At the initial appointment with a specialist, the patient is given the first measurement of arterial parameters, using a mechanical, semi-automatic or automatic device for measuring blood pressure - a tonometer.
Considering that restoration of intravascular tension can take years, the patient will need to purchase his own blood pressure measuring device in order to determine the cause of poor health in time and take medications.
A tonometer is a modern medical device used for non-invasive measurement of blood pressure (the device causes pain and does not violate the integrity of the skin during examination).
Thanks to this equipment, you can control blood pressure painlessly, quickly and without the help of medical personnel, and avoid complications that can lead to hypotension or hypertension.
Devices for measuring blood pressure non-invasively are divided into several types, this greatly simplifies their operation. Today, semi-automatic and automatic blood pressure monitoring devices are in demand, but the mechanical one is also not inferior to its improved counterpart. Let's consider all the features and advantages of pressure measuring devices: which one is better? It is important to decide how to choose a device that performs high-performance blood pressure measurement.
A little about pressure
Blood pressure levels are expressed as two numbers, written as a fraction. The numbers mean the following: at the top is systolic pressure, which is popularly called upper, at the bottom is diastolic, or lower. Systolic is recorded when the heart contracts and pushes out blood, diastolic - when it relaxes to its maximum. The unit of measurement is millimeter of mercury. The optimal blood pressure level for adults is 120/80 mmHg. pillar Blood pressure is considered elevated if it is more than 139/89 mmHg. pillar
A condition in which its level remains consistently high is called hypertension, and a stable decrease is called hypotension. The difference between the upper and lower should be 40-50 mmHg. Blood pressure changes throughout the day for all people, but in hypertensive patients these fluctuations are much sharper.
Interpretation of indicators
The blood pressure of an adult is distributed by doctors as follows:
- optimal. 120 by 80 units and slightly lower;
- normally acceptable. Up to 130 to 85;
- moderately elevated. Up to 139 to 89.
Numbers above the moderately elevated limit indicate hypertension.
Children's blood pressure may have different standards depending on age; they are determined by the doctor.
Why do you need to know your blood pressure?
Even a slight increase in blood pressure increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, ischemia, heart and kidney failure. And the higher it is, the greater the risk. Very often, hypertension in the initial stage occurs without symptoms, and a person is not even aware of his condition.
Measuring blood pressure is the first thing to do if you complain of frequent headaches, dizziness, or weakness.
Hypertensive patients should measure their blood pressure every day and monitor its level after taking the pills. People with high blood pressure should not sharply reduce it with medications.
Ophthalmotonus - why is it so important?
A change in ophthalmotonus should be considered an alarming symptom that indicates pathological processes in the functioning of the visual organs.
Increased intraocular pressure is a consequence of disturbances in the outflow of fluid that is located under the membrane of the eye. Circulation becomes impossible due to the presence of plugs in the tubules that drain fluid. Moisture gradually accumulates, which leads to increased pressure on the shell.
High pressure inside the eye causes pressure on the fundus vessels. As a result, the retina is injured and the photosensitive elements die. Compression of the optic nerve is also observed, which threatens to disrupt the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to cells. If this happens over a long period of time, the tissues of the organ atrophy, vision gradually decreases and, as a result, disappears completely.
Reduced ophthalmotonus also indicates the development of pathological processes. Low pressure leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to the organ, due to which the tissues atrophy and the eyes gradually cease to see.
Changes in ophthalmotonus may result from problems in the functioning of certain organs and systems. Thus, high intraocular pressure is often observed in people with heart and vascular diseases, and low intraocular pressure may be a concomitant sign of liver failure or the initial stages of retinal detachment.
Methods for measuring blood pressure
Blood pressure levels can be determined directly and indirectly.
Straight
This invasive method is highly accurate, but it is traumatic because it involves directly inserting a needle into a vessel or cavity of the heart. The needle is connected to the pressure gauge by a tube containing an anti-clotting agent. The result is a curve of blood pressure fluctuations recorded by a scribe. This method is most often used in cardiac surgery.
Indirect methods
Typically, pressure is measured in the peripheral vessels of the upper extremities, namely in the elbow bend of the arm.
Nowadays, two non-invasive methods are widely used: auscultatory and oscillometric.
The first (auscultatory), proposed by the Russian surgeon N. S. Korotkov at the beginning of the 20th century, is based on clamping the shoulder artery with a cuff and listening to the tones that appear when air is slowly released from the cuff. Upper and lower pressure are determined by the appearance and disappearance of sounds that are characteristic of turbulent blood flow. Blood pressure measurement using this method is carried out using a very simple device consisting of a pressure gauge, a phonendoscope and a cuff with a pear-shaped balloon.
When measuring blood pressure in this way, a cuff is placed on the shoulder area, into which air is pumped until the pressure in it exceeds systolic pressure. At this moment, the artery is completely pinched, the blood flow in it stops, and no sounds are heard. As the cuff begins to deflate, the pressure decreases. When the external pressure is compared with the systolic pressure, blood begins to pass through the compressed area, noises appear that accompany the turbulent flow of blood. These are called Korotkoff sounds and can be heard with a phonendoscope. At the moment when they occur, the value on the pressure gauge is equal to systolic blood pressure. When the external pressure is compared with the arterial pressure, the sounds disappear, and at this moment the diastolic pressure is determined using the manometer.
To measure Korotkoff blood pressure, a mechanical tonometer is used.
The microphone of the measuring device picks up Korotkoff sounds and converts them into electrical signals, which are sent to a recording device, on the display of which the values of the upper and lower blood pressure appear. There are other devices in which the arising and disappearing characteristic noises are determined using ultrasound.
The Korotkoff blood pressure measurement method is officially considered a standard. It has both pros and cons. Among the advantages include high resistance to hand movement. There are several more disadvantages:
- Sensitive to noise in the room where measurements are taken.
- The accuracy of the result depends on whether the head of the phonendoscope is correctly positioned and on the individual qualities of the person measuring blood pressure (hearing, vision, hands).
- Skin contact with the cuff and microphone head is required.
- It is technically complex, which causes errors in measurements.
- This requires special preparation.
Oscillometric With this method, blood pressure is measured with an electronic tonometer. The principle of this method is that the device registers pulsations in the cuff, which appear when blood passes through a compressed area of the vessel. The main disadvantage of this method is that the hand must be motionless when measuring. There are quite a lot of advantages:
- No special training is required.
- The individual qualities of the person measuring (vision, hands, hearing) do not matter.
- Resistant to noise present in the room.
- Determines blood pressure with weak Korotkoff sounds.
- The cuff can be worn over a thin jacket, and this does not affect the accuracy of the result.
Professional devices measuring eye pressure
Measuring intraocular pressure is a mandatory step in any ophthalmological examination. To accurately determine this indicator, an eye tonometer is used. The principle of operation of any of its varieties is based on measuring the level of deformation of the eyeball under the influence of a strictly dosed external factor.
Using this device, the doctor quickly, accurately and painlessly performs the studies necessary to make a diagnosis. The use of a tonometer does not create any discomfort even in patients with increased sensitivity of the cornea.
Types of tonometers
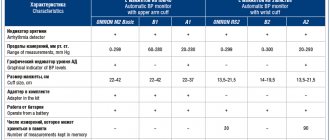
Today, aneroid (or mechanical) devices and electronic ones are used to determine blood pressure.
The former are used to measure pressure using the Korotkoff method in a medical facility, since they are too complex for home use, and untrained users receive results with errors when taking measurements.
An electronic device can be automatic or semi-automatic. Such tonometers are intended for daily home use.
Anyone can use an electronic tonometer to measure their own blood pressure and pulse.
Price
Several factors influence pricing:
- Brand. The more popular and advertised the manufacturer is, the higher the price will be.
- Design. New models are always more expensive than outdated ones. They look more modern, are often more compact than their predecessors and have more functionality. In a sense, there is also a fashion in the field of medical devices.
- Additional functions. Expensive models of electronic tonometers are equipped with functions for storing a certain number of measurements, detecting arrhythmia, motion and position indicators, and alert signals. A clock, calendar and thermometer can be built-in.
- Type of tonometer. Mechanical is the most budget option (~ 1000 rubles). Semi-automatic blood pressure monitors are more expensive – from 1200 rubles. Automatic blood pressure monitors can cost from 1800 rubles and more.
General rules for measuring blood pressure
Blood pressure is most often measured while sitting, but is sometimes done while standing or lying down.
People's daily blood pressure is constantly changing. It increases with emotional and physical stress. It can be measured not only in a calm state, but also during physical activity, as well as in breaks between different types of loads.
Since blood pressure depends on a person's condition, it is important to provide the patient with a comfortable environment. The patient himself needs to not eat, not engage in physical labor, not smoke, not drink alcoholic beverages, and not be exposed to cold for half an hour before the procedure.
During the procedure, you should not make sudden movements or talk.
It is recommended to take measurements more than once. If a series of measurements is made, between each approach you need a break of about one minute (at least 15 seconds) and a change of position. During the break, it is recommended to loosen the cuff.
The pressure on different hands can vary significantly; therefore, measurements are best taken on the one where the level is usually higher.
There are patients whose blood pressure is always higher in the clinic than when measured at home. This is explained by the excitement that many feel when they see medical workers in white coats. For some, this can happen at home as well, as a reaction to measurement. In such cases, it is recommended to take measurements three times and calculate the average value.
Measuring IOP at home
Patients with glaucoma in extreme stages are advised to monitor eye pressure throughout the day. To perform such measurements, special portable instruments are used. One of them is the ICare device. It helps determine the degree of ophthalmotonus by applying special replaceable sensors to the cornea of the eye.
Among the advantages of this technique are:
- minimal error in the obtained data;
- efficiency of the procedure;
- no negative consequences for the cornea;
- patient comfort during the examination;
- eliminating the risk of infection.
Since the device has a memory function and stores the results of the last 10 measurements, this increases the convenience of monitoring changes.
The procedure for determining blood pressure in different categories of patients
In the elderly
This category of people often experiences unstable blood pressure, which is associated with disturbances in the blood flow regulation system, decreased vascular elasticity, and atherosclerosis. Therefore, elderly patients need to take a series of measurements and calculate the average value.
In addition, they need to measure their blood pressure while standing and sitting, since they often experience a sharp drop in blood pressure when changing positions, for example, when getting out of bed and sitting.
In children
It is recommended that children measure blood pressure with a mechanical tonometer or an electronic semi-automatic device, and use a children's cuff. Before measuring your child’s blood pressure yourself, you need to consult with your pediatrician about the amount of air pumped into the cuff and the measurement time.
In pregnant women
Blood pressure can tell you how well your pregnancy is going. For expectant mothers, it is very important to constantly monitor blood pressure in order to start treatment on time and avoid serious complications in the fetus.
During pregnancy, blood pressure monitoring is mandatory
Pregnant women need to measure their blood pressure while reclining. If its level exceeds the norm or, conversely, is much lower, you should immediately consult your doctor.
For cardiac arrhythmia
People who have irregular heartbeat sequence, rhythm and frequency should measure their blood pressure several times in a row, discard clearly incorrect results and calculate the average value. In this case, the air from the cuff must be released at a lower speed. The fact is that with cardiac arrhythmia, its level can vary significantly from beat to beat.
St. Petersburg State Budgetary Healthcare Institution "Polyclinic No. 98"
Blood pressure level is one of the clearest indicators of health status. True, most often the need to monitor blood pressure is remembered in diseases of the cardiovascular system. In fact, everyone should know everything about their blood pressure, because it changes for various reasons.
What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure that blood exerts on the walls of the arteries. It is uneven and fluctuates depending on the phase of the heart. During systole, when the heart contracts and releases another portion of blood into the vessels, the pressure increases. And in diastole, when the heart relaxes and fills with blood, the pressure in the arteries decreases. The blood pressure on the walls of the arteries in systole is called “upper” or systolic, and in diastole – “lower” or diastolic. It is customary to write the blood pressure value using a fraction: the first is the upper, the second is the lower.
Blood pressure is one of the most important indicators of the cardiovascular system. In most healthy people it is relatively constant. But under the influence of stress, physical activity, overwork, drinking large amounts of liquid and under the influence of other factors, its value may change. Typically, such changes are either not too frequent or not too strong, and do not exceed 20 mm during the day. rt. Art. – for systolic, 10 mm. rt. Art. – for diastolic. But, a repeated or persistent decrease or increase in pressure beyond the normal range may be an alarming signal of illness and requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
Blood pressure standards according to WHO classification
| Blood pressure (category) | Upper blood pressure (mm Hg) | Lower blood pressure (mm Hg) |
| Hypotension (low) | below 100 | below 60 |
| Optimal pressure | 100–119 | 60–79 |
| Normal pressure | 120–129 | 80–84 |
| High normal pressure | 130–139 | 85–89 |
| Moderate hypertension (increased) | 140–159 | 90–99 |
| Moderate hypertension | 160–179 | 100–109 |
| Severe hypertension | more than 180 | more than 110 |
The ideal “cosmonaut pressure” is 120/80 mm. rt. Art. However, many doctors agree that everyone has their own ideal, and therefore often ask about the patient’s “working” pressure. Working blood pressure is the usual constant blood pressure interval that provides a person with good health. Since this interval is individual, for someone 115/80 with a working 130/90 may be lower, although it falls within the normal range. And, conversely, with a working level of 110/80, 130/90 may become elevated. Knowing the working pressure helps the doctor to timely identify pathology, make a more accurate diagnosis and choose the right treatment.
However, it is worth remembering that pressure beyond the lower and upper limits of the norm is not working for a healthy person. And feeling normal in this case is only an additional reason to seek advice from a specialist.
Who needs to monitor blood pressure levels and how?
One of the most common disorders of blood pressure regulation is hypertension. Often behind it lies hypertension, leading to myocardial infarction, stroke and other serious complications. Unfortunately, arterial hypertension is often asymptomatic, so everyone needs to monitor their blood pressure. People who are prone to increasing it, who are exposed to risk factors for developing hypertension and experiencing its symptoms should be especially careful and measure blood pressure from time to time. For the rest, annual monitoring during the medical examination period is quite sufficient. But for those who have been diagnosed with arterial hypertension, it would be good to make friends with a tonometer and check the pressure level at least twice a day - in the morning and in the evening.
It is imperative to measure blood pressure if you experience weakness, dizziness, headache, darkening, “veil” in the eyes, tinnitus, difficulty breathing, pain and heaviness in the heart area or behind the sternum, or when other symptoms appear that usually accompany an increase or decrease in pressure.
It is also worth monitoring blood pressure during exercise, especially when selecting a load.
How to measure blood pressure correctly?
If the blood pressure measurement is planned, then one hour before the measurement you should not drink alcohol, drinks containing caffeine (tea, cola, coffee) or smoke, and five minutes before the measurement, ensure yourself a state of rest.
At the first visit to the doctor, the pressure is measured on both arms alternately. If the results differ by more than 10 mm. rt. Art., then the subsequent measurement is carried out on the arm with a high blood pressure value. However, normally the readings are approximately the same. The difference between them exceeds 10 mm. rt. Art., indicates an increased risk of diseases of the cardiovascular system and death from them or an existing pathology.
Blood pressure is usually measured while sitting or lying down. The hand on which the measurement is taken should be freed from clothing and compressive objects, relaxed and motionless. To avoid unwanted tension, it can be placed on an object that provides a support point, such as a table or the edge of a bed. It is best to position the limb so that the elbow is at the level of the heart. The arm should not have arteriovenous fistulas for dialysis, traces of a section of the brachial artery, or lymphedema.
The cuff is placed on the shoulder 2 cm above the elbow. It is important that it fits your hand tightly, but does not squeeze it.
Ideally, blood pressure is measured twice with an interval of 2 minutes. If the result differs by more than 5 mm. rt. Art. – after 2 minutes, take the third measurement and calculate the average value.
The method of measuring pressure depends on the device used and is indicated in the operating instructions.
How to choose a pressure measuring device?
The device for measuring pressure is called a tonometer. There are two types of tonometers - mechanical and electronic (automatic and semi-automatic).
A mechanical tonometer is inexpensive, reliable, lasts a long time, guarantees high measurement accuracy, is easy to use, but requires certain skills and is more difficult to use without assistance.
The electronic tonometer is convenient and simple; you can easily use it yourself. In addition to devices that measure pressure on the shoulder, there are also those that measure it on the wrist. This tonometer can be carried with you, which is sometimes important for some hypertensive patients. And devices with large dials come in very handy for older people. Many of the electronic tonometers show the pulse, remember the data of the latest measurements and are equipped with some other functions, the quantity and quality of which largely depends on the price of the device. But automatic and semi-automatic devices are more expensive than mechanical ones, less accurate and may last slightly less. In addition, in some diseases, blood pressure is very difficult to measure with an electronic tonometer, for example, with atrial fibrillation.
When purchasing a tonometer, you must pay attention to the presence of instructions in Russian, a passport of the device, a warranty card and the absence of visible defects. And when purchasing an electronic device, it also depends on the country of origin. Japanese and German devices are traditionally considered the best.
If the choice falls on a mechanical tonometer, it is worth remembering that it requires a phonendoscope. It is often not included in the package.
It is best to buy pressure measuring devices at a pharmacy or specialty store. If the device is purchased secondhand, the accuracy of the measurement and its service life cannot be guaranteed.
The average width of the cuff should be 13–17 cm, for children - a little less, for overweight people - a little more.
Before use, the tonometer should be checked and, if necessary, adjusted. It is easier and more correct to do this with the help of a doctor.
How to measure blood pressure with a mechanical tonometer?
Not everyone can measure pressure independently with a mechanical tonometer, so the help of another person is advisable.
In addition to a tonometer, you will need a phonendoscope for measurements.
A phonendoscope is a device for listening to sounds accompanying the work of internal organs. It consists of a “head” that is applied to the body, tubes that conduct sound, and tips that are inserted into the ears.
Measurement procedure:
- A cuff is placed on the shoulder, 2 cm above the elbow.
- The pulse is determined at the radial artery at the wrist.
- Air is quickly inflated into the cuff. After the pulse disappears, the cuff is inflated by another 30–40 mm Hg. Art.
- The head of a phonendoscope is placed along the lower edge of the cuff in the elbow bend, slightly inward from the center of the ulnar fossa.
- The air from the cuff is slowly released at a speed of 2-3 mmHg. Art. in 1 s. In this case, the instrument scale is constantly under control. The scale value at which the first sound appears is considered the systolic pressure value, and the value at which it disappears is considered the diastolic pressure value.
- When the pulse wave beats become inaudible, the air from the cuff is quickly released.
Measuring blood pressure with an electronic tonometer for a specific device may have its own subtleties and is described in detail in the operating instructions.
Blood pressure measurement algorithm
Blood pressure measurements should be taken in the following order:
- The patient is seated comfortably on a chair so that his back is adjacent to the back, that is, has support.
- The hand is freed from clothing and placed on the table with the palm up, placing a roll of a towel or the patient’s fist under the elbow.
- A blood pressure cuff is placed on the bare shoulder (two to three centimeters above the elbow, approximately at heart level). Two fingers should fit between the hand and the cuff, its tubes pointing down.
- The tonometer is at eye level, its needle is at the zero mark.
- Find the pulse in the ulnar fossa and apply a phonendoscope to this place with slight pressure.
- The valve on the tonometer bulb is screwed on.
- The pear-shaped balloon is compressed and air is pumped into the cuff until pulsation in the artery can no longer be heard. This occurs when the pressure in the cuff exceeds 20-30 mmHg. pillar
- Open the valve and release air from the cuff at a speed of about 3 mmHg. pillar, while listening to Korotkoff sounds.
- When the first constant tones appear, record the pressure gauge readings - this is the upper pressure.
- Continue to release air. As soon as the weakening Korotkoff sounds disappear, the pressure gauge readings are recorded - this is the lower pressure.
- Release air from the cuff, listening to sounds, until the pressure in it becomes equal to 0.
- Allow the patient to rest for about two minutes and measure blood pressure again.
- Then remove the cuff and record the results in a diary.
Correct position of the patient during blood pressure measurement
How to prepare for the test
It is recommended to wear comfortable clothing, such as a short-sleeved T-shirt and loose, wide-sleeved outerwear. Before the test (at least 24 hours), you should stop drinking alcohol. There is no ban on pharmaceuticals: before the examination, the patient can take all medications prescribed by the doctor.
The patient may be asked to keep a special diary in which to record important information that may affect blood pressure values. For example:
- the time when a person falls asleep, wakes up, gets out of bed;
- meal times;
- time and name of medications taken;
- any feeling of discomfort;
- other events that can affect blood pressure (stress, exercise, etc.).
Registration of ABPM does not interfere with the patient’s normal life; at this time he can work and perform all daily activities. But there will still be minimal discomfort: it is not recommended to lie on the arm that is wearing the cuff, and you cannot remove it from one arm and put it on the other. It is also important to protect the ABPM device from moisture and direct sunlight.
Wrist blood pressure measurement technique
To measure blood pressure at the wrist with an electronic device with a cuff, you must follow the following instructions:
- Remove watches or bracelets from your wrist, unbutton the sleeve and fold it back.
- Place the tonometer cuff 1 centimeter above the hand with the display facing up.
- Place the hand with the cuff on the opposite shoulder, palm down.
- With your other hand, press the “Start” button and place it under the elbow of your cuffed arm.
- Remain in this position until the air is automatically released from the cuff.
This method is not suitable for everyone. It is not recommended for people with diabetes, atherosclerosis and other blood supply disorders and changes in the vascular walls. Before using such a device, you need to measure the pressure with a tonometer with a cuff on the shoulder, then with a cuff on the wrist, compare the obtained values and make sure that the difference is small.
A wrist blood pressure monitor has both advantages and disadvantages.
What to consider when measuring pressure
- Stress can significantly change the readings, so you need to measure it in a calm state.
- Blood pressure increases with constipation, immediately after eating, after smoking and drinking alcohol, with excitement, and in a sleepy state.
- It is best to carry out the procedure one to two hours after eating.
- Blood pressure should be measured immediately after urination, since it is elevated before urination.
- The pressure changes when taking a shower or bath.
- A nearby mobile phone can change the tonometer readings.
- Tea and coffee can change blood pressure.
- To stabilize it, you need to take five deep breaths.
- It increases when you are in a cold room.
Interpretation of measurement results
Normal pressure is approximately equal in both eyes. The permissible difference in measurements should be no more than 3-4 mm Hg. Art. If the difference is greater than this value, then we may be talking about the early stages of glaucoma development.
As a person gets older, intraocular pressure changes, but these changes are minor. For example, in 20-year-old patients, IOP increases with age, and after reaching 70 years, on the contrary, it decreases.
Main pressure is an important criterion for determining the overall health of the eyes. If abnormalities occur, IOP should be measured regularly to avoid complications. Today, doctors have a huge arsenal of tools and methods that allow them to perform such studies. The most widely used are non-contact tonometry methods that exclude direct contact with the eye. Since science does not stand still, methods and equipment for measuring IOP are constantly being improved, making the process even safer and the results as accurate as possible.