400 ml of hot water. Boil for 10 – 15 minutes, wait for it to cool and filter through cheesecloth. Take 1 glass per day. The recipe reduces heart rate and has a positive effect on the heart. 2. Valerian. To prepare the recipe, you need to take 1 tbsp. dry ingredient and 1 glass of hot water. Cook over low heat for 20 - 30 minutes, leave for 2 - 3 hours, filter through cheesecloth. Take 1 tbsp. 3 times a day. |
| Short | Natural recipes for low heart rate: 1. Vegetable mixture. To prepare, you need to take 500 g of chopped walnuts and 250 ml of sesame oil. Next, finely chop 4 lemons and add 1 liter of hot water. Mix everything, add 20 g of powdered sugar. Take 1 tbsp solution. 3 times a day. 2. Yarrow decoction. To prepare the recipe, you need to take 1 tbsp. herbs and 1 glass of hot water. Boil for 10 – 15 minutes, wait for it to cool, filter through cheesecloth. Take 3 times a day, 1/3 cup. |
Proper nutrition
Maintaining proper nutrition makes a person feel better and helps restore the heart rate to its optimal value.
The diet includes compliance with the following rules:
- eat 5 – 6 times a day with breaks of 3 – 4 hours;
- do not exceed the serving size of 300 g;
- exclude fried, fatty, salty foods;
- reduce the consumption of sweets and starchy foods;
- exclude alcohol, strong coffee and black tea - it is better to drink green tea, compote, juice;
- We should not forget about the drinking regime - at least 1 - 1.5 liters of clean still water per day;
- prepare dishes in the oven, steam and boiled methods;
- Vegetable soups and cereals should predominate in the diet;
- It is better to replace high-calorie foods with low-calorie ones - for example, buy chicken or turkey instead of pork.
Physical activity
Sport allows you to strengthen the human immune system and make you feel better. Physical activity does not involve too much stress. Enough charging in the morning. You also need to pick up an additional activity. For example, swimming, cycling, walking.
Possible complications
It is necessary to find out the cause of the constant high or low pulse and begin timely treatment. If this rule is ignored, there is a high probability of complications.
Possible consequences:
- loss of consciousness;
- impaired blood circulation in the brain and other organs;
- the formation of blood clots in the heart;
- heart failure;
- death.
Pulse is a criterion by which the state of human health can be determined. PS has different characteristics - frequency, rhythm, content. Most often, the pulse is detected at the wrist or neck. After measurement, the value is compared with the norm. In adolescence (12–17 years), the pulse is slightly higher than in adults. PS may deviate from the optimal value up or down.
This indicates physiological (stress, poor diet, being in an unventilated area) or pathological (cardiovascular, endocrine diseases) reasons. If the pulse deviates from the norm for a long time, you need to visit a specialist.
The doctor will prescribe diagnosis and treatment. The most important thing is to reduce the likelihood of complications. To do this, you must follow your doctor's recommendations.
How to prevent problems?
A timely ultrasound of a child’s heart is an opportunity to diagnose the disease at an early stage and begin timely treatment. You should not engage in “self-medication”, since some medications can only relieve symptoms and pain, but the problem itself will remain, and the disease will progress.
On the official website of the Heratsi Medical Center, you can make an appointment with an experienced cardiologist who will be able to recognize the problem,, if necessary, prescribe additional tests and draw up a treatment plan that will be aimed at eliminating the problem, and not relieving symptoms. For additional information and answers to any questions, the medical center’s 24-hour telephone number is 8-863-333-20-11.