Features of measuring blood pressure in children.
Before measuring blood pressure in children, be sure to consult a pediatrician!
During an individual consultation, the pediatrician will provide detailed information on the general rules of measurement, and will also determine the required measurement time, the level of air injection into the cuff and the acceptable intervals of blood pressure values for your child. Blood pressure standards for children have been developed for doctors, in accordance with their age, weight, height, and gender.
According to the recommendations of leading European pediatricians, it is necessary to periodically measure blood pressure in children over three years of age or even earlier, especially if there are any risk factors.
Your child’s blood pressure readings are very dependent on his mood, nutrition, physiological characteristics and may go beyond normal limits, which should not cause much panic. But if lethargy, drowsiness, refusal to eat, complaints of headache, nausea, etc. are added to pressure disorders, then you must immediately contact a pediatrician who will conduct additional research and, if necessary, prescribe adequate and effective treatment.
It is preferable to measure a child’s blood pressure in the first half of the day, an hour after a hearty lunch, active physical exercise, games or school activities.
To measure blood pressure in children in medical institutions, aneroid tonometers are used (auscultatory measurement method). At home, it is preferable to use automatic and semi-automatic tonometers, which are based on the oscillometric measurement method with a special children's cuff with an internal chamber size of 9x16 cm (corresponding to size S). As a rule, a special table of cuff sizes is attached to the tonometer passport. If high blood pressure is detected by an electronic device, control is carried out in a medical institution with an aneroid blood pressure meter.
The procedure for measuring blood pressure should be repeated three times with an interval of three minutes, since a single measurement is not enough to assess the real picture.
Blood pressure in newborns is measured using oscillographic and ultrasound methods, which make it possible to determine pressure indicators, regardless of the baby’s mobility and restlessness.
Suitable tonometers for measuring
It is not necessary to buy a separate blood pressure monitor for a child; it is enough to purchase a children’s cuff. When purchasing a tonometer, pay attention to its functionality. For a large family, it is worth choosing a tonometer with measurement memory for two users with recording of measurement time. This will help track the slightest deviations in pressure from the norm. For hypertensive patients, morning hypertension monitoring functions and a high blood pressure indicator will not be superfluous.
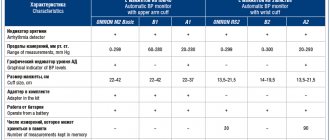
Tonometer Omron M1 Eco Approximate price: 1,700 rubles
- semi-automatic tonometer;
- memory for 42 results + date and time registration;
- indicators of arrhythmia and high blood pressure;
- calculation of the average blood pressure value from the last three results;
- large display.
Tonometer Omron M10-IT Approximate price: 8,900 rubles
- automatic tonometer;
- memory for 2 users for 84 measurements + guest mode;
- indicators of movement, arrhythmia, high blood pressure;
- the presence of a function for calculating the average blood pressure value from three measurements;
- It is possible to connect to a computer.
Measuring blood pressure in older people.
In an elderly person, it is more difficult to achieve complete and lasting normalization of blood pressure.
There may be several reasons. With age, the severity of arterial hypertension and the number of concomitant diseases increase; it is more difficult to persuade an elderly person to undergo treatment regularly, especially with decades of experience of high blood pressure. In older people, instability of blood pressure is more common. This is influenced by a decrease in the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels and atherosclerosis due to aging, as well as disturbances in the functioning of blood flow regulation systems. When measuring blood pressure in the elderly, it is especially important to take several consecutive measurements (at least 3) and record their average value. This procedure is greatly simplified by electronic blood pressure meters with MAM technology (Microlife Average Measurement), which perform sequential triple measurements with calculation of an optimized result.
In the elderly, episodes of a sudden drop in blood pressure are common - postural hypotension (a sharp drop in pressure during the transition from the “lying” state to the “sitting” or “standing” state). It is recommended that arterial blood measurements be taken both while sitting and standing, especially in the presence of hypotension or during antihypertensive therapy. In persons over 65 years of age, with concomitant diabetes mellitus and antihypertensive therapy, blood pressure should also be measured after 2 minutes of standing.
ANNEX 1
24-hour BP monitoring diary
Child's full name _________________________________________________
Date of birth _________________ Age (years) ____________________
Weight ___________ Height __________ Body mass index (kg/m2) __________
FULL NAME. mother of the child _____________________________________________________
Address: ________________________________________________________
Telephone: ______________________________________________________
Study start date ________ Study start time ________
Cuff: on the right hand on the left hand.
Prescriptions (drug, dose) – _____________________________________
| Time | Kind of activity | Complaints | |||||||||
| (hour) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Notes |
| 06–07 | |||||||||||
| 07–08 | |||||||||||
| 08–09 | |||||||||||
| 09–10 | |||||||||||
| 10–11 | |||||||||||
| 11–12 | |||||||||||
| 12–13 | |||||||||||
| 13–14 | |||||||||||
| 14–15 | |||||||||||
| 15–16 | |||||||||||
| 16–17 | |||||||||||
| 17–18 | |||||||||||
| 18–19 | |||||||||||
| 19–20 | |||||||||||
| 20–21 | |||||||||||
| 21–22 | |||||||||||
| 22–23 | |||||||||||
| 23–24 | |||||||||||
| 00–01 | |||||||||||
| 01–02 | |||||||||||
| 02–03 | |||||||||||
| 03–04 | |||||||||||
| 04–05 | |||||||||||
| 05–06 | |||||||||||
where, types of activities: 1 – sleep, 2 – eating, 3 – taking medications, 4 – lying down, 5 – emotional stress, 6 – physical activity; complaints: 7 – headaches, 8 – dizziness, 9 – palpitations, 10 – fatigue
Measuring blood pressure in people with arrhythmia.
Arrhythmia is a violation of the frequency, rhythm and sequence of contractions of the heart. In people with arrhythmias, systolic pressure can vary significantly from beat to beat.
To assess the level of blood pressure in such a situation and obtain a reliable result, it is necessary to perform several consecutive measurements (at least 3), and then calculate the average value of the measurements. Modern devices with MAM (Microlife Average Measurement) technology allow you to do this by pressing only one button. When using mechanical blood pressure monitors, deflate the cuff more slowly.
Today, there are electronic blood pressure meters with PAD (Pulse Arrhythmia Detection) technology, which makes it possible to obtain an accurate result in individuals with pulse arrhythmia.
How to measure a child's blood pressure correctly
A few tips and rules.
| Choose the right cuff size! The blood pressure cuff should cover approximately 2/3 of the length of the upper arm. Therefore, cuffs of different sizes are used for children of different age groups. | ||||||||||
| Do you need a stethoscope to measure blood pressure? If you use a mechanical tonometer, yes, it is necessary. The most inexpensive one will do, but preferably a stethoscope with a flat head; during measurements it is convenient to slip it under the tonometer cuff. | ||||||||||
| To what numbers should I inflate the blood pressure cuff? To avoid causing unnecessary discomfort to the child, do not inflate the cuff too much - it is enough to inflate it by 20 mmHg. higher than expected figures. The table below shows normal values of systolic (SD) and diastolic (DD) pressure in children of different ages. | ||||||||||
| Age | up to 2 weeks | 2-4 weeks | up to 1 year | 2-3 years | 3-5 years | 6-9 years | 10-12 years | 13-25 years old | ||
| Blood pressure, mmHg | SD | min | 60 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 110 | 110 |
| max | 96 | 112 | 112 | 112 | 116 | 122 | 126 | 136 | ||
| DD | min | 40 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 70 | 70 | |
| max | 50 | 74 | 74 | 74 | 76 | 78 | 82 | 86 | ||
* BP is blood pressure, SD is systolic (“cardiac”) pressure, DD is diastolic (“venous”) pressure.
Is it possible to use an adult automatic wrist blood pressure monitor for children under 3 years of age? NO! Using a wrist tonometer to measure pressure on the shoulder is not an accurate method and is not used in professional medical practice. Will I be able to learn how to measure my child's blood pressure?Learning to measure blood pressure for a child, even a newborn, is not difficult, it is accessible to everyone! It just takes a little practice. If you have never used a tonometer, it is advisable that your actions be monitored by a medical professional at the initial stage. It is important that the child remains calm while measuring blood pressure. The procedure itself is painless, but does cause some discomfort. Children quickly get used to regular blood pressure measurement, and you will have the necessary experience to carry out the procedure quickly - blood pressure measurement will become a routine procedure that will not cause concern to either you or your baby. Where to buy a children's blood pressure monitor?Not all manufacturers of tonometers produce models designed specifically for children. Children's tonometers Rudolf Riester (Germany) are a rare case when the assortment includes not one, but several models.Measuring blood pressure in people with a large upper arm circumference.
The measurement cuff must be selected according to the ruler supplied with the tonometer.
In persons with a large upper arm circumference (obesity, well-developed muscles) or those with a conical-shaped arm, it is difficult to position the cuff correctly, which makes it much more difficult to accurately measure blood pressure. In this case, you need to choose a larger cuff of 32-42 cm with an inner chamber of 15x30 cm (corresponding to size L) or a universal cuff of 22-42 cm.
Blood pressure monitors with a wrist cuff can be used, but the possible difference in pressure between the shoulder and the wrist should be taken into account (with age or disease, the elasticity of the wrist vessels decreases faster than the brachial vessels, which leads to lower blood pressure readings at the wrist).
A little bit of theory
The method of measuring blood pressure in both adults and children is standard - a cuff of the required size is placed on the shoulder, and the head of a stethoscope is placed in the area of the cubital fossa (under the lower edge of the cuff).
| The head of the stethoscope is installed in the projection of the ulnar fossa. |
Having inflated the cuff to the required numbers, we begin a smooth deflation of air. The numbers on the pressure gauge corresponding to the appearance of rhythmic noise in the stethoscope mean systolic pressure (synonyms: upper, cardiac), the moment the noise disappears - diastolic pressure (synonyms: lower, venous).
In the case of using an automatic tonometer, the role of a stethoscope and a bulb for pumping air is performed by the device.
Measuring blood pressure in pregnant women.
Blood pressure in pregnant women is one of the important indicators on which general and uterine blood circulation and the successful course of pregnancy depend.
The presence of arterial hypertension before pregnancy or that develops during pregnancy can often interfere with successful delivery. In order to minimize the likelihood of serious complications in the mother and child by normalizing blood pressure, there are modern control methods, including mandatory and repeated blood pressure measurements during pregnancy and training pregnant women in self-control skills.
Blood pressure in pregnant women should be measured in a reclining position. The “white coat effect” is observed in 30% of pregnant women. To avoid unnecessary treatment, you need to regularly monitor your blood pressure at home!
What blood pressure is considered normal?
When working with children, it cannot be said that some blood pressure numbers are a universal norm. Doctors use special tables and graphs in which pressure is distributed by age and gender. These values are called percentiles.
Blood pressure is considered elevated if it is more than the 95th percentile, low if it is less than 5. This may seem like a rather complicated and incomprehensible approach; for ease and clarity, a table of normal indicators is presented.
Table 1. Girls:
| Age | 5th percentile | 50th percentile | 95th percentile |
| 1 year | 101/57 | 104/58 | 107/60 |
| 6 years | 108/71 | 111/73 | 114/60 |
| 12 years | 120/79 | 123/80 | 126/82 |
| 17 years | 126/83 | 129/84 | 132/86 |
Table 2. Boys:
| Age | 5th percentile | 50th percentile | 95th percentile |
| 1 year | 98/55 | 102/53 | 106/59 |
| 6 years | 109/72 | 114/74 | 117/76 |
| 12 years | 119/79 | 123/81 | 127/83 |
| 17 years | 132/85 | 136/87 | 140/89 |
A child whose blood pressure is above the 95th percentile should visit the pediatrician at least three times and have their blood pressure measured. If the numbers are persistently high, a diagnosis of arterial hypertension is made and therapy is selected.
What is ABI used for?
The ankle-brachial index is necessary to assess the functioning of blood flow in the lower and upper extremities in order to identify possible arterial diseases. Measuring the ankle-brachial index is an effective preliminary method for diagnosing damage to the arteries of the upper and lower extremities in patients at risk: heavy smokers, diabetics. Measurement of the ankle-brachial index is indicated in the presence of hereditary cardiovascular diseases, elevated blood cholesterol levels and age over 50 years.