Obstetricians-gynecologists begin to listen to the baby’s heart during the period of its intrauterine development. Before birth, a baby's heart murmur cannot be detected. Doctors focus on the sonority of tones and the frequency of contractions, indicators of “good health” of the fetus, and the uncomplicated course of pregnancy in the expectant mother.
After birth, on the first day, the newborn is examined by a special pediatrician in the maternity hospital. Large perinatal centers have neonatologists. These are pediatricians specially trained to diagnose and treat early childhood pathologies and congenital diseases. They conduct the first auscultation of the baby, and if noise is detected, they are required to establish the cause.
Features of auscultation in children
The therapist gets “scared” when listening to the child. The auscultatory picture is the same as in an adult, but audibility is several times stronger. Especially in infants.
- The baby's chest wall is much thinner, all sounds are transmitted very clearly.
- A newborn needs to be able to listen to a scream. They try to carry out examinations of an infant after feeding, so that he is in a good mood and has the opportunity to listen to the heart in silence.
- Older children have to be distracted by their mothers.
- There are always toys in the offices of local pediatricians; it should be warm.
- The doctor tries to warm the head of the phonendoscope in his hands so as not to frighten the patient by touching a cold object.
This is how you have to explain yourself to a little person
In assessing tones, it is important that in children and adolescents, unlike adults, the third additional tone is heard more often. It does not indicate ventricular pathology, is better audible after exercise and gives a “gallop rhythm”.
Congenital heart defects (CHD) in children
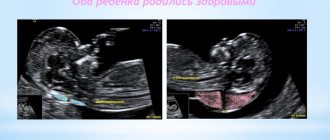
The formation of the fetal heart occurs towards the end of the first trimester of pregnancy. Using a method such as ultrasound, most congenital heart defects can be detected already at 16-18 weeks. The diagnosis is made definitively in the 2nd or 3rd trimester. With congenital heart disease, children may have cyanosis if the amount of reduced erythrocyte hemoglobin is increased to 50 g/l. This is influenced by factors such as:
- an increase in the amount of venous blood entering the systemic circulation in the presence of blood discharge from the right parts of the heart to the left
- degree of blood oxygenation in the lungs
- degree of oxygen utilization by tissues
Cyanosis affects changes in peripheral blood: polycythemia and hyperhemoglobinemia. Chronic oxygen deficiency causes changes in the nail phalanges - the fingers resemble drumsticks.
There are 3 phases of the course of congenital heart defects :
The first phase is when reactions of adaptation and compensation to disturbances in the dynamics of blood circulation occur. If hemodynamics are significantly impaired, unstable myocardial hyperfunction appears, an emergency option according to V.V. Larin and F. Z. Meerson, so decompensation easily develops.
The second phase is relative compensation. The child’s physical development improves, as does his motor activity.
The third phase is terminal. It occurs when compensatory capabilities are exhausted and dystrophic and degenerative changes develop in the heart muscle and parenchymal organs. Various diseases and complications bring the development of this phase of the disease closer, which necessarily ends in death.
F. 3. Meerson and his colleagues distinguish 3 stages of compensatory hyperfunction of the heart :
1. Emergency
The intensity of functioning of myocardial structures increases. Signs of acute heart failure appear. The exchange change appears.
2. Second stage
The normal intensity of functioning of the myocardial structures is recorded. Disorders of metabolism, structure and regulation of the heart progress.
3. Stage of progressive cardiosclerosis and gradual exhaustion
The intensity of synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins in the hypertrophied myocardium decreases.
During the period of relative compensation, the syndrome of capillary-trophic insufficiency of the hemomicrocirculation system gradually develops, leading to a discrepancy between transcapillary blood flow and cardiac output. As a consequence of this, metabolic disorders appear in tissues, as well as dystrophic, atrophic and sclerotic changes in internal organs.
Why does noise occur in children?
You can read about the causes and possible mechanisms of the formation of heart murmur in a child here.
Most often, murmurs in a child’s heart are associated with growth processes and are functional.
Newborns often have a slight systolic murmur due to the transition of the heart to independent circulation and the gradual occlusion of the ductus arteriosus.
Functional murmur occurs in children of different ages and adolescents due to a discrepancy in the growth rate of muscle tissue and valve leaflets. It intensifies after exercise, is systolic in nature, and disappears with age. At the same time, the child grows and develops normally, does not lag behind his peers, and is fully involved in physical education.
As body temperature rises, noise is caused by increased blood flow velocity
It is possible to listen to a systolic murmur during acute childhood infections, against a background of high temperature. In this case, the doctor must monitor residual effects during the recovery period. Intoxication and the effects of infectious agents on the myocardium often cause myocarditis with shortness of breath, tachycardia, and weakness. Therefore, such manifestations cannot be excluded from diagnosis.
From 1 to 1.5% of newborns are born with organic changes (defects). Auscultation indicates congenital pathology from the first day of life.
The cause of noise in organic defects is:
- narrowing of the openings between the atria and ventricles, at the exit to the aorta and pulmonary artery;
- insufficient fixation of the valves when they close, the formation of a gap for the return flow of blood;
- the presence of interatrial and interventricular defects in the septum;
- additional communication between the aorta and pulmonary artery along the patent ductus botallus;
- several combined defects in tetralogy of Fallot and other rare defects.
In adolescents, you should be especially attentive to any newly detected murmurs. This is the only way to promptly diagnose the onset of rheumatic carditis with the formation of acquired heart disease.
Features of CVS in children
The cardiovascular system of children differs significantly from the cardiovascular system of adults. The difference is clearly visible both during a routine examination and according to the results of electrocardiography (ECG). These differences greatly frighten parents and force them to urgently consult a doctor. Therefore, in this article we will try to consider all the main features of the cardiovascular system in a child, which may cause concern to his parents.
The cardiovascular system of children has its own anatomical and physiological characteristics compared to the cardiovascular system of adults. For example, when compared with the total body weight, the heart of a newborn is much larger than the heart of an adult, and rapid growth is observed, and by about three years the heart weight increases almost 3 times, and by 6 years almost 11 times.
Due to the peculiarities of the nervous regulation of the heart and the high intensity of metabolism, the heart rate in children is much higher than in an adult, and only by about 15 years does the heart rate become like that of an adult. The decrease in heart rate (HR) with the age of the child is directly related to the onset of the influence of the vagus nerve on the heart.
In addition, sex differences in heart rate are noticeable in children. So, boys have a lower heart rate than girls.
But the main feature of the heart in a child is respiratory arrhythmia, which is manifested by an increase in heart rate during inhalation and a slowdown during exhalation. In early childhood, arrhythmia is slightly expressed, and from preschool age to 15 years, respiratory arrhythmia is expressed to a significant extent. In children over 15 years of age, as a rule, only isolated cases of respiratory arrhythmia occur.
The heartbeat in young children is very pronounced. This is due to the small amount of subcutaneous fat. As the child ages, subcutaneous fat increases, as a result the heartbeat becomes almost invisible.
The electrocardiogram of a child and an adult has significant differences. First of all, arrhythmia, and secondly, due to the active growth and development of the heart muscle and conduction pathways, changes in the QRS complex are possible, which are manifested by splitting and narrowing of the complex. ECG conclusion: incomplete blockade of the left or right bundle branch.
In addition, all ECG waves are more pronounced in children than in adults. Migration of the pacemaker through the atria may occur, which is due to the formation of new short-term sources of excitation.
In older children, remodeling of the conduction system of the heart occurs, which causes the development of cardiac arrhythmias.
The most common diseases of the cardiovascular system in children
1. Congenital heart defects (CHD) are defects in the structure of the heart cavities or heart vessels, which lead to disruption of their functioning. Congenital defects are most often recorded either on ultrasound during pregnancy or in the first month after birth. Children with congenital heart disease experience rapid fatigue, weakness, small increase in height and weight in the first year of life, and frequent respiratory diseases. Most often, surgical treatment of defects is required.
2. Arterial hypertension. Almost 20% of schoolchildren experience increased blood pressure. Children of prepubertal and pubertal age are most predisposed to increased blood pressure. Depending on the age when the increase in blood pressure first appeared, there may be various reasons. In younger people, increased blood pressure is associated with congenital pathology of the kidneys and cardiovascular system. As you grow older, increased body weight, heredity, etc. take first place among the reasons. Very often, the child does not feel the increased pressure and it is an accidental finding during medical examination. Sometimes children may complain of fatigue, dizziness and headache. At the first stage of treatment, non-drug methods are used, which include normalizing the daily routine, sleep, nutrition and physical activity. If positive dynamics are not observed for some time, then medications are added.
FOR REFERENCE!
Nekrasova Anastasia Mikhailovna.
Doctor – pediatrician, pediatric cardiologist.
Medical
Elektrougli, st. Shkolnaya, no. 49, no. 38.
www.family-mts.rf
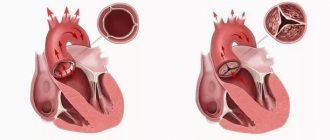
Auscultatory picture of common congenital defects in children
Organic heart murmurs always indicate pathology and require further diagnosis and a decision on conservative or surgical treatment of the child.
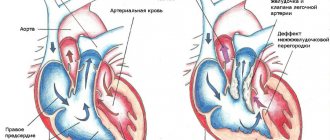
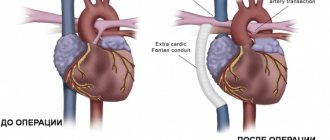
- A patent ductus bollus is manifested in an infant by a typical murmur in the second intercostal space to the left of the sternum. It has a rough systolic prolonged character (“machine noise”), weakens during inspiration.
- With narrowing of the pulmonary artery, stenosis of the aortic isthmus, a noise is also heard to the left of the sternum, but it is carried out in the third intercostal space, on the carotid arteries, in the interscapular space.
- Defects of the interatrial and interventricular septa are characterized by systolic and diastolic uniform murmurs along the left edge of the sternum at the level of the attachment of the third and fourth ribs, carried to the apex, but not audible on the vessels.
- Gallery
- Reviews
- Articles
- Licenses
- Vacancies
- Insurance partners
- Partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- Online consultation with a doctor
- Documentation
The most common reason for referral to a pediatric cardiologist for infants and children under 5 years of age is a murmur heard in the heart area.
Let's try to figure out what the reason is. The human heart is a rather complex organ that produces a peculiar sound during its operation - noise.
There are different types of murmurs in a child's heart. The murmur can be a consequence of significant circulatory disorders caused by congenital heart disease, or accompany minor deviations in the structure of the heart that do not significantly affect its functioning. Now noises are divided into “innocent” and “pathological”.
“Innocent” noises do not affect the condition of the heart and the general condition of the child’s body. Such a murmur is described as a fuzzy, “short”, limited in area, barely audible sound, not accompanied by other abnormalities; when examining the heart, it is normal. In essence, it is the sound of a healthy heart working due to the peculiarities of its structure.
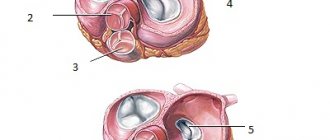
Quite often, the causes of a murmur in a child’s heart are minor anomalies in the development of the heart. The inner surface of the heart chambers is not perfectly smooth; it has muscle bridges (trabeculae) and pits; the ventricles contain papillary muscles and chordae connected to the leaflets of the atrioventricular valves. When the ventricles contract, protrusions may appear in their lumen, and the configuration of the cavity changes. Moreover, even one single chord or trabecula located in the path of blood flow can create a significant noise picture.
Each heart is unique, having its own individual “trabecular pattern,” just like the pattern on the fingers. There can always be an “anomalous” structure, or even more than one, creating noise.
“Innocent” noises are often heard in newborns and infants and are a consequence of the processes of circulatory restructuring that take place in the cardiovascular system when adapting to extrauterine life.
Noises of a “rough” timbre , clearly audible, sometimes even at a distance, “long-lasting”, spreading over the surface of the chest are called pathological, such noises are usually a consequence of the presence of congenital heart disease (CHD), and may be accompanied (not always) by changes in the electrocardiogram , changes in the X-ray picture of the heart.
Some newborns may not have a murmur at all. Its appearance can occur only after a month, when a certain restructuring of the baby’s blood circulation occurs. A pathological sign is an increase in noise over time.
Unfortunately, it should be noted that the absence of murmur does not mean the absence of heart disease . There are so-called “silent” defects, when there is a defect, but due to the characteristics of the blood circulation it cannot be heard, since there are no specific sounds; an example of such heart defects are:
- atrial septal defect,
- ventricular septal defect in the muscular part,
- open ductus arteriosus with a diameter of 1-2 mm. and etc.
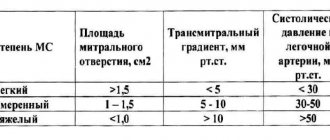
The most informative method of examining children when detecting a murmur in the heart area is an echocardiographic examination (ultrasound of the heart), which is recommended to be carried out without delay, as soon as it comes to the fact that some murmurs are heard in the heart area. This study is safe for the baby’s health and can (should) be carried out immediately after birth, if necessary.
In the presence of congenital heart pathology, observation by a pediatric cardiologist is necessary at intervals corresponding to the severity of the disease. If correction of the defect is necessary, the child should be sent to a cardiac surgery hospital.
Patients with innocent murmurs also require periodic monitoring, as they may experience age-related changes in heart structures. The value and timbre of the noise may change. For this reason, it is recommended to visit the same pediatric cardiologist, who can record the timbre and nature of the noise and their dynamics over time . However, as experience shows, in most cases, no serious problems arise for a long time; children can engage in dancing and sports associated with heavy physical activity.
Make an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist and examination by phone +7(495)150-60-03
Services and prices
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis (in PW, CW mode) and color two-dimensional Doppler mapping for children under one year old
RUB 3,800
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis (in PW, CW mode) and color two-dimensional Doppler mapping for children from 1 year to 7 years
3,700 rub.
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis (in PW, CW mode) and color two-dimensional Doppler mapping for children over 7 years old
3,600 rub.
Make an appointment
How to make a diagnosis
The diagnosis takes into account:
- clinical symptoms - cyanosis of the child’s lips and face, shortness of breath when moving, changes in rhythm, trembling of the chest when palpating the heart area, the presence of a visible venous network under the skin, pulsating vessels;
- phonocardiography and ECG - clarify the localization of damage to the heart chambers;
- Ultrasound and Dopplerography - allow you to establish blood flow in different phases of myocardial contraction, direction, volume of return, degree of adaptability of the ventricles and atria.
What is recommended for parents
Listening to a heart murmur in a child should cause concern for parents. It is necessary to bring the diagnosis to full confidence in the causes. If necessary, consult with a cardiac surgeon several times.
Only a specialist can recommend the correct observation and treatment, and plan a specific date for the operation. If the risk of surgical treatment in terms of complications exceeds the possibility of the expected development of decompensation, then parents are informed about this.
The child must be registered at the dispensary and examined at least once a quarter. The baby needs to be protected from infections, colds, and the sufficiency of vitamins in the diet must be monitored. If necessary, the doctor prescribes supportive therapy and exempts the student from physical education.
Functional noise does not require significant restrictions. You should talk to your pediatrician about the possibility of playing sports. Regular physical exercise is not contraindicated.
How healthy a child grows up depends on the adults. Given the current widespread trend towards a reduction in specialized healthcare services, parents should be prepared for paid consultations.