By the frequency, rhythm and strength of oscillatory blood beats, one can judge a person’s physical health as a whole, record dangerous cardiac disorders, and determine the effectiveness of sports training. Changes in heart rate are symptoms of many life-threatening conditions and diseases, so it is important to know physiological norms. They are different for people of different ages.
Normal heart rate for an adult: table by age
The normal heart rate of an adult by year (age) is given in the table:
| Age | Maximum and minimum limit | Average value |
| 15-50 years | 60-80 | 70 |
| 50-70 years | 66-87 | 76 |
| From 70 years old | 72-92 | 81 |
In an adult, the heart rate norms by age and the permissible heart rate limits in a child under 15 years of age differ significantly, which can be seen in the following table:
| Age | Maximum and minimum limit | Average value |
| Up to 3-4 weeks | 115-165 | 135 |
| From 1 to 12 months | 105-160 | 130 |
| 1-3 years | 90-150 | 122 |
| 3-5 years | 85-135 | 110 |
| 5-7 years | 80-120 | 100 |
| 7-9 years | 72-112 | 92 |
| 9-11 years | 65-105 | 85 |
| 11-15 years | 58-97 | 77 |
Knowing what the normal heart rate is for women and men by age, you can avoid many diseases. Measurements should be taken at rest. Under the influence of other factors (sports, pregnancy), slight deviations are possible.
Heart rate while walking
While walking, there is a slight increase in heart rate. How many heartbeats there will be per minute depends on the person’s fitness. For people leading a sedentary lifestyle, the heart rate can jump to 120, but for people who like to walk, it will remain within 90-100. To calculate the maximum permissible limit, subtract the person's age from 180.
When walking, the permissible heart rate is as follows:
- 15 years - 165;
- 35 years old - 145;
- 55 years old - 125;
- 75 years old - 105.
Heart rate at rest
The resting pulse is determined in the morning.
A person needs to sit on a chair and count his pulse. Changing body positions or taking measurements in the evening is not recommended, as the final result will be distorted. Generally accepted norms at rest:
- adults – 60-80;
- elderly – 70-90;
- teenagers - 70-80;
- children under 2 years old - 90-100;
- newborns - 130-140.
Heart rate while running
While jogging, a lot of stress is placed on the heart. People trying to lose weight should keep their heart rate close to the upper limit. If the goal is to strengthen the cardiovascular system, then you need to stop at a figure not exceeding 60-70%. To calculate the norm, you need to subtract your age from 200:
| Age | Maximum allowable heart rate | Pulse for weight loss | Pulse to strengthen the heart and increase endurance |
| 30 | 170 | 155-160 | 110-120 |
| 50 | 150 | 135-140 | 90-110 |
| 70 | 130 | 115-120 | 70-90 |
If, against the background of an increase in the pulse (within acceptable limits), the pressure readings remain normal, then the development of pathologies will not follow. Elderly people need to be especially careful. Their body is unable to withstand heavy loads.
Permissible heart rate during pregnancy
A woman who is expecting a baby experiences increased heart rate around the 5th month. This phenomenon is associated with an increase in circulating blood volume during fetal development. Usually the increase is insignificant and gradually the indicators return to the acceptable limit:
- Heart rate norms in children: table of heart rate correspondences from newborn age to adulthood
- at 14-26 weeks there is an increase of 10-15 contractions from the norm;
- the maximum increase occurs between 27 and 32 weeks;
- gradual normalization occurs closer to the birth of the child.
What makes the heart beat?
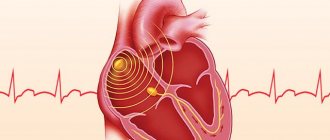
Like any organ, the heart has a conducting system, in other words, wires through which “current” flows to its various parts. The “electric current” originates spontaneously in the sinus node (a small point in the wall of the right atrium). This node is necessary for generating an impulse and adjusting the frequency of contractions depending on the needs of the body, for example, when we run it speeds up the heart, and when we sleep it slows it down.
From the sinus node, the impulse first goes to the atria, causing them to contract. Then the “wires” merge into one so-called “switch” or AV node (it is located in the middle of the heart between the atria and ventricles, in this node there is a slight delay in the passing “current” for the full contraction of the atria), then the impulse passes to the ventricles. In the ventricles, the “wires” branch and are called the bundle branches (left and right; the left, in turn, is further divided into the anterior branch and the posterior branch) with their help, the impulse causes contraction of the ventricles of the heart.
Measurement
Pulse measurement is usually performed at the wrist. It is enough for a person to count the number of pulse waves in 1 minute. To obtain more accurate data, it is recommended to take measurements on both limbs. As a comprehensive examination in a hospital setting, the doctor will first find out the heart rate, then he will count the number of respiratory movements (RR) in 1 minute and determine the type of breathing. The resulting indicator is especially important for assessing the child’s development.
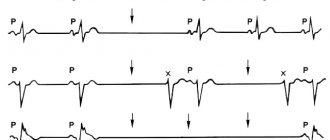
When measuring your pulse, you need to pay attention to its rhythm. The shocks should be of equal strength and at equal intervals of time. If there are no deviations, it is enough to spend 30 seconds on the procedure, and then multiply the result by 2. If a clear disturbance in the heartbeat is detected, it is better to spend at least 1 minute on the measurement and consult a doctor. The specialist will prescribe instrumental examination methods. The main one among them is electrocardiography (ECG). It will allow you to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart and identify the causative factor of arrhythmia. As a supplement, the following tests are prescribed:
- Daily ECG monitoring will allow you to see changes in heart function throughout the day under the influence of various factors.
- A treadmill test is prescribed to assess heart rate under the influence of physical activity.
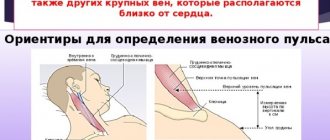
Due to problems with blood vessels or injuries, it is sometimes necessary to count pulse waves in other arteries. Instead of the wrist, you can palpate the neck. The vibrations will come from the carotid artery.
Features of bradycardia
A slowing of the heart rate to 50 beats or below is called bradycardia. It is a sign of physiological and pathological factors. In the first case, the list of reasons for a decrease in heart rate is as follows:
- During sleep, a person's metabolism slows down, body temperature drops slightly and heart rate decreases by about 10% of normal. The reason for the change in indicators is the complete relaxation of the body.
- Stimulating reflex zones (eyeballs, carotid artery) can inadvertently cause a slight slowing of the pulse.
- In older people, bradycardia can be a consequence of age-related cardiosclerosis. Areas of connective tissue scattered throughout the myocardium impair cardiac contractility, which contributes to a decrease in heart rate
- When exposed to cold for a long time, the heart rate slows down as a protective reaction. The body begins to save resources in order to resist adverse effects longer.
- Constant physical activity forces the heart to work harder than it should. Tissue hypertrophy begins, against the background of which bradycardia develops. For professional athletes, a heart rate in the region of 40-45 beats per minute is considered normal.
The pathological form of bradycardia is a consequence of the following factors:
- inflammatory diseases of the heart muscle;
- myocardial infarction;
- taking antihypertensive medications;
- impulse conduction disturbance;
- hypothyroidism (thyroid hormone deficiency);
- hypotension (low blood pressure);
- stomach ulcer;
- high intracranial pressure.
If it is not possible to identify the causative factor, a diagnosis of “idiopathic bradycardia” is made. If it is not accompanied by other disorders and the symptoms are not particularly pronounced, then it is also equated to physiological forms.
general information
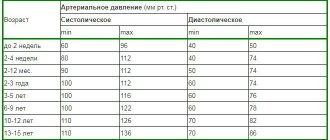
As a general rule, any primary medical examination begins with checking the basic indicators of the normal functioning of the human body. The doctor examines the skin, palpates the lymph nodes, palpates certain areas of the body in order to assess the condition of the joints or identify superficial changes in the blood vessels, listens to the lungs and heart with a stethoscope, and also measures temperature and pressure .
The listed manipulations allow the specialist to collect the necessary minimum information about the patient’s health status (make an anamnesis) and indicators of arterial or blood pressure play an important role in the diagnosis of many different diseases. What is blood pressure, and what are its norms for people of different ages?
For what reasons does blood pressure increase or, conversely, decrease, and how do such fluctuations affect a person’s health? We will try to answer these and other important questions on the topic in this material. We will start with general, but extremely important aspects.
Pathological causes
The heart rate can vary in one direction or the other due to pathological changes in the body. We are talking about six main diseases.
- Algorithms for measuring respiratory rate, pulse and blood pressure in children
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a deficiency of thyroid hormones and the reverse process is hyperthyroidism with an excess of substances in the bloodstream. Hemodynamic disturbances affect the third reflex zone of the heart.
In the first situation, tachycardia occurs, in the second - a decrease in heart rate per minute. Prolonged course of both conditions is associated with an increased risk of fatal or disabling complications.
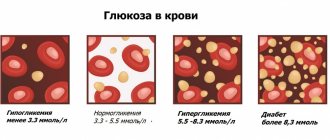
Diabetes
Generally destroys organs and systems, right down to the visual analyzer. With endocrine pathology, the heart wears out faster; without proper treatment, natural death occurs 10-15 years ahead of schedule.
Diabetes of the first type is especially dangerous, since it is not treated, but only corrected with medication, and not always to a sufficient extent.
Hypercortisolism or Addison's disease (reverse phenomenon)
Impaired synthesis of cortisol and other corticosteroids (to a lesser extent). Maintenance hormonal therapy and surgery to eliminate the root cause are required (in the vast majority of cases, the main factor is a tumor in the adrenal glands or pituitary gland).
Congestive heart failure
Causes cardiac ischemia and accelerates the rhythm, sometimes to significant levels. The course without therapy entails a heart attack, sooner or later (usually within 3-5 years from the onset of the first symptoms, by which time the disease is far from at the initial stage of development).
The first signs of heart failure are described in this article.
- Why calculate your heart rate if you decide to play sports?
Acute myocardial ischemia
Leads to death in 35-50% of cases. An extensive type of heart attack is fatal in 95% of clinical situations. Arrhythmia is the hallmark of the process, along with accompanying manifestations.
Why is the pulse called arterial?
The arterial bed receives the entire volume of blood that is pushed out by the heart chamber at the time of contraction. The periods of systole - an increase in pressure as blood comes out - are accompanied by rhythmic beats. The subsequent stages of relaxation of the myocardium for new filling with blood - diastole, make it possible to determine the frequency and strength of these impulses. The oscillations made by the arterial walls are called the pulse. Damage to these vessels, especially large ones, is the most dangerous, as they are accompanied by massive rapid bleeding.
The stronger the pulse beats, the greater the blood flow through the arteries, the more active the oxygen supply to internal organs and overall metabolism. The main “impact” force is provided by the walls of the left ventricle of the myocardium. The following pulse characteristics are important:
- frequency;
- rhythm;
- speed;
- voltage.
Violation of one or more points indicates acute or chronic pathology. Changes in pulse intervals, for example, are a sign of cardiac arrhythmia. An increase or decrease in speed indicates hypertension or a hypotonic state.